R語言if..else語句
2019-10-16 23:03:14
一個if語句可以跟隨一個可選的else語句,當布林表示式為false時執行else語句中的語句塊程式碼。
語法
在R語言中建立if..else語句的基本語法是 -
if(boolean_expression) {
// statement(s) will execute if the boolean expression is true.
} else {
// statement(s) will execute if the boolean expression is false.
}
如果布林表示式求值為真(true),那麼將執行if語句中的程式碼塊,否則將執行else語句中的程式碼塊。
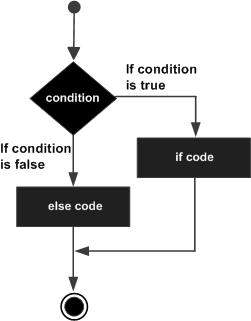
if...else語句的流程圖如下 -
範例
x <- c("what","is","truth")
if("Truth" %in% x) {
print("Truth is found")
} else {
print("Truth is not found")
}
當上述程式碼被編譯和執行時,它產生以下結果 -
[1] "Truth is not found"
註:這裡 「Truth」 和 「truth」 是兩個不同的字串。
if…else if…else語句
一個if語句可以跟隨一個可選的else if...else語句,這對使用單個if...else else語句來測試各種條件非常有用。
當使用if,else if, else語句時要注意幾點。
if語句可以有零個或一個else,但如果有else if語句,那麼else語句必須在else if語句之後。if語句可以有零或多else if語句,else if語句必須放在else語句之前。- 當有一個
else if條件測試成功,其餘的else...if或else將不會被測試。
語法
在R中建立if...else if...else語句的基本語法是 -
if(boolean_expression 1) {
// Executes when the boolean expression 1 is true.
} else if( boolean_expression 2) {
// Executes when the boolean expression 2 is true.
} else if( boolean_expression 3) {
// Executes when the boolean expression 3 is true.
} else {
// executes when none of the above condition is true.
}
範例程式碼
x <- c("what","is","truth")
if("Truth" %in% x) {
print("Truth is found the first time")
} else if ("truth" %in% x) {
print("truth is found the second time")
} else {
print("No truth found")
}
執行上面範例程式碼,得到以下結果 -
[1] "truth is found the second time"