Java 7 HashMap 詳解
HashMap<K, V>
是 AbStractMap 的子類,實現了 Map、Cloneable 和 Serializable(後面有關於 Serializable 的一個問題) 。
public class HashMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, SerializableDEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY(預設初始容量)
常數,值為 16,必須是 2 的冪。
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4;MAXIMUM_CAPACITY(最大容量)
常數,值為 2 的 30 次冪,即使建構函式 public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) 和 public HashMap(int initialCapacity) 的引數 initialCapacity 比 MAXIMUM_CAPACITY 大,域 table 陣列的長度仍為 MAXIMUM_CAPACITY。
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR(預設載入因子)
常數,值為 0.75,除了建構函式 public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor),其它建構函式建立的 HashMap 物件的載入因子都為 DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR。
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;EMPTY_TABLE
常數,值為 Entry<?, ?> 型別的空陣列,當 inflateTable 方法沒有被呼叫時,table 域的初始值為它。為什麼不用 null?Java 8 中用 null。
static final Entry<?,?>[] EMPTY_TABLE = {};table
雜湊表,必要時調整大小,長度必須總是 2 的冪。為什麼長度必須總是 2 的冪?見靜態方法 indexFor(int h, int length)。為什麼 table 等域被修飾符 transient 修飾? Object 類的 hashCode 方法是本地方法,在不同計算機上的返回值可能不同。

transient Entry<K,V>[] table = (Entry<K,V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE;threshold
閾值,如果 table == EMPTY_table,以剛好比 threshold 大於等於的 2 的冪為長度「初始化」 table。
int threshold;loadFactor
載入因子。閾值 = 容量 * 載入因子。
final float loadFactor;modCount
在結構上被修改的次數,結構修改是那些更改對映數或以其他方式修改內部結構(例如,rehash 方法)的次數,此欄位用來使集合檢視上的迭代器 fail-fast(參見 ConcurrentModificationException)。
transient int modCount;ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD_DEFAULT(替代雜湊閾值預設)、Holder、hashSeed
一般情況下,指定虛擬機器器引數 jdk.map.althashing.threshold 開啟替代雜湊。
HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)
使用 initialCapacity 和 loadFactor 構造一個空的 HashMap,先校驗引數,再給 loadFactor 和 threshold 域賦值,最後呼叫 init 方法,在 HashMap 中,init 方法什麼都不做。
在此類外和其他三個建構函式中都被呼叫。
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
threshold = initialCapacity;
init();
}
void init() {
}HashMap(Map m)
用指定的對映構造一個新的 HashMap,它是用預設載入因子建立的,初始容量足夠大,先呼叫建構函式,然後「初始化」 table 域,最後將引數 m 中的鍵值對映放入 table 陣列中。
public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this(Math.max((int) (m.size() / DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR) + 1,
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY), DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
inflateTable(threshold);
putAllForCreate(m);
}inflateTable(int toSize)
「初始化」表。先呼叫 roundUpToPowerOf2 方法獲得剛好比 threshold 大於等於的 2 的冪,然後初始化 threshold 和 table 域。
private void inflateTable(int toSize) {
int capacity = roundUpToPowerOf2(toSize);
// loadFactor 是可以大於 1 的,但是會加劇雜湊衝突,所以保持預設值 0.75 就好
threshold = (int) Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
table = new Entry[capacity];
initHashSeedAsNeeded(capacity);
}
private static int roundUpToPowerOf2(int number) {
// assert number >= 0 : "number must be non-negative";
return number >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY
? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY
: (number > 1) ? Integer.highestOneBit((number - 1) << 1) : 1;
}indexFor(int h, int length)
返回雜湊的位置,長度必須總是 2 的冪,這樣 h & (length - 1) 和 h % length 等價,& 的效率比 % 高。
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
// assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 : "length must be a non-zero power of 2";
return h & (length-1);
}get(Object key)
key 為空時呼叫 getForNullKey(),xxxForNullKey() 都是為了效能,遍歷 table 陣列的 0 位置,遇到 key 為空的對映,返回它的值,否則返回空。在 addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) 中,為空的 key 被放在 table 陣列的 0 位置;不為空時呼叫 getEntry()。
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
Entry<K,V> entry = getEntry(key);
return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue();
}
private V getForNullKey() {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null)
return e.value;
}
return null;
}getEntry(Object key)
返回與引數 key 關聯的 Entry 物件,先獲得 key 的雜湊,為了避免衝突,雜湊函數被設計得很複雜,然後獲得 key 在 table 中的位置,最後遍歷那個位置的所有 Entry 並返回與 key 對應的 Entry。
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
// key 和 e.key 的參照相同(含同時為 null 的情況)
((k = e.key) == key ||
(key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
}
return null;
}
final int hash(Object k) {
int h = hashSeed;
// 如果禁用了替代雜湊且 k 是 String 的範例
if (0 != h && k instanceof String) {
