springCloud框架學習-從入門到精通
SpringCloud階段的學習 筆記
作者:小傑
微服務架構4個核心問題
服務很多,用戶端怎麼存取?
這麼多服務,服務之間如何通訊?
這麼多服務,如何治理?
服務掛了怎麼辦?
核心問題解決方案
springcloud 生態
Spring Cloud NetFlix 一站式解決方案
api閘道器,zuul元件
Feign—基於Httpclient —Http通訊方式:同步、阻塞
服務註冊發現:Eureka
熔斷機制 機製:Hystrix
Apache Dubbo Zookeeper半自動,需要整合別人的
API:沒有,找第三方元件,或者自己實現
Dubbo:高效能的基於JAVA RPC的通訊框架
服務註冊發現:Zookeeper
熔斷機制 機製 沒有,可以藉助Hystrix
Dubbo和Zookeeper這個方案並不完善
Spring Cloud Alibaba 一站式解決方案,更簡單
springboot是構建 springcloud是協調
常見的面試問題?帶着這些去學習
什麼是微服務
微服務之間是如何獨立通訊的
SpringCloud和Dubbo有哪些區別
Springboot和SpringCloud,談談對他們的理解
什麼是服務熔斷?什麼是服務降級
微服務的優缺點分別是什麼?說下在專案中遇到的坑
Eureka與dubbo+zookeeper都可提供註冊和發現功能,兩者有何區別?
你所知道的技術棧有哪些? 列舉一二
微服務的概述
什麼是微服務?
微服務(Microservice Architecture)最近幾年流行的一種架構思想,關於他的概念很難一言蔽之。
原文:https://martinfowler.com/articles/microservice.html
漢化:https://www.cnblogs.com/liuning8023/p/4493156.html
就目前而言,對於微服務,業界並沒有一個統一的, 標準的定義
但通常而言,微服務架構是一種架構模式,或者說是一種架構風格, 它提倡將單一的應用程式劃分成一組小的服務,每個服務執行在其獨立的自己的進程內,服務之間互相協調,互相設定,爲使用者提供最終價值。服務之間採用輕量級的通訊機制 機製互相溝通,每個服務都圍繞着具體的業務進行構建,並且能夠被獨立的部署到生產不境中,另外,應儘量避免統一的,集中式的服務管理機制 機製,對具體的一個服務而言,應根據業務上下文,選聖合適的語言,工具對其進行構建,可以有一個非常輕量級的集中式管理來協調這些服務,可以使用不同的語言來編寫服務,也可以使用不同的數據儲存;
官方的話太過於生澀,我們從技術維度來理解下
微服務話的核心就是將傳統的一站式應用,根據業務拆分成一個一個服務。徹底的去耦合,每一個微服務提供單個業務功能的服務,一個服務做一件事情,從技術角度看就是一種小而獨立的處理過程,類似進程的概念,能夠自行單獨啓動或銷燬,擁有自己獨立的數據庫
微服務與微服務架構
微服務
強調的是服務的大小,他關注的是某一個點,是具體解決某一問題 提供落地對應服務的一個服務應用,狹義的看,可以看做是IDEA中的一個微服務工程或者Moudel
IDEA 工具裏面使用Maven開發的一個個獨立的Moudle,它具體使用springboot開發的一個小模組,專門的事交給專業的模組來做,一個模組就做一件事情敲掉的是一個個的個體,每個個體完成一個具體的任務或者功能
微服務架構
一種新的架構形式,Martin Fowler,2014提出
微服務架構是一種架構模式,它提倡將單- -應用程式劃分成一組小的服務,服務之間互相協調,互相配合,爲使用者提供最終價值。每個服務執行在其獨立的進程中,服務於服務間採用輕量級的通訊機制 機製互相共同作業,每個服務都圍繞着具體的業務進行構建,並且能夠被獨立的部署到生產環境中,另外,應儘量避免統一的, 集中式的服務管理機制 機製,對具體的一個服務而言,應根據業務上下文,選擇合適的語言,工具對其進行構建。
微服務優缺點
優點
每個服務足夠內聚,足夠小,程式碼容易理解,這樣能聚焦一個指定的業務功能或業務需求;
開發簡單,開發效率提高,一個服務可能就是專- -的只幹一件事;
微服務能夠被小團隊單獨開發,這個小團隊是2~5人的開發人員組成;
微服務是松耦合的,是有功能意義的服務,無論是在開發階段或部署階段都是獨立的。
微服務能使用不同的語言開發。
易於和第三方整合,微服務允許容易且靈活的方式整合自動部署,通過持續整合工具,如jenkins, Hudson,
微服務易於被一個開發人員理解,修改和維護,這樣小團隊能夠更關注自己的工作成果。無需通過合作才能 纔能體實現價值
微服務允許你利用融合最新技術。
微服務只是業務邏輯的程式碼,不會和HTML, CSS或其他介面混合
每個微服務都有自己的儲存能力,可以有自己的數據庫,也可以有統一數據庫
缺點
開發人員要處理分佈式系統的複雜性
多服務運維難度,隨着服務的增加,運維的壓力也在增大
系統部署依賴
服務間通訊成本
數據一致性
系統整合測試
效能監控
微服務通訊機制 機製
系統中的各個微服務可被獨立部署,各個微服務之間是松耦合的。每個微服務僅關注於完成一件任務並很好地完成該任務。
圍繞業務能力組織服務、自動化部署、智慧端點、對語言及數據的去集中化控制。
將元件定義爲可被獨立替換和升級的軟體單元。
以業務能力爲出發點組織服務的策略。
倡導誰開發,誰運營的開發運維一體化方法。
RESTful HTTP協定是微服務架構中最常用的通訊機制 機製。
每個微服務可以考慮選用最佳工具完成(如不同的程式語言)。
允許不同微服務採用不同的數據持久化技術。
微服務非常重視建立架構及業務相關指標的實時監控和日誌機制 機製,必須考慮每個服務的失敗容錯機制 機製。
注重快速更新,因此係統會隨時間不斷變化及演進。可替代性模組化設計。
微服務的技術棧有哪些?
| 微服務條目 | 落地技術 |
|---|---|
| 服務開發 | SpringBoot、Spring、SpringMVC |
| 服務設定與管理 | Netflix公司的Archaius、阿裡的Diamond等 |
| 服務註冊與發現 | Eureka、Consul、Zookeeper等 |
| 服務呼叫 | Rest、RPC、gRPC |
| 服務熔斷器 | Hystrix、Envoy等 |
| 負載均衡 | Ribbon、Nginx等 |
| 服務介面呼叫(用戶端呼叫服務的簡化工具) | Feign等 |
| 訊息佇列 | Kafka、RabbitMQ、ActiveMQ等 |
| 服務設定中心管理 | SpringCloudConfig、cher等 |
| 服務路由(API閘道器) | zuul等 |
| 服務監控 | Zabbix、Nagios、Metrice、Specatator等 |
| 全鏈路追蹤 | Zipkin、Brave、Dapper等 |
| 服務部署 | Docker、OpenStack、Kubernetes等 |
| 數據流操作開發包 | SpringCloud Stream(封裝與Redis、Rabbit、Kafka等發送接收訊息) |
| 事件訊息匯流排 | SpringCloud Bus |
爲什麼選擇SpringCloud作爲微服務架構
1、選型依據
- 整體解決方案和框架成熟度
- 社羣熱度
- 可維護性
- 學習曲線
2、當前各大IT公司用的微服務架構有哪些?
-
阿裡:dubbo+HFS
-
京東:JSF
-
新浪:Motan
-
噹噹網: DubboX
…
3、各服務架構對比
| 功能點/服務架構 | Netfilx/SpringCloud | Motan | gRPC | Thrift | Dubbo/Dubbox |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 功能定位 | 完整的微服務架構 | RPC框架,但整合了ZK或Consul,實現叢集環境的基本服務註冊/發現 | RPC框架 | RPC框架 | 服務架構 |
| 支援Rest | 是,Ribbon支援多種可插拔的序列化選擇 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| 支援RPC | 否 | 是(Hession2) | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 支援多語言 | 是(Rest形式) | 否 | 是 | 是 | 否 |
| 負載均衡 | 是(服務zuul+用戶端Ribbon),zuul-服務,動態路由,雲端負載均衡,Eureka(針對中間層伺服器) | 是(用戶端) | 是 | 否 | 是(用戶端) |
| 設定服務 | Netfix Archaius,Spring Cloud Config Server集中設定 | 是(zookeeper提供) | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| 服務呼叫鏈監控 | 是(zuul),zuul提供邊緣服務,API閘道器 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| 高可用/容錯 | 是(伺服器端Hystrix+用戶端Ribbon) | 是 | 否 | 否 | 是(用戶端) |
| 典型應用案例 | Netflix | sina | |||
| 社羣活躍程度 | 高 | 一般 | 高 | 一般 | 2017年後開始維護,之前中斷了5年 |
| 學習難度 | 中斷 | 低 | 高 | 高 | 低 |
| 文件豐富 | 高 | 一般 | 一般 | 一般 | 高 |
| Spring Cloud Bus爲我們的應用程式帶來了更多管理斷點 | 支援降級 | Netflix內部在開發整合gRPC | IDL定義 | 實踐的公司比較多 |
SpringCloud入門概述
SpringCloud是什麼
Spring官網:https://spring.io/
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-aM7lhw8u-1591614361938)(D:/typora/Typora/img/SpringCloud/1591061598738.png)]](https://s3.ap-northeast-1.wasabisys.com/img.tw511.com/202008/20200608191128681wdjdnlzhuuf.png)
SpringCloud,基於SpringBoot提供了-套微服務解決方案,包括服務註冊與發現,設定中心,全鏈路監控,服務閘道器,負載均衡,熔斷器等元件,除了基於NetFlix的開源元件做高度抽象封裝之外,還有一些選型中立的開源元件。
SpringCloud利用SpringBoot的開發便利性,巧妙地簡化了分佈式系統基礎設施的開發,SpringCloud爲開發人員提供了快速構建分佈式系統的一些工具,包括設定管理,服務發現,斷路器,路由,微代理,事件匯流排,全域性鎖,決策競選,分佈式對談等等,他們都可以用SpringBoot的開發風格做到一鍵啓動和部署。
SpringBoot並沒有重複造輪子,它只是將目前各家公司開發的比較成熟,經得起實際考研的服務架構組合起來,通過SpringBoot風格進行再封裝,遮蔽掉了複雜的設定和實現原理,最終給開發者留出了一套簡單易懂,易部署和易維護的分佈式系統開發工具包
SpringCloud是分佈式微服務架構下的一些站式解決方案,是各個微服務架構落地技術的集合體,俗稱微服務全家桶。
SpringCloud和SpringBoot關係
- SpringBoot專注於快速方便的開發單個個體微服務。
- SpringCloud是關注全域性的微服務協調整理治理框架,它將SpringBoot開發的一 個個單體微服務整合併管理起來,爲各個微服務之間提供:設定管理,服務發現,斷路器,路由,微代理,事件匯流排,全域性鎖,決策競選,分佈式對談等等整合服務。
- SpringBoot可以離開SpringClooud獨立使用,開發專案,但是SpringCloud離不開SpringBoot, 屬於依賴關係
- SpringBoot專注於快速、方便的開發單個個體微服務, SpringCloud關注 全域性 的服務治理框架
Dubbo和SpringCloud技術選型
1、分佈式+服務治理Dubbo
目前成熟的網際網路架構:應用服務化拆分+訊息中介軟體
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-5ai4vrsR-1591614361940)(D:/typora/Typora/img/SpringCloud/1591063474805.png)]](https://s3.ap-northeast-1.wasabisys.com/img.tw511.com/202008/202006081912141835r14vxye0q.png)
2、Dubbo和SpringCloud對比
可以看下社羣活躍度
https://github.com/dubbo
https://github.com/spring-cloud
結果:
| Dubbo | Spring | |
|---|---|---|
| 服務註冊中心 | Zookeeper | Spring Cloud Netfilx Eureka |
| 服務呼叫中心 | RPC | REST API |
| 服務監控 | Dubbo - monitor | Spring Boot Admin |
| 斷路器 | 不完善 | Spring Cloud Netflix Hystrix |
| 服務閘道器 | 無 | Spring Cloud Netflix Zuul |
| 分佈式設定 | 無 | Spring Cloud Config |
| 服務跟蹤 | 無 | Spring Cloud Sleuth |
| 訊息匯流排 | 無 | Spring Cloud Bus |
| 數據流 | 無 | Spring Cloud Stream |
| 批次任務 | 無 | Spring Cloud Task |
最大區別: SpringCloud拋棄 了Dubbo的RPC通訊,採用的是基於HTTP的REST方式。
嚴格來說,這兩種方式各有優劣。雖然從- -定程度上來說,後者犧牲了服務呼叫的效能,但也避免了上面提到的原生RPC帶來的問題。而且REST相比RPC更爲靈活,服務提供方和呼叫方的依賴只依靠-紙契約, 不存在程式碼級別的強依賴,這在強調快速演化的微服務環境下,顯得更加合適。
品牌機與組裝機的區別
很明顯,Spring Cloud的功能比DUBBO更加強大,涵蓋面更廣,而且作爲Spring的拳頭專案,它也能夠與SpringFramework. Spring Boot. Spring Data. Spring Batch等其他Spring專案完美融合,這些對於微服務而言是至關重要的。使用Dubb構建的微服務架構就像組裝電腦,各環節我們的選擇自由度很高,但是最終結果很有可能因爲一條記憶體品質不行就點不亮了,總是讓人不怎麼放心,但是如果你是一名高手,那這些都不是問題;而SpringCloud就像品牌機,在Spring Source的整合下,做了大量的相容性測試,保證了機器擁有更高的穩定性,但是如果要在使用非原裝元件外的東西,就需要對其基礎有足夠的瞭解。
社羣支援與更新力度
最爲重要的是,DUBBO停止了5年左右的更新,雖然2017.7重新啓動了。 對於技術發展的新需求,需要由開發者自行拓展升級(比如噹噹網弄出了DubboX) , 這對於很多想要採用微服務架構的中小軟體組織,顯然是不太合適的,中小公司沒有這麼強大的技術能力去修改Dubbo原始碼+周邊的一-整套解決方案,並不是每一個公司都有阿裡的大牛+真實的線上生產環境測試過。
總結
曾風靡國內的開源RPC服務架構Dubbo在重新啓動維護後,令許多使用者爲之雀躍,但同時,也迎來了-一些質疑的聲音。網際網路技術發展迅速,Dubbo 是否還能跟上時代? Dubbo與Spring Cloud相比又有何優勢和差異?是否會有相關舉措保證Dubbo的後續更新頻率?
