RGB源數據操作:圖片順時針90°旋轉
2020-08-13 14:15:41
一、執行環境介紹
Linux系統: Redhat6.3 (32位元)
gcc 版本 4.4.6 20120305 (Red Hat 4.4.6-4) (GCC)
二、功能介紹
開啓一張BMP圖片,實現順時針90°旋轉後生成一張新的圖片。
三、核心程式碼
可以傳入任意尺寸的BMP圖片進行生成旋轉。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#pragma pack(1) //強制1個位元組對齊
//BMP的檔案頭
struct _BMP_HEAD
{
char type[2]; //圖片的型別 "BM"
unsigned int size; //檔案大小
unsigned short r1; //保留1
unsigned short r2; //保留2
unsigned int seek; //數據偏移位元組(真實畫素點數據)
};
//BMP的參數資訊
struct _BMP_INFO
{
unsigned int size; //當前結構體大小
unsigned int w; //寬度
unsigned int h; //高度
unsigned short flag; //固定爲1
unsigned short bit; //畫素點的位數
unsigned int r1; //壓縮方式 0
unsigned int r2; //水平解析度
unsigned int r3; //垂直解析度
unsigned int r4; //垂直解析度
unsigned int r5; //參照色彩
unsigned int r6; //關鍵色彩
};
int main(int argc,char **argv)
{
int cnt;
if(argc!=3)
{
printf("傳入的參數格式: ./a.out <原圖片的名稱> <新圖片的名稱>\n");
return 0;
}
/*1. 開啓原圖片*/
FILE *src_fp=fopen(argv[1],"rb");
if(src_fp==NULL)
{
printf("%s 圖片開啓失敗.\n",argv[1]);
return 0;
}
/*2. 讀取圖片的頭資訊*/
struct _BMP_HEAD src_bmp_head;
cnt=fread(&src_bmp_head,1,sizeof(struct _BMP_HEAD),src_fp);
printf("原圖片頭讀取%d位元組.\n",cnt);
printf("原圖片型別:%c%c.\n",src_bmp_head.type[0],src_bmp_head.type[1]);
printf("原檔案大小:%d.\n",src_bmp_head.size);
printf("原檔案的數據偏移量:%d.\n",src_bmp_head.seek);
/*3. 讀取圖片的參數資訊*/
struct _BMP_INFO src_bmp_info;
cnt=fread(&src_bmp_info,1,sizeof(struct _BMP_INFO),src_fp);
printf("原圖片參數結構讀取%d位元組.\n",cnt);
printf("原圖片寬:%d\n",src_bmp_info.w);
printf("原圖片高:%d\n",src_bmp_info.h);
printf("原圖片畫素位:%d\n",src_bmp_info.bit);
/*4. 建立一張新的BMP圖片*/
FILE *new_fp=fopen(argv[2],"wb");
if(new_fp==NULL)
{
printf("%s 檔案建立失敗.\n",argv[2]);
