拓撲排序(C語言)
2020-08-13 10:31:10
拓撲排序使用的是廣度優先遍歷
要求:圖中沒有環
給定一個圖 選出一個沒有入度的點 作爲起始點 之後 將這個點從圖中刪除 並且以該點爲入度的點要-1
[圖片選自數據結構與演算法分析© P229 圖9-4]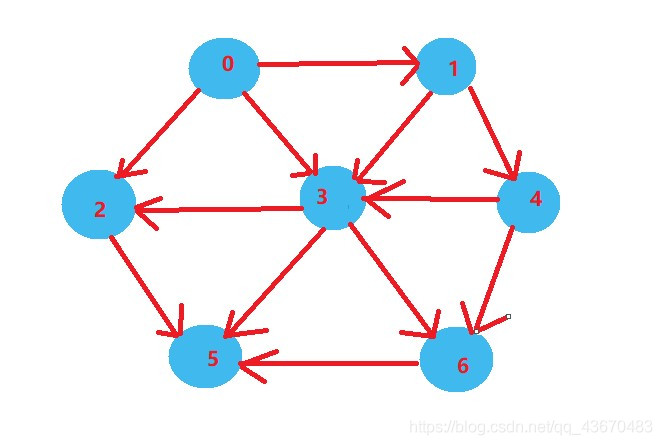
如上圖 第一次存取0點 並且將0點從圖中刪除 並且將與之相鄰的點的入度減1 如果存在入度爲0的點 則選擇 那麼這裏能夠選擇的點是 1 依次類推 直到選擇完 如果無法選擇點 那麼圖中就存在環 就無法使用拓撲排序
使用的鄰接表+佇列
首先定義出鄰接表和佇列的結構
#define MAX 10
#define WHITE 0 // 未存取
#define BLACK 1 // 已經存取
typedef int bool;
// 鄰接表實現對有向圖的儲存
typedef struct Node Node;
typedef struct Node* Vertex;
typedef struct Node* adjustlist;
struct Node {
int visit; // 用來標記是否存取
int item; // item用來記錄標號
int indegree; // 入度
int outdegree; // 出度
struct Node* next; // 指向下一個節點
};
typedef struct queue queue;
typedef struct queue* pqueue;
typedef pqueue* ppqueue; // 指向佇列節點的指針
struct queue
{
adjustlist vertex; //指向 鄰接表的節點的指針
struct queue* next; // 指向佇列的下一個元素
};
上面寫出了的WHITE 和BLACK 是後續廣度優先遍歷的時候 用來記錄點是否已經存取 防止多次存取
生成鄰接鏈表和初始化賦值鄰接表
// 生成一個鄰接表
static adjustlist createadjustlist(int vertex)
{
// vertex 是圖的頂點
// 假定 圖的頂點都是從0開始到vertex
adjustlist ad = (adjustlist)malloc(sizeof(Node) * vertex);
if (ad == NULL)
{
printf(" Out of space\n");
return NULL;
}
// 順便初始化
for (int i = 0; i < vertex; i++)
{
ad[i].visit = ad[i].item = ad[i].indegree = ad[i].outdegree = 0;
ad[i].next = NULL;
}
return ad;
}
static void initialadjustlist(adjustlist ad, int vertex)
{
for (int i = 0; i < vertex; i++)
{ // 圖頂點從0開始
int k, v, u; // v 用來確定出度 u用來確定入度 k表示標號
scanf("%d %d %d", &k, &v, &u); // 確定每一個點的出度 出度表明這個頂點到那幾個點
ad[k].item = k;
ad[k].indegree = u; // 入度
ad[k].outdegree = v; // 出度
for (int j = 0; j < v; j++)
{
adjustlist V = (adjustlist)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (V == NULL)
{
printf("Out of space\n");
return;
}
scanf("%d", &V->item); // 確定後續得節點是什麼
// 使用頭插法
V->next = ad[k].next;
ad[k].next = V;
}
}
}
關於後續節點的儲存 我使用的是新生成一個鄰接節點 然後儲存 實際上由於是數位節點 可以在鄰接節點中使用 int陣列或者指針 實現儲存 這個大家可以去實現一下
佇列的建立
static pqueue createqueue()
{
// 構造一個佇列 實際上就是一個鏈表 所以並不需要大小
// 但是 使用頭結點 第一個節點用於空出來
pqueue Q = (pqueue)malloc(sizeof(queue));
if (Q == NULL)
{
printf(" Out of space\n");
return NULL;
}
Q->next = NULL;
Q->vertex = NULL;
return Q;
}
佇列的方法 加入 刪除 釋放
static pqueue Enqueue(adjustlist V, pqueue tail)
{ // tail 指向生成的佇列Q的末尾