人物
Dubbo重新啓動維護開發的劉軍,主要負責人之一
劉軍,阿裡巴巴中介軟體高階研發工程師,主導了Dubbo重新啓動維護以後的幾個發版計劃,專注於高效能RPC框架和微服務相關領域。曾負責網考拉RPC框架的研發及指導在內部使用,參與了服務治理平臺、分佈式跟蹤系統、分佈式一致性框架等從無到有的設計與開發過程。
解決的問題域不一樣:Dubbo 的定位是一款RPC框架,Spring Cloud的目標是微服務架構的一站式解決方案
SpringCloud能幹什麼
- Distributed/versioned configuration (分佈式/版本控制設定)
- Service registration and discovery (服務註冊與發現)
- Routing (路由)
- Service-to-service calls (服務到服務的呼叫)
- Load balancing (負載均衡設定)
- Circuit Breakers (斷路器)
- Distributed messaging (分佈式訊息管理)
- …
SpringCloud在哪裏下載
官網:http://projects.spring.io/spring-cloud/
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-4FaRqHOR-1591614361943)(D:/typora/Typora/img/SpringCloud/1591065273790.png)]](https://s3.ap-northeast-1.wasabisys.com/img.tw511.com/202008/2020060819130193brl0ljwc5uv.png)
spring cloud是一個由衆多獨立子專案組成的大型綜合專案,每個子專案有不同的發行節奏,都維護着自己的發佈版本號。spring Cloud通過一 一個資源清單BOM (Bi11 of Materials)來管理每個版本的子專案清單。爲避免與子項月的發佈號混淆,所以沒有採用版本號的方式,而是通過命名的方式。
這些版本 名稱的命名方式採用了倫敦地鐵站的名稱,同時根據字母表的順序來對應版木時間順序,比如:最早的Release版本: Ange1, 第二個Release版本: Brixton. 然後是Camden、Dalston. Edgware, 目前最新的是Finch1ey版本。
參考文件:
- https://springcloud.cc/spring-cloud-netflix.html
- 中文API文件: https://springcloud.cc/spring-cloud-dalston.html
- SpringCloud中國社羣: http://springcloud.cn/
- SpringCloud中文網: https://springcloud.cc
SpringCloud起步 搭建父工程
1、 總體介紹
- 我們會使用一個Dept部門模組做一個微服務通用案例Consurmer消費者(Client)通過REST呼叫Provider提供者(Server)提供的服務
- 回憶Spring、SpringMVC、Mybatis等以往學習的知識
- Maven的分包模組架構複習
一個簡單的Maven模組結構是這樣的
--app-aperent:一個父專案(app-parent) 聚合很多子專案(app-util、aop-dao、app-web...)
|-- pom.xml
|
|-- app-core
||-- pom.xml
|
|-- app-web
||-- pom.xml
....
一個父工程帶着多個子Module子模組
- microservicecloud-api [封裝的整體entity/介面/公共設定等]
- microservicecloud-provider-dept-8001 [服務提供者]
- microservicecloud-consumer-dept-80 [服務消費者]
- springcloud-eureka-7001[Eureka註冊中心]
- …
springboot和springcloud版本的對應
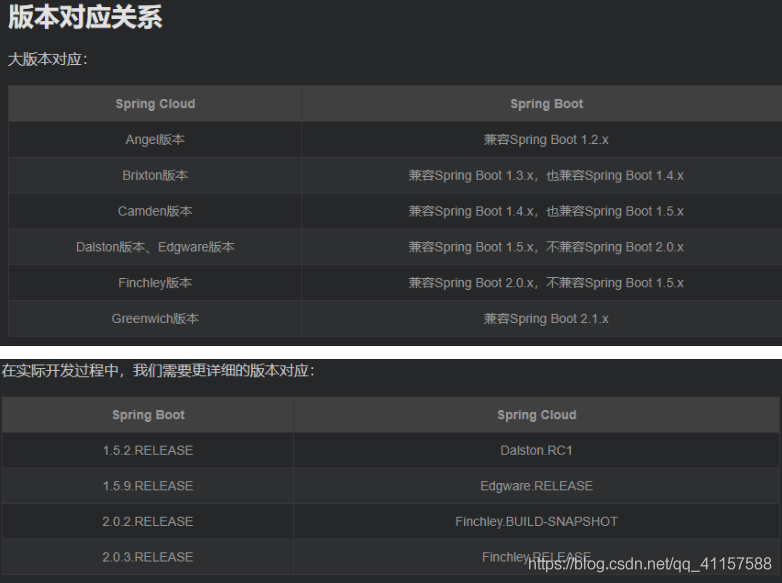
2、SpringCloud版本選擇
大版本說明
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ofjU2XVj-1591614361953)(D:/typora/Typora/img/SpringCloud/1591066424302.png)]](https://s3.ap-northeast-1.wasabisys.com/img.tw511.com/202008/20200608191446238bdv4dorb4v5.png)
實際開發版本關係
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-6lRMtNfz-1591614361955)(D:/typora/Typora/img/SpringCloud/1591066524317.png)]](https://s3.ap-northeast-1.wasabisys.com/img.tw511.com/202008/20200608191459676m05gkybn3p2.png)
使用最後的兩個版本…
3、建立父工程maven
com.lemon.springcloud
刪掉src檔案
匯入依賴
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.lemon</groupId>
<artifactId>springcloud</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<modules>
<module>springcloud-api</module>
<module>springcloud-provider-dept-8001</module>
</modules>
<!--打包方式 pom-->
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<!--maven依賴版本宣告-->
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<junit.version>4.12</junit.version>
<lombok.version>1.16.18</lombok.version>
<log4j.version>1.2.17</log4j.version>
<logback-core.version>1.2.3</logback-core.version>
</properties>
<!--maven的管理 需要使用直接呼叫即可-->
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>0.2.0.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<!--springcloud依賴-->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.cloud/spring-cloud-dependencies -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>Greenwich.SR1</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<!--SpringBoot-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.1.4.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<!--數據庫-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.47</version>
</dependency>
<!--數據庫數據源-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
<!--SpringBoot啓動器-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
<!--日誌測試-->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-core</artifactId>
<version>${logback-core.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--Junit-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>${junit.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--Lombok-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>${lombok.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--Log4j-->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>${log4j.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
</project>
4、建立maven專案公共實體
springcloud-api結構圖
建立部門數據庫
CREATE TABLE `dept` (
`deptno` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`dname` varchar(60) DEFAULT NULL,
`db_source` varchar(60) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`deptno`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='部門表'
INSERT INTO dept(dname,db_source) VALUES ('開發部',DATABASE());
INSERT INTO dept(dname,db_source) VALUES ('專案部',DATABASE());
INSERT INTO dept(dname,db_source) VALUES ('研發部',DATABASE());
INSERT INTO dept(dname,db_source) VALUES ('運維部',DATABASE());
INSERT INTO dept(dname,db_source) VALUES ('市場部',DATABASE());
INSERT INTO dept(dname,db_source) VALUES ('人事部',DATABASE());
引入lombok
<!--當前的Module自己需要的依賴,如果父依賴中已經設定版本,這裏不需要寫依賴版本-->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
1234567
建立Dept實體類
@Data//get 和 set
@NoArgsConstructor//無參構造
@Accessors(chain = true)//開啓鏈式寫法 例:new Dept().setid(1).setname("test")....
