Python while迴圈語句
只要給定條件為真(True),Python程式設計語言中的while迴圈語句將重複執行目標語句。
語法
Python程式設計語言中的while迴圈的語法是 -
while expression:
statement(s)
在這裡,語句(statement(s))可以是一個單一的語句或一組具有統一縮排的語句。條件(expression)可以是任何表示式,True是任何非零值。迴圈在條件為真時執行。
當條件(expression)變為false時,程式控制傳遞到迴圈之後的程式碼行。
在Python中,在程式設計結構之後由相同數量的字元空格縮排的所有語句都被認為是單個程式碼塊的一部分。 Python使用縮排作為對語句進行分組的方法。
流程圖
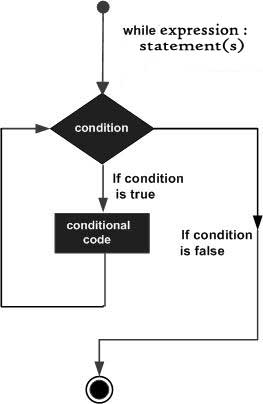
在這裡,while迴圈的一個關鍵點在於迴圈可能不會執行。 當條件被測試並且結果為假時,迴圈體將被跳過,並且while迴圈塊之後的第一個語句將被執行。
範例
#!/usr/bin/python3
count = 0
while (count < 9):
print ('The count is:', count)
count = count + 1
print ("Good bye!")
當執行上述程式碼時,會產生以下結果 -
The count is: 0
The count is: 1
The count is: 2
The count is: 3
The count is: 4
The count is: 5
The count is: 6
The count is: 7
The count is: 8
Good bye!
在上面輸出結果中,列印和增量語句組成的塊將重複執行,直到count大於9時退出。在每次疊代中,列印顯示count的當前值,然後增加1。
無限迴圈
如果條件從不變為FALSE,則迴圈變為無限迴圈。 使用while迴圈時必須謹慎,因為在無法解析為FALSE值的這種情況時,將導致永遠不會結束的迴圈。這樣的迴圈被稱為無限迴圈。
無限迴圈可能在用戶端/伺服器程式設計中有用,伺服器需要連續執行,以便用戶端程式可以在需要時與其進行通訊。
範例
#!/usr/bin/python3
var = 1
while var == 1 : # This constructs an infinite loop
num = int(input("Enter a number :"))
print ("You entered: ", num)
print ("Good bye!")
當執行上述程式碼時,會產生以下結果 -
Enter a number :20
You entered: 20
Enter a number :29
You entered: 29
Enter a number :3
You entered: 3
Enter a number :11
You entered: 11
Enter a number :22
You entered: 22
Enter a number :Traceback (most recent call last):
File "examples\test.py", line 5, in
num = int(input("Enter a number :"))
KeyboardInterrupt
上面的例子進入一個無限迴圈,在執行後需要使用CTRL + C來退出程式。
在迴圈中使用else語句
Python支援與迴圈語句相關聯的else語句。
- 如果
else語句與for迴圈一起使用,則在迴圈遍歷列表時回圈執行else語句。 - 如果
else語句與while迴圈一起使用,則在條件變為false時執行else語句。
以下範例說明了else語句與while語句的組合,該語句在變數 count 小於5時印數位,當count大於5時執行else語句。
#!/usr/bin/python3
count = 0
while count < 5:
print (count, " is less than 5")
count = count + 1
else:
print (count, " is not less than 5")
當執行上述程式碼時,會產生以下結果 -
0 is less than 5
1 is less than 5
2 is less than 5
3 is less than 5
4 is less than 5
5 is not less than 5
單個語句套件
類似於if語句的語法,如果while子句只包含一個語句,那麼它可能被放在與while頭相同的行上。
範例
以下是一行while子句的語法和範例 -
#!/usr/bin/python3
flag = 1
while (flag): print ('Given flag is really true!')
print ("Good bye!")
上述範例進入無限迴圈,需要按CTRL + C鍵退出。