// sun.misc.Hashing 這個類在 JDK 8 中被移除
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
h ^= k.hashCode();
// 此函數確保僅在每個位位置以常數倍數不同的雜湊程式碼具有有限的衝突數(預設載入因子下約為 8)
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}put(K key, V value)
先確保 table 陣列被初始化,key 為空時呼叫 putForNullKey(V value) 將 鍵值對放在 table 陣列的 0 位置,不為空時先獲得 key 的雜湊,然後獲得 key 在 table 中的位置,最後遍歷那個位置的所有 Entry,如果找到與 key 對應的 Entry,覆蓋它的值,如果找不到就呼叫 addEntry 方法在 table 陣列中新增一個 Entry,返回值為被覆蓋的值。
public V put(K key, V value) {
// 如果 table 與 EMPTY_TABLE 共用空表範例(表未初始化時)
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
// 對錶初始化或擴容
inflateTable(threshold);
}
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key);
// 返回雜湊值 h 的索引
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
// key 和 e.key 的參照相同(含同時為 null 的情況)
((k = e.key) == key ||
key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
// 當呼叫 HashMap 中已有的鍵 k 的 put(k,v) 覆蓋條目中的值時,就會呼叫此方法
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}resize(int newCapacity)
如果舊容量為 MAXIMUM_CAPACITY,將閾值賦值為 Integer.MAX_VALUE,返回,防止此方法再次被呼叫。先建立容量為引數 newCapacity 的新 table,然後呼叫 transfer 方法轉移所有的 Entry 從當前 table 到新 table,最後替換 table 和 threhold。
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity));
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
}transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash)
轉移所有的 Entry 從當前 table 到新 table,被多個執行緒呼叫時可能會出現迴圈連結串列,執行緒不安全。
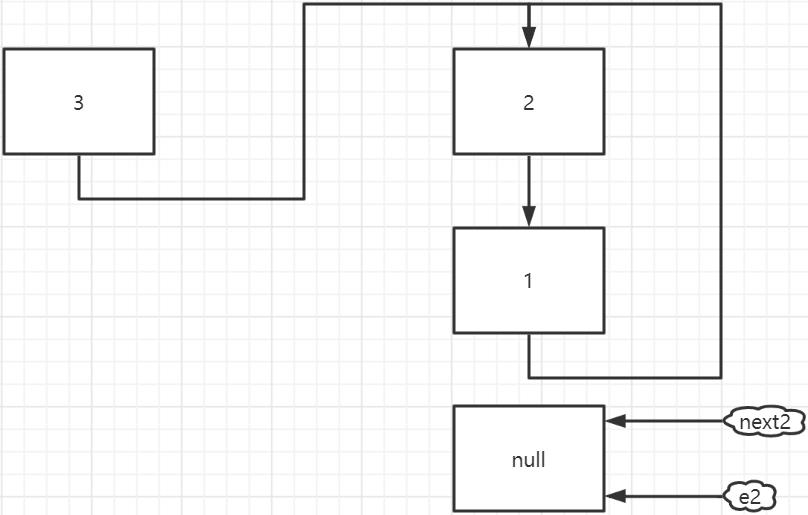
假設 table 中的某個位置如下圖所示(有三個 Entry),thread1 和 thread2 都剛剛執行完 這個位置的第一次 while 迴圈的 Entry next = e.next;
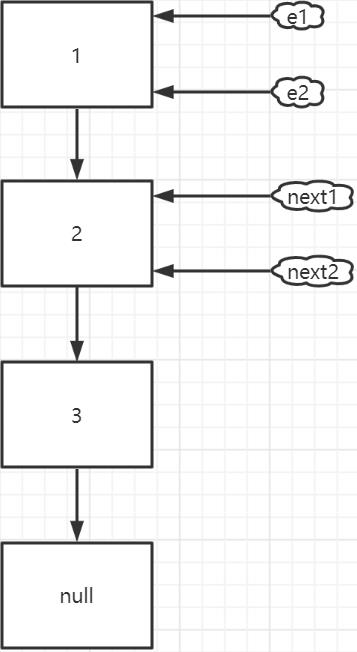
thread1 執行完 while 迴圈
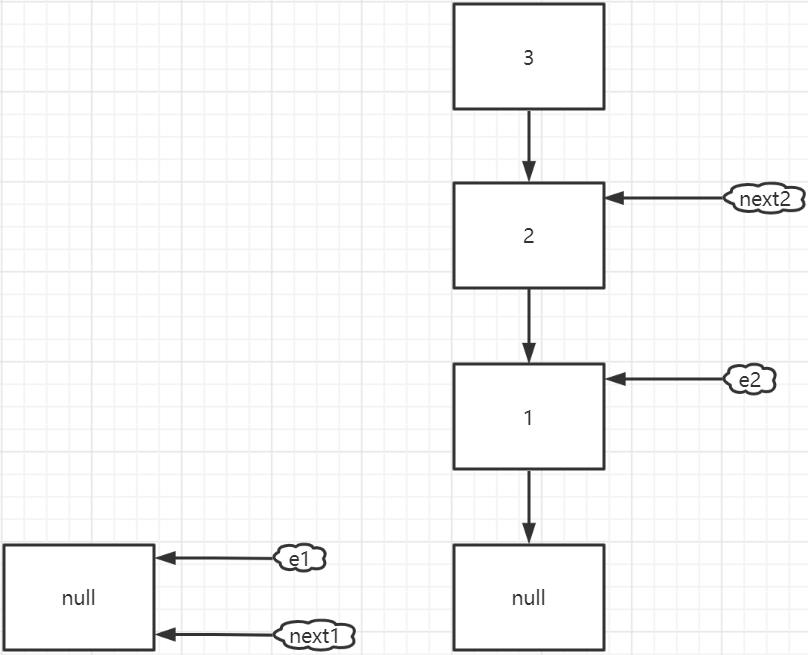
thread2 執行完第一次 while 迴圈
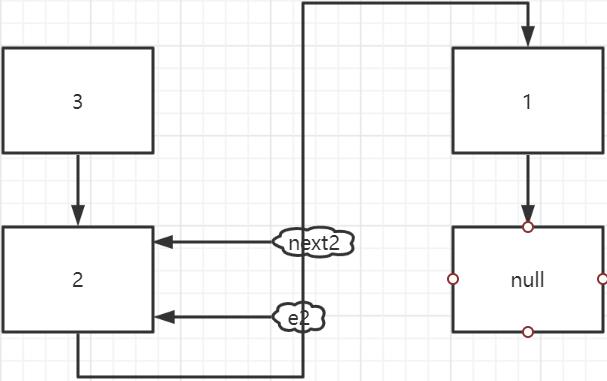
thread2 執行完第二次 while 迴圈
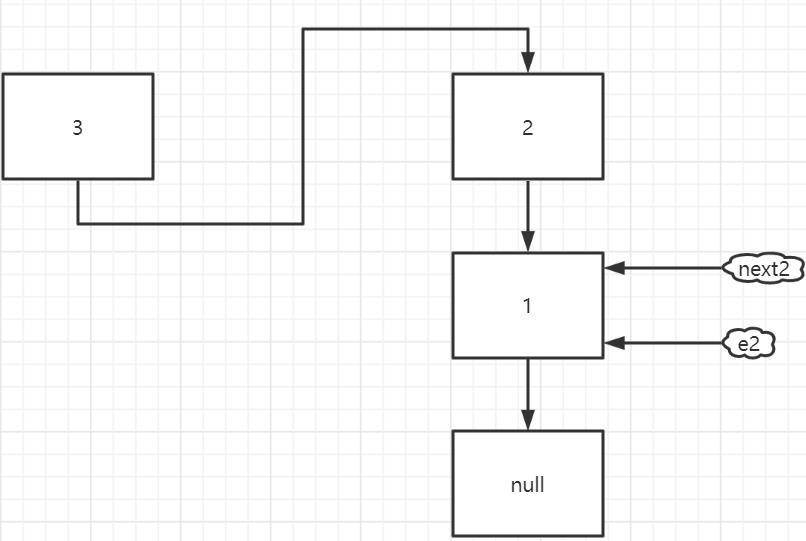
thread2 執行完第三次 while 迴圈
可能出現 CPU 佔用過高的問題,結合 Linux 和 JDK 的命令一起分析:
- top 找出 CPU 佔比最高的程序的 PID
- ps -ef 或 jps 進一步定位這個程序是一個什麼樣的後臺程式
- ps -mp PID -o THREAD, tid, time 找出這個程序中 CPU 佔比最高的執行緒的 TID
- jstack PID | grep TID 的十六進位制的小寫 -A60 定位到具體程式碼行
void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (Entry<K,V> e : table) {
while(null != e) {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
if (rehash) {
