R語言二項分布
二項分布模型用來處理在一系列實驗中只發現兩個可能結果的事件的成功概率。 例如,擲硬幣總是兩種結果:正面或反面。使用二項式分佈估算在重複拋擲硬幣10次時正好準確地找到3次是正面的概率。
R具有四個內建函式來生成二項分布,它們在下面描述。
dbinom(x, size, prob)
pbinom(x, size, prob)
qbinom(p, size, prob)
rbinom(n, size, prob)
以下是使用的引數的描述 -
- x - 是數位的向量。
- p - 是概率向量。
- n - 是觀察次數。
- size - 是試驗的次數。
- prob - 是每次試驗成功的概率。
1.dbinom()函式
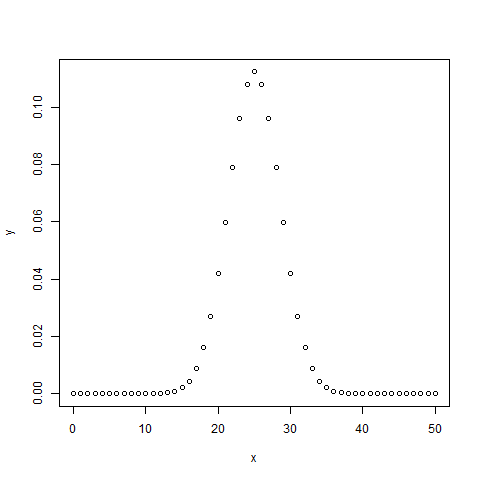
該函式給出了每個點的概率密度分布。參考以下程式碼實現 -
setwd("F:/worksp/R")
# Create a sample of 50 numbers which are incremented by 1.
x <- seq(0,50,by = 1)
# Create the binomial distribution.
y <- dbinom(x,50,0.5)
# Give the chart file a name.
png(file = "dbinom.png")
# Plot the graph for this sample.
plot(x,y)
# Save the file.
dev.off()
當我們執行上述程式碼時,會產生以下結果 -
2.pbinom()函式
該函式給出事件的累積概率,它用於表示概率的單個值。參考以下程式碼實現 -
setwd("F:/worksp/R")
# Probability of getting 26 or less heads from a 51 tosses of a coin.
x <- pbinom(26,51,0.5)
print(x)
當我們執行上述程式碼時,會產生以下結果 -
[1] 0.610116
3.qbinom()函式
該函式採用概率值,並給出其累積值與概率值匹配的數位。參考以下程式碼實現 -
setwd("F:/worksp/R")
# How many heads will have a probability of 0.25 will come out when a coin is tossed 51 times.
x <- qbinom(0.25,51,1/2)
print(x)
當我們執行上述程式碼時,會產生以下結果 -
[1] 23
4.rbinom()函式
該函式從給定樣本生成所需數量的給定概率的隨機值。參考以下程式碼實現 -
# Find 8 random values from a sample of 150 with probability of 0.4.
x <- rbinom(8,150,.4)
print(x)
當我們執行上述程式碼時,會產生以下結果 -
[1] 58 61 59 66 55 60 61 67