資料探勘中的12種距離度量原理及實現程式碼
2021-05-05 07:00:43
本文介紹了12種常用的距離度量原理、優缺點、應用場景,以及基於Numpy和Scipy的Python實現程式碼。
筆記工具:Notability
文章目錄
- 1. 個人筆記
- 2. 程式碼實現
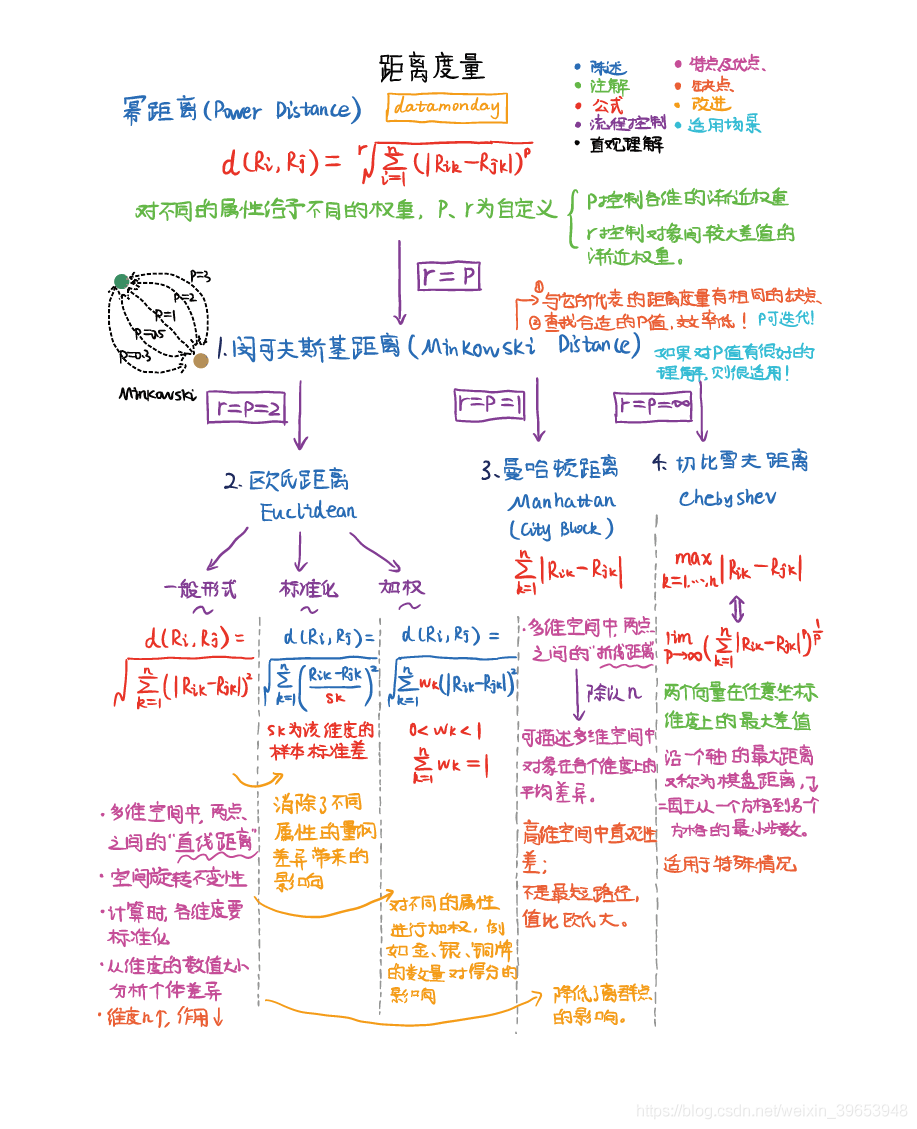
- 1)閔可夫斯基距離(Minkowski Distance)
- 2) 歐氏距離(Euclidean Distance)
- 3) 曼哈頓距離(Manhattan/City Block Distance)
- 4) 切比雪夫距離(Chebyshev Distance)
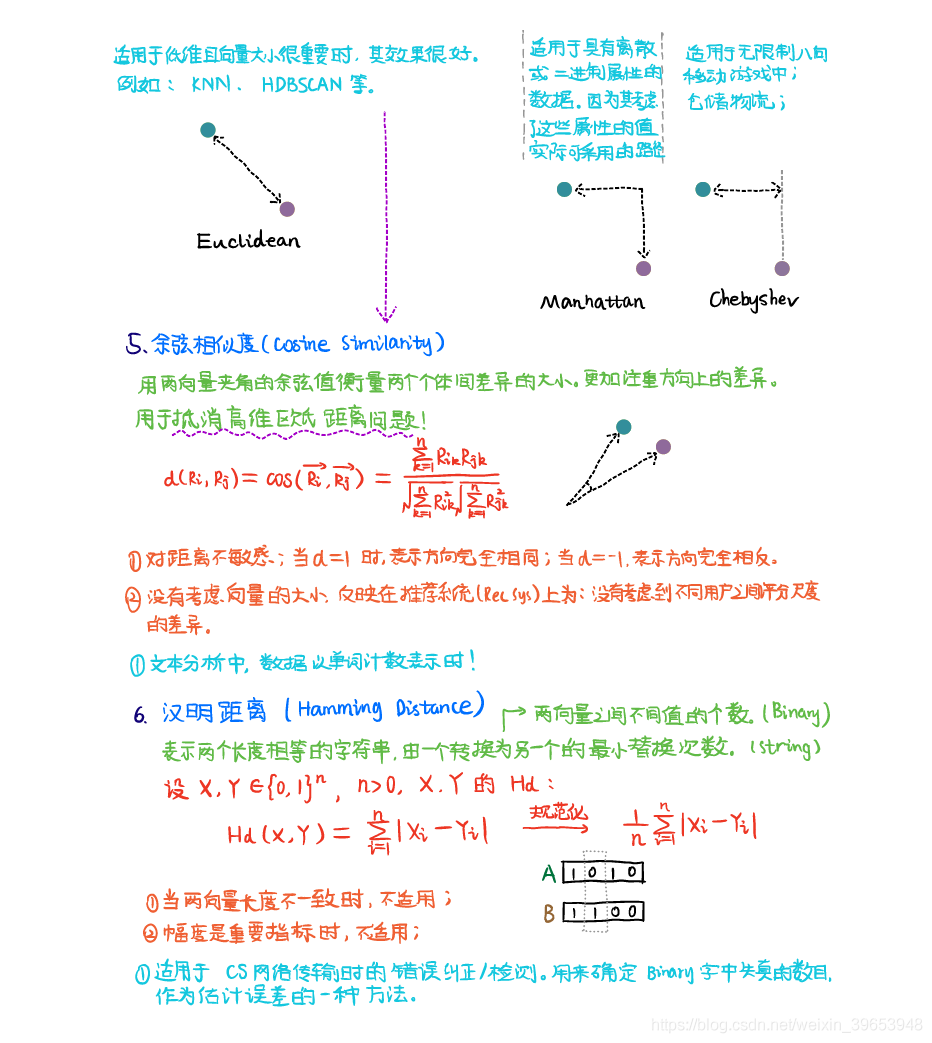
- 5) 餘弦相似度(Cosine Similarity)
- 6) 漢明距離(Hamming Distance)
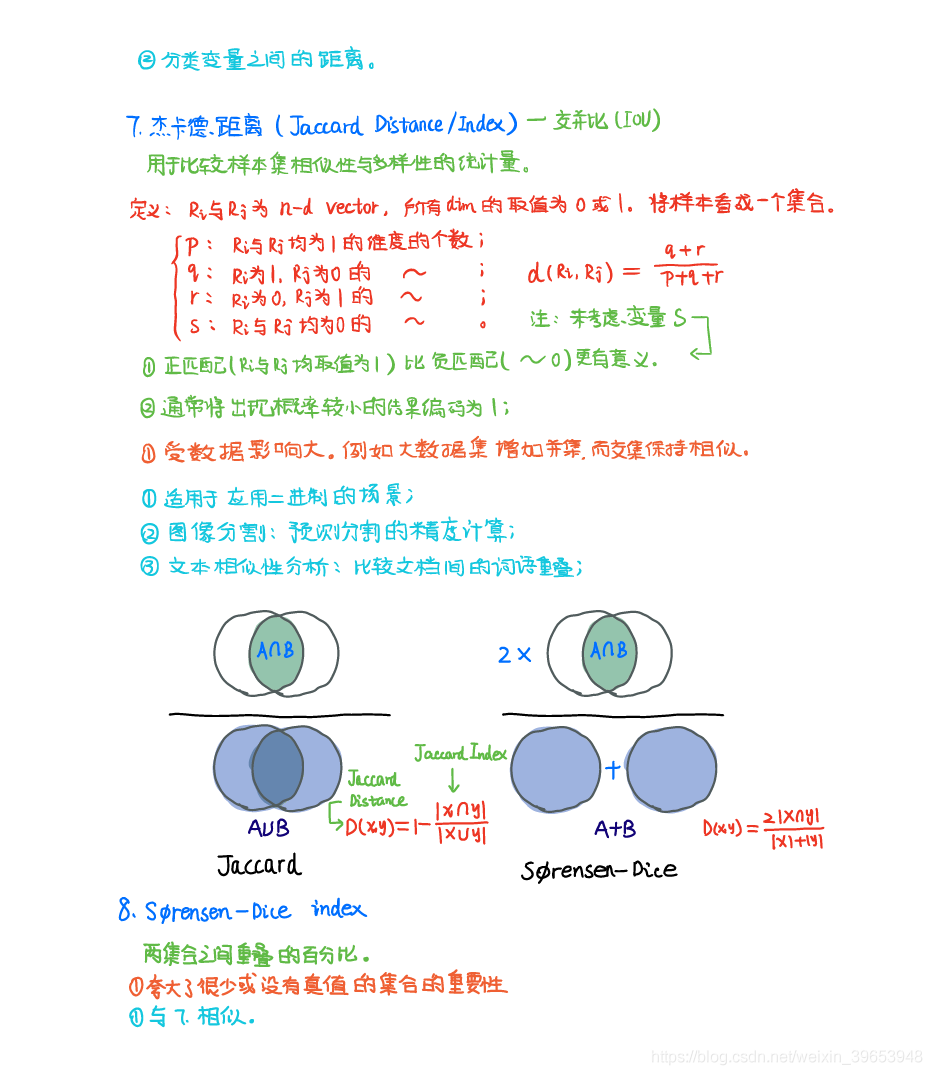
- 7) 傑卡德距離(Jaccard Distance)
- 8) S Φ rensen-Dice
- 9) 半正矢距離(Haversine Distance)
- 10) 斜交空間距離(Oblique Space Distance)
- 11) 蘭氏距離(Canberra Distance)
- 12) 馬氏距離(Mahalanobis Distance)
1. 個人筆記
筆記工具:Notability
筆記獲取:
- 公眾號: datazero 回覆:DM 獲取下載地址。(主頁左側邊欄掃碼)