e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);
}
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
}
}
}putAll(Map m)
先確保 table 陣列被初始化,然後如果引數 m 中鍵值對映的數量比閾值大,用載入因子計算出目標容量,並調整 table 陣列的大小為剛好大於等於目標容量的 2 的冪,最後呼叫 put 方法將引數 m 中的鍵值對映放入 table 陣列中。
public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
int numKeysToBeAdded = m.size();
if (numKeysToBeAdded == 0)
return;
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable((int) Math.max(numKeysToBeAdded * loadFactor, threshold));
}
/*
* 如果要新增的對映數大於或等於閾值,則展開對映。
* 這是保守的;明顯的條件是(m.size() + size)>= threshold,
* 但是如果要新增的鍵與此對映中已有的鍵重疊,則此條件可能導致具有兩倍於適當容量的對映。
* 通過使用保守的計算方法,我們最多可以對自己進行一次額外的調整。
*/
if (numKeysToBeAdded > threshold) {
int targetCapacity = (int)(numKeysToBeAdded / loadFactor + 1);
if (targetCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
targetCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
int newCapacity = table.length;
while (newCapacity < targetCapacity)
newCapacity <<= 1;
if (newCapacity > table.length)
resize(newCapacity);
}
for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet())
put(e.getKey(), e.getValue());
}clear()
將 table 域中的每個位置賦值為空,size 域賦值為 0,但 modCount 域加 1(結構修改)。
public void clear() {
modCount++;
Arrays.fill(table, null);
size = 0;
}containsValue(Object value)
如果 value 為空,返回 containsNullValue() 的返回值,因為 null 可以直接用 == 比較,物件要用 euqals 方法比較。
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
if (value == null)
return containsNullValue();
Entry[] tab = table;
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length ; i++)
for (Entry e = tab[i] ; e != null ; e = e.next)
if (value.equals(e.value))
return true;
return false;
}
private boolean containsNullValue() {
Entry[] tab = table;
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length ; i++)
for (Entry e = tab[i] ; e != null ; e = e.next)
if (e.value == null)
return true;
return false;
}Entry<K,V>
是 Map.Entry<K, V> 的子類,有 hash、key、value 和 next 四個域。在它的 equals 方法中,如果引數 o 是 Map.Entry 的範例且引數 o 的 key 和 value 域和它的相同,返回 true,否則返回 false。在它的 hashCode() 中,返回值是鍵的雜湊與值的雜湊的互斥或結果。
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
int hash;
/**
* Creates new entry.