pqueue q = createqueue();
q->vertex = V;
tail->next = q;
tail = tail->next;
return tail;
}
static adjustlist dequeue(pqueue head, ppqueue tail)
{
// 也要變換tail指針內容
pqueue q = head->next; // head是頭結點 實際上是無法儲存數據 也就是從head.next開始儲存數據
head->next = head->next->next;
if (q == *tail)
{ // 說明 佇列中只有一個元素 並且要刪除它
*tail = head; // 將其指向 head
}
adjustlist ad = q->vertex;
free(q);
return ad;
}
static bool IsEmpty(pqueue head)
{ // 判斷佇列是否爲空
return head->next == NULL;
}
static void freequeue(pqueue Q)
{
pqueue head = Q;
pqueue p;
while (head->next != NULL)
{
p = Q->next;
head->next = Q->next->next;
free(p);
}
free(head);
}
拓撲排序和展示
static int path[MAX] = { 0 };
static void Topsort(adjustlist ad, int vertex)
{
pqueue Q = createqueue(); // 建立的一個佇列
pqueue head = Q;
pqueue tail = head;
for (int i = 0; i < vertex; i++)
if (ad[i].indegree == 0)
{
tail = Enqueue(&ad[i], tail);
// 此時將加入的點標記成存取狀態
ad[i].visit = BLACK;
}
int counter = 0;
while (!IsEmpty(Q))
{
adjustlist V = dequeue(Q, &tail);
path[V->item] = ++counter; // 記錄下路徑的存取順序
adjustlist tmp = V;
for (int i = 0; i < V->outdegree; i++) // 遍歷出度 表示有多少的後繼
{
int t = tmp->next->item; // 選取第一個
adjustlist T = &(ad[t]); // 固定下標從0開始 所以 item也就是剛好在ad陣列的相應位置上
if (T->visit == BLACK)
continue;
T->indegree--;
if (T->indegree == 0)
tail = Enqueue(&ad[t], tail); // 如果T的入度爲0 則加入佇列中
tmp = tmp->next;
}
}
if (counter != vertex)
{
printf(" Graph have a cirecle\n");
return;
}
//銷燬佇列
freequeue(Q);
}
static void showpath(int vertex)
{
for (int i = 0; i < vertex; i++)
{
printf("%d\t", path[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
static void showgraph(adjustlist ad, int vertex)
{
for (int i = 0; i < vertex; i++)
{
printf("頂點%d\t", ad[i].item);
adjustlist T = ad[i].next;
for (int j = 0; j < ad[i].outdegree; j++)
{
printf("後繼是%d\t", T->item);
T = T->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
主方法
void main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
adjustlist ad = createadjustlist(MAX); // MAX 給定的最大範圍
initialadjustlist(ad, n);
showgraph(ad, n);
Topsort(ad, n);
showpath(n);
}
結果
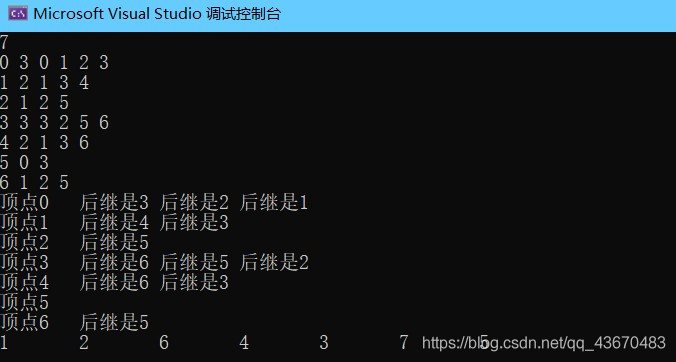
輸入
7
0 3 0 1 2 3
1 2 1 3 4
2 1 2 5
3 3 3 2 5 6
4 2 1 3 6
5 0 3
6 1 2 5
(有錯誤請在下方指出,輕噴)