堆疊的連結串列實現
堆疊也可以使用連結串列來實現,而不是只能使用陣列來實現。連結串列動態可以分配記憶體。 然而,兩種情況下的時間複雜度對於所有操作是相同的,即推入,彈出和窺視。
在堆疊的連結串列實現中,節點在儲存器中非連續地維護。 每個節點都包含一個指向堆疊中直接後繼節點的指標。 如果記憶體堆中剩餘的空間不足以建立節點,則稱堆疊溢位。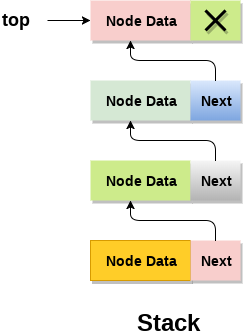
堆疊中最頂層的節點的地址欄位中始終包含null。 下面來討論一下每個操作在堆疊的連結串列實現中執行的方式。
1. 將節點新增到堆疊(推播操作)
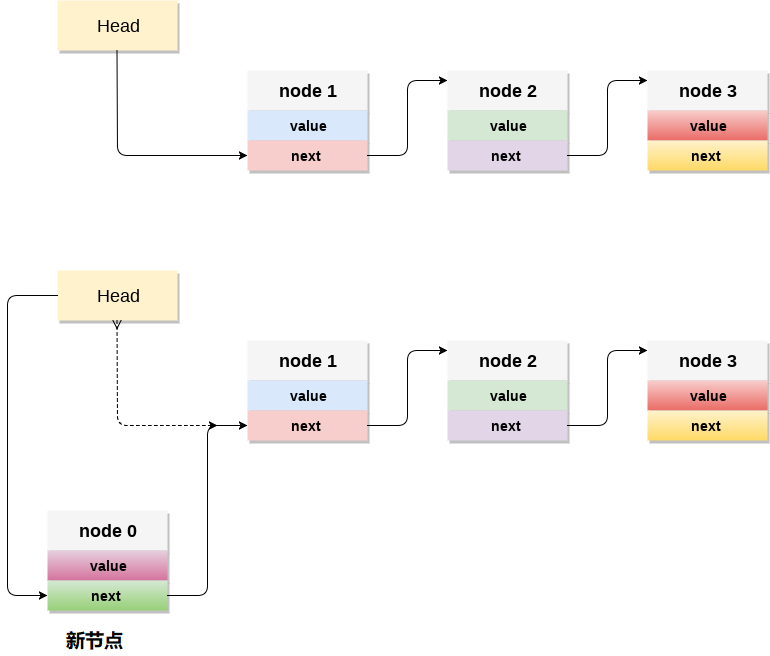
將節點新增到堆疊稱為推播操作。 在連結串列實現中將元素推播到堆疊不同於陣列實現的元素。 為了將元素推入堆疊,涉及以下步驟。
- 首先建立一個節點並為其分配記憶體。
- 如果連結串列為空,則將資料項作為連結串列的起始節點推入。 這包括將值分配給節點的資料部分,並將
null分配給節點的地址部分。 - 如果連結串列中已經有一些節點,那麼需要在連結串列的開頭新增新元素(不違反棧的屬性)。 為此,將起始元素的地址分配給新節點的地址欄位,並建立新節點,即連結串列的起始節點。
時間複雜度: o(1)
C語言的程式碼實現
void push ()
{
int val;
struct node *ptr =(struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if(ptr == NULL)
{
printf("not able to push the element");
}
else
{
printf("Enter the value");
scanf("%d",&val);
if(head==NULL)
{
ptr->val = val;
ptr -> next = NULL;
head=ptr;
}
else
{
ptr->val = val;
ptr->next = head;
head=ptr;
}
printf("Item pushed");
}
}
2. 從堆疊中刪除節點(彈出操作)
從堆疊頂部刪除節點稱為彈出操作。 從堆疊的連結串列實現中刪除節點與陣列實現中的節點不同。 要從堆疊中彈出元素,需要按照以下步驟操作:
- 檢查下溢情況 :當嘗試從已經空的堆疊彈出時就會發生下溢情況。 如果連結串列的頭指標指向
null,則堆疊將為空。 - 相應地調整頭指標:在堆疊中,元素僅從一端彈出,因此,必須刪除儲存在頭指標中的值,並且必須釋放節點。 頭節點的下一個節點現在成為頭節點。
時間複雜度:o(n)
C語言程式碼實現
void pop()
{
int item;
struct node *ptr;
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("Underflow");
}
else
{
item = head->val;
ptr = head;
head = head->next;
free(ptr);
printf("Item popped");
}
}
3. 顯示節點(遍歷)
顯示堆疊的所有節點需要遍歷以堆疊形式組織的連結串列的所有節點。 為此,需要遵循以下步驟。
- 將頭指標複製到臨時指標中。
- 將臨時指標移動到連結串列的所有節點,並列印附加到每個節點的值。
時間複雜度:o(n)
C語言的程式碼實現
void display()
{
int i;
struct node *ptr;
ptr=head;
if(ptr == NULL)
{
printf("Stack is empty\n");
}
else
{
printf("Printing Stack elements \n");
while(ptr!=NULL)
{
printf("%d\n",ptr->val);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
}
C語言完整的程式碼實現如下
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void push();
void pop();
void display();
struct node
{
int val;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head;
void main()
{
int choice = 0;
printf("*********Stack operations using linked list*********\n");
printf("----------------------------------------------\n");
while (choice != 4)
{
printf("Chose one from the below options...\n");
printf("1.Push\n2.Pop\n3.Show\n4.Exit");
printf("Enter your choice \n");
scanf("%d", &choice);
switch (choice)
{
case 1:
{
push();
break;
}
case 2:
{
pop();
break;
}
case 3:
{
display();
break;
}
case 4:
{
printf("Exiting....");
break;
}
default:
{
printf("Please Enter valid choice ");
}
};
}
}
void push()
{
int val;
struct node *ptr = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if (ptr == NULL)
{
printf("not able to push the element");
}
else
{
printf("Enter the value");
scanf("%d", &val);
if (head == NULL)
{
ptr->val = val;
ptr->next = NULL;
head = ptr;
}
else
{
ptr->val = val;
ptr->next = head;
head = ptr;
}
printf("Item pushed");
}
}
void pop()
{
int item;
struct node *ptr;
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("Underflow");
}
else
{
item = head->val;
ptr = head;
head = head->next;
free(ptr);
printf("Item popped");
}
}
void display()
{
int i;
struct node *ptr;
ptr = head;
if (ptr == NULL)
{
printf("Stack is empty\n");
}
else
{
printf("Printing Stack elements \n");
while (ptr != NULL)
{
printf("%d\n", ptr->val);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
}