機器學習——神經網路Neural Network(2020最新版)
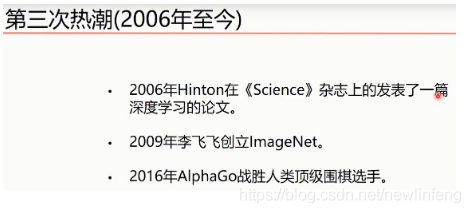
1、深度學習三次熱潮


2、深度學習爆發的三要素
大數據、計算能力、演算法
3、深度學習三巨頭(三個代表人物)


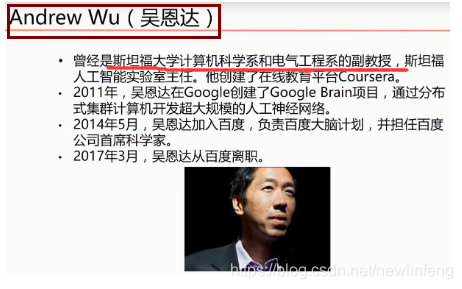
此外,還有一個人也是很著名的,華裔科學家吳恩達:
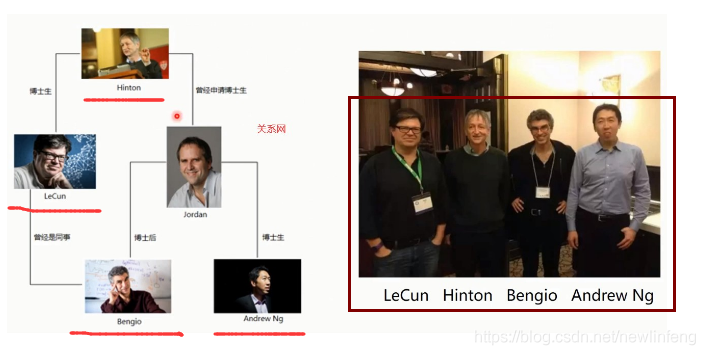
他們之間的關係網:
4、單層感知器
4.1 人體神經網路
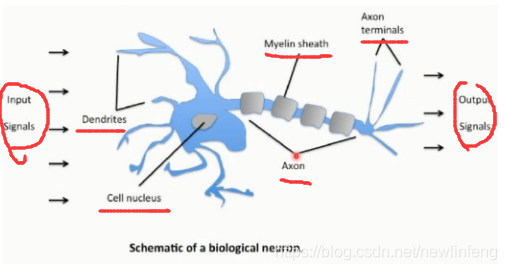
人工設計的神經元:
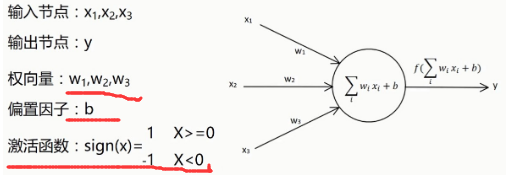
例如:
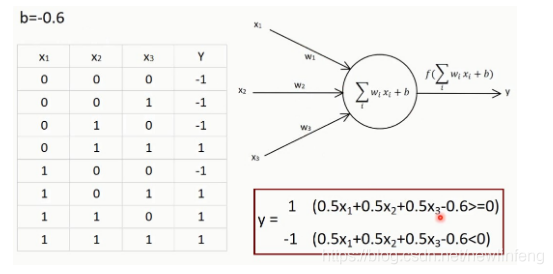
另外一種神經元結構:
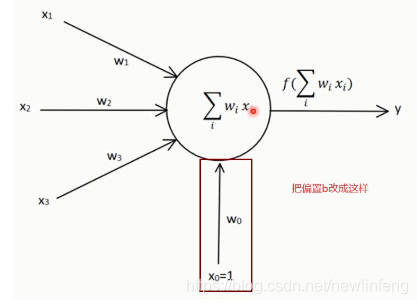
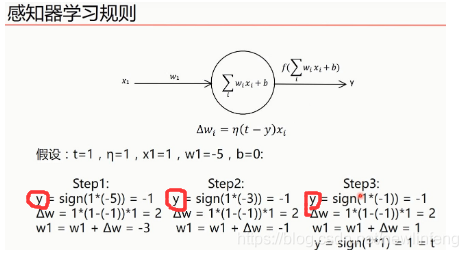
4.2 感知器的學習規則

例如:
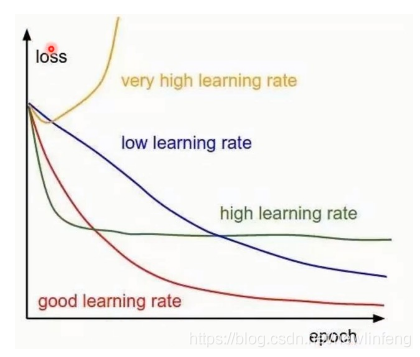
學習率的取值:

不同的學習率隨着迭代次數的變化,loss值的變化:
模型收斂的條件(loss達到何值時收斂?):

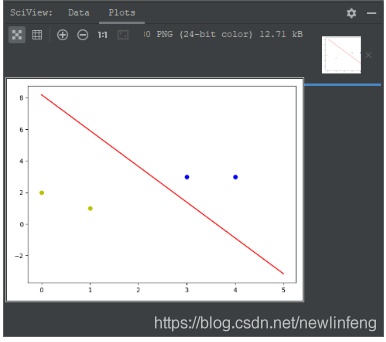
4.3 單層感知器程式
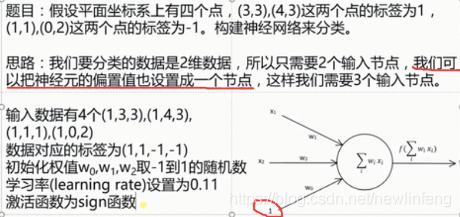
單層感知器程式:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- #
"""
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
FileName: sig_layer_perception
Author: newlinfeng
Date: 2020/7/29 0029 22:05
Description: 關於單層感知器的題目,每次的執行結果都是不一樣的
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
"""
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#輸入數據
X = np.array([[1, 3, 3],
[1, 4, 3],
[1, 1, 1],
[1, 0, 2]])
#標籤
Y = np.array([[1],
[1],
[-1],
[-1]])
#權值初始化,3行1列,數值範圍-1到1
W = (np.random.random([3, 1])-0.5)*2
print(W)
#學習率的設定
lr = 0.11
#神經網路輸出
O = 0
#用來更新權值矩陣的函數
def update():
global X, Y, W, lr
O = np.sign(np.dot(X, W)) #shape:(3, 1)
W_C = lr*(X.T.dot(Y-O))/int(X.shape[0])
W = W + W_C
for i in range(100):
update()#更新權值
print(W)#列印當前權值
print(i)#列印當前迭代次數
O = np.sign(np.dot(X, W))#計算當前輸出
#all() O、Y矩陣(4*1)完全表示完全相等時
if(O == Y).all(): #如果實際輸出等於期望輸出,模型收斂,回圈結束
print("Finished")
print('epoch:', i)#列印當前迭代次數
break
#正樣本
x1 = [3, 4]
y1 = [3, 3]
#負樣本
x2 = [1, 0]
y2 = [1, 2]
#計算分界線的斜率以及截距,依據w0+x*w1+y*w2 = 0求出的斜率和截距
k = -W[1]/W[2]
d = -W[0]/W[2]
print('k=', k)
print('d=', d)
xdata = (0, 5)
plt.figure()
plt.plot(xdata, xdata*k+d, 'r')
plt.scatter(x1, y1, c='b')
plt.scatter(x2, y2, c='y')
plt.show()
4.4 單層感知器-互斥或問題
互斥或:如果a、b兩個值不相同,則互斥或結果爲1。如果a、b兩個值相同,互斥或結果爲0。
或:是有真就是真;
同或:同真,不同假;
互斥或:同假,不同真;
單層感知器-互斥或問題:對於測試點,無法使用直線來分割,例如如下程式的結果(非線性問題),即使用單層感知器無法解決這個問題。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- #
"""
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
FileName: sig_layer_perception_互斥或
Author: newlinfeng
Date: 2020/7/31 0031 14:32
Description: 單層感知器的互斥或問題(無法解決,但是使用線性神經網路可以解決)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
"""
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 輸入數據
X = np.array([[1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 1]])
# 標籤
Y = np.array([[-1],
[1],
[1],
[-1]])
# 權值初始化
W = (np.random.random([3, 1]) - 0.1) * 2
print(W)
# 學習率的設定
lr = 0.11
# 神經網路的輸出
O = 0
def update():
global X, Y, W, lr
O = np.sign(np.dot(X, W)) # shape:(3, 1)
W_C = lr * (X.T.dot(Y - O)) / int(X.shape[0])
W = W + W_C
for i in range(100):
update() # 更新權值
print(i) # 列印迭代次數
O = np.sign(np.dot(X, W)) # 計算當前輸出
if (O == Y).all(): # 如果實際輸出等於期望輸出,模型收斂,回圈結束
print("Finished")
print('epoch:', i)
break
# 正樣本
x1 = [0, 1]
y1 = [1, 0]
# 負樣本
x2 = [0, 1]
y2 = [0, 1]
# 計算分界線的斜率以及截距
k = -W[1] / W[2]
b = -W[0] / W[2]
print('k=', k)
print('b=', b)
xdata = (-2, 3)
plt.figure()
plt.plot(xdata, xdata * k + b, 'r')
plt.scatter(x1, y1, c='b')
plt.scatter(x2, y2, c='y')
plt.show()
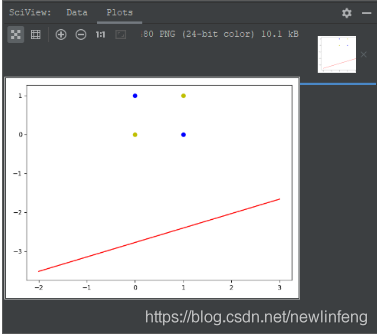
(1) 具體使用什麼方法來解決非線性的問題,後面會給出解決方案。
5、線性神經網路、Delta學習規則
5.1 線性神經網路(linear neural network)
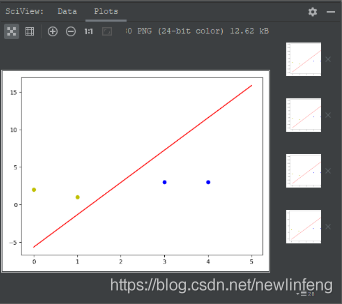
線性神經網路在結構上與感知器非常相似,只是啓用函數不同。在模型訓練時把原來的sign函數改成了purelin函數:y=x。
使用purelin作爲啓用函數的程式:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- #
"""
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
FileName: linear_neural_network
Author: newlinfeng
Date: 2020/7/31 0031 14:56
Description: 線性神經網路-purelin函數
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
"""
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#輸入數據
X = np.array([[1, 3, 3],
[1, 4, 3],
[1, 1, 1],
[1, 0, 2]])
#標籤
Y = np.array([[1],
[1],
[-1],
[-1]])
#權值初始化,3行1列,取值範圍-1到1
W = (np.random.random([3, 1])-0.5)*2
print(W)
#學習率設定
lr = 0.11
#神經網路輸出
O = 0
def update():
global X, Y, W, lr
O = np.dot(X, W) #單層感知器使用的啓用函數是np.sign(np.dot(X, W))
W_C = lr*(X.T.dot(Y-O))/int(X.shape[0])
W += W_C
for _ in range(100):
update()
# 正樣本
x1 = [3, 4]
y1 = [3, 3]
# 負樣本
x2 = [1, 0]
y2 = [1, 2]
# 計算分界線的斜率以及截距,依據w0+x*w1+y*w2 = 0求出的斜率和截距
k = -W[1] / W[2]
d = -W[0] / W[2]
print('k=', k)
print('d=', d)
xdata = (0, 5)
plt.figure()
plt.plot(xdata, xdata * k + d, 'r')
plt.scatter(x1, y1, c='b')
plt.scatter(x2, y2, c='y')
plt.show()
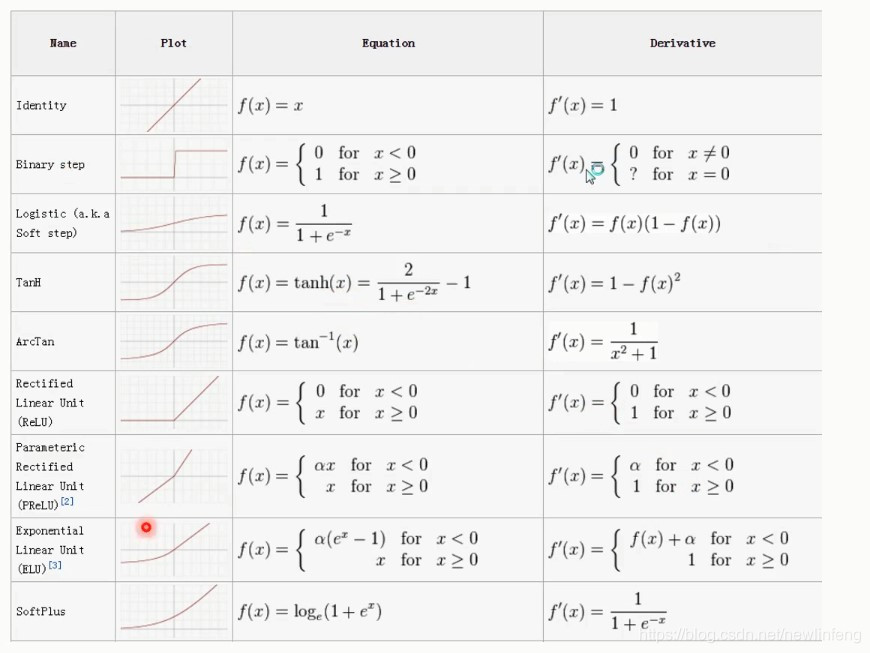
還有很多的啓用函數類別,比如:
5.2 Delta函數(調整權值W的一種方法)

(1) 而之前使用的感知器的學習規則(調整w)是很簡單的,如下圖:

Delta函數學習規則:

關於梯度下降法-一維情況:
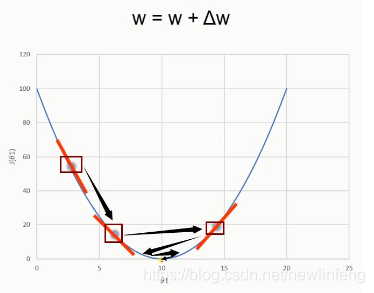
關於梯度下降法-二維情況:
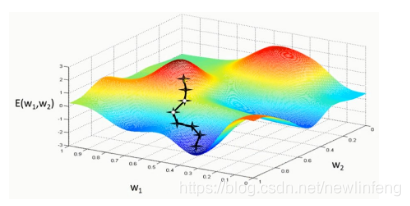
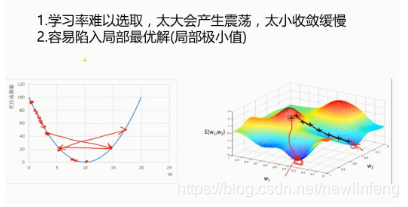
梯度下降法的問題:
5.3 解決互斥或問題(使用線性神經網路來做)
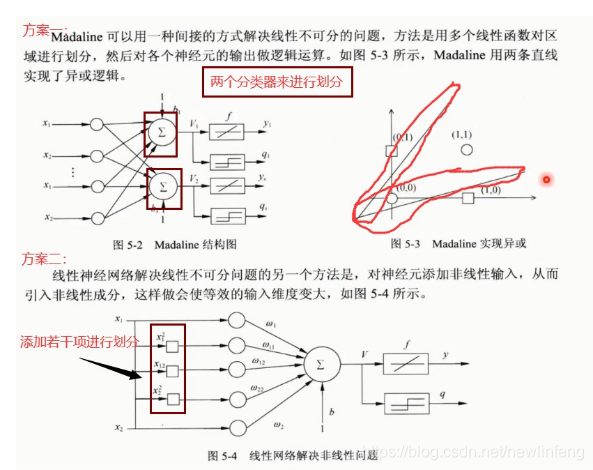
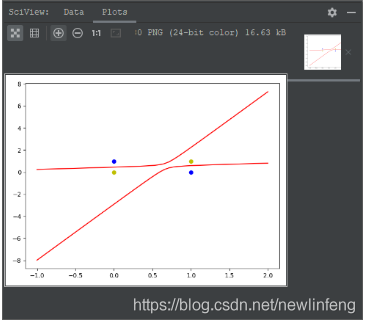
我這裏使用第二種方案:引入非線性的輸入,再加一些輸入項,再做神經網路——從而解決互斥或問題。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- #
"""
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
FileName: linear_neural_network_互斥或
Author: newlinfeng
Date: 2020/7/31 0031 17:35
Description: 使用線性神經網路+第二種方案解決互斥或問題
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
"""
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 輸入數據
X = np.array([[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]])
# 標籤
Y = np.array([-1, 1, 1, -1])
# 權值初始化,6行1列,數值範圍-1到1
W = (np.random.random(6) - 0.5) * 2
print(W)
# 學習率的設定
lr = 0.11
# 計算迭代次數
n = 0
# 神經網路輸出
O = 0
# 用來更新權值矩陣的函數
def update():
global X, Y, W, lr, n
n += 1
O = np.dot(X, W.T)
W_C = lr * (X.T.dot(Y - O.T)) / int(X.shape[0])
W = W + W_C
for _ in range(10000):
update() # 更新權值
# 正樣本
x1 = [0, 1]
y1 = [1, 0]
# 負樣本
x2 = [0, 1]
y2 = [0, 1]
def calculate(x, root):
a = W[5]
b = W[2] + x * W[4]
c = W[0] + x * W[1] + x * x * W[3]
if root == 1:
return (-b + np.sqrt(b * b - 4 * a * c)) / (2 * a)
if root == 2:
return (-b - np.sqrt(b * b - 4 * a * c)) / (2 * a)
xdata = np.linspace(-1, 2)
plt.figure()
plt.plot(xdata, calculate(xdata, 1), 'r')
plt.plot(xdata, calculate(xdata, 2), 'r')
plt.plot(x1, y1, 'bo')
plt.plot(x2, y2, 'yo')
plt.show()
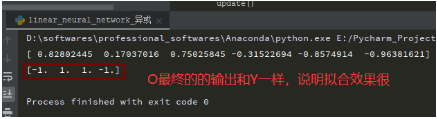
O = np.dot(X, W.T)
print(O)
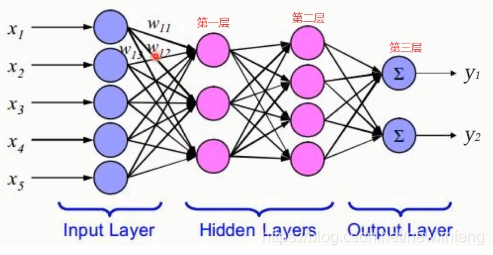
6、BP神經網路(Back Propagation Neural Network)反向傳播
6.1 BP神經網路的由來

6.2 網路結構

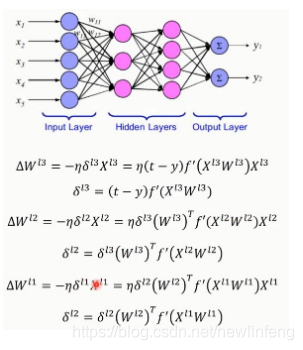
(1) 關於BP演算法的推到過程,可以後面的推導過程
例如:
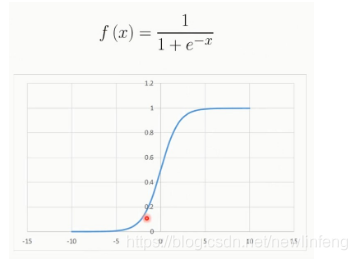
6.3 幾種常用的啓用函數
<1> Sigmoid函數(就是之前的邏輯迴歸的那個 函數):
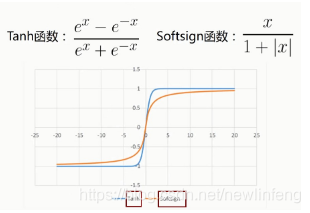
<2> Tanh函數、Softsign函數
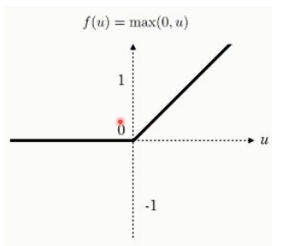
<3> ReLU函數(用的最多的啓用函數)
6.4 BP神經網路推導(Back Propagation Neural Network)
空!
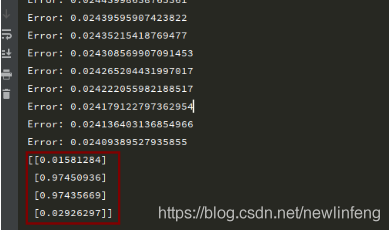
6.5 BP神經網路應用(解決互斥或問題)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- #
"""
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
FileName: BP_neural_network_互斥或
Author: newlinfeng
Date: 2020/8/1 0001 7:58
Description: 使用BP(反向傳播)神經網路解決互斥或問題
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
"""
# 輸入數據
import numpy as np
X = np.array([[1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 1]])
# 標籤
Y = np.array([[0, 1, 1, 0]])
# 權值初始化,二層,數值範圍-1到1
V = np.random.random((3, 4)) * 2 - 1
W = np.random.random((4, 1)) * 2 - 1
print(V)
print(W)
# 學習率的設定
lr = 0.11
# sigmoid函數的定義
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
# sigmoid函數的導數
def dsigmoid(x):
return x*(1 - x)
# 定義一個更新權值的函數
def update():
global X, Y, W, V, lr
# 隱藏層的輸出(4, 4)
L1 = sigmoid(np.dot(X, V))
# 輸出層的輸出(4, 1)
L2 = sigmoid(np.dot(L1, W))
L2_delta = (Y.T - L2) * dsigmoid(L2)
L1_delta = L2_delta.dot(W.T) * dsigmoid(L1)
W_C = lr * L1.T.dot(L2_delta)
V_C = lr * X.T.dot(L1_delta)
W = W + W_C
V = V + V_C
for i in range(20000):
update()
if i%50 == 0:
L1 = sigmoid(np.dot(X, V))
L2 = sigmoid(np.dot(L1, W))
print('Error:', np.mean(np.abs(Y.T-L2)))
L1 = sigmoid(np.dot(X, V))
L2 = sigmoid(np.dot(L1, W))
print(L2)
6.6 BP神經網路的一篇論文
Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks
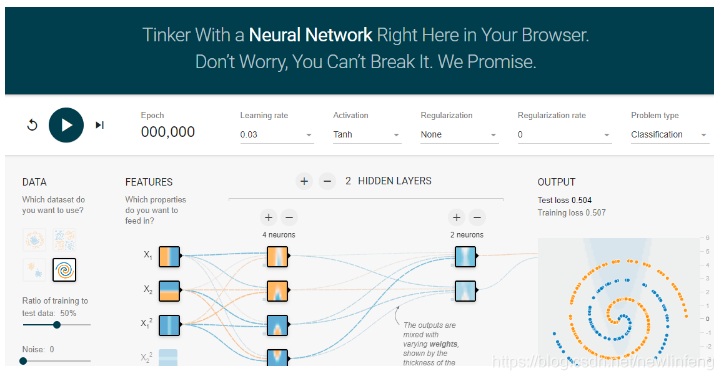
6.7 Google神經網路演示平臺
網址:http://playground.tensorflow.org/ ,可以自己去玩一玩
2020-08-10 更新