public class Dept implements Serializable {//Dept實體類 orm 類表關係對映
private Long deptno;//主鍵
private String dname;
//存在於哪個數據庫的欄位 ~ 微服務,一個服務對應一個數據庫,同一個資訊可能存在於不同的數據庫
private String db_source;
//dname的有參構造
public Dept(String dname) {
this.dname = dname;
}
}
5、建立服務的提供者maven專案
springcloud-provider-dept-8001結構圖
匯入maven依賴
<!--服務提供者8001埠 maven專案-->
<artifactId>springcloud-provider-dept-8001</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<!--要拿到實體類,要設定api module-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.lemon</groupId>
<artifactId>springcloud-api</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<!--Junit-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--Mysql驅動-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--數據庫數據源-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--日誌測試-->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-core</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--SpringBoot啓動器-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--SpringBoot web啓動-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--jetty 類似於tomcat 在此無實際作用-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--熱部署工具-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
設定8001提供者的application.yml
server:
port: 8001
#mybatis設定
mybatis:
type-aliases-package: com.lemon.springcloud.pojo
config-location: classpath:mybatis/mybatis-config.xml
mapper-locations: classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml
#spring的設定
spring:
application:
name: springcloud-provider-dept
#數據源的設定
datasource:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource #數據源爲druid
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver #數據庫驅動
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springcloud1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&servetTimeZone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password: 12345678
建立DeptDao介面
@Mapper
public interface DeptDao {
//新增一個部門
public boolean addDept(Dept dept);
//根據id查出一個部門
public Dept queryById(Long id);
//查詢所有部門資訊
public List<Dept> queryAll();
}
在resource包下建立mybatis包
在mybtis/mapper包下 建立DeptMapper.xml 實現DeptDao方法的sql
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--核心組態檔-->
<mapper namespace="com.lemon.springcloud.dao.DeptDao">
<!--增加一個部門-->
<insert id="addDept" parameterType="Dept">
insert into dept (dname,db_source) values (#{dname},DATABASE())
</insert>
<!--根據id查詢部門資訊-->
<select id="queryById" resultType="Dept">
select * from dept where deptno = #{depono};
</select>
<!--查詢所有的部門資訊-->
<select id="queryAll" resultType="Dept">
select * from dept;
</select>
</mapper>
在mybtis下建立mybatis-config.xml的設定
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<!--核心組態檔-->
<configuration>
<settings>
<!--開啓二級快取-->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings>
</configuration>
建立service包
DeptService介面
public interface DeptService {
//增加一個部門
boolean addDept(Dept dept);
//根據id查詢部門資訊
Dept queryById(Long id);
//查詢所有的部門資訊
List<Dept> queryAll();
}
DeptServiceImpl實現service的介面
@Service
public class DeptServiceImpl implements DeptService{
@Autowired
private DeptDao deptDao;
@Override
public boolean addDept(Dept dept) {
return deptDao.addDept(dept);
}
@Override
public Dept queryById(Long id) {
return deptDao.queryById(id);
}
@Override
public List<Dept> queryAll() {
return deptDao.queryAll();
}
}
建立controller包
DeptController類
//提供Restful服務
@RestController
public class DeptController{
@Autowired
private DeptService deptService;
@PostMapping("/dept/add")
public boolean addDept(Dept dept) {
return deptService.addDept(dept);
}
@RequestMapping("/dept/get/{id}")
public Dept queryById(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
return deptService.queryById(id);
}
@RequestMapping("/dept/list")
public List<Dept> queryAll() {
return deptService.queryAll();
}
}
在當前專案 目錄下建立DeptProvider_8001的啓動類
//啓動類
@SpringBootApplication
public class DeptProvider_8001 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DeptProvider_8001.class);
}
}
執行啓動類,根據controller的路徑測試
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-0fZT3rk1-1591614361959)(D:/typora/Typora/img/SpringCloud/1591090073135.png)]](https://s3.ap-northeast-1.wasabisys.com/img.tw511.com/202008/20200608191644732uwfrc4t4ruw.png)
ok 完成 服務提供者的構建
6、Rest環境搭建,服務消費者
在父類別專案下 建立maven專案
springcloud-consumer-dept-80 專案結構圖
匯入實體類相關依賴
<!--服務消費者 80埠 maven專案。存取直接localhost/xxx/xx-->
<artifactId>springcloud-consumer-dept-80</artifactId>
<!--實體類+web-->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.lemon</groupId>
<artifactId>springcloud-api</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
建立application.yml,設定埠爲80
server:
port: 80
建立消費者controller/DeptConsumerController控制器,去提供者中拿
@RestController
public class DeptConsumerController {
// 理解:消費者,不該有service層
// RestTemplate.. 裏面有方法供我們呼叫即可,註冊到spring中
//(String url,實體, Class<T> responseType)
//提供多種便捷存取遠端http服務的方法,簡單的Restful服務模板
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
//宣告提供者的localhost路徑
private static final String rest_url_prefix = "http://localhost:8001";
//呼叫8001提供者的控制器=>根據id查詢數據
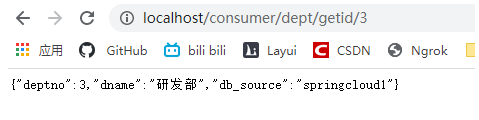
@RequestMapping("/consumer/dept/get/{id}")
public Dept get(@PathVariable("id") Long id){
// restTemplate.注意和提供者的getmapping或postmapping保持一致
return restTemplate.getForObject(rest_url_prefix+"/dept/get/"+id,Dept.class);
}
//呼叫8001提供者的控制器=>新增方法
@RequestMapping("/consumer/dept/add")
public Boolean add(Dept dept){
// restTemplate.注意和提供者的getmapping或postmapping保持一致
return restTemplate.postForObject(rest_url_prefix+"/dept/add",dept,Boolean.class);
}
//呼叫8001提供者的控制器=>查詢所有
@RequestMapping("/consumer/dept/list")
public List<Dept> queryall(){
// restTemplate.注意和提供者的getmapping或postmapping保持一致
return restTemplate.getForObject(rest_url_prefix+"/dept/list",List.class);
}
}
建立config檔案包
config/ConfigBean
@Configuration
public class ConfigBean {//@Configuration=spring的 application.xml
@Bean
public RestTemplate getRestTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
建立DeptConsumer_80啓動類
//消費者 執行方式80可省略 例:localhost/consumer/dept/list
@SpringBootApplication
public class DeptConsumer_80 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DeptConsumer_80.class,args);
}
}
啓動8001提供者 和 80消費者埠 測試。
至此 服務消費者 呼叫 提供者 專案與搭建結束。
Eureka服務註冊與發現
什麼是Eureka
- Netflix在設計Eureka時,遵循的就是AP原則
- Eureka是Netflix的一個子模組,也是核心模組之-。 Eureka是一個基於REST的服務,用於定位服務,以實現雲端中間層服務發現和故障轉移,服務註冊與發現對於微服務來說是非常重要的,有了服務發現與註冊,只需要使用服務的識別符號,就可以存取到服務,而不需要修改服務呼叫的組態檔了,功能類似於Dubbo的註冊中心,比如Zookeeper
原理講解
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-j8gxXw9D-1591614361971)(D:/typora/Typora/img/SpringCloud/1591423642205.png)]](https://s3.ap-northeast-1.wasabisys.com/img.tw511.com/202008/20200608191839803yapn4cwm4ve.png)
Eureka的基本架構
- SpringCloud封裝了NetFlix公司開發的Eureka模組來實現服務註冊和發現(對比Zookeeper)
- Eureka採用了C-S的架構設計,EurekaServer 作爲服務註冊功能的伺服器,他是服務註冊中心
- 而系統中的其他微服務。使用Eureka的用戶端連線到EurekaServer並維持心跳連線。 這樣系統的維護人員就可以通過EurekaServer來監控系統中各個微服務是否正常執行,SpringCloud的一 些其他模組(此如Zuul)就可以通過EurekaServer來發現系統中的其他微服務, 並執行相關的邏輯;和Dubbo架構對比
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ZeK0OJYY-1591614361973)(D:/typora/Typora/img/SpringCloud/1591143279326.png)]](https://s3.ap-northeast-1.wasabisys.com/img.tw511.com/202008/20200608191857882ba0msnlgxi5.png)
- Eureka包含兩個元件:Eureka Server 和 Eureka Client
- Eureka Server提供服務註冊服務,各個節點啓動後,會在EurekaServer中進行註冊, 這樣Eureka Server中的服務註冊表中將會村粗所有可用服務節點的資訊,服務節點的資訊可以在介面中直觀的看到。
- Eureka Client是一 -個Java用戶端, 用於簡化EurekaServer的互動,用戶端同時也具備一個內建的,使用輪詢負載演算法的負載均衡器。在應用啓動後,將會向EurekaServer發送心跳 (預設週期爲30秒) .如果Eureka Server在多個心跳週期內沒有接收到某個節點的心跳, EurekaServer將會從服務註冊表中把這個服務節點移除掉(預設週期爲90秒)
Eureka 三大角色
- Eureka Server:提供服務註冊與發現。和zookeeper用戶端一樣
- Service Provider:將自身服務註冊到Eureka中,從而使消費方能夠找到
- Service Consumer:服務消費方從Eureka中獲取註冊服務列表,從而找到消費服務
Eureka註冊中心構建
Eureka專案結構圖
建立springcloud-eureka-7001 maven專案
匯入maven依賴
<!--Eureka註冊中心 7001-->
<artifactId>springcloud-eureka-7001</artifact
<dependencies>
<!--eureka的服務提供者包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-eureka-server</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--熱部署工具-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
設定application.yml
server:
port: 7001
#Eureka設定
eureka:
instance:
hostname: localhost #Eureaka伺服器端的範例名稱
client:
register-with-eureka: false #表示是否向Eureka註冊中心註冊自己
fetch-registry: false #如果fetch-registry爲false,則表示自己爲註冊中心
service-url: #監控頁面
#點進去參考原始碼,可看到預設的url埠設定爲8761,我們設定爲自己的埠。
defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka
設定EurekaServer_7001啓動類
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer //表示爲Eureka伺服器端的啓動類,可以接收別人註冊進來
public class EurekaServer_7001 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaServer_7001.class,args);
}
}
此時,我們的Eureka註冊中心已經搭建完畢,
總共分爲4步:
- 1.匯入依賴
- 2.編寫組態檔
- 3.開啓這個功能 @Enablexxx
- 4.設定類
一個Eureka範例搭建是不是特別的容易呢?
執行當前 7001啓動類。瀏覽器存取 可以看到已經搭建成功。 ok success
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-FcL9S7Mh-1591614361974)(D:/typora/Typora/img/SpringCloud/1591167049517.png)]](https://s3.ap-northeast-1.wasabisys.com/img.tw511.com/202008/2020060819202580x02js44hiik.png)
Eureka服務消費 註冊、資訊設定、自我保護機制 機製
在springcloud-provider-dept-8001新增Eureka依賴
<!--Eureka服務 沒有server-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-eureka</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
在application.yml新增Eureka註冊中心的設定
#Eureka的設定。 服務註冊到Eureka中,需要一個路徑地址
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka
instance:
#修改Eureka中status的預設描述資訊。不設定預設爲DESKTOP-XXX描述
instance-id: springcloud-provider-dept8001
修改Eureka中status的預設描述資訊
當我們加上 instance: instance-id:springcloud-provider-dept8001設定後,7001註冊中心status就會捕獲到被註冊的提供類預設描述資訊
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-B3AQRhRT-1591614361976)(D:/typora/Typora/img/SpringCloud/1591428182267.png)]](https://s3.ap-northeast-1.wasabisys.com/img.tw511.com/202008/20200608192050137aq5rutotjwk.png)
在主啓動類上加上EnableEurekaClient註解
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient//在服務啓動後,自動註冊到Eureka註冊中心中
public class DeptProvider_8001 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DeptProvider_8001.class,args);
}
}
執行7001註冊中心啓動類,在執行8001提供者啓動類。
開啓localhost:7001我們可以看到,8001服務提供者已經設定進來。
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-RaXBaHXV-1591614361983)(D:/typora/Typora/img/SpringCloud/1591169800909.png)]](https://s3.ap-northeast-1.wasabisys.com/img.tw511.com/202008/20200608192110951qtkwuarrqfm.png)
當我們關閉8001埠後,停止幾分鐘後,檢視7001頁面會出現以下內容

這個是Eureka的自我保護機制 機製
**設定 Eureka的status的xx/info鏈接點開後的info監控資訊 **
在8001提供者中 新增actuator依賴
<!--Eureka的status鏈接xx/info點選後監控資訊-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
在application.yml中設定
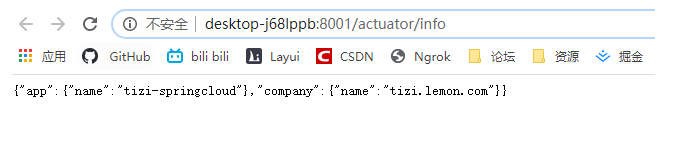
#info設定 Eureka的status的xx/info鏈接點開後的info監控資訊。沒有太大意義
info:
app.name: ti zi zui bang,jiayou
company.name: tizi.lemon.com
test.name: hahah test
啓動7001 8001埠 點開7001中status下的8001鏈接就可看到我們設定的info資訊
自我保護機制 機製:好死不如賴活着
一句話總結: 某時刻某一個微服務不可以用了 , eureka不會立刻清理,依舊會對該微服務的資訊進行儲存!
- 預設情況下,如果EurekaServer在一定時間內沒有接收到某 個微服務範例的心跳,EurekaServer將會註銷該範例(預設90秒)。 但是當網路分割區故障發生時,微服務與Eureka之間無法正常通行,以上行爲可能變得非常危險了---- 因爲微服務本身其實是健康的,此時本不應該註銷這個服務。Eureka通過 自我保護機制 機製來解決這個問題–當EurekaServer節點在短時間內丟失過多用戶端時(可能發生了網路分割區故障) , 那麼這個節點就會進入自我保護模式。一旦進入該模式,EurekaServer就會保護服務註冊表中的資訊,不再刪除服務註冊表中的數據(也就是不會註銷任何微服務) .當網路故障恢復後,該EurekaServer節 點會自動退出自我保護模式。
- 在自我保護模式中,EurekaServer會保護服務註冊表中的資訊, 不再註銷任何服務範例。當它收到的心跳數重新恢復到閾值以上時,該EurekaServer節點就會 自動退出自我保護模式。它的設計哲學就是寧可保留錯誤的服務註冊資訊,也不盲目註銷任何可能健康的服務範例。一句話:好死不如賴活着
- 綜上,自我保護模式是-種應對網路異常的安全保護措施。它的架構哲學是寧可同時保留所有微服務(健康的微服務和不健康的微服務都會保留),也不盲目註銷任何健康的微服務。使用自我保護模式,可以讓Eureka叢集更加的健壯和穩定
- 在SpringCloud中, 可以使用
eureka. server. enable-self-preservation = false禁用自我保護模式[不推薦關閉自我保護機制 機製]
服務發現 設定
在8001的 DeptController 控制器中新增
//獲取一些設定的資訊,得到具體的微服務
@Autowired
private DiscoveryClient client;
//註冊進來的微服務,獲取一些資訊。沒有實際作用
@RequestMapping("/dept/discovery")
public Object discovery(){
//獲取微服務列表的清單
List<String> services = client.getServices();
System.out.println("discovery=>services "+services);
//得到一個具體的微服務資訊,通過具體的微服務id,7001中的applicationName
List<ServiceInstance> instances = client.getInstances("SPRINGCLOUD-PROVIDER-DEPT");
for (ServiceInstance instance : instances) {
System.out.println(
instance.getHost()+"\t\t\t"+
instance.getPort()+"\t\t\t"+
instance.getUri()+"\t\t\t"+
instance.getServiceId());
}
return this.client;
}
在當前8001的啓動類上加上@EnableDiscoveryClient 服務發現 註解
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient//在服務啓動後,自動註冊到Eureka註冊中心中
@EnableDiscoveryClient //註冊進來的微服務,獲取一些資訊。服務發現,擴充套件內容
public class DeptProvider_8001 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DeptProvider_8001.class,args);
}
}
啓動7001註冊中心 8001提供者 。輸入連線檢視服務發現

檢視控制檯輸出內容
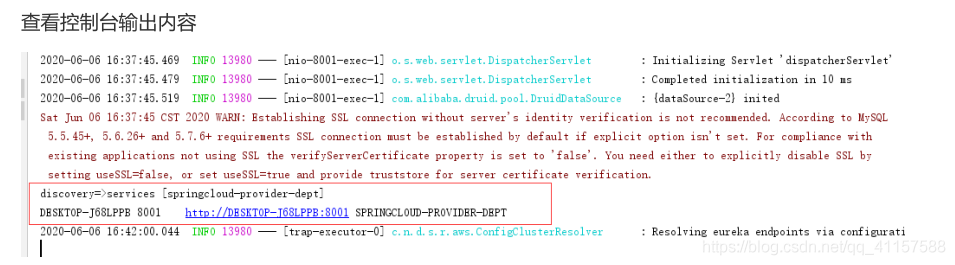
Eureka叢集環境設定
建立 springcloud-eureka-7002 Maven專案
建立 springcloud-eureka-7003 Maven專案
可複製springcloud-eureka-7001專案的所有依賴及內容,更改埠 啓動類 等等設定。
分別匯入依賴
<!--Eureka註冊中心 7001...7002...7003-->
<artifactId>springcloud-eureka-7001</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<!--eureka服務提供者包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-eureka-server</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--熱部署工具-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
7002 7003設定application.yml
server:
port: 7002 ..7003
#Eureka設定
eureka:
instance:
hostname: localhost #Eureka伺服器端的範例名稱
client:
register-with-eureka: false #表示是否向Eureka註冊中心註冊自己
fetch-registry: false #如果爲false 則表示自己爲註冊中心
service-url: #監控頁面
defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/ #預設的url埠設定爲8761,需要設定爲自己的埠
分別設定啓動類
@SpringBootApplication(exclude= {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})
@EnableEurekaServer //EnablerEurekaServer 伺服器端的啓動類,可以接受別人註冊進來
public class EurekaServer_7002...7003 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaServer_7002.class,args);
}
}
1234567
可以在C槽的hosts中設定三個鏈接,用於模擬叢集域名對映
127.0.0.1 eureka7001.com
127.0.0.1 eureka7002.com
127.0.0.1 eureka7003.com
設定application.yml。 hostname和defaultzone更改爲本地hosts設定的鏈接
eureka7001.com中叢集包含eureka7002.com和eureka7003.com
eureka7002.com中叢集包含eureka7001.com和eureka7002.com
eureka7003.com中叢集包含eureka7001.com和eureka7002.com
三個maven專案都需設定yml,只需更改當前的hostname,和defaultZone其他關聯地址
server:
port: 7001
#Eureka設定
eureka:
instance:
hostname: eureka7001.com #Eureaka伺服器端的範例名稱
client:
register-with-eureka: false #表示是否向Eureka註冊中心註冊自己
fetch-registry: false #如果fetch-registry爲false,則表示自己爲註冊中心
service-url: #監控頁面
#單機:點進去參考原始碼,可看到預設的url埠設定爲8761,我們設定爲自己的埠。
#defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka
#叢集(除自身外 關聯其他所有)
defaultZone: http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka/,http://eureka7003.com:7003/eureka/
叢集設定完畢後,我們8001服務提供者服務註冊到Eureka中,需要更改設定的路徑地址
更改springcloud-provider-dept-8001的application.yml Eureka服務註冊defaultZone地址

設定完畢後啓動eureka7001,eureka7002,eureka7003的註冊中心 和 8001服務提供者埠
同時存取localhost:7001 7002 7003 可以看到當前服務中掛載的另外兩個服務
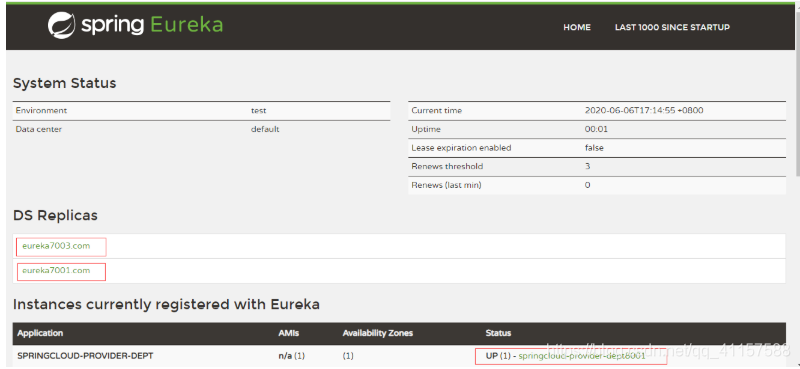
當我們隨機關機一個叢集,我們可看到另外兩個叢集還可使用。不影響使用
ok,至此 .Eureka叢集搭建完畢
在本例中服務註冊請求在 eureka7001 中註冊成功,
即 eureka7001 對應的 Eureka Server服務的狀態是UP,
則不會向另外兩個節點(eureka7002,eureka7003)發送請求,
相應地頁面上也就沒有顯示。一旦停止 eureka7001 服務註冊中心,則 dept-8001 服務會向 eureka7002 發送註冊請求。
Eureka:CAP原則及對比Zookeeper
回顧CAP原則
RDBMS (Mysql. Oracle. sqlServer) ==> ACID
NoSQL (redis. mongdb) ==>CAP
ACID是什麼?
- A (Atomicity)原子性
- C (Consistency)- 致性
- I (Isolation) 隔離性
- D (Durability) 永續性
CAP是什麼?
-
C (Consistency) 強一致性
-
A (Availabilty)可用性
-
P (Partition tolerance)分割區容錯性
CAP的三進二: CA、AP、 CP
經典CAP圖
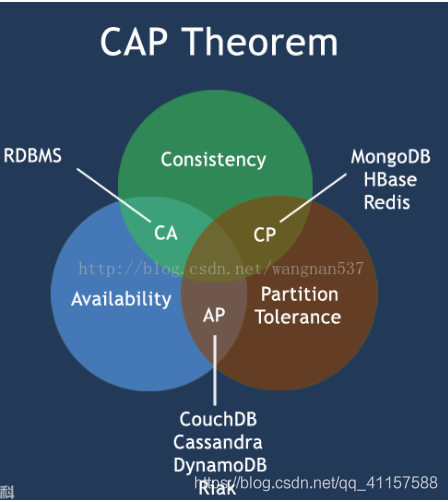
CAP理論的核心
- 一個分佈式系統不可能同時很好的滿足-致性,可用性和分割區容錯性這三個需求
- 根據CAP原理,將NoSQL數據庫分成了滿足CA原則,滿足CP原則和滿足AP原則三大類:
- CA:單點叢集,滿足-致性,可用性的系統,通常可延伸性較差
- CP: 滿足- -致性,分割區容錯性的系統,通常效能不是特別高
- AP:滿足可用性。分割區容錯性的系統,通常可能對一致性要求低一些
作爲服務註冊中心,Eureka比Zookeeper好在哪裏?
著名的CAP理論指出,一個分佈式系統不可能同時滿足C (一致性)、A (可用性)、P (容錯性) .
由於分割區容錯性P在分佈式系統中是必須要保證的,因此我們只能在A和C之間進行權衡。
- Zookeeper保證的是
CP - Eureka保證的是
AP
Zookeeper保證的是CP
當向註冊中心查詢服務列表時,我們可以容忍註冊中心返回的是幾分鐘以前的註冊資訊,但不能接受服務直接down掉不可用。也就是說,服務註冊功能對可用性的要求要高於一致性。但是zk會出現這樣一種情況,當master節點因爲網路故障與其他節點失去聯繫時,剩餘節點會重新進行leader選舉。問題在於,選舉leader的時間太長,30 ~ 120s, 且選舉期間整個zk叢集都是不可用的,這就導致在選舉期間註冊服務癱瘓。在雲部署的環境下,因網路問題使得zk叢集失去master節點是較大概率會發生的事,雖然服務能夠最終恢復,但是漫長的選舉時間導致的註冊長期不可用是不能容忍的。
Eureka保證的是AP
Eureka看明白了這一點,因此在設計時就優先保證可用性。Eureka各個節點都是平等的,幾個節點掛掉不會影響正常節點的工作,剩餘的節點依然可以提供註冊和查詢服務。而Eureka的用戶端在向某個Eureka註冊或如果發現連線失敗,則會自動切換至其它節點,只要有一臺Eureka還在,就能保證註冊服務可用(保證可用性),只不過查到的資訊可能不是最新的(不保證強一致性)。除此之外,Eureka還有一種自我保護機制 機製,如果在15分鐘內超過85%的節點都沒有正常的心跳,那麼Eureka就認爲用戶端與註冊中心出現了網路故障,此時會出現以下幾種情況:
- Eureka不再從註冊列表中移除因爲長時間沒收到心跳而應該過期的服務
- Eureka仍然能夠接受新服務的註冊和查詢請求,但是不會被同步到其它節點上(即保證當前節點依然可用)
- 當網路穩定時,當前範例新的註冊資訊會被同步到其它節點中
因此,Eureka可以很好的應對因網路故障導致部分節點失去聯繫的情況,而不會像zookeeper那樣使整個註冊服務癱瘓。
Ribbno
ribbno是什麼
- Spring Cloud Ribbon是基於Netflix Ribbon實現的一套
用戶端負載均衡的工具。 - 簡單的說,Ribbon是Netflix發佈的開源專案, 主要功能是提供用戶端的軟體負載均衡演算法,將NetFlix的中間層服務連線在一起。 Ribbon的用戶端元件提供一系列完整的設定項如:連線超時、重試等等。簡單的說,就是在組態檔中列出LoadBalancer (簡稱LB: 負載均衡)後面所有的機器,Ribbon會自動的幫助你基於某種規則(如簡單輪詢,隨機連線等等)去連線這些機器。我們也很容易使用Ribbon實現自定義的負載均衡演算法!
ribbon能幹什麼?
- LB,即負載均衡(Load Balance) ,在微服務或分佈式叢集中經常用的一種應用。
- 負載均衡簡單的說就是將使用者的請求平攤的分配到多個服務上,從而達到系統的HA (高可用) .
- 常見的負載均衡軟體有
Nginx,Lvs等等
- 常見的負載均衡軟體有
- dubbo、SpringCloud中均給我們提供了負載均衡,SpringCloud的負載均衡演算法可以自定義
- 負載均衡簡單分類:
- 集中式LB
- 即在服務的消費方和提供方之間使用獨立的LB設施,如Nginx, 由該設施負責把存取請求通過某種策略轉發至服務的提供方!
- 進程式LB
- 將LB邏輯整合到消費方,消費方從服務註冊中心獲知有哪些地址可用,然後自己再從這些地址中選出一個合適的伺服器。
- Ribbon就屬於進程內LB,它只是一個類庫,整合於消費方進程,消費方通過它來獲取到服務提供方的地址!
- 集中式LB
整合ribbon 在的消費者用戶端
在消費者 80 埠設定 Eureka和Ribbon負載均衡依賴
<!--Eureka-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-eureka</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--Ribbon負載均衡-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-ribbon</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
在 config類中加入@loadBalanced 註解。實現負載均衡
@Configuration
public class ConfigBean {//@Configuration=spring的 application.xml
//設定負載均衡實現RestTemplate
@Bean
@LoadBalanced //ribbon負載均衡的作用
public RestTemplate getRestTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
在application.yml中新增Eureka的設定
server:
port: 80
#Eureka設定
eureka:
client:
register-with-eureka: false #不向Eureka中註冊自己
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka/,http://localhost:7002/eureka/,http://localhost:7003/eureka/
DeptConsumerController中的路徑更改
//宣告提供者的localhost路徑
//private static final String rest_url_prefix = "http://localhost:8001";
//通過ribbon去實現負載均衡,這裏服務應該是一個變數,通過服務名來存取 *
private static final String rest_url_prefix = "http://SPRINGCLOUD-PROVIDER-DEPT";
在80啓動類加上@EnableEurekaClient的註解
//消費者 執行方式80可省略 例:localhost/consumer/dept/list
//Ribbon 和 Eureka 整合後,用戶端可直接呼叫,不用關心Ip地址和埠號,會在定義的多個地址中隨機選擇
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient//在服務啓動後,自動註冊到Eureka註冊中心中
public class DeptConsumer_80 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DeptConsumer_80.class,args);
}
}
啓動7001 7002 7003註冊中心 8001提供者埠 80消費者埠
[外連圖片轉存失敗,源站可能有防盜鏈機制 機製,建議將圖片儲存下來直接上傳(img-6EHixtOs-1591614362003)(D:/typora/Typora/img/SpringCloud/1591441549697.png)]
localhost/consumer/dept/list 查出所有數據。
當前提供方只有一個專案,當前體會不到負載均衡,所以需要建立多個提供方來實現負載均衡
使用Ribbon實現負載均衡
使用Ribbon實現負載均衡要更直觀的感受的負載均衡,需要建立多個提供者,因此也需要多個數據庫。
複製
springcloud1數據庫表
再建立兩個數據庫
springcloud2springcloud3
CREATE TABLE `dept` (
`deptno` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`dname` varchar(60) DEFAULT NULL,
`db_source` varchar(60) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`deptno`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='部門表'
INSERT INTO dept(dname,db_source) VALUES ('開發部',DATABASE());
INSERT INTO dept(dname,db_source) VALUES ('專案部',DATABASE());
INSERT INTO dept(dname,db_source) VALUES ('研發部',DATABASE());
INSERT INTO dept(dname,db_source) VALUES ('運維部',DATABASE());
INSERT INTO dept(dname,db_source) VALUES ('市場部',DATABASE());
INSERT INTO dept(dname,db_source) VALUES ('人事部',DATABASE());
1234567891011121314
注意 只有每個欄位的db_source不同,其餘數據一致.
複製springcloud-provider-dept-8001專案所有的內容.
建立maven專案 springcloud-provider-dept-8002,複製8001提供方的所有內容.
建立maven專案 springcloud-provider-dept-8003,複製8001提供方的所有內容.
分別更改application.yml中的數據庫的地址和埠號,更改啓動類的名稱,修改Eureka中status的預設描述資訊
啓動7001 7002 7003註冊中心
啓動8001 8002 8003提供者埠
啓動80消費者埠
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ShK3vKrv-1591614362007)(D:/typora/Typora/img/SpringCloud/1591446351400.png)]](https://s3.ap-northeast-1.wasabisys.com/img.tw511.com/202008/2020060819294574tugecobtwqe.png)
localhost/consumer/dept/list 存取,多次重新整理,我們這次可以直觀的看到顯示不同服務的數據,這次我們可直觀的感受到負載均衡的應用。
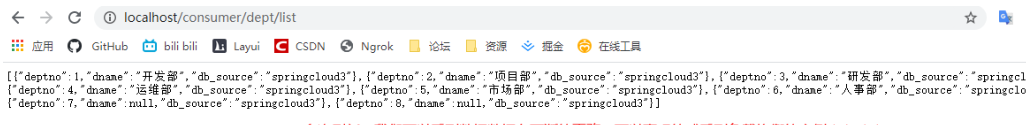
success,使用Ribbon實現負載均衡已完成。
Ribbon 自定義負載均衡演算法
在主目錄外 建立myrule檔案包
在myrule下建立RuleConfig
//自定義Ribbon設定的負載均衡類,用戶端RibbonConfiguration中已存在的元件與FooConfiguration中的任何元件組成(後者通常會覆蓋前者)
//自定義的元件請注意 它不在|程式的上下文的ComponentScan中,所以要放在單獨的不重疊的包中
@Configuration
public class RuleConfig {
@Bean
public IRule myRule(){
//預設是輪詢,現在我們自定義爲DiyRandomRule 自定義負載均衡
return new DiyRandomRule();
}
}
12345678910
在myrule包下建立DiyRandomRule,雙擊shift搜尋 RandomRule 全部複製,改爲自己自定義演算法負載均衡
public class DiyRandomRule extends AbstractLoadBalancerRule {
//程式碼全是複製的 DiyRandomRule.class的,自定義負載均衡需要自己修改
//當前自定義負載均衡:
//每個服務存取5次。換下一個服務
//total=0,預設=0,如果=5,指向下一個服務節點
//index=0,預設0,如果total=5,則inedx+1
private int totla=0;//被呼叫的次數
private int currentIndex=0;//當前是誰在提供服務
public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) {
if (lb == null) {
return null;
} else {
Server server = null;
while (server == null) {
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
return null;
}
List<Server> upList = lb.getReachableServers();//獲得活着的服務
List<Server> allList = lb.getAllServers();//獲得全部的服務
int serverCount = allList.size();
if (serverCount == 0) {
return null;
}
//int index = this.chooseRandomInt(serverCount);//生成區間亂數
//server = (Server) upList.get(index);//從活着的服務中,隨機獲取一個
//================自定義負載均衡演算法==================
if(totla<5){
server = upList.get(currentIndex);
totla++;
}else{
totla=0;
currentIndex++;
if (currentIndex>=upList.size()){//當前節點大於活着的數量
currentIndex = 0;
}
server=upList.get(currentIndex);//從活着的服務中,獲取指定的服務來進行操作
}
//====================================================
if (server == null) {
Thread.yield();
} else {
if (server.isAlive()) {
return server;
}
server = null;
Thread.yield();
}
}
return server;
}
}
protected int chooseRandomInt(int serverCount) {
return ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(serverCount);
}
public Server choose(Object key) {
return this.choose(this.getLoadBalancer(), key);
}
public void initWithNiwsConfig(IClientConfig clientConfig) {
}
}
在80啓動器上新增自定義負載均衡設定參照的@RibbonClien註解
//消費者 執行方式80可省略 例:localhost/consumer/dept/list
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient//在服務啓動後,自動註冊到Eureka註冊中心中
//在微服務啓動的時候就能去載入我們自定義Ribbon設定的負載均衡類,自定義爲跳轉5次切換節點
@RibbonClient(name="SPRINGCLOUD-PROVIDER-DEPT",configuration = RuleConfig.class)
public class DeptConsumer_80 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DeptConsumer_80.class,args);
}
}
啓動多個註冊中心,服務提供者和80消費埠。
多次重新整理存取 localhost/consumer/dept/list
我們可直觀的看到頁面每重新整理五次值會更改
至此 Ribbon自定負載均衡 完成、
Feign 負載均衡
Feign 簡介
Feign是宣告式的web service用戶端,它讓微服務之間的呼叫變得更簡單了,類似controller呼叫service. SpringCloud整合了Ribbon和Eureka,可在使用Feign時提供負載均衡的http用戶端。
只需要建立一一個介面,然後新增註 加注解即可!
feign 主要是社羣,大家都習慣面向介面程式設計。這個是很多開發人員的規範。呼叫微服務存取兩種方法
- 微服務名字 [ribbon]
- 介面和註解 [feign]
Feign 能幹什麼
- Feign旨在使編寫Java Http用戶端變得更容易
- 前面在使用Ribbon + RestTemplate時,利用RestTemplate對Http請求的封裝處理, 形成了一套模板化的呼叫方法。但是在實際開發中,由於對服務依賴的呼叫可能不止一處,往往一個介面會被多處呼叫,所以通常都會針對每個微服務自行封裝一些用戶端類來包裝這些依賴服務的呼叫。 所以,Feign在此基礎. 上做了進一步封裝,由他來幫助我們定義和實現依賴服務介面的定義,==在Feign的實現下,我們只需要建立一個介面並使用註解的方式來設定它(類似於以前Dao介面上標註Mapper註解,現在是一個微服務介面上面標註-個Feign註解即可。)==即可完成對服務提供方的介面系結,簡化了使用Spring Cloud Ribbon時,自動封裝服務呼叫用戶端的開發量。
Ribbon和Feign的區別
Ribbon和Feign都是用於呼叫其他服務的,不過方式不同。
Ribbon RestFul風格
Feign 面向介面
1.啓動類使用的註解不同,Ribbon用的是@RibbonClient,Feign用的是@EnableFeignClients。
2.服務的指定位置不同,Ribbon是在@RibbonClient註解上宣告,Feign則是在定義抽象方法的介面中使用@FeignClient宣告。
3.呼叫方式不同,Ribbon需要自己構建http請求,模擬http請求然後使用RestTemplate發送給其他服務,步驟相當繁瑣。
Feign則是在Ribbon的基礎上進行了一次改進,採用介面的方式,將需要呼叫的其他服務的方法定義成抽象方法即可,
不需要自己構建http請求。不過要注意的是抽象方法的註解、方法簽名要和提供服務的方法完全一致。
Feign使用介面方法呼叫服務
在 springcloud-api專案的springcloud下建立service包
也可建立springcloud-api-feignmaven專案,更直觀專案不凌亂,匯入springcloud-api所有內容。
匯入Feign依賴
<!--Feign-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-feign</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
在service中建立DeptClientService
@FeignClient(value = "SPRINGCLOUD-PROVIDER-DEPT")
public interface DeptClientService {
@GetMapping("/dept/get/{id}")
public Dept queryById(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
@PostMapping("/dept/list")
public List<Dept> queryAll();
@GetMapping("/dept/add")
public boolean addDept(Dept dept);
}
新建立maven專案 springcloud-consumer-dept-feign
複製springcloud-consumer-dept-80專案的所有內容,更改啓動類名稱爲FeignDeptConsumer_80
匯入feign依賴
<!--feign-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-feign</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
DeptConsumerController的內容
@RestController
public class DeptConsumerController {
//Feign面向介面程式設計
//springcloud-api-feign 下的service
@Autowired
private DeptClientService deptClientService =null;
//新增數據
@RequestMapping("/consumer/dept/add")
public boolean add(Dept dept){
return deptClientService.addDept(dept);
}
//通過id查詢
@RequestMapping("/consumer/dept/get/{id}")
public Dept get(@PathVariable("id") Long id){
return deptClientService.queryById(id);
}
//查詢所有
@RequestMapping("/consumer/dept/list")
public List<Dept> queryAll(){
return deptClientService.queryAll();
}
}
在DeptConsumer_feign啓動類加上Feign相關注解@EnableFeignClients(…)
//消費者 執行方式80可省略 例:localhost/consumer/dept/list
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient //在服務啓動後,自動註冊到Eureka註冊中心中
@EnableFeignClients(basePackages = {"com.lemon.springCloud"}) //Feign被掃描到
public class DeptConsumer_feign {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DeptConsumer_feign.class,args);
}
}
啓動註冊中心,啓動服務提供者,啓動當前80埠。執行瀏覽器,根據控制器設定的路徑存取,執行沒問題,完成、
Hystrix 服務熔斷
分佈式系統面臨的問題
複雜分佈式結構中的應用程式有數十個依賴關係,每個依賴關係在某些時候將不可避免的失效
服務雪崩
多個微服務之間呼叫的時候,假設微服務A呼叫微服務B和微服務C,微服務B和微服務C又呼叫其他的微服務,這就是所謂的「扇出」、如果扇出的鏈路上某個微服務的呼叫響應時間過長或者不可用,對微服務A的呼叫就會佔用越來越多的系統資源,進而引起系統崩潰,所謂的「雪崩效應"。
對於高流量的應用來說,單一的後端依賴可能會導致所有伺服器上的所有資源都在幾秒中內飽和。比失敗更糟糕的是,這些應用程式還可能導致服務之間的延遲增加,備份佇列,執行緒和其他系統資源緊張,導致整個系統發生更多的級聯故障,這些都表示需要對故障和延遲進行隔離和管理,以便單個依賴關係的失敗,不能取消整個應用程式或系統。
我們需要:棄車保帥.
什麼是Hystrix
Hystrix是一個用於處理分佈式系統的延遲和容錯的開源庫,在分佈式系統裡,許多依賴不可避免的會呼叫失敗,比如超時,異常等,Hystrix能夠保證在一 個依賴出問題的情況下, 不會導致整體服務失敗,避免級聯故障,以提高分佈式系統的彈性。
「斷路器」本身是一種開關裝置,當某個服務單元發生故障之後,通過斷路器的故障監控(類似熔斷保險絲) , 向呼叫方返回-一個服務預期的,可處理的備選響應(FallBack),而不是長時間的等待或者拋出呼叫方法無法處理的異常,這樣就可以保證了服務呼叫方的執行緒不會被長時間,不必要的佔用,從而避免了故障在分佈式系統中的蔓延,乃至雪崩
Hystrix能幹什麼
-
服務降級
-
服務熔斷
-
服務限流
-
接近實時的監控
-
·····
Hystrix官網資料=> https://github.com/Netflix/Hystrix/wiki
服務熔斷
服務熔斷是什麼
熔斷機制 機製是對應雪崩效應的一種微服務鏈路保護機制 機製。
當扇出鏈路的某個微服務不可用或者響應時間太長時,會進行服務的降級,進而熔斷該節點微服務的呼叫,快速返回錯誤的響應資訊。當檢測到該節點微服務呼叫響應正常後恢復呼叫鏈路。在SpringCloud框架裡熔斷機制 機製通過Hystrix實現。Hystrix會監控微服務間呼叫的狀況, 當失敗的呼叫到一定閾值,預設是5秒內20次呼叫失敗就會啓動熔斷機制 機製。熔斷機制 機製的註解是@HystrixCommand.
Hystrix服務熔斷環境搭建
建立maven專案 springcloud-provider-dept-hystrix-8001
複製springcloud-provider-dept-8001專案的所有內容
修改啓動類名字爲:eptProviderHystrix_8001
修改application.yml中的Eureka的instance-id爲 springcloud-provider-dept-hystrix-8001
匯入springcloud-provider-dept-8001所有依賴,再加一個Hystrix服務熔斷依賴
<!--Hystrix-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-hystrix</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
更改DeptController的所有內容
//提供Restful服務
@RestController
public class DeptController{
@Autowired
private DeptService deptService;
@RequestMapping("/dept/get/{id}")
@HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "hystrixGet") //如果失敗 去呼叫Hystrix的備選方案
public Dept get(@PathVariable("id") Long id){
Dept dept = deptService.queryById(id);
if (dept==null){//如果當前id值爲空 拋出異常
throw new RuntimeException("id=> "+ id+"不存在該使用者,或者該資訊無法找到");
}
return dept;
}
//如果出現異常 採取Hystrix的備選方案
public Dept hystrixGet(@PathVariable("id") Long id){
return new Dept()
.setDeptno(id)
.setDname("id=> "+id+"沒有找到相關資訊,null by Hystrix")
.setDb_source("not found database in mysql");
}
}
在DeptProviderHystrix_8001的啓動類上加上@EnableCircuitBreaker服務熔斷 斷路器的支援註解
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient//在服務啓動後,自動註冊到Eureka註冊中心中
@EnableDiscoveryClient //註冊進來的微服務,獲取一些資訊。服務發現,擴充套件內容
@EnableCircuitBreaker //新增Hystrix服務熔斷 斷路器的支援
public class DeptProviderHystrix_8001 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DeptProviderHystrix_8001.class,args);
}
}
啓動 7001 7002 7003註冊中心,可啓動1-2個。啓動hystrix80埠
存取 localhost:8001/dept/get/id值
輸入存在的id可查詢到當前值
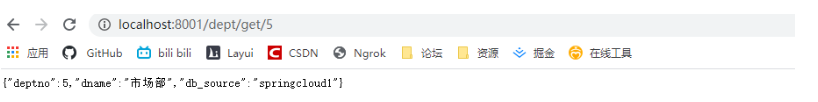
輸入不存在的id,可以看到
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-9fXnCxkr-1591614362015)(D:/typora/Typora/img/SpringCloud/1591498427437.png)]](https://s3.ap-northeast-1.wasabisys.com/img.tw511.com/202008/20200608193217676w505lopiwab.png)
我們可以清楚的看到 當查詢不存在的id時,將會自動採取Hystrix的備選方案去處理值。
成功執行後,Hystrix服務熔斷環境搭建完成咯 -.-
application如下設定後,eureka註冊中心會顯示出鏈接的真實ip地址,而不再是desptop …鏈接 預設是:不顯示 false
prefer-ip-address: true #改爲true後 Eureka中的status就會顯示真實ip地址
Hystrix 服務降級
所謂降級,就是當某個服務出現異常之後,伺服器將不再被呼叫,此時伺服器端可以自己準備一個原生的fallback回撥,返回一個預設值。
這樣做,雖然服務水平下降,但好歹可用,比直接掛掉要強
在springcloud-api中或者新建的springcloud-api-feign專案中的service包中建立DeptClientServiceFallbackFactory降級服務類
//Hystrix 降級,當伺服器端關閉後的提示資訊
@Component
public class DeptClientServiceFallbackFactory implements FallbackFactory {
@Override
public DeptClientService create(Throwable throwable) {
return new DeptClientService() {
@Override
public Dept queryById(Long id) {
return new Dept()
.setDeptno(id)
.setDname("id=>" +id+"沒有對應的資訊,用戶端提供了降級的資訊,這個服務現在已經關閉")
.setDb_source("已降級 未查詢到數據");
}
@Override
public List<Dept> queryAll() {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean addDept(Dept dept) {
return false;
}
};
}
}
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627
在DeptClientService中新增服務降級的註解,@FeignClient(value=「xxx」,fallbackFactory=「降級的類」)
@Component
@FeignClient(value = "SPRINGCLOUD-PROVIDER-DEPT",fallbackFactory = DeptClientServiceFallbackFactory.class)
public interface DeptClientService {
@GetMapping("/dept/get/{id}")
public Dept queryById(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
@PostMapping("/dept/list")
public List<Dept> queryAll();
@PostMapping("/dept/add")
public boolean addDept(Dept dept);
}
123456789101112
切換專案,在springcloud-consumer-dept-feign消費者專案中設定降級的application.yml
#開啓降級Feign Hystrix
feign:
hystrix:
enabled: true
1234
啓動7001 7002註冊中心,啓動8001提供者介面。啓動當前80埠。
瀏覽器中輸入localhost/consumer/dept/getid/10 我們可看到查詢到數據
當關閉了8001提供者服務後,再次重新整理,頁面不會報錯。而是會加載出自定義的降級資訊
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-EWFRlsFv-1591614362024)(D:/typora/Typora/img/SpringCloud/1591521460799.png)]](https://s3.ap-northeast-1.wasabisys.com/img.tw511.com/202008/20200608193406306xjy2h2beuar.png)
Hystrix服務熔斷和降級對比
服務熔斷:
Hystrix是一個用於處理分佈式系統的延遲和容錯的開源庫,在分佈式系統中,許多依賴不可避免的會呼叫失敗,超時、異常等,Hystrix能夠保證在一個依賴出問題的情況下,不會導致整體服務失敗,避免級聯故障,提高分佈式系統的彈性
熔斷機制 機製是應對雪崩效應的一種微服務鏈路保護機制 機製,當扇出鏈路的某個微服務不可用或者響應時間太長時,會進行服務的降級,進而熔斷該節點微服務的呼叫,快速返回錯誤的相應資訊。當檢測當該節點微服務呼叫響應正常後恢復呼叫鏈路,熔斷機制 機製的註解是@HystrixCommand
「熔斷器」本身是一種開關裝置,當某個服務單元發生故障之後,通過斷路器的故障監控,,某個異常條件被觸發,直接熔斷整個服務。,向呼叫方法返回一個符合預期的、可處理的備選響應(FallBack),而不是長時間的等待或者拋出吊牌用方法無法處理的異常,就保證了服務呼叫方的執行緒不會被長時間佔用,避免故障在分佈式系統中蔓延,乃至雪崩
服務降級:
服務降級處理是在用戶端實現完成的,與伺服器端沒有關係
當某個服務熔斷或關閉之後,服務將不再被呼叫,此時用戶端我們可準備一個FallbackFactory,返回一個預設的值(預設值)
整體資源快不夠了,忍痛將某些服務單元先關掉,關閉後還要返回一些可處理的備選方法,待渡服務解決完問題,再開啓回來,即恢復正常操作。
Hystrix:Dashboard流監控
新建Maven專案 springcloud-consumer-hystrix-dashboard
將 springcloud-consumer-dept-80 專案中所有依賴複製到當前專案,並新增Hystrix和dashboard流監控依賴
<!--Hystrix的dashboard視覺化流監控-->
<artifactId>springcloud-consumer-hystrix-dashboard</artifactId>
<!--Hystrix服務熔斷依賴-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-hystrix</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--dashboard流監控-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-hystrix-dashboard</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
在resource中建立application.yml,設定啓動埠
#Hystrix的dashboard流監控 埠
server:
port: 9001
設定DeptConsumerDashboard_9001啓動類
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableHystrixDashboard//開啓監控
public class DeptConsumerDashboard_9001 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DeptConsumerDashboard_9001.class,args);
}
}
檢視springcloud-provider-dept-hystrix-8001伺服器端是否有監控相關依賴actuator
啓動註冊中心,啓動DeptProviderHystrix_8001服務提供者,啓動當前9001監控埠
localhost:9001/hystrix,可以看到監控頁面,當前設定還不足以監控,所以需在8001伺服器端新增設定

切換到 springcloud-provider-dept-hystrix-8001專案
在DeptProviderHystrix_8001 啓動類中 新增 dashboard監控 設定
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient//在服務啓動後,自動註冊到Eureka註冊中心中
@EnableDiscoveryClient //註冊進來的微服務,獲取一些資訊。服務發現,擴充套件內容
@EnableCircuitBreaker //新增Hystrix服務熔斷 斷路器的支援
public class DeptProviderHystrix_8001 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DeptProviderHystrix_8001.class,args);
}
//增加一個servlet,配合dashboard監控使用,固定的程式碼 http://localhost:8001/actuator/hystrix.stream存取監控
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean hystrixMetricsStreamServlet(){
ServletRegistrationBean registrationBean = new ServletRegistrationBean(new HystrixMetricsStreamServlet());
registrationBean.addUrlMappings("/actuator/hystrix.stream");
return registrationBean;
}
}
設定完後,啓動註冊中心,啓動hystrix8001伺服器端,啓動當前9001監控服務。
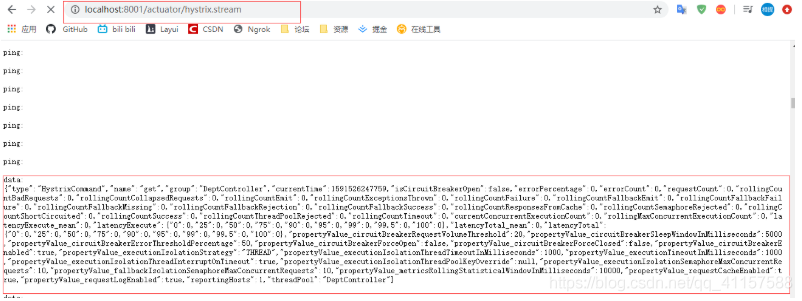
在頁面輸入localhost:8001/actuator/hystrix.stream,可以看到監控捕獲到的內容
如無任何監控資訊,在瀏覽器輸入 localhost:8001/dept/get/1鏈接,查詢一條值資訊,可以看到會載入到一些監控資訊
localhost:9001/hystrix 要監控的頁面地址,時間及標題設定
存取成功後,可以看到一個視覺化監控的面板,可以直觀的看到一些監控到的資訊
在8001服務中多次執行查詢,會看到心跳會越來越大。隨之也會縮小,波動值也會隨之增加/減少
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-feskGQc7-1591614362032)(D:/typora/Typora/img/SpringCloud/1591526846764.png)]](https://s3.ap-northeast-1.wasabisys.com/img.tw511.com/202008/202006081937471721leua12u50p.png)
多次存取查詢看效果。
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-KRehPotF-1591614362034)(D:/typora/Typora/img/SpringCloud/1591527117453.png)]](https://s3.ap-northeast-1.wasabisys.com/img.tw511.com/202008/202006081938053601ucrvpg0ri.png)
-
如何看
- 7色
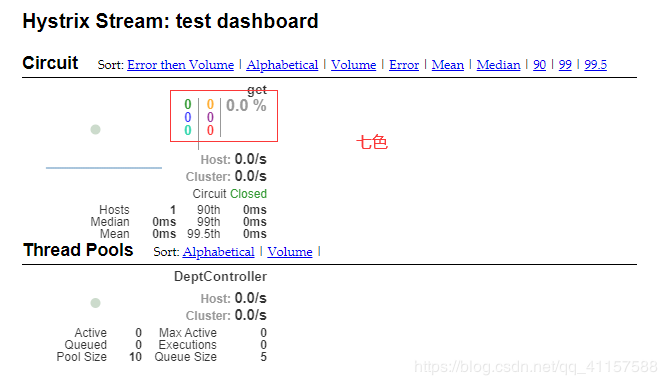
-
一圓
實心圓: 共有兩種含義,他通過顏色的變化代表了範例的健康程度
它的健康程度從綠色<黃色<橙色<紅色遞減
該實心圓除了顏色的變化之外,它的大小也會根據範例的請求流量發生變化,流量越大,該實心圓就
越大,所以通過該實心圓的展示,就可以在大量的範例中快速發現故障範例和高壓力範例
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-PN3B0Rfx-1591614362035)(D:/typora/Typora/img/SpringCloud/1591527284663.png)]](https://s3.ap-northeast-1.wasabisys.com/img.tw511.com/202008/20200608193853150tt2pcnofm4z.png)
-
一線
曲線:用來記錄2分鐘內流量的相對變化,可以通過它來觀察到流量的上升和下降趨勢
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-DbDqrQJ2-1591614362039)(D:/typora/Typora/img/SpringCloud/1591527485282.png)]](https://s3.ap-northeast-1.wasabisys.com/img.tw511.com/202008/202006081939226112dflauofkv4.png)
-
整圖說明

監控設定的步驟:
- 建立springcloud-consumer-hystrix-dashboard專案,複製springcloud-consumer-dept-80專案所有依賴,匯入Hystrix和dashboard依賴
- 編寫application.yml埠設定
- 設定監控的啓動類,設定監控註解
- 切換至hystrix8001服務提供者專案,檢視是否有 actuator相關監控資訊依賴
- 要監控流,需要在hystrix8001啓動類中設定流監控
- 啓動註冊中心,hystrix8001服務,9001監控測試
Zuul 路由閘道器
概述
什麼是Zuul
Zuul包含了對請求的路由和過濾兩個最主要的功能:
其中路由功能負責將外部請求轉發到具體的微服務範例上,是實現外部存取統一入口的基礎,而過濾器功能則負責對請求的處理過程進行幹預,是實現請求校驗,服務聚合等功能的基礎。Zuul和Eureka進行整合, 將Zuu自身註冊爲Eureka服務治理下的應用,同時從Eureka中獲得其他微服務的訊息,也即以後的存取微服務都是通過Zuul跳轉後獲得。
注意:Zuul服務最終還是會註冊進Eureka
提供:代理+路由+過濾 三大功能
Zuul能幹什麼
- 路由
- 過濾
官網文件=> https://github.com/Netflix/zuul
爲什麼要建立Zuul
Netfix. API流量的數量和多樣性有時會導致生產問題迅速出現而沒有警告。我們需要一個允許我們快
速改支行爲以對這些情況做出反應的系統。
Zuul使用了各種不同類型的過濾器,這使我們能夠快速靈活地將功能應用於邊緣服務。這些過濾器幫
助我們執行以下功能 :
- 身份驗證和安全性識別每個資源的身份驗證要求,井拒絕不滿足要求的請求。
- 見解和監控在邊緣跟族有意義的數據和統計資訊,以便爲我們提供準確的生產規圖。
- 動態路由根據需要將請求動態路由到不同的後端羣集
- 壓力測試逐漸增加到羣集的流量以評估效能。
- 減載-小每種型別的清求分配容量,並丟棄超出限制的請求。
- 靜態響應處理-直接在邊緣構建一 些響應。而不是將其轉發到內部叢集
- 多區域彈性在AWS區域之間路由請求,以多樣化我們的ELB使用並將我們的優勢拉近我們的成員
有關更多詳細資訊:我們如何在Netfio中使用2uul
Zuul元件
- zuul-core–zuul核心庫,包含編譯和執行過濾器的核心功能
- zuul-simple-webapp–zuul Web應用程式範例,展示瞭如何使用zuul-core構建應用程式
- zuul-netflix–lib包,將其他NetflixOSS元件新增到Zuul中,例如使用功能區進去路由請求處理
- zuul-netflix-webapp–webapp,它將zuul-core和zuul-netflix封裝成一個簡易的webapp工程包
Zuul路由閘道器 專案搭建
建立maven專案 springcloud/springcloud-zuul-9527
匯入 springcloud-consumer-hystrix-dashboard 專案所有依賴,並加上Zuul依賴
<!--Zuul路由閘道器 9527埠-->
<artifactId>springcloud/springcloud-zuul-9527</artifactId>
<!--Zuul路由閘道器-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-zuul</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
建立application.yml,設定
server:
port: 9527
spring:
application:
name: springcloud-zuul
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka/,http://localhost:7002/eureka/,http://localhost:7003/eureka/
instance:
#修改Eureka中status的預設描述資訊。不設定預設爲DESKTOP-XXX描述
instance-id: zuul9527.com #自定義名稱
prefer-ip-address: true #改爲true後 Eureka中的status就會顯示真實ip地址
info: #鏈接點開後顯示的info資訊
app.name: tizi => zuul test
company.name: tizi=> zuul.com
version.name: tizi.01
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts 模擬zuul閘道器
127.0.0.1 www.lijie.com
啓動Eureka7001 或者7002 7003都行,啓動一個提供者8001 啓動9527
www.lijie.com:9527/springcloud-provider-dept/dept/get/3 存取
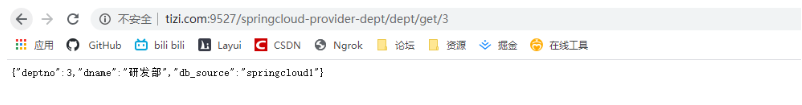
我們可以看到能查詢到數據,但是專案路徑中已暴露出真實的微服務地址,還需要進行修改設定。
在application.yml 設定zuul閘道器
zuul:
routes:
mydept.serviceId: springcloud-provider-dept
#之前的查詢鏈接地址 http://www.lijie.com:9527/springcloud-provider-dept/dept/get/1
#現在的查詢鏈接地址,設定後爲 http://www.lijie.com:9527/mydept/dept/get/1
#兩者都皆可存取(原路徑+現配路徑)。設定自定義的字首後 可不讓用戶端知道真實的ip地址
mydept.path: /mydept/**
再次執行專案。可看到只能通過我們指定的設定中的path路徑存取
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-RHBHK362-1591614362045)(D:/typora/Typora/img/SpringCloud/1591575012071.png)]](https://s3.ap-northeast-1.wasabisys.com/img.tw511.com/202008/2020060819404076lkzrmo5wty3.png)
我們還可以新增設定,全部的設定
zuul:
routes:
mydept.serviceId: springcloud-provider-dept
#之前的查詢鏈接地址 http://www.lijie.com:9527/springcloud-provider-dept/dept/get/1
#現在的查詢鏈接地址,設定後爲 http://www.lijie.com:9527/mydept/dept/get/1
#兩者都皆可存取(原路徑+現配路徑)。設定自定義的字首後 可不讓用戶端知道真實的ip地址
mydept.path: /mydept/**
#加上此設定後 原路徑不能存取(springcloud-provider-dept/dept/get/6),只能通過自定義的規則路徑存取。
#ignored-services: springcloud-provider-dept
#星號(*) 隱藏全部的專案真實名字
ignored-services: "*"
prefix: /li #設定公共的地址字首 設定後鏈接爲:www.lijie.com:9527/li/mydept/dept/get/11
再次啓動zuul啓動類,可看到是我們自定義的路由規則,可有效的隱藏真實服務名及地址。
存取:www.lijie.com:9527/li/mydept/dept/get/11
SpringCloud config分佈式設定
概述
分佈式系統面臨的 —— 組態檔的問題
微服務意味着要將單體應用中的業務拆分成一個個子服務, 每個服務的粒度相對較小,因此係統中會出現大量的服務,由於每個服務都需要必要的設定資訊才能 纔能執行,所以一套集中式的,動態的設定管理設施是必不可少的。SpringCloud提供了ConfigServer來解決這個問題,我們每一個微服務自己帶着一個application.yml,那上百的的組態檔要修改起來,豈不是要feng了嗎?
什麼是Springcloud config分佈式設定中心
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-fEP9Lr38-1591614362049)(D:/typora/Typora/img/SpringCloud/1591576333159.png)]](https://s3.ap-northeast-1.wasabisys.com/img.tw511.com/202008/20200608194136445yimwdjbpnkj.png)
Spring Cloud Config爲微服務架構中的微服務提供集中化的外部設定支援,設定伺服器爲各個不同微服務應用的所有環節提供了一個中心化的外部設定。
Spring Cloud Config 分爲伺服器端和用戶端兩部分;
伺服器端也稱爲分佈式設定中心,它是一 個獨立的微服務應用,用來連線設定伺服器併爲用戶端提供獲取設定資訊,加密,解密資訊等存取介面。
用戶端則是通過指定的設定中心來管理應用資源,以及與業務相關的設定內容,並在啓動的時候從設定中心獲取和載入設定資訊。設定伺服器預設採用git來儲存設定資訊,這樣就有助於對環境設定進行版本管理。並且可以通過git用戶端工具來方便的管理和存取設定內容。
SpringCloud config分佈式設定中心能幹嘛
- 集中管理組態檔
- 不同環境,不同設定,動態化的設定更新,分環境部署,比如/dev /test/ /prod /beta /release
- 執行期間動態調整設定,不再需要在每個服務部署的機器上編寫組態檔,服務會向設定中心統一拉取設定自己的資訊。
- 當設定發生變動時,服務不需要重新啓動,即可感知到設定的變化,井應用新的設定
- 將設定資訊以REST介面的形式暴露
springcloud config環境搭建設定
springcloud config環境搭建設定
註冊碼雲賬號 https://gitee.com/。可qq 微信登錄
新建倉庫 springcloud-config,設定爲公開,語言和模板都選擇java。開源許可證GPL-3.0,倉庫建立後複製當前倉庫的SSH隧道地址
在電腦新建資料夾,用GitBash工具 執行 git clone springcloud-config複製的SSH地址,進行拉取倉庫內容,拉去後選擇yes,因爲許可權不存在,需要設定當前Git
Git大全 [https://gitee.com/all-about-git
# 顯示當前的Git設定
$ git config --list
# 設定提交程式碼時的使用者資訊
$ git config --global user.name "[name]"
$ git config --global user.email "[email address]"
複製倉庫中的 https 中的地址,直接 在 GitBash中,git clone 複製的地址
此時我們已經拿到遠端的程式碼
拿到遠端的程式碼後,在當前的目錄中建立 application.yml 檔案,開啓yml檔案設定
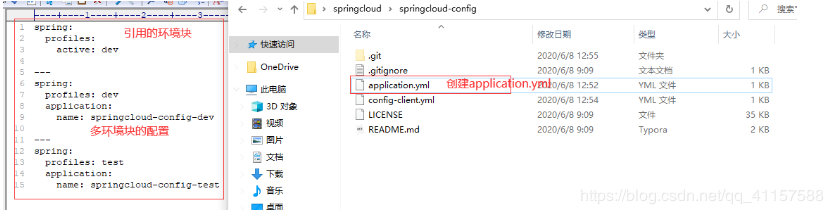
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
---
spring:
profiles: dev
application:
name: springcloud-config-dev
---
spring:
profiles: test
application:
name: springcloud-config-test
將當前編寫的application.yml提交到碼雲上
GitBash開啓命令工具
cd 至 springcloud-config
git add . 將檔案新增到暫存區
git status 檢視狀態
git commit -m 「一次提交」 本地提交,-m爲提交時寫的資訊
git push origin master 提交到遠端的當前路徑分枝
當前的application.yml已成功push新增至遠端倉庫中
伺服器端連線Git設定
新建maven專案=> springcloud-config-server-3344
匯入依賴
<!--伺服器端連線Git-->
<artifactId>springcloud-config-server-3344</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<!--springboot啓動-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--springcloud-config的設定-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--監控資訊 可不加-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
設定application.yml
server:
port: 3344
spring:
application:
name: springcloud-config-server
#連線遠端的倉庫
cloud:
config:
server:
git:
uri: https://gitee.com/xxx/springcloud-config.git #自己遠端倉庫的https地址
# 通過 config-server可以連線到git,存取其中的資源以及設定~
建立啓動類Config_Server_3344
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigServer //開啓設定服務
public class Config_Server_3344 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Config_Server_3344.class,args);
}
}
啓動 Config_Server_3344埠
瀏覽器輸入 localhost:3344/application-test.yml
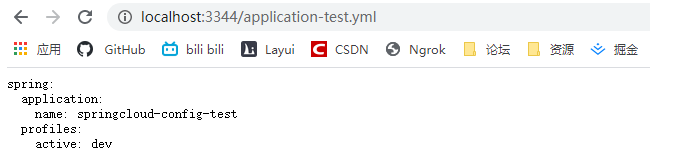
瀏覽器輸入 localhost:3344/application-dev.yml
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-FVRPmC8I-1591614362058)(D:/typora/Typora/img/SpringCloud/1591601128169.png)]](https://s3.ap-northeast-1.wasabisys.com/img.tw511.com/202008/20200608194416220t3b2ihe0ta5.png)
可以看到已獲得git倉庫中application.yml的設定
用戶端連線伺服器端存取遠端
提交遠端倉庫
在遠端倉庫拉取出來的檔案中建立 config-client.yml
#啓動環境選擇的設定
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
#springboot啓動多環境的設定
---
server:
port: 8201
#spring的設定
spring:
profiles: dev
application:
name: springcloud-config-client-dev
#Eureka的設定。 服務註冊到Eureka中,需要一個路徑地址
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka/
---
server:
port: 8202
#spring的設定
spring:
profiles: test
application:
name: springcloud-config-client-test
#Eureka的設定。 服務註冊到Eureka中,需要一個路徑地址
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka/
將config-client.yml push到遠端倉庫
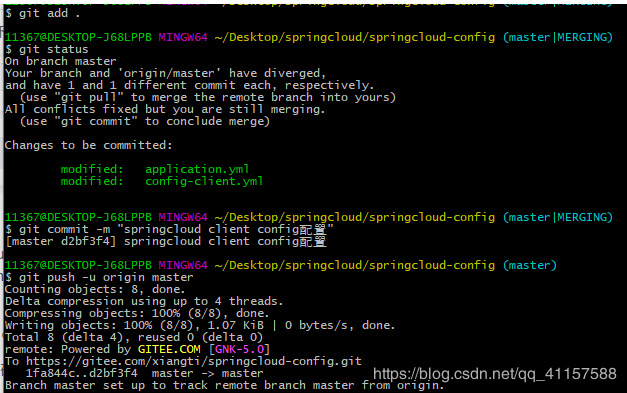
GitBash開啓命令工具
cd 至 springcloud-config
git add . 將檔案新增到暫存區
git status 檢視狀態
git commit -m 「一次提交」 本地提交,-m爲提交時寫的資訊
git push origin master 提交到遠端的當前路徑分枝
12345678910
用戶端連線伺服器端存取遠端設定
新建Maven專案=> springcloud-config-client-3355
匯入依賴
<!--用戶端連線伺服器端存取遠端 3355埠-->
<artifactId>springcloud-config-client-3355</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<!--springboot啓動-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--springcloud-config啓動的設定 和伺服器端的不同-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--監控資訊 可不加-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
建立application.yml,並設定
#使用者級別的設定 設定去讀取誰
spring:
application:
name: springcloud-config-client-3355
建立bootstrap.yml,設定以下內容。注意建立此yml一定要匯入springcloud-config的設定依賴
# 系統級別的設定
spring:
cloud:
config:
name: config-client # 需要從git上讀取的資源名稱,不要後綴
profile: dev #dev環境埠:8201 test環境埠:8202
label: master #需要在git上的哪個分支拿
#連線到3344服務,中轉站的形式連線伺服器端存取遠端地址
uri: http://localhost:3344
建立ConfigClientController控制器
//@Value爲git上的client-config的值
@RestController
public class ConfigClientController {
@Value("${spring.application.name}")
private String applicationName;
@Value("${eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone}")
private String eurekaServer;
@Value("${server.port}")
private String port;
@RequestMapping("/config")
public String getConfig(){
return "applicationName: "+applicationName+
"eurekaServer: "+eurekaServer+
"port: "+port;
}
}
建立Config_Client_3355主啓動類
@SpringBootApplication
public class Config_Client_3355 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Config_Client_3355.class,args);
}
}
啓動3344伺服器端
localhost:3344/application-dev.yml 不同的啓動環境 查到不同的倉庫application.yml的設定資訊
localhost:3344/application-test.yml 不同的啓動環境 查到不同的查到倉庫application.yml的設定資訊
都可查詢到 git倉庫裡application.yml相關內容
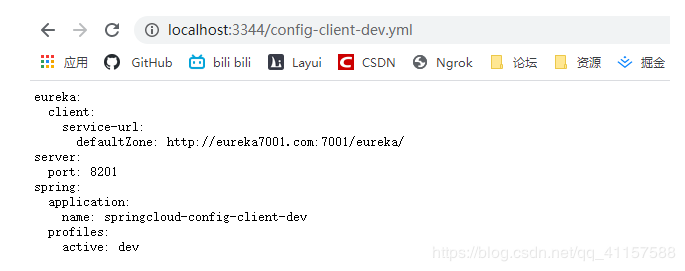
localhost:3344/config-client-dev.yml 不同的啓動環境 查到不同的查詢到倉庫設定的config-client的資訊
localhost:3344/config-client-dev.yml 不同的啓動環境 查到不同的查詢到倉庫設定的config-client的資訊
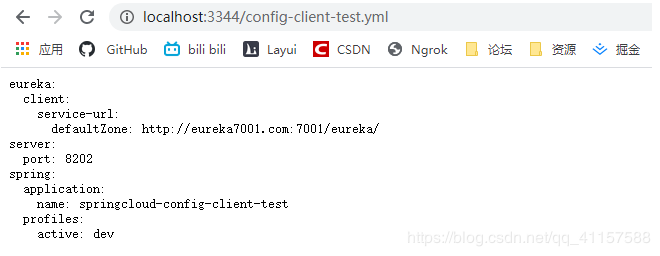
啓動3344伺服器端和3355用戶端的啓動類
因3355中的application.yml設定的git倉庫中的dev環境,dev環境的埠爲8201,所以是通過8201存取專案
localhost:8201/config
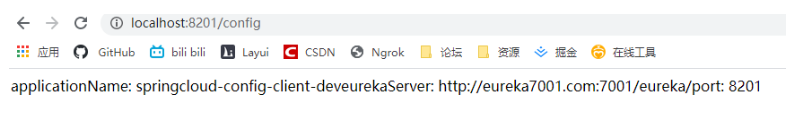
可以看到我們通過遠端的形式 獲得了控制器範例中返回了git倉庫中的數據資訊
可以將 application.yml 中的環境切換爲test,這時存取的埠爲8202
這時,我們已經成功通過用戶端連線到伺服器 得到了遠端倉庫的數據資訊
遠端設定實戰測試
在遠端倉庫拉取出來的檔案中建立 config-eureka.yml
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-SV69ngWy-1591614362070)(D:/typora/Typora/img/SpringCloud/1591607939820.png)]](https://s3.ap-northeast-1.wasabisys.com/img.tw511.com/202008/202006082019501201pa01xym50n.png)
#啓動環境選擇的設定
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
---
server:
port: 7001
#spring的設定
spring:
profiles: dev
application:
name: springcloud-config-eureka-dev
#Eureka設定
eureka:
instance:
hostname: eureka7001.com #Eureaka伺服器端的範例名稱
client:
register-with-eureka: false #表示是否向Eureka註冊中心註冊自己
fetch-registry: false #如果fetch-registry爲false,則表示自己爲註冊中心
service-url: #監控頁面
#單機:點進去參考原始碼,可看到預設的url埠設定爲8761,我們設定爲自己的埠。
#defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka
#叢集(除自身外 關聯其他所有)
defaultZone: http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka/,http://eureka7003.com:7003/eureka/
---
server:
port: 7001
#spring的設定
spring:
profiles: test
application:
name: springcloud-config-eureka-test
#Eureka設定
eureka:
instance:
hostname: eureka7001.com #Eureaka伺服器端的範例名稱
client:
register-with-eureka: false #表示是否向Eureka註冊中心註冊自己
fetch-registry: false #如果fetch-registry爲false,則表示自己爲註冊中心
service-url: #監控頁面
#單機:點進去參考原始碼,可看到預設的url埠設定爲8761,我們設定爲自己的埠。
#defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka
#叢集(除自身外 關聯其他所有)
defaultZone: http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka/,http://eureka7003.com:7003/eureka/
在遠端倉庫拉取出來的檔案中建立 config-dept.yml
#啓動環境選擇的設定
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
---
server:
port: 8001
#mybatis設定
mybatis:
type-aliases-package: com.lemon.springcloud.pojo
config-location: classpath:mybatis/mybatis-config.xml
mapper-locations: classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml
#spring的設定
spring:
profiles: dev
application:
name: springcloud-config-dept-dev
#數據源的設定
datasource:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource #數據源爲druid
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver #數據庫驅動
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springcloud1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&servetTimeZone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password: 12345678
#Eureka的設定。 服務註冊到Eureka中,需要一個路徑地址
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka/,http://localhost:7002/eureka/,http://localhost:7003/eureka/
instance:
#修改Eureka中status的預設描述資訊。不設定預設爲DESKTOP-XXX描述
instance-id: springcloud-provider-dept8001
prefer-ip-address: true #改爲true後 Eureka中的status就會顯示真實ip地址
#info設定 Eureka的status的xx/info鏈接點開後的info監控資訊。沒有太大意義
info:
app.name: ti zi zui bang,jiayou
company.name: tizi.lemon.com
test.name: hahah test
---
server:
port: 8001
#mybatis設定
mybatis:
type-aliases-package: com.lemon.springcloud.pojo
config-location: classpath:mybatis/mybatis-config.xml
mapper-locations: classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml
#spring的設定
spring:
profiles: test
application:
name: springcloud-config-dept-test
#數據源的設定
datasource:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource #數據源爲druid
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver #數據庫驅動
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springcloud2?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&servetTimeZone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password: 12345678
#Eureka的設定。 服務註冊到Eureka中,需要一個路徑地址
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka/,http://localhost:7002/eureka/,http://localhost:7003/eureka/
instance:
#修改Eureka中status的預設描述資訊。不設定預設爲DESKTOP-XXX描述
instance-id: springcloud-provider-dept8001
prefer-ip-address: true #改爲true後 Eureka中的status就會顯示真實ip地址
#info設定 Eureka的status的xx/info鏈接點開後的info監控資訊。沒有太大意義
info:
app.name: ti zi zui bang,jiayou
company.name: tizi.lemon.com
test.name: hahah test
將建立的檔案push到遠端倉庫中
GitBash開啓命令工具
cd 至 springcloud-config
git add . 將檔案新增到暫存區
git status 檢視狀態
git commit -m 「一次提交」 本地提交,-m爲提交時寫的資訊
git push origin master 提交到遠端的當前路徑分枝
成功新增至遠端倉庫
建立Maven專案=> springcloud-config-eureka-7001 遠端存取倉庫實現註冊中心
匯入pom依賴
<!--通過遠端中的Eureka設定 實現倉庫中程式碼的呼叫實現Eureka註冊中心-->
<artifactId>springcloud-config-eureka-7001</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<!--eureka服務提供者包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-eureka-server</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--springcloud-config啓動的設定-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
複製 springcloud-eureka-7001 專案所有的內容,刪掉application.yml所有設定,因爲此設定已經在git遠端倉庫中設定,新增以下的設定內容
spring:
application:
name: sorubgckiyd-config-eureka-7001
123
建立bootstrap.yml 注意建立此yml一定要匯入springcloud-config的設定依賴
# 系統級別的設定
spring:
cloud:
config:
name: config-client # 需要從git上讀取的資源名稱,不要後綴
profile: dev #dev環境埠:8201 test環境埠:8202
label: master #需要在git上的哪個分支拿
#連線到3344服務,中轉站的形式連線伺服器端存取遠端地址
uri: http://localhost:3344
123456789
啓動3344伺服器端 ,啓動後自測。本地需要連線到3344,確定ConfigEureka7001啓動後能夠連線到遠端
localhost:3344/config-eureka-dev.yml
localhost:3344/config-eureka-dev.yml
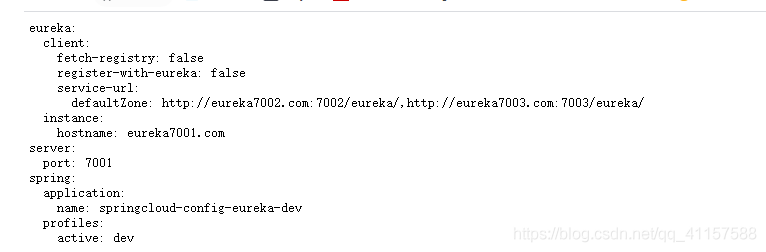
此時 已讀取到遠端倉庫中Eureka的相關資訊
localhost:3344/config-dept-dev.yml
localhost:3344/config-dept-test.yml
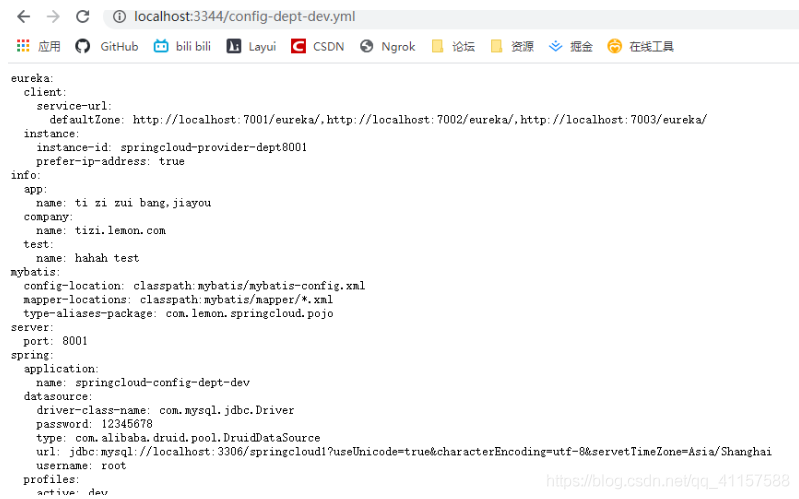
可以看到,Eureka註冊中心設定的程式碼也可獲取 沒有問題
啓動config-eureka-7001註冊中心
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-GiitWpPf-1591614362081)(D:/typora/Typora/img/SpringCloud/1591610264061.png)]](https://s3.ap-northeast-1.wasabisys.com/img.tw511.com/202008/20200608202201305gqgvv15nzzy.png)
ok 通過用戶端 呼叫 伺服器端 以中轉站的形式連線伺服器端存取遠端地址 設定Eureka成功
建立Maven專案=> springcloud-config-dept-8001 遠端存取倉庫實現8001服務提供者
複製 springcloud-provider-dept-8001 專案所有的內容及依賴
刪掉application.yml所有設定,因爲此設定已經在git遠端倉庫中設定,新增以下的設定內容
spring:
application:
name: springcloud-config-dept-8001
123
建立bootstrap.yml 注意建立此yml一定要匯入springcloud-config的設定依賴
#系統級的設定
# 系統級別的設定
spring:
cloud:
config:
name: config-dept # 需要從git上讀取的資源名稱,不要後綴
profile: dev #dev環境埠:8201 test環境埠:8202
label: master #需要在git上的哪個分支拿
#連線到3344服務,中轉站的形式連線伺服器端存取遠端地址
uri: http://localhost:3344
12345678910
啓動3344伺服器端 ,config-eureka-7001註冊中心,當前8001服務提供者
可以看到,通過遠端存取git,也獲取到了相應的數據.
結束
好好學習,天天向上!