Java運算子
java中的運算子是用於執行運算(加,減,乘,除等)操作的符號。例如:+, - ,*,/等。
Java中有許多型別的運算子,如下所示:
- 一元運算子
- 算術運算子
- 移位運算子
- 關係運算子
- 按位元運算子
- 邏輯運算子
- 三元運算子
- 分配運算子
| 運算子 | 優先順序 |
|---|---|
| 字尾 | expr++, expr-- |
| 一元 | ++expr, --expr, +expr, -expr,~,! |
| 乘、除法 | *, /,% |
| 加、減法 | +, - |
| 移位 | <<, >>, >>> |
| 關係 | <, >, <=,>=, instanceof |
| 相等 | ==, != |
| 按位元與 | & |
| 按位元互斥或 | ^ |
| 按位元或 | 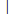 |
| 邏輯與 | && |
| 邏輯或 | 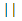 |
| 三元 | ? : |
| 賦值 | =, +=, -=, *=, /=,%=,&=, ^=, <<=, >>=, >>>=,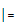 |
下面分別來看上述執行算的範例:
1. Java一元運算子範例:++ 和 —
class OperatorExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
int x=10;
System.out.println(x++);//10 (11)
System.out.println(++x);//12
System.out.println(x--);//12 (11)
System.out.println(--x);//10
}
}
輸出結果如下:
10
12
12
10
2. Java一元運算子範例2:++ 和 —
class OperatorExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 10;
int b = 10;
System.out.println(a++ + ++a);// 10+12=22
System.out.println(b++ + b++);// 10+11=21
}
}
輸出結果如下:
22
21
3. Java一元運算子範例3:? 和 !
class OperatorExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 10;
int b = -10;
boolean c = true;
boolean d = false;
System.out.println(~a);// -11 (minus of total positive value which
// starts from 0)
System.out.println(~b);// 9 (positive of total minus, positive starts
// from 0)
System.out.println(!c);// false (opposite of boolean value)
System.out.println(!d);// true
}
}
輸出結果如下:
-11
9
false
true
4. Java算術運算子範例
class OperatorExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 10;
int b = 5;
System.out.println(a + b);// 15
System.out.println(a - b);// 5
System.out.println(a * b);// 50
System.out.println(a / b);// 2
System.out.println(a % b);// 0
}
}
輸出結果如下:
15
5
50
2
0
5. Java算術運算子範例:表示式
class OperatorExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println(10 * 10 / 5 + 3 - 1 * 4 / 2);
}
}
輸出結果如下:
21
6. java的移位運算範例:左移
class OperatorExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println(10 << 2);// 10*2^2=10*4=40
System.out.println(10 << 3);// 10*2^3=10*8=80
System.out.println(20 << 2);// 20*2^2=20*4=80
System.out.println(15 << 4);// 15*2^4=15*16=240
}
}
輸出結果如下:
40
80
80
240
7. java的移位運算範例:右移
class OperatorExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println(10 >> 2);// 10/2^2=10/4=2
System.out.println(20 >> 2);// 20/2^2=20/4=5
System.out.println(20 >> 3);// 20/2^3=20/8=2
}
}
輸出結果如下:
2
5
2
8. java的移位運算範例:>> 和 >>>
class OperatorExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// For positive number, >> and >>> works same
System.out.println(20 >> 2);
System.out.println(20 >>> 2);
// For nagative number, >>> changes parity bit (MSB) to 0
System.out.println(-20 >> 2);
System.out.println(-20 >>> 2);
}
}
輸出結果如下:
5
5
-5
1073741819
9. Java AND運算子範例:邏輯&&和位&
如果第一個條件為假(false),則邏輯&&運算子不檢查第二個條件。它只有在第一個條件為真(true)時才會檢查第二個條件。
按位元與(&)運算子總是檢查兩個條件,不管第一個條件是真還是假。
class OperatorExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 10;
int b = 5;
int c = 20;
System.out.println(a < b && a < c);// false && true = false
System.out.println(a < b & a < c);// false & true = false
}
}
輸出結果如下:
false
false
10. Java與執行算範例:邏輯&&與按位元&
class OperatorExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 10;
int b = 5;
int c = 20;
System.out.println(a < b && a++ < c);// false && true = false
System.out.println(a);// 10 because second condition is not checked
System.out.println(a < b & a++ < c);// false && true = false
System.out.println(a);// 11 because second condition is checked
}
}
輸出結果如下:
false
10
false
11
11. Java 或運算子範例:邏輯|| 和按位元 |
邏輯|| 如果第一個條件為真(true),運算子不檢查第二個條件。它只在第一個條件為假(false)時才會檢查第二個條件。
按位元或 | 運算子總是檢查兩個條件,不管第一個條件是真(true)還是假(false)。
class OperatorExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 10;
int b = 5;
int c = 20;
System.out.println(a > b || a < c);// true || true = true
System.out.println(a > b | a < c);// true | true = true
// || vs |
System.out.println(a > b || a++ < c);// true || true = true
System.out.println(a);// 10 because second condition is not checked
System.out.println(a > b | a++ < c);// true | true = true
System.out.println(a);// 11 because second condition is checked
}
}
輸出結果如下:
true
true
true
10
true
11
12. Java 或運算子範例:邏輯|| 和按位元 |
class OperatorExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 2;
int b = 5;
int min = (a < b) ? a : b;
System.out.println(min);
}
}
輸出結果如下:
2
另一個例子:
class OperatorExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 10;
int b = 5;
int min = (a < b) ? a : b;
System.out.println(min);
}
}
輸出結果如下:
5
13. Java分配運算子範例
class OperatorExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
a += 4;// a=a+4 (a=10+4)
b -= 4;// b=b-4 (b=20-4)
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
}
}
輸出結果如下:
14
16
14. Java分配運算子範例:相加short型別資料
class OperatorExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
short a = 10;
short b = 10;
// a+=b;//a=a+b internally so fine
a = a + b;// 編譯時錯誤,因為 10+10=20 現在是 int 型別
System.out.println(a);
}
}
輸出結果如下:
編譯時錯誤....
型別轉換後:
class OperatorExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
short a = 10;
short b = 10;
a = (short) (a + b);// 20 which is int now converted to short
System.out.println(a);
}
}
輸出結果如下:
20