Linux系統學習——shell程式設計入門篇學習
2020-08-12 16:35:38
Linux 系統學習——shell程式設計入門學習
一、介紹:
1. shell是一個作爲使用者和linux系統間介面的程式,允許使用者向操作系統輸入需要執行的命令
2、執行指令碼:
1、./檔名
2、sh 檔名
3、#source 檔名
3、在shell上 # 爲註釋
4、每個shell程式需要寫在 #!/bin/sh 開始 ,相當於標頭檔案 ,這是對shell宣告
簡單書寫 :
#!/bin/sh //必須要帶上這個 shell 宣告
A="hello" // 這裏不能 A = "hello" , 帶有空格的話會識別錯誤
echo "A is"
echo $A
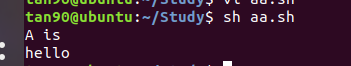
注意:shell 在解釋命令時的原則是第一個符號標記只能是程式或者命令,有空格的時候第一個符號標記就是「A」,當然就不成立了,而沒有空格的時候,第一個標記是A=「hello world」 ,shell 將解釋爲變數賦值指令,因此可以通過。
5、 檔案結束後綴:
Linux :\n 爲回車換行
windows : \r\n 爲回車換行
二、重定向 > 或 >> 解析:
以 ll > aa 爲例子
> 作用是 把 ll 內容寫進 aa檔案裡頭,但是裡頭原來的檔案內容會被刪除掉
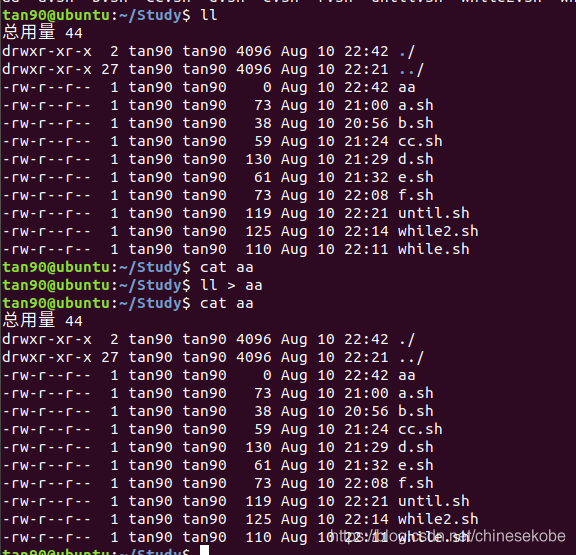
>> 作用是把 ll 內容寫進 aa檔案裡頭,但是裡頭原來的檔案內容不會被刪除掉,重新另外換行新增內容
管道 :|
ll | grep "s" // 通過管道 | ,檢視 ll 下 含有 s 的內容
三、環境變數、系統變數 :
環境變數:

系統變數:

