Java NIO管道
Java NIO管道用於在兩個執行緒之間建立單向資料連線。它有一個槽通道和源通道。資料正在寫入槽通道,然後可以從源通道讀取該資料。
在Java NIO中,包java.nio.channel.pipe用於按順序讀取和寫入資料。管道用於確保資料必須以寫入管道的相同順序讀取。
下面來看看管道工作原理的示意圖說明:
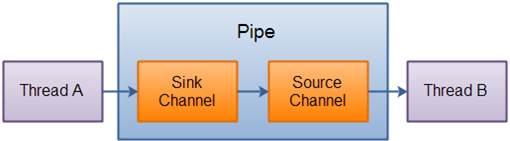
建立管道
要建立一個管道,可通過呼叫Pipe.open()方法開啟管道。
開啟或建立管道的語法是:
Pipe pp = Pipe.open();
從管道讀取資料
要從管道讀取資料,需要先存取源通道。 因此,用於存取源通道的語法是:
Pipe.SourceChannel sc= pipe.source();
要從SourceChannel讀取資料,可呼叫read()方法,如下所示:
ByteBuffer bb= ByteBuffer.allocate(512);
int bytesRead = inChannel.read(bb);
read()方法返回的整數值用於確定讀入緩衝區的位元組數。
寫入管道
要將資料寫入管道,需要存取接收器通道。存取宿通道的語法是:
Pipe.SinkChannel sc= pipe.sink();
要將資料寫入SinkChannel,可呼叫write()方法,如下所示:
String newData = "The new String is writing in a Pipe..." + System.currentTimeMillis();
ByteBuffer bb= ByteBuffer.allocate(512);
bb.clear();
bb.put(newData.getBytes());
bb.flip();
while(bb.hasRemaining()) {
SinkChannel.write(bb);
}
基本管道範例:
package com.yiibai;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.Pipe;
public class PipeExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// The Pipe is created
Pipe pipe = Pipe.open();
// For accessing the pipe sink channel
Pipe.SinkChannel skChannel = pipe.sink();
String td = "Data is successfully sent for checking the java NIO Channel Pipe.";
ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocate(512);
bb.clear();
bb.put(td.getBytes());
bb.flip();
// write the data into a sink channel.
while (bb.hasRemaining()) {
skChannel.write(bb);
}
// For accessing the pipe source channel
Pipe.SourceChannel sourceChannel = pipe.source();
bb = ByteBuffer.allocate(512);
// The data is write to the console
while (sourceChannel.read(bb) > 0) {
bb.flip();
while (bb.hasRemaining()) {
char TestData = (char) bb.get();
System.out.print(TestData);
}
bb.clear();
}
}
}
執行上面範例程式碼,得到以下結果 -
Data is successfully sent for checking the java NIO Channel Pipe.