C語言運算子
在C語言中,運算子是一個符號,告訴編譯器執行特定的數學或邏輯函式,C語言提供豐富的內建運算子,並提供以下型別的運算子 -
- 算術運算子
- 關係運算子
- 邏輯運算子
- 按位元運算子
- 賦值運算子
- 其它運算子
在本章中,我們將學習每個運算子的工作方式。開啟Visual Studio 2017建立一個Win32 Console Application 專案,名稱為:c-operators 。
1.算術運算子
下表顯示了C語言支援的所有算術運算子。假設變數A的值是10,變數B的值是20,那麼 -
| 運算子 | 描述 | 範例 |
|---|---|---|
+ |
將兩個運算元相加 | A + B = 30 |
- |
從第一個運算元減去第二個運算元 | A ? B = -10 |
* |
將兩個運算元相乘 | A * B = 200 |
/ |
將第一個運算元除以第二個運算元 | |
% |
模數運算子和整數除法後的餘數。 | B % A = 0 |
++ |
遞增運算子將整數值增加1。 |
A++ = 11 |
-- |
遞減運算子將整數值減1。 | A-- = 9 |
建立一個原始碼檔案:arithmetic_operators.c,如下程式碼 -
#include <stdio.h>
void main() {
int a = 21;
int b = 10;
int c ;
c = a + b;
printf("Line 1 - Value of c is %d\n", c );
c = a - b;
printf("Line 2 - Value of c is %d\n", c );
c = a * b;
printf("Line 3 - Value of c is %d\n", c );
c = a / b;
printf("Line 4 - Value of c is %d\n", c );
c = a % b;
printf("Line 5 - Value of c is %d\n", c );
c = a++;
printf("Line 6 - Value of c is %d\n", c );
c = a--;
printf("Line 7 - Value of c is %d\n", c );
}
執行上面範例程式碼,得到以下結果 -
Line 1 - Value of c is 31
Line 2 - Value of c is 11
Line 3 - Value of c is 210
Line 4 - Value of c is 2
Line 5 - Value of c is 1
Line 6 - Value of c is 21
Line 7 - Value of c is 22
請按任意鍵繼續. . .
2.關係運算子
下表顯示了C語言支援的關係運算子。假設變數A=10,變數B=20,則 -
| 運算子 | 描述 | 範例 |
|---|---|---|
== |
檢查兩個運算元的值是否相等。 如果相等,則條件成立。 | (A == B)結果為false |
!= |
檢查兩個運算元的值是否相等。 如果值不相等,則條件成立。 | (A != B) 結果為true |
> |
檢查左運算元的值是否大於右運算元的值。 如果是,則條件成立。 | (A > B) 結果為false |
< |
檢查左運算元的值是否小於右運算元的值。 如果是,則條件成立。 | (A < B)結果為true |
>= |
檢查左運算元的值是否大於等於右運算元的值。 如果是,則條件成立。 | (A >= B) 結果為false |
<= |
檢查左運算元的值是否小於等於右運算元的值。 如果是,則條件成立。 | (A <= B)結果為true |
建立一個原始碼檔案:relational_operators.c,如下程式碼 -
#include <stdio.h>
main() {
int a = 21;
int b = 10;
int c ;
if( a == b ) {
printf("Line 1 - a is equal to b\n" );
}
else {
printf("Line 1 - a is not equal to b\n" );
}
if ( a < b ) {
printf("Line 2 - a is less than b\n" );
}
else {
printf("Line 2 - a is not less than b\n" );
}
if ( a > b ) {
printf("Line 3 - a is greater than b\n" );
}
else {
printf("Line 3 - a is not greater than b\n" );
}
/* Lets change value of a and b */
a = 5;
b = 20;
if ( a <= b ) {
printf("Line 4 - a is either less than or equal to b\n" );
}
if ( b >= a ) {
printf("Line 5 - b is either greater than or equal to b\n" );
}
}
執行上面範例程式碼,得到以下結果 -
Line 1 - a is not equal to b
Line 2 - a is not less than b
Line 3 - a is greater than b
Line 4 - a is either less than or equal to b
Line 5 - b is either greater than or equal to b
請按任意鍵繼續. . .