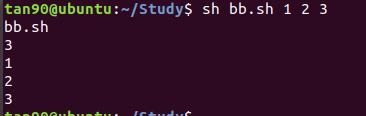
演示bb.sh:
#!/bin/sh
echo $0
echo $#
echo $1
echo $2
echo $3
四、shell 常用Linux 指令 :
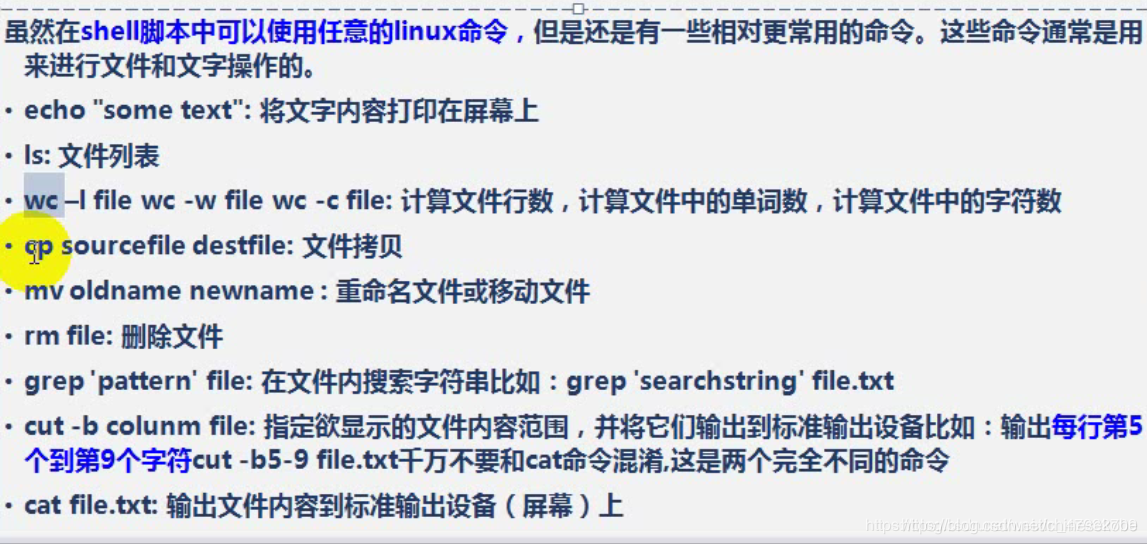
以 mv 爲例子 :
鍵盤輸入功能實現 (read):
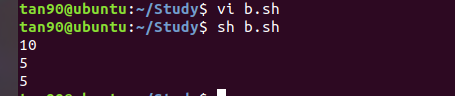
#!/bin/sh
A=10
echo $A // 先列印 A =10 值
read A //從鍵盤讀入數據
echo $A
結果 :
五、語法結構
(1)條件判斷:
if else
使用模式一:
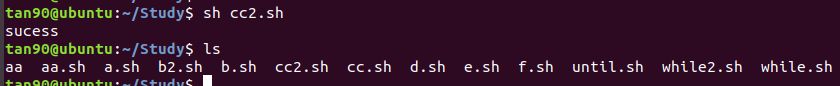
#!/bin/sh
if test -f a.sh #如果成立就執行then
then #一定要加
echo "sucess"
else
echo "failed"
fi #一定要加結束符號
常用這種:
#!/bin/sh
if [ -f a.sh ] // 格式 [ ] 左右兩邊都要一個空格
then
echo "yes"
else
echo "no"
fi
注意:
使用[ ]時,必須要在 [符號和被檢查的條件之間留出空格,可以把符號看作和test樣,test和後面的條件之間總是有一個空格。
程式碼最後不要忘了寫 fi 來結束這個判斷


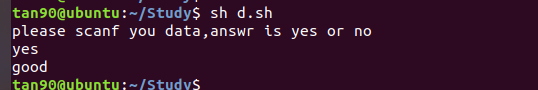
#!/bin/sh
echo "please scanf you data,answr is yes or no"
read data
if [ $data = "yes" ]
then
echo "good"
else
echo "Fuck"
fi
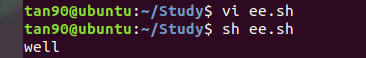
多重條件 如c語言中的 if () else if () else :
#!/bin/sh
if [ 10 -lt 2 ] //如果 10 小於 2 ,纔列印 good
then
echo "good"
elif [ 10 -gt 5 ] // 如果 10 大於5 ,列印 well
then
echo "well"
else
echo "NO"
fi

