Assembly 算術指令
INC指令
INC指令是一個用於運算元遞增。它可以在一個單一的運算元,可以是在一個暫存器或記憶體。
語法:
INC指令的語法如下:
INC destination
運算元目標可能是8位元,16位元或32位元運算元。
例子:
INC EBX ; Increments 32-bit register INC DL ; Increments 8-bit register INC [count] ; Increments the count variable
DEC指令
DEC指令用於由一個運算元遞減。它可以在一個單一的運算元,可以是在一個暫存器或記憶體。
語法:
DEC指令的語法如下:
DEC destination
運算元目標可以是8位元,16位元或32位元運算元。
例子:
segment .data count dw 0 value db 15 segment .text inc [count] dec [value] mov ebx, count inc word [ebx] mov esi, value dec byte [esi]
ADD和SUB指令
ADD和SUB指令用於執行二進位制資料位元組,字和雙字的大小,即簡單的加法/減法,8位元,16位元或32位元運算元分別相加或相減。
語法:
ADD和SUB指令的語法如下:
ADD/SUB destination, source
ADD/ SUB指令之間可能發生:
-
暫存器到暫存器
-
記憶體到暫存器
-
暫存器到記憶體
-
暫存器到常數資料
-
記憶體到常數資料
然而,像其他指令,記憶體到記憶體的操作是不可能使用ADD/ SUB指令。 ADD或SUB操作設定或清除溢位和進位標誌。
例子:
下面的例子會從使用者要求的兩個數位,分別在EAX和EBX暫存器儲存的數位,增加值,並將結果儲存在一個記憶體位置'清晰度',並最終顯示結果。
SYS_EXIT equ 1 SYS_READ equ 3 SYS_WRITE equ 4 STDIN equ 0 STDOUT equ 1 segment .data msg1 db "Enter a digit ", 0xA,0xD len1 equ $- msg1 msg2 db "Please enter a second digit", 0xA,0xD len2 equ $- msg2 msg3 db "The sum is: " len3 equ $- msg3 segment .bss num1 resb 2 num2 resb 2 res resb 1 section .text global _start ;must be declared for using gcc _start: ;tell linker entry yiibai mov eax, SYS_WRITE mov ebx, STDOUT mov ecx, msg1 mov edx, len1 int 0x80 mov eax, SYS_READ mov ebx, STDIN mov ecx, num1 mov edx, 2 int 0x80 mov eax, SYS_WRITE mov ebx, STDOUT mov ecx, msg2 mov edx, len2 int 0x80 mov eax, SYS_READ mov ebx, STDIN mov ecx, num2 mov edx, 2 int 0x80 mov eax, SYS_WRITE mov ebx, STDOUT mov ecx, msg3 mov edx, len3 int 0x80 ; moving the first number to eax register and second number to ebx ; and subtracting ascii '0' to convert it into a decimal number mov eax, [number1] sub eax, '0' mov ebx, [number2] sub ebx, '0' ; add eax and ebx add eax, ebx ; add '0' to to convert the sum from decimal to ASCII add eax, '0' ; storing the sum in memory location res mov [res], eax ; print the sum mov eax, SYS_WRITE mov ebx, STDOUT mov ecx, res mov edx, 1 int 0x80 exit: mov eax, SYS_EXIT xor ebx, ebx int 0x80
上面的程式碼編譯和執行時,它會產生以下結果:
Enter a digit: 3 Please enter a second digit: 4 The sum is: 7
該程式用寫死的變數:
section .text global _start ;must be declared for using gcc _start: ;tell linker entry yiibai mov eax,'3' sub eax, '0' mov ebx, '4' sub ebx, '0' add eax, ebx add eax, '0' mov [sum], eax mov ecx,msg mov edx, len mov ebx,1 ;file descriptor (stdout) mov eax,4 ;system call number (sys_write) int 0x80 ;call kernel mov ecx,sum mov edx, 1 mov ebx,1 ;file descriptor (stdout) mov eax,4 ;system call number (sys_write) int 0x80 ;call kernel mov eax,1 ;system call number (sys_exit) int 0x80 ;call kernel section .data msg db "The sum is:", 0xA,0xD len equ $ - msg segment .bss sum resb 1
上面的程式碼編譯和執行時,它會產生以下結果:
The sum is: 7
MUL/ IMUL指令
有兩個指令乘以二進位制資料。 MUL(乘)指令處理無符號資料和IMUL(整數乘法)處理有符號資料。這兩個指令影響進位和溢位標誌。
語法:
MUL/ IMUL指令,語法如下:
MUL/IMUL multiplier
在這兩種情況被乘數是在累加器中,根據被乘數和乘數的大小,所產生的產物也被儲存在運算元,大小取決於兩個暫存器。下面一節的解釋MULL有三種不同的情況指令:
| SN | Scenarios |
|---|---|
| 1 |
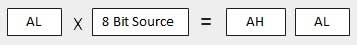
When two bytes are multiplied The multiplicand is in the AL register, and the multiplier is a byte in the memory or in another register. The product is in AX. High order 8 bits of the product is stored in AH and the low order 8 bits are stored in AL
|
| 2 |
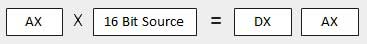
When two one-word values are multiplied The multiplicand should be in the AX register, and the multiplier is a word in memory or another register. For example, for an instruction like MUL DX, you must store the multiplier in DX and the multiplicand in AX. The resultant product is a double word, which will need two registers. The High order (leftmost) portion gets stored in DX and the lower-order (rightmost) portion gets stored in AX.