3.邏輯運算子
下表顯示了C語言支援的所有邏輯運算子。 假設變數A=1,變數B=0,則 -
| 運算子 | 描述 | 範例 |
|---|---|---|
&& |
邏輯與運算子。 如果兩個運算元都不為零,則條件成立。 | (A && B)結果為false |
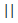 |
稱為邏輯或運算子。如果兩個運算元中的任何一個非零,則條件成立。 | (A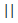 B)結果為 B)結果為true |
! |
稱為邏輯非運算子,它用於反轉其運算元的邏輯狀態。如果條件為真,則邏輯NOT運算子將使其結果為false。 |
範例:建立一個原始檔:logical_operators.c,程式碼如下 -
#include <stdio.h>
main() {
int a = 5;
int b = 20;
int c ;
if ( a && b ) {
printf("Line 1 - Condition is true\n" );
}
if ( a || b ) {
printf("Line 2 - Condition is true\n" );
}
/* lets change the value of a and b */
a = 0;
b = 10;
if ( a && b ) {
printf("Line 3 - Condition is true\n" );
}
else {
printf("Line 3 - Condition is not true\n" );
}
if ( !(a && b) ) {
printf("Line 4 - Condition is true\n" );
}
}
執行上面程式碼,得到以下結果 -
Line 1 - Condition is true
Line 2 - Condition is true
Line 3 - Condition is not true
Line 4 - Condition is true
4.按位元運算子
按位元運算子對位進行操作,並執行逐位運算。 &,|和^的真值表如下 -
| p | q | p & q | p/q | p ^ q |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
假設A = 60,B = 13,二進位制格式如下:
A = 0011 1100
B = 0000 1101
-----------------
A&B = 0000 1100
A|B = 0011 1101
A^B = 0011 0001
~A = 1100 0011
下表列出了C語言支援的按位元運算子。假設變數A=60,變數B=13,則 -
| 運算子 | 描述 | 範例 |
|---|---|---|
& |
如果二進位制AND運算子存在於兩個運算元中,則二進位制AND運算子將對結果複製一位。 | (A&B)= 12,即0000 1100 |
 |
二進位制OR運算子如果存在於任一運算元中,則複製一位。 | (A  B) = 61, 即 B) = 61, 即 0011 1101 |
^ |
二進位制XOR操作符複製該位,如果它設定在一個運算元中,而不是兩者。 | (A ^ B) = 49, 即, 0011 0001 |
~ |
二進位制二補數運算子是一元的,具有「翻轉」位的作用。 | (~A)= -61,即 1100 0011的二補數形式。 |
<< |
二進位制左移操作符,左運算元值左移由右運算元指定的位數。 | A << 2 = 240 即, 1111 0000 |
>> |
二進位制右移操作符,左運算元值被右運算元指定的位移動。 | A >> 2 = 15 即,0000 1111 |
範例: 建立一個原始碼檔案:bitwise_operators.c,程式碼如下所示 -
#include <stdio.h>
main() {
unsigned int a = 60; /* 60 = 0011 1100 */
unsigned int b = 13; /* 13 = 0000 1101 */
int c = 0;
c = a & b; /* 12 = 0000 1100 */
printf("Line 1 - Value of c is %d\n", c );
c = a | b; /* 61 = 0011 1101 */
printf("Line 2 - Value of c is %d\n", c );
c = a ^ b; /* 49 = 0011 0001 */
printf("Line 3 - Value of c is %d\n", c );
c = ~a; /*-61 = 1100 0011 */
printf("Line 4 - Value of c is %d\n", c );
c = a << 2; /* 240 = 1111 0000 */
printf("Line 5 - Value of c is %d\n", c );
c = a >> 2; /* 15 = 0000 1111 */
printf("Line 6 - Value of c is %d\n", c );
}
執行上面程式碼,得到以下結果 -
Line 1 - Value of c is 12
Line 2 - Value of c is 61
Line 3 - Value of c is 49
Line 4 - Value of c is -61
Line 5 - Value of c is 240
Line 6 - Value of c is 15
請按任意鍵繼續. . .