- Github:https://github.com/datamonday/BigDataAnalysis


2. 程式碼實現
匯入必要的包,並構造資料。
import numpy as np
from scipy.spatial.distance import pdist
x = np.random.random(5)
# array([0.75173729, 0.34763686, 0.71927609, 0.24151473, 0.22294162])
y = np.random.random(5)
# array([0.98036113, 0.45482745, 0.87472311, 0.92923963, 0.62922737])
1)閔可夫斯基距離(Minkowski Distance)
# p = 2 ——> 歐氏距離
pdist(xy, metric="minkowski", p=2)
2) 歐氏距離(Euclidean Distance)
# 根據公式求解
np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(x - y) ) )
# 0.8520305805970781
# 根據scipy庫求解
xy = np.vstack([x, y])
pdist(xy, metric="euclidean")
# array([0.85203058])
3) 曼哈頓距離(Manhattan/City Block Distance)
np.sum(np.abs(x - y))
# 1.585272101374208
pdist(xy, metric="cityblock")
# array([1.5852721])
4) 切比雪夫距離(Chebyshev Distance)
np.max(np.abs(x - y))
# 0.6877248997688814
pdist(xy, metric="chebyshev")
# array([0.6877249])
5) 餘弦相似度(Cosine Similarity)
np.dot(x, y) / ( np.linalg.norm(x) * np.linalg.norm(y) )
# 0.9232011981703329
1 - pdist(xy, metric="cosine")
# array([0.9232012])
6) 漢明距離(Hamming Distance)
np.mean( x != y )
# 1.0
pdist(xy, metric="hamming")
# array([1.])
7) 傑卡德距離(Jaccard Distance)
molecular = np.double( (x != y).sum() )
denominator = np.double(np.bitwise_or( x != 0, y != 0).sum() )
molecular / denominator
# 1.0
pdist(xy, metric="jaccard")
# array([1.])
8) S Φ rensen-Dice
pdist(xy, metric="dice")