*/
Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
}
...
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o;
Object k1 = getKey();
Object k2 = e.getKey();
// k1 和 k2 的參照相同(含同時為 null 的情況)
if (k1 == k2 ||
(k1 != null && k1.equals(k2))) {
Object v1 = getValue();
Object v2 = e.getValue();
if (v1 == v2 || (v1 != null && v1.equals(v2)))
return true;
}
return false;
}
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(getKey()) ^ Objects.hashCode(getValue());
}
...
}void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex)
如果在將鍵值對映放入 table 陣列中之前,鍵值對映的數量大於等於閾值且 table 陣列的對應位置不為空,以當前 table 陣列長度的二倍調整大小,重新計算雜湊和對應位置,呼叫 createEntry 方法從連結串列頭部放入 Entry 物件。
如果不考慮調整大小,用 createEntry 方法代替 addEntry 方法。
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
// 如果此對映中包含的鍵值對映數大於等於閾值且表雜湊索引的位置為空
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
// 先擴容
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
// 頭插法
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}entrySet()
entrySet() 返回 entrySet0() 的返回值。
如果 entrySet 不為空,entrySet0() 返回 entrySet;如果為空,初始化 entrySet 並返回。
entrySet 的預設值為空。
EntrySet 的構造方法繼承自 AbstractSet>,什麼都不做。
hashMap.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.println(key + "=" + value)); 先呼叫 entrySet 的 iterator() 獲得迭代器,iterator() 返回 HashMap 的 newEntryIterator() 的返回值,newEntryIterator() 建立一個 EntryIterator 物件並返回。
然後通過 EntryIterator 物件的 next() 遍歷 entrySet,next() 返回 nextEntry() 的返回值。
nextEntry() 先判斷 modCount 與預期的是否相等和下一個 Entry 是否為空,如果相等且不為空,將下一個 Entry 的 next 域賦值給 EntryIterator 的 next 域並判斷是否為空,如果為空,將 table 陣列中下一個位置的 Entry 賦值給 next 域,返回下一個 Entry。
keySet() 和 values() 同理,最後返回的是 nextEntry.getKey() 的返回值和 nextEntry.value。
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {
return entrySet0();
}
private Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet0() {
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> es = entrySet;
return es != null ? es : (entrySet = new EntrySet());
}
private transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet = null;
private final class EntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {
return newEntryIterator();
}
...
}
public abstract class AbstractSet<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements Set<E> {
...
protected AbstractSet() {
}
...
}
Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> newEntryIterator() {
return new EntryIterator();
}
private final class EntryIterator extends HashIterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public Map.Entry<K,V> next() {
return nextEntry();
}
}
private abstract class HashIterator<E> implements Iterator<E> {
Entry<K,V> next; // next entry to return
int expectedModCount; // For fast-fail
int index; // current slot
Entry<K,V> current; // current entry
HashIterator() {
expectedModCount = modCount;
if (size > 0) { // advance to first entry
Entry[] t = table;
while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null)
;
}
}
public final boolean hasNext() {
return next != null;
}
final Entry<K,V> nextEntry() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
Entry<K,V> e = next;
if (e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
if ((next = e.next) == null) {
Entry[] t = table;
while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null)
;
}
current = e;
return e;
}
...
}