5.賦值運算子
下表列出了C語言支援的賦值運算子 -
| 運算子 | 描述 | 範例 |
|---|---|---|
= |
簡單賦值運算子,將右側運算元的值分配給左側運算元 | C = A + B,將A + B的值分配給C |
+= |
相加與賦值運算子。它將右運算元新增到左運算元,並將結果分配給左運算元。 | C + = A等價於C = C + A |
-= |
相減與賦值運算子。它從左運算元中減去右運算元,並將結果分配給左運算元。 | C -= A等價於 C = C - A |
*= |
乘以與賦值運算子。它將右運算元與左運算元相乘,並將結果分配給左運算元。 | C * = A等價於C = C * A |
/= |
除以與賦值運算子。它將左運算元與右運算元分開,並將結果分配給左運算元。 | C /= A等價於C = C / A |
%= |
模數與賦值運算子。它需要使用兩個運算元的模數,並將結果分配給左運算元。 | C %= A等價於C = C % A |
<<= |
左移與賦值運算子 | C <<= 2等價於C = C << 2 |
>>= |
右移與賦值運算子 | C >> = 2等價於C = C >> 2 |
&= |
按位元與賦值運算子 | C &= 2等價於C = C & 2 |
^= |
按位元互斥或運算子和賦值運算子。 | C ^= 2等價於C = C ^ 2 |
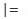 |
按位元包含OR和賦值運算子。 | 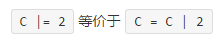 |
範例: 建立一個原始檔:assignment_operators.c ,其程式碼如下 -
#include <stdio.h>
void main() {
int a = 21;
int c ;
c = a;
printf("Line 1 - = Operator Example, Value of c = %d\n", c );
c += a;
printf("Line 2 - += Operator Example, Value of c = %d\n", c );
c -= a;
printf("Line 3 - -= Operator Example, Value of c = %d\n", c );
c *= a;
printf("Line 4 - *= Operator Example, Value of c = %d\n", c );
c /= a;
printf("Line 5 - /= Operator Example, Value of c = %d\n", c );
c = 200;
c %= a;
printf("Line 6 - %= Operator Example, Value of c = %d\n", c );
c <<= 2;
printf("Line 7 - <<= Operator Example, Value of c = %d\n", c );
c >>= 2;
printf("Line 8 - >>= Operator Example, Value of c = %d\n", c );
c &= 2;
printf("Line 9 - &= Operator Example, Value of c = %d\n", c );
c ^= 2;
printf("Line 10 - ^= Operator Example, Value of c = %d\n", c );
c |= 2;
printf("Line 11 - |= Operator Example, Value of c = %d\n", c );
}
執行上面程式碼,得到以下結果 -
Line 1 - = Operator Example, Value of c = 21
Line 2 - += Operator Example, Value of c = 42
Line 3 - -= Operator Example, Value of c = 21
Line 4 - *= Operator Example, Value of c = 441
Line 5 - /= Operator Example, Value of c = 21
Line 6 - = Operator Example, Value of c = 11
Line 7 - <<= Operator Example, Value of c = 44
Line 8 - >>= Operator Example, Value of c = 11
Line 9 - &= Operator Example, Value of c = 2
Line 10 - ^= Operator Example, Value of c = 0
Line 11 - |= Operator Example, Value of c = 2
請按任意鍵繼續. . .
6.其他操作符:sizeof和三元運算子
除了上面討論的運算子,還有一些其他重要的運算子,包括sizeof和? :也被C語言所支援。
| 運算子 | 描述 | 範例 |
|---|---|---|
sizeof() |
返回變數的大小 | sizeof(a),其中a為整數,將返回4。 |
& |
返回變數的地址 | &a; 返回變數的實際地址。 |
* |
指向變數的指標 | *a; |
? : |
條件表示式 | 如果條件是真的? 那麼返回值X:否則返回Y |
範例: 建立一個原始檔:sizeof_operator.c ,其程式碼如下 -
#include <stdio.h>
void main() {
int a = 4;
short b;
double c;
int* ptr;
/* example of sizeof operator */
printf("Line 1 - Size of variable a = %d\n", sizeof(a));
printf("Line 2 - Size of variable b = %d\n", sizeof(b));
printf("Line 3 - Size of variable c= %d\n", sizeof(c));
/* example of & and * operators */
ptr = &a; /* 'ptr' now contains the address of 'a'*/
printf("value of a is %d\n", a);
printf("*ptr is %d.\n", *ptr);
/* example of ternary operator */
a = 10;
b = (a == 1) ? 20 : 30;
printf("Value of b is %d\n", b);
b = (a == 10) ? 20 : 30;
printf("Value of b is %d\n", b);
}
執行上面程式碼,得到以下結果 -
Line 1 - Size of variable a = 4
Line 2 - Size of variable b = 2
Line 3 - Size of variable c= 8
value of a is 4
*ptr is 4.
Value of b is 30
Value of b is 20
請按任意鍵繼續. . .
7.運算子優先順序
運算子優先順序決定表示式中術語的分組,並決定如何評估計算表示式。 某些運算子的優先順序高於其他運營商; 例如,乘法運算子的優先順序高於加法運算子,則先要執行乘法運算子的運算。
讓我們通過下面的例子了解優先順序:
int value = 10 + 20 * 10;
value變數計算結果為:210,因為*(乘法運算子)的優先順序比+(加法運算子)高,所以在+(加法運算子)之前進行求值。
C語言運算子的優先順序和關聯性如下:
| 分類 | 運算子 | 關聯性 |
|---|---|---|
| 字尾 | () [] -> . ++ - - |
左到右 |
| 一元 | + - ! ~ ++ - - (type)* & sizeof |
右到左 |
| 乘法 | * / % |
左到右 |
| 加法 | + - |
左到右 |
| 位移 | << >> |
左到右 |
| 關係 | < <= > >= |
左到右 |
| 等於 | == != |
左到右 |
| 按位元與 | & |
左到右 |
| 位互斥或 | ^ |
左到右 |
| 按位元或 | / |
左到右 |
| 邏輯與 | && |
左到右 |
| 邏輯或 | // |
左到右 |
| 條件 | ?: |
右到左 |
| 賦值 | = += -= *= /= %=>>= <<= &= ^= /= |
右到左 |
| 逗號 | , |
左到右 |
範例: 建立一個原始檔:operators_precedence.c ,其程式碼如下 -
#include <stdio.h>
void main() {
int a = 20;
int b = 10;
int c = 15;
int d = 5;
int e;
e = (a + b) * c / d; // ( 30 * 15 ) / 5
printf("Value of (a + b) * c / d is : %d\n", e);
e = ((a + b) * c) / d; // (30 * 15 ) / 5
printf("Value of ((a + b) * c) / d is : %d\n", e);
e = (a + b) * (c / d); // (30) * (15/5)
printf("Value of (a + b) * (c / d) is : %d\n", e);
e = a + (b * c) / d; // 20 + (150/5)
printf("Value of a + (b * c) / d is : %d\n", e);
return 0;
}
執行上面程式碼,得到以下結果 -
Value of (a + b) * c / d is : 90
Value of ((a + b) * c) / d is : 90
Value of (a + b) * (c / d) is : 90
Value of a + (b * c) / d is : 50
請按任意鍵繼續. . .