# array([0.])
9) 半正矢距離(Haversine Distance)
"""
計算Ezeiza機場(阿根廷布宜諾斯艾利斯)和戴高樂機場(法國巴黎)之間的距離。
"""
from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import haversine_distances
from math import radians
bsas = [-34.83333, -58.5166646]
paris = [49.0083899664, 2.53844117956]
bsas_in_radians = [radians(_) for _ in bsas]
paris_in_radians = [radians(_) for _ in paris]
result = haversine_distances([bsas_in_radians, paris_in_radians])
# multiply by Earth radius to get kilometers
result * 6371000/1000
輸出:
array([[ 0. , 11099.54035582],
[11099.54035582, 0. ]])
10) 斜交空間距離(Oblique Space Distance)
11) 蘭氏距離(Canberra Distance)
np.sum( np.true_divide( np.abs(x - y), np.abs(x) + np.abs(y) ) )
# 1.4272762731136441
pdist(xy, metric="canberra")
# array([1.42727627])
12) 馬氏距離(Mahalanobis Distance)
-
馬氏距離要求樣本個數>維數,此處重新生成樣本集:10個樣本,2個屬性;
-
馬氏距離計算兩兩樣本之間的距離,故結果包含: C 10 2 = 45 C^{2}_{10} = 45 C102=45 個距離分量。
data = np.random.random([10, 2])
data # (10, 2)
array([[0.16057991, 0.03173777],
[0.04984203, 0.63608966],
[0.0965663 , 0.54125706],
[0.14562222, 0.50749436],
[0.12384608, 0.66895134],
[0.38362246, 0.96750912],
[0.66204458, 0.34832719],
[0.62169272, 0.76812896],
[0.55320254, 0.59736334],
[0.53135375, 0.97430267]])
# 求解個維度之間協方差矩陣
S = np.cov(data.T)
# 計算協方差矩陣的逆矩陣
ST = np.linalg.inv(S)
ST
array([[18.39262731, -4.22549979],
[-4.22549979, 13.68987876]])
n = data.shape[0]
d1 = []
for i in range(0, n):
for j in range(i + 1, n):
delta = data[i] - data[j]
d = np.sqrt( np.dot( np.dot(delta, ST), delta.T) )
d1.append(d)
print(len(d1))
d1
45
[2.4064983868149823,
1.9761163000756812,
1.778448926503528,
2.404430793536302,
3.3375019493285927,
2.1576814382238196,
2.9094250412104405,
2.3104822379986585,
3.426008151540264,
0.4480137866843753,
0.7065459737678685,
0.30815685501580464,
1.618002146140689,
3.0847744520164553,
2.3696411013587313,
2.2012364723722557,
2.1104688855720037,
0.2717792884385083,
0.4554926318973598,
1.7230353296945067,
2.7042335514201556,
2.183968292942155,
1.9135693479813816,
2.1102154148029593,
0.6287347650129346,
1.735958615801837,
2.438573435905017,
2.012440681515558,
1.6900976084983395,
2.048918972209157,
1.3438862451280977,
2.862373485815439,
2.067854534269353,
1.928870122984677,
1.8108503250774675,
2.851523901145603,
1.409891022070067,
1.7131869461579778,
0.6273442013634126,
1.608018006961265,
1.1384164544766362,
2.5238527095532692,
0.6218088758251554,
0.94309743685501,
1.422491582300723]
pdist(data, metric="mahalanobis")
array([2.40649839, 1.9761163 , 1.77844893, 2.40443079, 3.33750195,
2.15768144, 2.90942504, 2.31048224, 3.42600815, 0.44801379,
0.70654597, 0.30815686, 1.61800215, 3.08477445, 2.3696411 ,
2.20123647, 2.11046889, 0.27177929, 0.45549263, 1.72303533,
2.70423355, 2.18396829, 1.91356935, 2.11021541, 0.62873477,
1.73595862, 2.43857344, 2.01244068, 1.69009761, 2.04891897,
1.34388625, 2.86237349, 2.06785453, 1.92887012, 1.81085033,
2.8515239 , 1.40989102, 1.71318695, 0.6273442 , 1.60801801,
1.13841645, 2.52385271, 0.62180888, 0.94309744, 1.42249158])
Reference:
- 《巨量資料分析與挖掘》 ch5:聚類演演算法
- 資料科學中常見的9種距離度量方法,內含歐氏距離、切比雪夫距離等
- 9 Distance Measures in Data Science