Java NIO通道
在Java NIO中,通道是用於在實體和位元組緩衝區之間有效傳輸資料的媒介。它從一個實體讀取資料,並將其放在緩衝區塊中以供消費。
通道作為Java NIO提供的閘道器來存取I/O機制。 通常,通道與作業系統檔案描述符具有一對一關係,用於提供平台獨立操作功能。
讓我們來看看java.nio.channels類的層次結構:
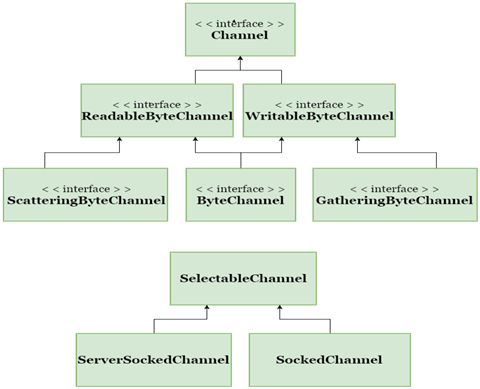
上述通道可以用於阻塞或非阻塞模式,但是我們主要關注在非阻塞模式下使用通道。
NIO通道基礎
通道實現是使用原生代碼執行實際工作。通道介面允許我們以便攜和受控的方式存取低階I/O服務。
在層次結構的頂部,通道介面如下所示:
package java.nio.channels;
public interface Channel{
public boolean isclose();
public void Open() throws IOException;
}
正如在上述通道介面中看到的,所有通道只有兩個常用操作:
- 檢查通道是否關閉(
isclose()) - 開啟關閉通道(
close())
通道實現
在Java NIO中,主要使用的通道如下:
- FileChannel:檔案通道用於從檔案讀取資料。它只能通過呼叫
getChannel()方法來建立物件。不能直接建立FileChannel物件。
下面是一個建立FileChannel物件的例子:FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\file-read.txt"); // Path of Input text file ReadableByteChannel rbc = fis.getChannel(); - DatagramChannel:資料報通道可以通過UDP(使用者資料報協定)通過網路讀取和寫入資料。它使用工廠方法來建立新物件。
下面是開啟DatagramChannel的語法:
用於關閉DatagramChannel ch = DatagramChannel.open();DatagramChannel的語法:DatagramChannel ch = DatagramChannel.close(); - SocketChannel:資料報通道可以通過TCP(傳輸控制協定)通過網路讀取和寫入資料。 它還使用工廠方法來建立新物件。
用於開啟SocketChannel的語法:
用於關閉SocketChannel ch = SocketChannel.open(); ch.connect(new InetSocketAddress("somehost", someport));SocketChannel的語法:SocketChannel ch = SocketChannel.close(); ch.connect(new InetSocketAddress("somehost", someport)); - ServerSocketChannel:
ServerSocketChannel允許使用者監聽傳入的TCP連線,與Web伺服器相同。對於每個傳入連線,都會為連線建立一個SocketChannel。
下面是開啟ServerSocketChannel的語法:
下面是關閉ServerSocketChannel ch = ServerSocketChannel.open(); ch.socket().bind (new InetSocketAddress (somelocalport));ServerSocketChannel的語法:ServerSocketChannel ch = ServerSocketChannel.close(); ch.socket().bind (new InetSocketAddress (somelocalport));
基本通道範例
下面來看看如何將資料從一個通道複製到另一個通道或從一個檔案複製到另一個檔案的範例:
package com.yiibai;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.ReadableByteChannel;
import java.nio.channels.WritableByteChannel;
public class ChannelDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
String relativelyPath = System.getProperty("user.dir");
FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream(relativelyPath + "/testin.txt");
ReadableByteChannel source = input.getChannel();
FileOutputStream output = new FileOutputStream(relativelyPath + "/testout.txt");
WritableByteChannel destination = output.getChannel();
copyData(source, destination);
source.close();
destination.close();
System.out.println("Copy Data finished.");
}
private static void copyData(ReadableByteChannel src, WritableByteChannel dest) throws IOException {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(20 * 1024);
while (src.read(buffer) != -1) {
// The buffer is used to drained
buffer.flip();
// keep sure that buffer was fully drained
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
dest.write(buffer);
}
buffer.clear(); // Now the buffer is empty, ready for the filling
}
}
}
執行上面範例程式碼,得到以下結果:
Copy Data finished.
上述程式將文字檔案filein.txt的內容複製到另一個文字檔案fileout.txt。