|
| 3 |
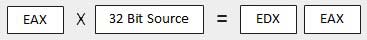
When two doubleword values are multiplied When two doubleword values are multiplied, the multiplicand should be in EAX and the multiplier is a doubleword value stored in memory or in another register. The product generated is stored in the EDX:EAX registers, i.e., the high order 32 bits gets stored in the EDX register and the low order 32-bits are stored in the EAX register.
|
例子:
MOV AL, 10 MOV DL, 25 MUL DL ... MOV DL, 0FFH ; DL= -1 MOV AL, 0BEH ; AL = -66 IMUL DL
例子:
下面的範例與2乘以3,並顯示結果:
section .text global _start ;must be declared for using gcc _start: ;tell linker entry yiibai mov al,'3' sub al, '0' mov bl, '2' sub bl, '0' mul bl add al, '0' mov [res], al mov ecx,msg mov edx, len mov ebx,1 ;file descriptor (stdout) mov eax,4 ;system call number (sys_write) int 0x80 ;call kernel mov ecx,res mov edx, 1 mov ebx,1 ;file descriptor (stdout) mov eax,4 ;system call number (sys_write) int 0x80 ;call kernel mov eax,1 ;system call number (sys_exit) int 0x80 ;call kernel section .data msg db "The result is:", 0xA,0xD len equ $- msg segment .bss res resb 1
上面的程式碼編譯和執行時,它會產生以下結果:
The result is: 6
DIV/IDIV 指令
除法運算產生兩個元素 - 一個商和餘數。在乘法運算的情況下,不會發生溢位,因為雙倍長度的暫存器是用來保持產生。然而,在除法的情況下,可能會發生溢位。處理器產生一個中斷,如果發生溢位。
DIV(除)指令或無符號資料和IDIV(整數除法)用於有符號資料。
語法:
DIV / IDIV指令的格式為:
DIV/IDIV divisor
被除數是在累加器。兩個指令可以處理8位元,16位元或32位元運算元。該操作會影響所有的6個狀態標誌。以下部分說明了三個例子的劃分有不同的運算元大小:
| SN | Scenarios |
|---|---|
| 1 |
When the divisor is 1 byte The dividend is assumed to be in the AX register (16 bits). After division, the quotient goes to the AL register and the remainder goes to the AH register.
|
| 2 |
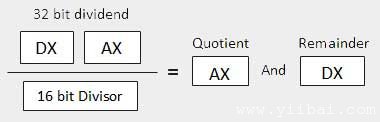
When the divisor is 1 word The dividend is assumed to be 32 bits long and in the DX:AX registers. The high order 16 bits are in DX and the low order 16 bits are in AX. After division, the 16 bit quotient goes to the AX register and the 16 bit remainder goes to the DX register.
|
| 3 |
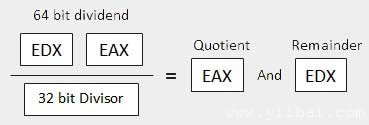
When the divisor is doubleword The dividend is assumed to be 64 bits long and in the EDX:EAX registers. The high order 32 bits are in EDX and the low order 32 bits are in EAX. After division, the 32 bit quotient goes to the EAX register and the 32 bit remainder goes to the EDX register.
|
例子:
下面的例子8除於2。8被儲存在16位元暫存器EAX和除數2被儲存在8位元BL暫存器。
section .text global _start ;must be declared for using gcc _start: ;tell linker entry yiibai mov ax,'8' sub ax, '0' mov bl, '2' sub bl, '0' div bl add ax, '0' mov [res], ax mov ecx,msg mov edx, len mov ebx,1 ;file descriptor (stdout) mov eax,4 ;system call number (sys_write) int 0x80 ;call kernel mov ecx,res mov edx, 1 mov ebx,1 ;file descriptor (stdout) mov eax,4 ;system call number (sys_write) int 0x80 ;call kernel mov eax,1 ;system call number (sys_exit) int 0x80 ;call kernel section .data msg db "The result is:", 0xA,0xD len equ $- msg segment .bss res resb 1
上面的程式碼編譯和執行時,它會產生以下結果:
The result is: 4