刪除單連結串列最後一個節點
2019-10-16 22:03:24
從連結串列的末尾刪除節點,有兩種情況。
- 連結串列中只有一個節點,需要刪除。
- 連結串列中有多個節點,連結串列的最後一個節點將被刪除。
1. 連結串列中只有一個節點
條件head → next = NULL將繼續存在,因此,連結串列的唯一節點head將被指定為null。 這將通過使用以下語句來完成。
ptr = head;
head = NULL;
free(ptr);
2. 連結串列中有多個節點
條件head→next = NULL將失敗,因此,必須遍歷節點才能到達連結串列的最後一個節點。
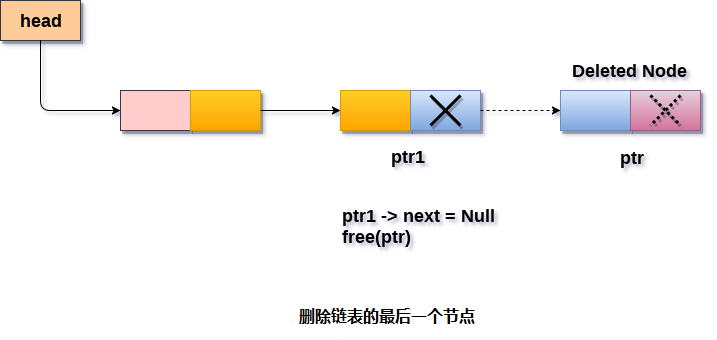
為此,只需宣告一個臨時指標temp並將其指定給連結串列的頭部。還需要跟蹤連結串列的倒數第二個節點。所以使用兩個指標ptr和ptr1,其中ptr將指向最後一個節點,ptr1將指向連結串列的倒數第二個節點。通過使用以下語句來完成。
ptr = head;
while(ptr->next != NULL)
{
ptr1 = ptr;
ptr = ptr ->next;
}
現在,只需要使指標ptr1指向下一個節點為NULL,並且ptr將變釋放。它將通過使用以下語句來完成。
ptr1->next = NULL;
free(ptr);
演算法
第1步:IF HEAD = NULL
列印記憶體溢位。
轉到第8步
[結束]
第2步:設定PTR = HEAD
第3步:重複第4步和第5步,同時PTR - > NEXT!= NULL
第4步:SET PREPTR = PTR
第5步:SET PTR = PTR - > NEXT
[迴圈結束]
第6步:SET PREPTR - > NEXT = NULL
第7步:釋放PTR
第8步:退出
示意圖 -
C語言範例程式碼 -
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
void create(int);
void end_delete();
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head;
void main()
{
int choice, item;
do
{
printf("1.Append List\n");
printf("2.Delete node\n");
printf("3.Exit\n");
printf("4.Enter your choice ? ");
scanf("%d", &choice);
switch (choice)
{
case 1:
printf("\nEnter the item\n");
scanf("%d", &item);
create(item);
break;
case 2:
end_delete();
break;
case 3:
exit(0);
break;
default:
printf("\nPlease enter valid choice\n");
}
} while (choice != 3);
}
void create(int item)
{
struct node *ptr = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node *));
if (ptr == NULL)
{
printf("\nOVERFLOW\n");
}
else
{
ptr->data = item;
ptr->next = head;
head = ptr;
printf("\nNode inserted\n");
}
}
void end_delete()
{
struct node *ptr, *ptr1;
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("\nlist is empty");
}
else if (head->next == NULL)
{
head = NULL;
free(head);
printf("\nOnly node of the list deleted ...");
}
else
{
ptr = head;
while (ptr->next != NULL)
{
ptr1 = ptr;
ptr = ptr->next;
}
ptr1->next = NULL;
free(ptr);
printf("\n Deleted Node from the last ...");
}
}
執行上面範例程式碼,得到以下結果 -
1.Append List
2.Delete node
3.Exit
4.Enter your choice?1
Enter the item
12
Node inserted
1.Append List
2.Delete node
3.Exit
4.Enter your choice?2
Only node of the list deleted ...