TensorFlow單詞嵌入
Word嵌入是從單詞之類的離散物件到向量和實數的對映的概念。對於機器學習的輸入很重要。該概念包括標準函式,它有效地將離散輸入物件轉換為有用的向量。
單詞嵌入輸入的範例說明如下所示 -
blue: (0.01359, 0.00075997, 0.24608, ..., -0.2524, 1.0048, 0.06259)
blues: (0.01396, 0.11887, -0.48963, ..., 0.033483, -0.10007, 0.1158)
orange: (-0.24776, -0.12359, 0.20986, ..., 0.079717, 0.23865, -0.014213)
oranges: (-0.35609, 0.21854, 0.080944, ..., -0.35413, 0.38511, -0.070976)
Word2vec
Word2vec是用於無監督字嵌入技術的最常用方法。它以這樣的方式訓練模型:給定的輸入詞通過使用skip-gram來預測單詞的上下文。
TensorFlow通過多種方式實現這種模型,提高了複雜程度和優化水平,並使用多執行緒概念和更高階別的抽象。
import os
import math
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.contrib.tensorboard.plugins import projector
batch_size = 64
embedding_dimension = 5
negative_samples = 8
LOG_DIR = "logs/word2vec_intro"
digit_to_word_map = {
1: "One",
2: "Two",
3: "Three",
4: "Four",
5: "Five",
6: "Six",
7: "Seven",
8: "Eight",
9: "Nine"}
sentences = []
# Create two kinds of sentences - sequences of odd and even digits.
for i in range(10000):
rand_odd_ints = np.random.choice(range(1, 10, 2), 3)
sentences.append(" ".join([digit_to_word_map[r] for r in rand_odd_ints]))
rand_even_ints = np.random.choice(range(2, 10, 2), 3)
sentences.append(" ".join([digit_to_word_map[r] for r in rand_even_ints]))
# Map words to indices
word2index_map = {}
index = 0
for sent in sentences:
for word in sent.lower().split():
if word not in word2index_map:
word2index_map[word] = index
index += 1
index2word_map = {index: word for word, index in word2index_map.items()}
vocabulary_size = len(index2word_map)
# Generate skip-gram pairs
skip_gram_pairs = []
for sent in sentences:
tokenized_sent = sent.lower().split()
for i in range(1, len(tokenized_sent)-1):
word_context_pair = [[word2index_map[tokenized_sent[i-1]],
word2index_map[tokenized_sent[i+1]]], word2index_map[tokenized_sent[i]]]
skip_gram_pairs.append([word_context_pair[1], word_context_pair[0][0]])
skip_gram_pairs.append([word_context_pair[1], word_context_pair[0][1]])
def get_skipgram_batch(batch_size):
instance_indices = list(range(len(skip_gram_pairs)))
np.random.shuffle(instance_indices)
batch = instance_indices[:batch_size]
x = [skip_gram_pairs[i][0] for i in batch]
y = [[skip_gram_pairs[i][1]] for i in batch]
return x, y
# batch example
x_batch, y_batch = get_skipgram_batch(8)
x_batch
y_batch
[index2word_map[word] for word in x_batch] [index2word_map[word[0]] for word in y_batch]
# Input data, labels train_inputs = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape = [batch_size])
train_labels = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape = [batch_size, 1])
# Embedding lookup table currently only implemented in CPU with
tf.name_scope("embeddings"):
embeddings = tf.Variable(
tf.random_uniform([vocabulary_size, embedding_dimension], -1.0, 1.0),
name = 'embedding')
# This is essentialy a lookup table
embed = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embeddings, train_inputs)
# Create variables for the NCE loss
nce_weights = tf.Variable(
tf.truncated_normal([vocabulary_size, embedding_dimension], stddev = 1.0 /
math.sqrt(embedding_dimension)))
nce_biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([vocabulary_size]))
loss = tf.reduce_mean(
tf.nn.nce_loss(weights = nce_weights, biases = nce_biases, inputs = embed,
labels = train_labels,num_sampled = negative_samples,
num_classes = vocabulary_size)) tf.summary.scalar("NCE_loss", loss)
# Learning rate decay
global_step = tf.Variable(0, trainable = False)
learningRate = tf.train.exponential_decay(learning_rate = 0.1,
global_step = global_step, decay_steps = 1000, decay_rate = 0.95, staircase = True)
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learningRate).minimize(loss)
merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
with tf.Session() as sess:
train_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(LOG_DIR,
graph = tf.get_default_graph())
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with open(os.path.join(LOG_DIR, 'metadata.tsv'), "w") as metadata:
metadata.write('Name\tClass\n') for k, v in index2word_map.items():
metadata.write('%s\t%d\n' % (v, k))
config = projector.ProjectorConfig()
embedding = config.embeddings.add() embedding.tensor_name = embeddings.name
# Link this tensor to its metadata file (e.g. labels).
embedding.metadata_path = os.path.join(LOG_DIR, 'metadata.tsv')
projector.visualize_embeddings(train_writer, config)
tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
for step in range(1000):
x_batch, y_batch = get_skipgram_batch(batch_size) summary, _ = sess.run(
[merged, train_step], feed_dict = {train_inputs: x_batch, train_labels: y_batch})
train_writer.add_summary(summary, step)
if step % 100 == 0:
saver.save(sess, os.path.join(LOG_DIR, "w2v_model.ckpt"), step)
loss_value = sess.run(loss, feed_dict = {
train_inputs: x_batch, train_labels: y_batch})
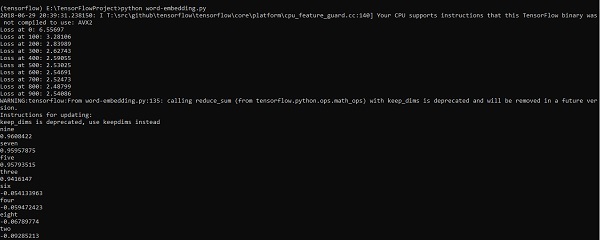
print("Loss at %d: %.5f" % (step, loss_value))
# Normalize embeddings before using
norm = tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(embeddings), 1, keep_dims = True))
normalized_embeddings = embeddings /
norm normalized_embeddings_matrix = sess.run(normalized_embeddings)
ref_word = normalized_embeddings_matrix[word2index_map["one"]]
cosine_dists = np.dot(normalized_embeddings_matrix, ref_word)
ff = np.argsort(cosine_dists)[::-1][1:10] for f in ff: print(index2word_map[f])
print(cosine_dists[f])
上面的程式碼生成以下輸出 -