Android RelativeLayout
Android 的 RelativeLayout 可以指定子檢視如何彼此相對定位。每個檢視的位置可以被指定為相對於同級元素或相對於父檢視。
RelativeLayout 屬性
以下是RelativeLayout 具體的屬性:
| 屬性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| android:id | 這是布局的唯一標識ID。 |
| android:gravity | 這指定物件應該如何定位它的內容,無論是X軸和Y軸。可能的值是top, bottom, left, right, center, center_vertical, center_horizontal等。 |
| android:ignoreGravity | 這表示什麼檢視應該不受到重力影響。 |
使用RelativeLayout可以調整兩個元素右邊界或使一個下面跟著另一個檢視,居中於螢幕上,中心,左側等等。預設情況下,所有子檢視都在左上角的布局,所以必須定義使用RelativeLayout.LayoutParams和一些重要屬性的布局屬性,每個檢視的位置如下給出:
| 屬性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| android:layout_above | 位置上面給定錨點檢視ID此檢視的底部邊緣,必須參照另一個資源,在形式 "@[+][package:]type:name" |
| android:layout_alignBottom | 使得此檢視的底部邊緣匹配給定的錨點檢視ID的底邊和必須是參照到另一個資源,在形式 "@[+][package:]type:name". |
| android:layout_alignLeft | 使得此檢視的左邊緣匹配給定的錨點檢視ID的左邊緣,並且必須是一個參考到另一個資源,在形式 "@[+][package:]type:name". |
| android:layout_alignParentBottom | 如果為true,使得此檢視的底邊緣相匹配的父的底部邊緣。必須是一個布林值,要麼“true”或“false”。 |
| android:layout_alignParentEnd | 如果為true,使得此檢視的端部邊緣相匹配的父的端部邊緣。必須是一個布林值,要麼“true”或“false”。 |
| android:layout_alignParentLeft | 如果為true,使得此檢視的左邊緣匹配父的左邊緣。必須是一個布林值,要麼“true”或“false”。 |
| android:layout_alignParentRight | 如果為true,使得此檢視的右邊緣匹配父的右邊緣。必須是一個布林值,要麼“true”或“false”。 |
| android:layout_alignParentStart | 如果為true,使得此檢視開始邊緣匹配父的開始邊緣。必須是一個布林值,要麼“true”或“false”。 |
| android:layout_alignParentTop | 如果為true,使得此檢視的頂部邊緣相匹配的父的頂部邊緣。必須是一個布林值,要麼“true”或“false”。 |
| android:layout_alignRight | 使得此檢視的右邊緣匹配給定的錨點檢視ID的右邊緣,並且必須是一個參照另一個資源,在形式 "@[+][package:]type:name". |
| android:layout_alignStart | 使得此檢視開始邊緣的匹配給定的錨點檢視ID開始邊緣,必須參照另一個資源,在表格 "@[+][package:]type:name". |
| android:layout_alignTop | 使得此檢視的頂部邊緣匹配給定的錨點檢視ID的頂邊緣,並且必須是一個參照到另一個資源,在形式 "@[+][package:]type:name". |
| android:layout_below | 定位此檢視低於給定錨點檢視ID的頂邊緣,並且必須是一個參照到另一個資源,在形式 "@[+][package:]type:name". |
| android:layout_centerHorizontal | 如果為true,中心這個子檢視水平在其父之內。必須是一個布林值,要麼“true”或“false”。 |
| android:layout_centerInParent | 如果為true,使此子檢視中心水平和垂直其父之內。必須是一個布林值,要麼“true”或“false”。 |
| android:layout_centerVertical | 如果為true,該中心子垂直在其父之內。必須是一個布林值,要麼“true”或“false”。 |
| android:layout_toEndOf | 此檢視給定錨點檢視ID結束邊緣位置,必須參照另一個資源,在格式 "@[+][package:]type:name". |
| android:layout_toLeftOf | 此檢視給定錨點檢視ID的左邊的右邊位置,必須做個參考其他資源,在形式 "@[+][package:]type:name". |
| android:layout_toRightOf | 定位此檢視為給定的錨點檢視ID的右左邊緣和必須是參照到另一個資源,在形式 "@[+][package:]type:name". |
| android:layout_toStartOf | 定位此檢視為給定的錨點檢視ID的開始的端部邊緣,並且必須是一個參照到另一個資源,在形式 "@[+][package:]type:name". |
範例
這個例子將通過簡單的步驟顯示了如何建立Android應用程式使用相對布局。按照下面的步驟來建立Android應用程式範例:
| 步驟 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 使用Eclipse IDE建立Android應用程式,在包 com.yiibai.relativelayout 下建立一個應用範例專案:RelativeLayout |
| 2 | 修改 res/layout/activity_main.xml 檔案的預設內容以包括幾個部件在相對布局。 |
| 3 | 定義所需的常數在 res/values/strings.xml 檔案中 |
| 4 | 執行該應用程式後啟動Android模擬器並驗證應用程式的結果。 |
以下是內容修改主activity檔案 src/com.yiibai.helloworld/MainActivity.java。這個檔案可以包括每個生命週期的基本方法。
package com.example.helloworld; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Calendar; import java.util.Date; import android.os.Bundle; import android.app.Activity; import android.text.format.DateFormat; import android.view.Menu; import android.widget.TextView; public class MainActivity extends Activity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd"); Date date = new Date(); String nowDate = dateFormat.format(date); TextView dateView = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.dates); dateView.setText(nowDate); SimpleDateFormat timeFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss"); String nowTime = timeFormat.format(date); TextView timeView = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.times); timeView.setText(nowTime); } @Override public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) { // Inflate the menu; getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu); return true; } }
res/layout/activity_main.xml 檔案的內容如下:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:paddingLeft="16dp" android:paddingRight="16dp" > <EditText android:id="@+id/name" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="@string/reminder" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/dates" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/name" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/times" /> <TextView android:id="@id/times" android:layout_width="96dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/name" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" /> <Button android:layout_width="96dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/times" android:layout_centerInParent="true" android:text="@string/done" /> </RelativeLayout>
res/values/strings.xml 檔案的內容中定義兩個常數:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <string name="app_name">RelativeLayout</string> <string name="action_settings">Settings</string> <string name="reminder">Enter your name</string> <string name="done">Done</string> </resources>
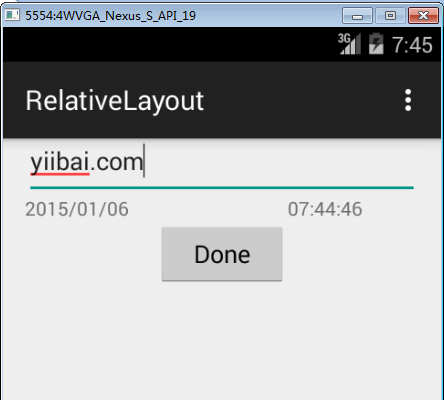
讓我們嘗試執行 RelativeLayout 應用程式,假設建立了AVD並同時設定好環境。從Eclipse中開啟專案,在活動檔案中執行應用程式,然後從Eclipse的工具列上單擊圖示  “Run” 執行。 Eclipse AVD安裝的應用程式並啟動,如果設定和應用都沒有問題,它會顯示以下模擬器視窗:
“Run” 執行。 Eclipse AVD安裝的應用程式並啟動,如果設定和應用都沒有問題,它會顯示以下模擬器視窗: