Hnswlib 介紹與入門使用
2023-12-13 15:00:41
Hnswlib是一個強大的近鄰搜尋(ANN)庫, 官方介紹 Header-only C++ HNSW implementation with python bindings, insertions and updates. 熱門的向量資料庫Milvus底層的ANN庫之一就是Hnswlib, 為milvus提供HNSW檢索。
HNSW 原理
HNSW 原理
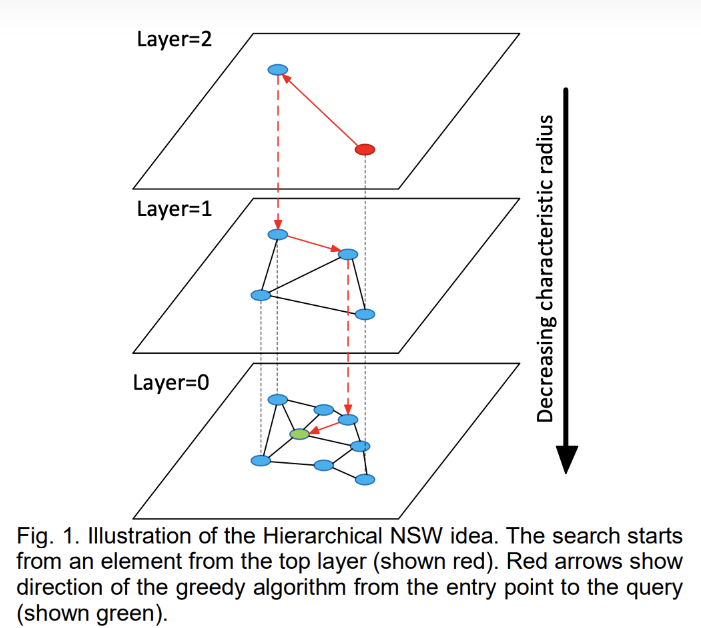
將節點劃分成不同層級,貪婪地遍歷來自上層的元素,直到達到區域性最小值,然後切換到下一層,以上一層中的區域性最小值作為新元素重新開始遍歷,直到遍歷完最低一層。
安裝使用
從原始碼安裝:
apt-get install -y python-setuptools python-pip
git clone https://github.com/nmslib/hnswlib.git
cd hnswlib
pip install .
或者直接pip安裝 pip install hnswlib
python 使用
import hnswlib
import numpy as np
dim = 16
num_elements = 10000
# Generating sample data
data = np.float32(np.random.random((num_elements, dim)))
# We split the data in two batches:
data1 = data[:num_elements // 2]
data2 = data[num_elements // 2:]
# Declaring index
p = hnswlib.Index(space='l2', dim=dim) # possible options are l2, cosine or ip
# Initializing index
# max_elements - the maximum number of elements (capacity). Will throw an exception if exceeded
# during insertion of an element.
# The capacity can be increased by saving/loading the index, see below.
#
# ef_construction - controls index search speed/build speed tradeoff
#
# M - is tightly connected with internal dimensionality of the data. Strongly affects memory consumption (~M)
# Higher M leads to higher accuracy/run_time at fixed ef/efConstruction
p.init_index(max_elements=num_elements//2, ef_construction=100, M=16)
# Controlling the recall by setting ef:
# higher ef leads to better accuracy, but slower search
p.set_ef(10)
# Set number of threads used during batch search/construction
# By default using all available cores
p.set_num_threads(4)
print("Adding first batch of %d elements" % (len(data1)))
p.add_items(data1)
# Query the elements for themselves and measure recall:
labels, distances = p.knn_query(data1, k=1)
print("Recall for the first batch:", np.mean(labels.reshape(-1) == np.arange(len(data1))), "\n")
# Serializing and deleting the index:
index_path='first_half.bin'
print("Saving index to '%s'" % index_path)
p.save_index("first_half.bin")
del p
# Re-initializing, loading the index
p = hnswlib.Index(space='l2', dim=dim) # the space can be changed - keeps the data, alters the distance function.
print("\nLoading index from 'first_half.bin'\n")
# Increase the total capacity (max_elements), so that it will handle the new data
p.load_index("first_half.bin", max_elements = num_elements)
print("Adding the second batch of %d elements" % (len(data2)))
p.add_items(data2)
# Query the elements for themselves and measure recall:
labels, distances = p.knn_query(data, k=1)
print("Recall for two batches:", np.mean(labels.reshape(-1) == np.arange(len(data))), "\n")
依次介紹:
distances
支援三種距離演演算法, l2, ip內積,以及cos。
| Distance | parameter | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| Squared L2 | 'l2' | d = sum((Ai-Bi)^2) |
| Inner product | 'ip' | d = 1.0 - sum(Ai*Bi) |
| Cosine similarity | 'cosine' | d = 1.0 - sum(AiBi) / sqrt(sum(AiAi) * sum(Bi*Bi)) |
API
定義 index
p = hnswlib.Index(space='l2', dim=dim) # possible options are l2, cosine or ip
space 指定Distance演演算法,dim是向量的維度。
初始化索引
p.init_index(max_elements=num_elements//2, ef_construction=100, M=16)
max_elements- 最大容量 (capacity),如果插入資料超過容量會報異常,可以動態擴容- ef_construction - 平衡索引構建速度和搜尋準確率,ef_construction越大,準確率越高但是構建速度越慢。 ef_construction 提高並不能無限增加索引的質量,常見的 ef_constructio n 引數為 128。
- M - 表示在建表期間每個向量的邊數目量,M會影響記憶體消耗,M越高,記憶體佔用越大,準確率越高,同時構建速度越慢。通常建議設定在 8-32 之間。
新增資料與查詢資料
# Controlling the recall by setting ef:
# higher ef leads to better accuracy, but slower search
p.set_ef(10)
# Set number of threads used during batch search/construction
# By default using all available cores
p.set_num_threads(4)
print("Adding first batch of %d elements" % (len(data1)))
p.add_items(data1)
# Query the elements for themselves and measure recall:
labels, distances = p.knn_query(data1, k=1)
print("Recall for the first batch:", np.mean(labels.reshape(-1) == np.arange(len(data1))), "\n")
p.set_ef(10):設定搜尋時的最大近鄰數量(ef),即在構建索引時最多保留多少個近鄰。較高的ef值會導致更好的準確率,但搜尋速度會變慢。p.set_num_threads(4):設定在批次搜尋和構建索引過程中使用的執行緒數。預設情況下,使用所有可用的核心。p.add_items(data1):將資料新增到索引中。labels, distances = p.knn_query(data1, k=1):對資料中的每個元素進行查詢,找到與其最近的鄰居,返回鄰居的標籤和距離。
保持與載入索引
# Serializing and deleting the index:
index_path='first_half.bin'
print("Saving index to '%s'" % index_path)
p.save_index("first_half.bin")
del p
# Re-initializing, loading the index
p = hnswlib.Index(space='l2', dim=dim) # the space can be changed - keeps the data, alters the distance function.
print("\nLoading index from 'first_half.bin'\n")
# Increase the total capacity (max_elements), so that it will handle the new data
p.load_index("first_half.bin", max_elements = num_elements)
print("Adding the second batch of %d elements" % (len(data2)))
p.add_items(data2)
# Query the elements for themselves and measure recall:
labels, distances = p.knn_query(data, k=1)
print("Recall for two batches:", np.mean(labels.reshape(-1) == np.arange(len(data))), "\n")
- 通過
save_index儲存索引 - 然後
load_index重新載入索引,只要未超過max_elements,可以再次add_items
C++使用
官方提供了C++ 例子,建立索引、插入元素、搜尋和序列化
#include "../../hnswlib/hnswlib.h"
int main() {
int dim = 16; // Dimension of the elements
int max_elements = 10000; // Maximum number of elements, should be known beforehand
int M = 16; // Tightly connected with internal dimensionality of the data
// strongly affects the memory consumption
int ef_construction = 200; // Controls index search speed/build speed tradeoff
// Initing index
hnswlib::L2Space space(dim);
hnswlib::HierarchicalNSW<float>* alg_hnsw = new hnswlib::HierarchicalNSW<float>(&space, max_elements, M, ef_construction);
// Generate random data
std::mt19937 rng;
rng.seed(47);
std::uniform_real_distribution<> distrib_real;
float* data = new float[dim * max_elements];
for (int i = 0; i < dim * max_elements; i++) {
data[i] = distrib_real(rng);
}
// Add data to index
for (int i = 0; i < max_elements; i++) {
alg_hnsw->addPoint(data + i * dim, i);
}
// Query the elements for themselves and measure recall
float correct = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < max_elements; i++) {
std::priority_queue<std::pair<float, hnswlib::labeltype>> result = alg_hnsw->searchKnn(data + i * dim, 1);
hnswlib::labeltype label = result.top().second;
if (label == i) correct++;
}
float recall = correct / max_elements;
std::cout << "Recall: " << recall << "\n";
// Serialize index
std::string hnsw_path = "hnsw.bin";
alg_hnsw->saveIndex(hnsw_path);
delete alg_hnsw;
// Deserialize index and check recall
alg_hnsw = new hnswlib::HierarchicalNSW<float>(&space, hnsw_path);
correct = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < max_elements; i++) {
std::priority_queue<std::pair<float, hnswlib::labeltype>> result = alg_hnsw->searchKnn(data + i * dim, 1);
hnswlib::labeltype label = result.top().second;
if (label == i) correct++;
}
recall = (float)correct / max_elements;
std::cout << "Recall of deserialized index: " << recall << "\n";
delete[] data;
delete alg_hnsw;
return 0;
}
Milvus 使用
milvus 通過cgo呼叫knowhere,knowhere是一個向量檢索的抽象封裝,整合了FAISS, HNSW等開源ANN庫。
knowhere 是直接將hnswlib程式碼引入,使用hnswlib的程式碼在
https://github.com/zilliztech/knowhere/blob/main/src/index/hnsw/hnsw.cc
主要是基於hnswlib的C介面,實現HnswIndexNode
namespace knowhere {
class HnswIndexNode : public IndexNode {
public:
HnswIndexNode(const int32_t& /*version*/, const Object& object) : index_(nullptr) {
search_pool_ = ThreadPool::GetGlobalSearchThreadPool();
}
Status
Train(const DataSet& dataset, const Config& cfg) override {
auto rows = dataset.GetRows();
auto dim = dataset.GetDim();
auto hnsw_cfg = static_cast<const HnswConfig&>(cfg);
hnswlib::SpaceInterface<float>* space = nullptr;
if (IsMetricType(hnsw_cfg.metric_type.value(), metric::L2)) {
space = new (std::nothrow) hnswlib::L2Space(dim);
} else if (IsMetricType(hnsw_cfg.metric_type.value(), metric::IP)) {
space = new (std::nothrow) hnswlib::InnerProductSpace(dim);
} else if (IsMetricType(hnsw_cfg.metric_type.value(), metric::COSINE)) {
space = new (std::nothrow) hnswlib::CosineSpace(dim);
} else if (IsMetricType(hnsw_cfg.metric_type.value(), metric::HAMMING)) {
space = new (std::nothrow) hnswlib::HammingSpace(dim);
} else if (IsMetricType(hnsw_cfg.metric_type.value(), metric::JACCARD)) {
space = new (std::nothrow) hnswlib::JaccardSpace(dim);
} else {
LOG_KNOWHERE_WARNING_ << "metric type not support in hnsw: " << hnsw_cfg.metric_type.value();
return Status::invalid_metric_type;
}
auto index = new (std::nothrow)
hnswlib::HierarchicalNSW<float>(space, rows, hnsw_cfg.M.value(), hnsw_cfg.efConstruction.value());
if (index == nullptr) {
LOG_KNOWHERE_WARNING_ << "memory malloc error.";
return Status::malloc_error;
}
if (this->index_) {
delete this->index_;
LOG_KNOWHERE_WARNING_ << "index not empty, deleted old index";
}
this->index_ = index;
return Status::success;
}
Status
Add(const DataSet& dataset, const Config& cfg) override {
// ...
std::atomic<uint64_t> counter{0};
uint64_t one_tenth_row = rows / 10;
for (int i = 1; i < rows; ++i) {
futures.emplace_back(build_pool->push([&, idx = i]() {
index_->addPoint(((const char*)tensor + index_->data_size_ * idx), idx);
uint64_t added = counter.fetch_add(1);
if (added % one_tenth_row == 0) {
LOG_KNOWHERE_INFO_ << "HNSW build progress: " << (added / one_tenth_row) << "0%";
}
}));
}
// ...
}
其他實現
- Go實現:https://github.com/Bithack/go-hnsw
- Java實現:https://github.com/jelmerk/hnswlib
- 使用Java Native Access的Java繫結:https://github.com/stepstone-tech/hnswlib-jna