Java for迴圈
Java for迴圈用於多次迭代程式的一部分,或者多次執行同一個程式碼塊。如果疊代次數是固定的,建議使用for迴圈。
java中有三種型別的for迴圈。如下所示 -
- 簡單
for迴圈 for-each或增強型for迴圈- 標記
for迴圈
1. Java簡單For迴圈
簡單的for迴圈與C/C++相同。我們可以初始化變數,檢查條件和增加/減少變數的值。
語法:
for(initialization;condition;incr/decr){
//code to be executed
}
執行流程圖如下所示 -
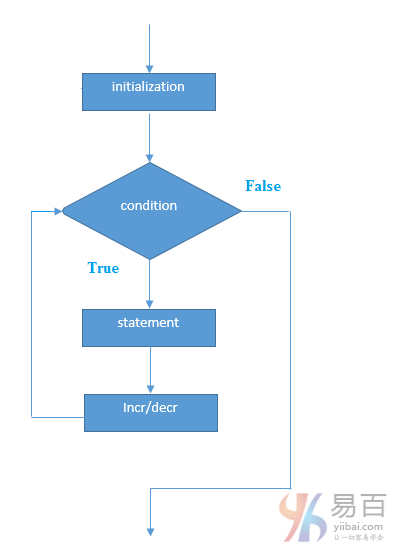
範例:
public class ForExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
執行上面的程式碼,輸出如下 -
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2. Java for-each迴圈
for-each迴圈用於在java中遍歷陣列或集合。它比簡單的for迴圈更容易使用,因為不需要遞增值和使用下標符號。
語法:
for(Type var:array){
//code to be executed
}
範例:
public class ForEachExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = { 12, 23, 44, 56, 78 };
for (int i : arr) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
執行上面的程式碼,得到如下結果 -
12
23
44
56
78
3. Java標記For迴圈
我們可以讓每個for迴圈的名稱。 為此,在for迴圈之前使用標籤。它是有用的,如果在巢狀for迴圈中,可以使用break/continue指定迴圈。
通常,break和continue關鍵字斷開/繼續最內迴圈。
語法:
labelname:
for(initialization;condition;incr/decr){
//code to be executed
}
範例:
public class LabeledForExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
aa: for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
bb: for (int j = 1; j <= 3; j++) {
if (i == 2 && j == 2) {
break aa;
}
System.out.println(i + " " + j);
}
}
}
}
執行上面的程式碼,得到如下結果 -
1 1
1 2
1 3
2 1
如果使用break bb;它將打斷內迴圈,這是任何迴圈的預設行為。
public class LabeledForExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
aa: for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
bb: for (int j = 1; j <= 3; j++) {
if (i == 2 && j == 2) {
break bb;
}
System.out.println(i + " " + j);
}
}
}
}
執行上面的程式碼,得到如下結果 -
1 1
1 2
1 3
2 1
3 1
3 2
3 3
4. Java無限迴圈
在for迴圈中,如果使用兩個分號;,則它對於迴圈將是不定式的。
語法:
for(;;){
//code to be executed
}
範例:
public class ForExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (;;) {
System.out.println("infinitive loop");
}
}
}
執行上面的程式碼,得到如下結果 -
infinitive loop
infinitive loop
infinitive loop
infinitive loop
infinitive loop
ctrl+c
提示: 在執行上面的程式時,您需要按
ctrl + c退出程式。