R語言線性回歸
回歸分析是一個廣泛使用的統計工具,用於建立兩個變數之間的關係模型。 這些變數之一稱為預測變數,其值通過實驗收集。 另一個變數稱為響應變數,其值來自預測變數。
線上性回歸中,這兩個變數通過一個等式相關聯,其中這兩個變數的指數(冪)是1。數學上,當繪製為圖形時,線性關係表示直線。任何變數的指數不等於1的非線性關係產生曲線。
線性回歸的一般數學方程為 -
y = ax + b
以下是使用的引數的描述 -
- y - 是響應變數。
- x - 是預測變數。
a和b- 叫作係數的常數。
建立回歸的步驟
一個簡單的線性回歸例子:是否能根據一個人的已知身高來預測人的體重。要做到這一點,我們需要有一個人的身高和體重之間的關係。
建立線性回歸關係的步驟是 -
- 進行收集高度和相應重量觀測值樣本的實驗。
- 使用R中的
lm()函式建立關係模型。 - 從所建立的模型中找到係數,並使用這些系數建立數學方程。
- 獲取關係模型的摘要,以了解預測中的平均誤差(也稱為殘差)。
- 為了預測新人的體重,請使用R中的
predict()函式。
輸入資料樣本
以下是表示觀察結果的樣本資料 -
# Values of height
151, 174, 138, 186, 128, 136, 179, 163, 152, 131
# Values of weight.
63, 81, 56, 91, 47, 57, 76, 72, 62, 48
lm()函式
該lm()函式建立預測變數與響應變數之間的關係模型。
語法
線性回歸中lm()函式的基本語法是 -
lm(formula,data)
以下是使用的引數的描述 -
- formula - 是表示
x和y之間的關係的符號。 - data - 是應用公式的向量。
範例: 建立關係模型並得到係數
x <- c(151, 174, 138, 186, 128, 136, 179, 163, 152, 131)
y <- c(63, 81, 56, 91, 47, 57, 76, 72, 62, 48)
# Apply the lm() function.
relation <- lm(y~x)
print(relation)
當我們執行上述程式碼時,會產生以下結果 -
Call:
lm(formula = y ~ x)
Coefficients:
(Intercept) x
-38.4551 0.6746
獲取關係的概要 -
x <- c(151, 174, 138, 186, 128, 136, 179, 163, 152, 131)
y <- c(63, 81, 56, 91, 47, 57, 76, 72, 62, 48)
# Apply the lm() function.
relation <- lm(y~x)
print(summary(relation))
當我們執行上述程式碼時,會產生以下結果 -
Call:
lm(formula = y ~ x)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-6.3002 -1.6629 0.0412 1.8944 3.9775
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) -38.45509 8.04901 -4.778 0.00139 **
x 0.67461 0.05191 12.997 1.16e-06 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 3.253 on 8 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.9548, Adjusted R-squared: 0.9491
F-statistic: 168.9 on 1 and 8 DF, p-value: 1.164e-06
predict()函式
語法
線性回歸中的predict()的基本語法是 -
predict(object, newdata)
以下是使用的引數的描述 -
- object - 是已經使用
lm()函式建立的公式。 - newdata - 是包含預測變數的新值的向量。
範例: 預測新人的體重
# The predictor vector.
x <- c(151, 174, 138, 186, 128, 136, 179, 163, 152, 131)
# The resposne vector.
y <- c(63, 81, 56, 91, 47, 57, 76, 72, 62, 48)
# Apply the lm() function.
relation <- lm(y~x)
# Find weight of a person with height 170.
a <- data.frame(x = 170)
result <- predict(relation,a)
print(result)
當我們執行上述程式碼時,會產生以下結果 -
1
76.22869
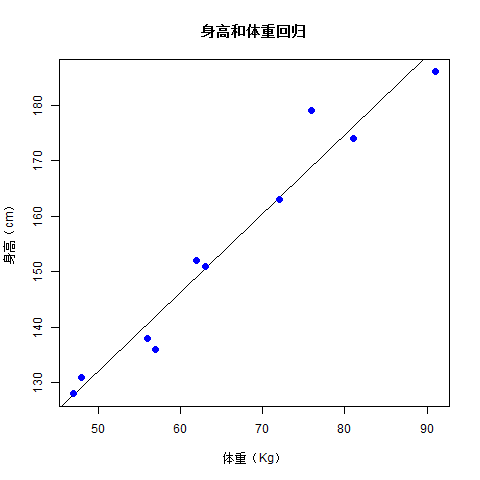
範例:以圖形方式視覺化線性回歸,參考以下程式碼實現 -
# Create the predictor and response variable.
x <- c(151, 174, 138, 186, 128, 136, 179, 163, 152, 131)
y <- c(63, 81, 56, 91, 47, 57, 76, 72, 62, 48)
relation <- lm(y~x)
# Give the chart file a name.
png(file = "linearregression.png")
# Plot the chart.
plot(y,x,col = "blue",main = "身高和體重回歸",
abline(lm(x~y)),cex = 1.3,pch = 16,xlab = "體重(Kg)",ylab = "身高(cm)")
# Save the file.
dev.off()
當我們執行上述程式碼時,會產生以下結果 -