資料挖掘的決策樹
決策樹是一種結構,其中包括根節點,分支和葉子節點。每個內部節點表示在一個屬性測試,每個分支表示測試的結果和每個葉節點包含類的標籤。在樹的最頂部的節點是根節點。
下面決策樹是概念buy_computer,這表明在公司客戶是否可能購買電腦或沒有。每個內部節點表示在屬性測試。每個葉節點代表一個類。
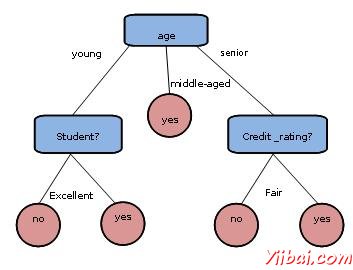
決策樹的優點
-
它不需要任何領域知識。
-
這是很容易被人吸收
-
學習和分類步驟決策樹是簡單和快速。
決策樹演算法
名為J.羅斯昆蘭在1980年一台機器研究員開發了一種決策樹演算法。這決策樹演算法被稱為ID3(疊代Dichotomiser)。後來,他給了C4.5這是ID3的繼任者。 ID3和C4.5採用貪心方法。在該演算法中,沒有回溯,樹木是建於自上而下的遞迴的分而治之的方式。
Generating a decision tree form training tuples of data partition D Algorithm : Generate_decision_tree Input: Data partition, D, which is a set of training tuples and their associated class labels. attribute_list, the set of candidate attributes. Attribute selection method, a procedure to determine the splitting criterion that best partitions that the data tuples into individual classes. This criterion includes a splitting_attribute and either a splitting yiibai or splitting subset. Output: A Decision Tree Method create a node N; if tuples in D are all of the same class, C then return N as leaf node labeled with class C; if attribute_list is empty then return N as leaf node with labeled with majority class in D;|| majority voting apply attribute_selection_method(D, attribute_list) to find the best splitting_criterion; label node N with splitting_criterion; if splitting_attribute is discrete-valued and multiway splits allowed then // no restricted to binary trees attribute_list = splitting attribute; // remove splitting attribute for each outcome j of splitting criterion // partition the tuples and grow subtrees for each partition let Dj be the set of data tuples in D satisfying outcome j; // a partition if Dj is empty then attach a leaf labeled with the majority class in D to node N; else attach the node returned by Generate decision tree(Dj, attribute list) to node N; end for return N;
樹木修剪
樹木修剪是為了在訓練資料中刪除異常由於噪聲或離群值執行。在修剪樹木是更小,更複雜。
樹木的修剪方法
下面是列出的樹修剪途徑:
-
修剪前 - 該樹是由早期停止其建設修剪。
-
修剪後 - 此方法將刪除子樹的形式完全成長樹。
成本複雜性
成本複雜性測量由以下兩個引數:
-
樹的葉子數量
-
樹的誤位元速率