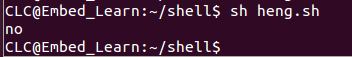
#!/bin/sh
if [ 3 -eq 4 ]
then
echo "yes"
else
echo "no"
fi
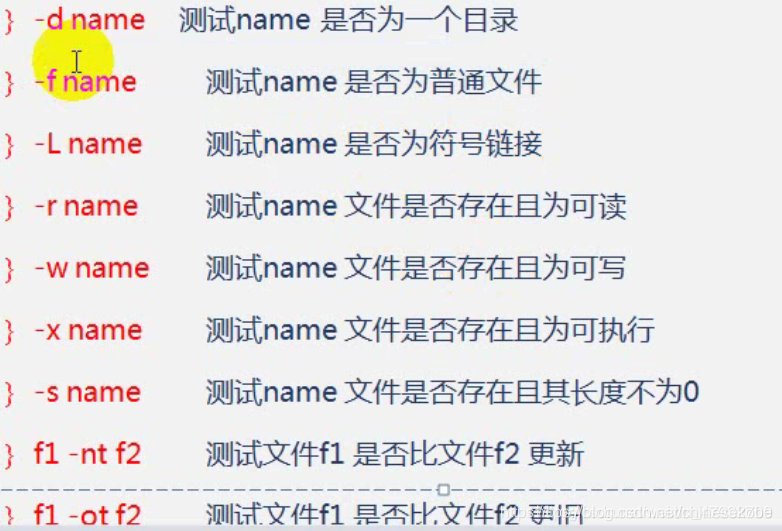
#!/bin/sh
if [ -d b.txt ]
then
echo "yes"
else
echo "no"
fi
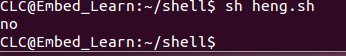
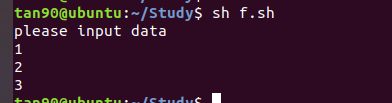
(2)回圈判斷:
1、for回圈 :

#!/bin/sh
echo "please input data"
for data in 1 2 3
do
echo $data
done
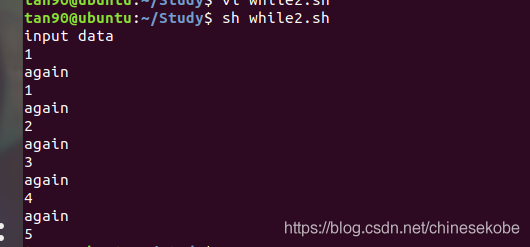
2、while回圈
#!/bin/sh
echo "input data"
#data=1
read data //從鍵盤輸入data
while [ $data != 6 ] // 從鍵盤 輸入data ,判斷data 是否不等於 6
do
echo "again"
echo $data
data=$(($data+1)) // data 依次相加 ,類似於C 語言中 data++
done //回圈必帶 結束符
exit 0
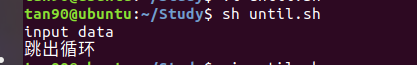
3、until :當滿足回圈條件的時候,直接跳出回圈。而 while 回圈是滿足回圈條件,繼續執行回圈條件裏面的語句
#!/bin/sh
echo "input data"
data=5
until [ $data -le 6 ]
do
echo $data
data=$(($data+1))
done
echo "跳出回圈"
exit 0
跳出回圈,沒有執行回圈裏面列印 data的值
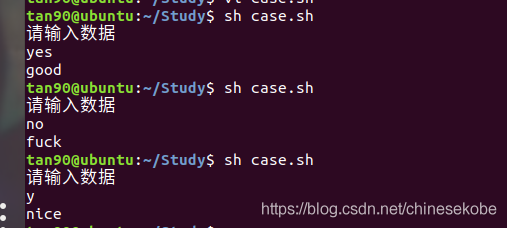
(3)選擇語句(相當於c語言swich):

#!/bin/sh
echo "請輸入數據"
read data
case "$data" in
yes) echo "good";; #注意一定要兩個 ;; 結尾
y) echo "nice";;
no) echo "fuck";;
n) echo "shift";;
esac # 選擇語句必帶
exit 0
注意每個模式都以 雙分號 ;; 結尾,因爲你可以在前後模式之間放置多條語句,所以需要使用一個雙分號來標記前一個語句的結束和後一個語句的開始
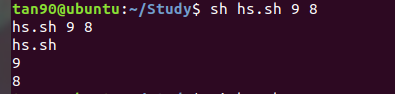
(4)函數( 直接函數名字+() 來使用 )

#!/bin/sh
foo() // 函數名字 + ()
{
echo $0 # 列印檔案名字
echo $1 # 列印第一個參數
echo $2 # 列印第二個參數
}
echo $0 $1 $2
foo $1 $2 # 這裏要給foo 函數 傳參數 纔會列印 $1 、$2
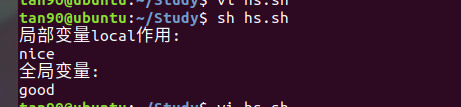
- 如果要在shell函數中宣告區域性變數,則要使用local關鍵字,區域性變數的作用域則侷限在函數範圍內。
- 此外,函數還可存取全域性作用範圍內的其他shell變數。如果全域性變數和區域性變數出現了同名,則區域性變數會覆蓋全
例子:
#!/bin/sh
A="good"
foo()
{
local A="nice"
echo $A
}
echo "區域性變數local作用:"
foo
echo "全域性變數:"
echo $A
exit 0
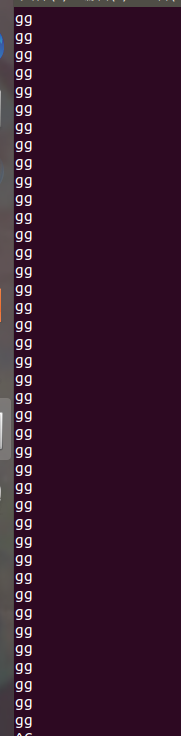
(5)無限回圈 指令 冒號 (:)
冒號(:)是一個空命令,它偶爾會被用於邏輯簡化,相當於true的一個別名,由於它是內建命令,所以它的執行效率要比true高
while : 相當於while true
#!/bin/sh
fun()
{
while :
do
echo "gg"
done
}
fun
exit 0
(6)break 跳出回圈
#!/bin/sh
A=10
B=15
while [ $A -ne $B ]
do
A=$(($A+1))
if [ $A -eq "12" ] # 當 A = 12時 跳出回圈
then
echo "good"
break; # 這個 ; 可加可不加
fi
done
exit 0
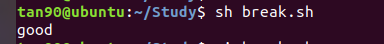
(7)函數返回值 return (在shell指令碼,0表示返回成功,相當於 c語言的 1)
#!/bin/sh
yes_or_no()
{
echo "is your name $*?"
while true
do
echo "please enter yes or no"
read a
case "$a" in
y|yes) return 0;; # 在shell指令碼,0表示返回成功,相當於 c語言的 1
n|no) return 1;;
* ) echo "error"
esac
done
}
echo "original parameters are $*"
if yes_or_no "$A" # shell指令碼程式設計中,注意:Linux中返回0表示成功
then # $A 用一個變數 A 來存放返回值,用其他字元也可以
echo "hi"
else
echo "never mind"
fi
exit 0
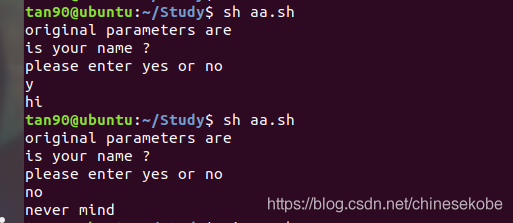
(8)continue命令(和c語言功能差不多):
#!/bin/sh
rm -rf fred*
echo > fred1
echo > fred2
mkdir fred3
echo > fred4
for file in fred*
do
if [ -d "$file" ]
then
echo skipping the directory $file
continue
fi
done
echo first direcyory starting fred was $file
rm -rf fred*
(9)exec命令:
將當前的shell替換爲一一個不同的程式
exec wall"hello world"
將當前的shell替換爲執行wall,exec後面的語句都不會執行了,因爲當前的shell已經不復存在了
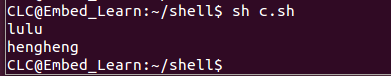
程式碼演示 :
#!/bin/sh
echo "lulu"
exec echo "hengheng"
echo "aa"
echo "bb"