D語言if...else語句
一個if語句後面可以跟一個可選的else語句,該語句執行時的布林表示式為false。
語法
在D程式設計語言的if... else語句的語法是:
if(boolean_expression) { /* statement(s) will execute if the boolean expression is true */ } else { /* statement(s) will execute if the boolean expression is false */ }
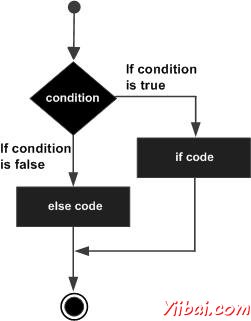
如果布林表示式的值為true,那麼if程式碼塊將被執行程式碼,否則else塊將被執行。
D程式設計語言假設任何非零和非空值作為true,如果是零或null,則假定為false。
流程圖:
例子:
import std.stdio; int main () { /* local variable definition */ int a = 100; /* check the boolean condition */ if( a < 20 ) { /* if condition is true then print the following */ writefln("a is less than 20" ); } else { /* if condition is false then print the following */ writefln("a is not less than 20" ); } writefln("value of a is : %d", a); return 0; }
當上面的程式碼被編譯並執行,它會產生以下結果:
a is not less than 20; value of a is : 100
if...else if...else語句
一個if後面可以跟一個可選的if... else語句,如果測試各種條件下... else if語句,可使用單一的else語句。
當使用 if , else if , else語句有幾點要記住:
-
if可以有零個或else,它必須跟在else if後面。
-
if 可以有零到多個else if,它們必須在else之前。
-
一旦一個 else if 匹配成功,剩餘else if不會被測試或計算。
語法
if...else if...else語句在D程式設計語言的語法是:
if(boolean_expression 1) { /* Executes when the boolean expression 1 is true */ } else if( boolean_expression 2) { /* Executes when the boolean expression 2 is true */ } else if( boolean_expression 3) { /* Executes when the boolean expression 3 is true */ } else { /* executes when the none of the above condition is true */ }
例子:
import std.stdio; int main () { /* local variable definition */ int a = 100; /* check the boolean condition */ if( a == 10 ) { /* if condition is true then print the following */ writefln("Value of a is 10" ); } else if( a == 20 ) { /* if else if condition is true */ writefln("Value of a is 20" ); } else if( a == 30 ) { /* if else if condition is true */ writefln("Value of a is 30" ); } else { /* if none of the conditions is true */ writefln("None of the values is matching" ); } writefln("Exact value of a is: %d", a ); return 0; }
當上面的程式碼被編譯並執行,它會產生以下結果:
None of the values is matching Exact value of a is: 100