Java五子棋遊戲(附帶原始碼和解析)
2020-07-16 10:05:13
首先定義一個二維陣列作為下棋的棋盤,每當一個棋手下一步棋後,也就是為二維陣列的一個陣列元素賦值。下面程式碼完成了這個程式的初步功能。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Gobang {
// 定義棋盤的大小
public static int BOARD_SIZE = 15;
// 定義一個二維陣列來充當棋盤
public static String[][] board = new String[BOARD_SIZE][BOARD_SIZE];
String black = "●"; // 黑子
String white = "○"; // 白子
/**
* 初始化械盤陣列
*/
public void initBoard() {
// 把每個元素賦為"╋",用於在控制台畫出棋盤
for (int i = 0; i < BOARD_SIZE; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < BOARD_SIZE; j++) {
board[i][j] = "╋";
}
}
}
/**
* 在控制台輸出棋盤的方法
*/
public void printBoard() {
// 列印毎個陣列元素
for (int i = 0; i < BOARD_SIZE; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < BOARD_SIZE; j++) {
// 列印陣列元素後不換行
System.out.print(board[i][j]);
}
// 毎列印完一行陣列元素後輸出一個換行符
System.out.print("n");
}
}
/**
* 判斷輸贏的方法
*/
public static boolean isWin(int x, int y, String color) {
if (color.equals("black")) {
color = "●";
}
if (color.equals("white")) {
color = "○";
}
// 橫向
for (int i = 0; i < board.length - 5; i++) {
if (board[x][i].equals(color) && board[x][i + 1].equals(color) && board[x][i + 2].equals(color)
&& board[x][i + 3].equals(color) && board[x][i + 4].equals(color)) {
return true;
}
}
// 豎向
for (int i = 0; i < board.length - 5; i++) {
if (board[i][y].equals(color) && board[i + 1][y].equals(color) && board[i + 2][y].equals(color)
&& board[i + 3][y].equals(color) && board[i + 4][y].equals(color)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 判斷指定坐標是否有棋子
*/
public static boolean isOk(int x, int y) {
if (!board[x - 1][y - 1].equals("╋")) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 電腦下棋
*/
public static String computer(String color) {
int x = (int) (Math.random() * 14) + 1; // 生成一個1~14之間的亂數
int y = (int) (Math.random() * 14) + 1; // 生成一個1~14之間的亂數
// 判斷電腦下棋的坐標有無棋子,有棋子則在重新生成亂數
if (isOk(x, y)) {
if (color.equals("black")) {
board[x][y] = "●";
} else if (color.equals("white")) {
board[x][y] = "○";
}
} else {
computer(color);
}
return "x,y";
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Gobang gb = new Gobang();
gb.initBoard();
gb.printBoard();
// 這是用於獲取鍵盤輸入的方法
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); // 使用Scanner類獲取使用者輸入
System.out.println("您想要選擇什麼顏色的棋,black或white,請輸入:");
String peopleColor = input.next(); // 定義使用者選擇棋子的顏色並返回使用者輸入的字串
// 如果使用者選擇的是白棋,則電腦先下(五子棋中黑棋先下)
if (peopleColor.equals("white")) {
System.out.println("您選擇的是白棋");
computer("black");
gb.printBoard();
}
String inputStr;
do {
System.out.println("輸入您下棋的坐標,應以x,y的格式:");
inputStr = input.next();
// 定義陣列並賦值坐標x,,y
String[] posStrArr = inputStr.split(",");
int x = Integer.parseInt(posStrArr[0]);
int y = Integer.parseInt(posStrArr[1]);
// 如果輸入坐標已有棋子,則重新輸入坐標
if (!isOk(x, y)) {
System.out.println("此處已有棋子,請換位置!");
continue;
}
// 將上面分隔完以後的字串轉換成使用者下棋的坐標
int xPos = x;
int yPos = y;
// 定義電腦棋子顏色
String comColor = null;
// 根據使用者選擇的棋子顏色給對應的陣列元素賦值
if (peopleColor.equals("black")) {
gb.board[xPos - 1][yPos - 1] = "●";
comColor = "white";
} else if (peopleColor.equals("white")) {
gb.board[xPos - 1][yPos - 1] = "○";
comColor = "black";
}
computer(comColor);
gb.printBoard();
// 判斷輸贏
if (isWin(xPos - 1, yPos - 1, peopleColor)) {
System.out.println(peopleColor + "獲勝!");
break;
}
if (isWin(xPos - 1, yPos - 1, comColor)) {
System.out.println(comColor + "獲勝!");
break;
}
} while (inputStr != null);
}
}
執行上面程式,可以看到如圖 1 所示的介面。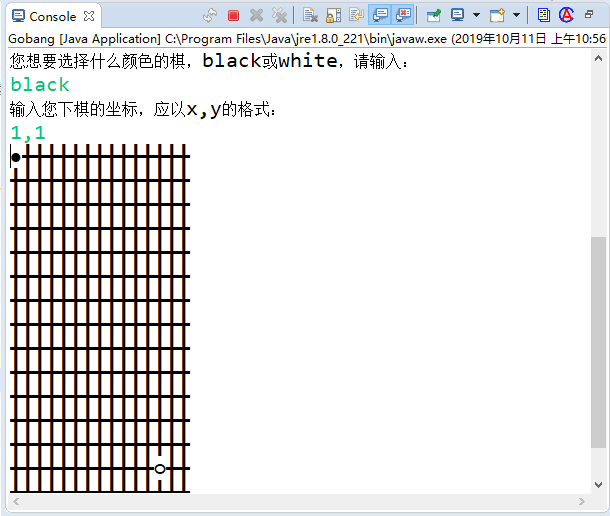
圖 1 五子棋的執行介面