return 0;
}
/*5. 建立BMP的檔案頭*/
struct _BMP_HEAD new_bmp_head;
memset(&new_bmp_head,0,sizeof(struct _BMP_HEAD));
//圖片的型別
new_bmp_head.type[0]='B';
new_bmp_head.type[1]='M';
//檔案大小
new_bmp_head.size=54+src_bmp_info.w*src_bmp_info.h*3;
//數據偏移量
new_bmp_head.seek=54;
//寫檔案頭
cnt=fwrite(&new_bmp_head,1,sizeof(struct _BMP_HEAD),new_fp);
printf("新圖片頭成功寫入:%d 位元組.\n",cnt);
/*6. 寫檔案參數資訊*/
struct _BMP_INFO new_bmp_info;
memset(&new_bmp_info,0,sizeof(struct _BMP_INFO));
//當前結構體大小
new_bmp_info.size=sizeof(struct _BMP_INFO);
//圖片的寬度和高度
new_bmp_info.w=src_bmp_info.h;
new_bmp_info.h=src_bmp_info.w;
//圖片的顏色位數
new_bmp_info.bit=24;
//標誌位
new_bmp_info.flag=1;
//寫入檔案參數資訊
cnt=fwrite(&new_bmp_info,1,sizeof(struct _BMP_INFO),new_fp);
printf("新圖片的參數結構成功寫入:%d 位元組.\n",cnt);
//計算原圖片寬度是否是4的倍數
int one_line_byte=src_bmp_info.w*3;
while(one_line_byte%4!=0)one_line_byte++;
int val_byte=one_line_byte-src_bmp_info.w*3; //相差的位元組數
printf("原圖片的寬度補齊%d位元組.\n",val_byte);
//計算新圖片寬度是否是4的倍數
int new_one_line_byte=new_bmp_info.w*3;
while(new_one_line_byte%4!=0)new_one_line_byte++;
int new_val_byte=new_one_line_byte-new_bmp_info.w*3; //相差的位元組數
printf("新圖片的寬度補齊%d位元組.\n",new_val_byte);
/*7. 寫入點陣圖數據*/
int w,h;
int seek=0;
int c=0;
for(w=0;w<src_bmp_info.w;w++)
{
for(h=src_bmp_info.h;h>0;h--)
{
seek=h*one_line_byte+54-one_line_byte+w*3;
//從頭開始偏移
fseek(src_fp,seek,SEEK_SET);
fread(&c,1,3,src_fp); //讀取圖片數據
fwrite(&c,1,3,new_fp); //寫數據
}
if(new_val_byte)fwrite(&c,1,new_val_byte,new_fp); //如果需要補齊,就寫補齊數據
}
/*8. 關閉檔案*/
fclose(new_fp);
fclose(src_fp);
return 0;
}
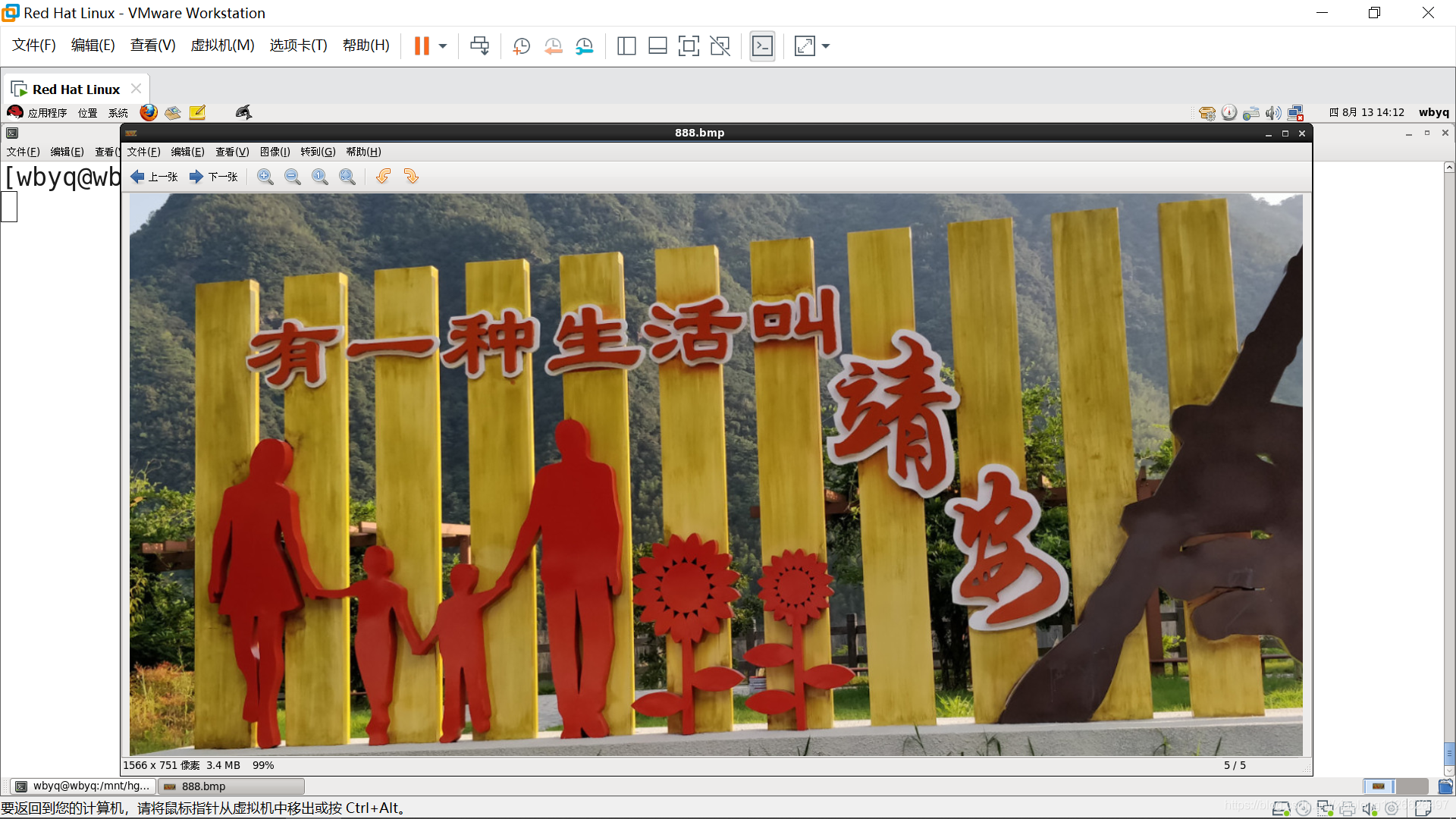
四、執行效果
原圖片:
旋轉之後的圖片:

下面 下麪公衆號有全套的微控制器、QT、C++、C語言、物聯網相關的教學,歡迎關注: