隨機漫步圖 | Pygal | 列表解析式
2020-08-10 12:21:53
Pygal官網:http://www.pygal.org/en/stable/documentation/configuration/serie.html
Pygal.XY類繪製Stroke範例
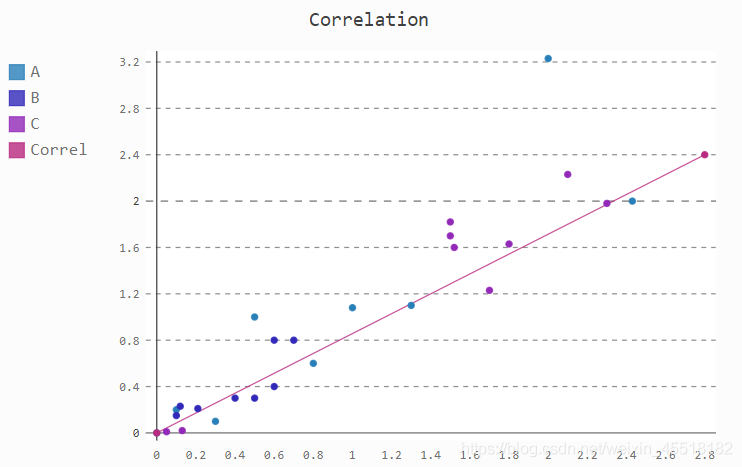
xy_chart = pygal.XY(stroke=False)
#範例化XY類,stroke=False:無需繪製折線,只要點
xy_chart.title = 'Correlation'
xy_chart.add('A', [(0, 0), (.1, .2), (.3, .1), (.5, 1), (.8, .6), (1, 1.08), (1.3, 1.1), (2, 3.23), (2.43, 2)])
xy_chart.add('B', [(.1, .15), (.12, .23), (.4, .3), (.6, .4), (.21, .21), (.5, .3), (.6, .8), (.7, .8)])
xy_chart.add('C', [(.05, .01), (.13, .02), (1.5, 1.7), (1.52, 1.6), (1.8, 1.63), (1.5, 1.82), (1.7, 1.23), (2.1, 2.23), (2.3, 1.98)])
xy_chart.add('Correl', [(0, 0), (2.8, 2.4)], stroke=True)
xy_chart.render()
add()方法參數:
第一個參數:‘A’,‘B’,'C’爲數據點的標籤
第二個參數:列表型別,列表內元素爲元組型別,每個元組存放一個點的橫縱座標。
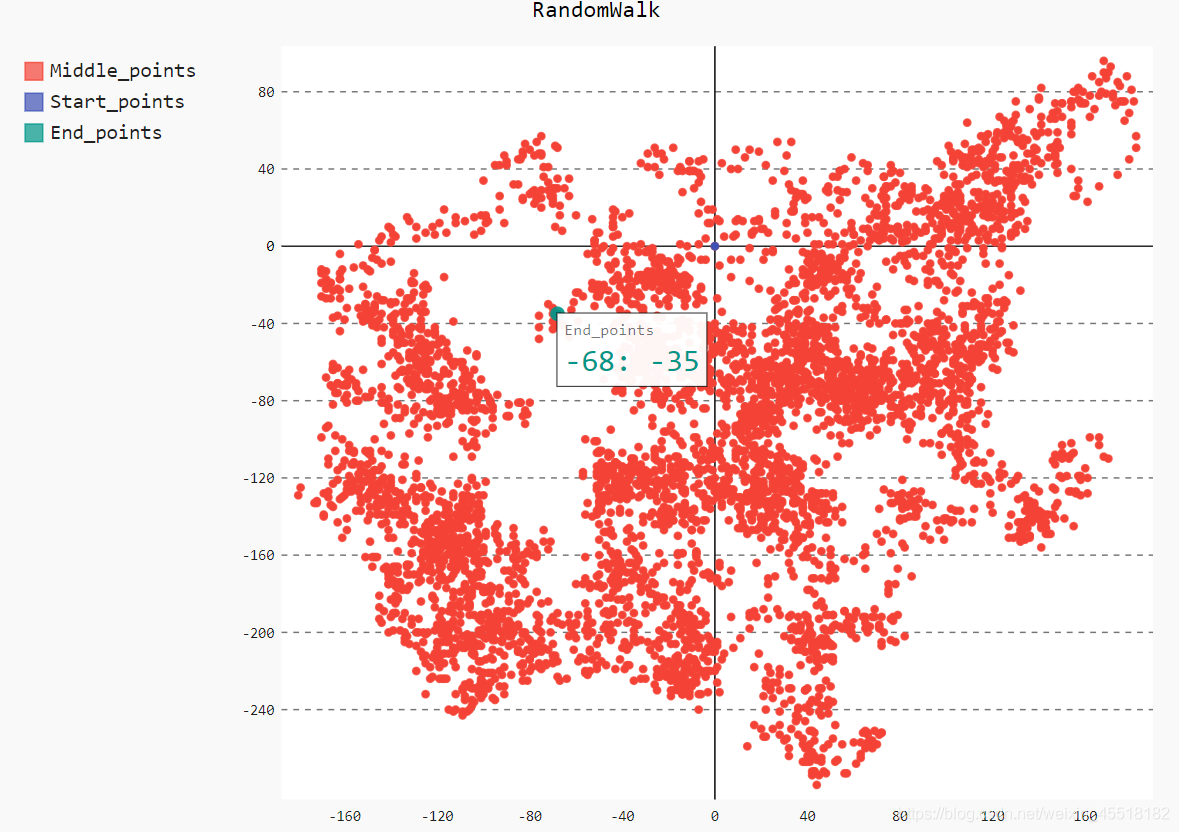
利用Pygal繪製隨機漫步圖
'''隨機漫步圖 random_walk.py'''
from random import choice
class RandomWalk():
'''一個生成隨機漫步數據的類'''
def __init__(self,num_points=5000):
#初始化隨機漫步的屬性
self.num_points=num_points
#列表儲存隨機漫步點的座標,所有隨機漫步都始於(0,0)
self.x_values=[0]
self.y_values=[0]
def get_step(self):
'''獲取前進方向及前進距離'''
direction=choice([-1,1])
distance=choice([0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8])
step=direction * distance
return step
def fill_walk(self):
'''計算隨機漫步包含的所有點'''
#不斷漫步,直到列表達到指定的長度
while len(self.x_values)<self.num_points:
#決定前進方向以及沿此方向前進的距離
x_step=self.get_step()
y_step=self.get_step()
#拒絕原地踏步
if x_step==0 and y_step==0:
continue
#計算下一個點的座標,x值和y值
next_x=self.x_values[-1] + x_step
next_y=self.y_values[-1] + y_step
self.x_values.append(next_x)
self.y_values.append(next_y)
'''隨機漫步圖範例化 rw_pygal_visual.py'''
import pygal
from random_walk import RandomWalk
'''模擬多次隨機漫步'''
while True:
#建立一個RandomWalk範例,並將其包含的點都繪製出來
rw=RandomWalk(5000)
rw.fill_walk()
points=list(zip(rw.x_values,rw.y_values))
#用內建函數zip()生成橫縱座標一一對應的對映
#再將得到的轉換器轉化爲列表,直接作爲add方法的第二個參數
xy_chart=pygal.XY(stroke=False)
#範例化XY類,參數stroke=false說明只繪製點,不需要繪製折線
xy_chart.add('Middle_points',points)
'''上述三行通過列表解析可表現爲:'''
#xy_chart=pygal.XY(stroke=False)
#xy_chart.add('randomwalk',[(rw.x_values[i],rw.y_values[i]) for i in range(rw.num_points)])
#突出隨機漫步的起點和終點
xy_chart.add('Start_points',[(0,0)])
xy_chart.add('End_points',[(rw.x_values[-1],rw.y_values[-1])])
xy_chart.title='RandomWalk'
xy_chart.render_to_file('RandomWalk.svg')
#只有關閉當前生成的隨機漫步圖視窗,纔會詢問是否再執行一次
keep_running=input("Make another walk?(y/n): ")
if keep_running=='n':
break
參考:
[1] https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44520259/article/details/89853531?utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-baidulandingword-1&spm=1001.2101.3001.4242
[2] https://blog.csdn.net/sidens/article/details/80710303