小白也能看懂的 AUC 詳解
簡介
上篇文章 小白也能看懂的 ROC 曲線詳解 介紹了 ROC 曲線。本文介紹 AUC。AUC 的全名為Area Under the ROC Curve,即 ROC 曲線下的面積,最大為 1。
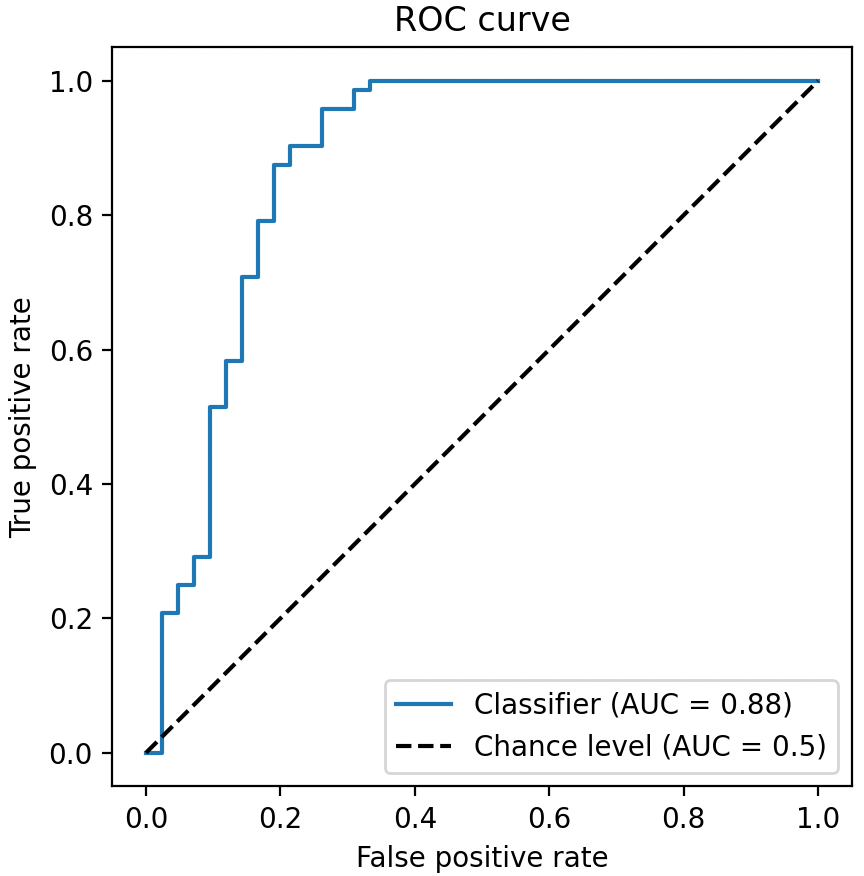
根據 ROC 和 AUC 的關係,我們可以得到如下結論
- ROC 曲線接近左上角 ---> AUC 接近 1:模型預測準確率很高
- ROC 曲線略高於基準線 ---> AUC 略大於 0.5:模型預測準確率一般
- ROC 低於基準線 ---> AUC 小於 0.5:模型未達到最低標準,無法使用
二分類 AUC
由 AUC 名稱可知,可以先計算 ROC 曲線,得到 TPR 和 FPR 的座標後再分段計算面積即可得到 AUC
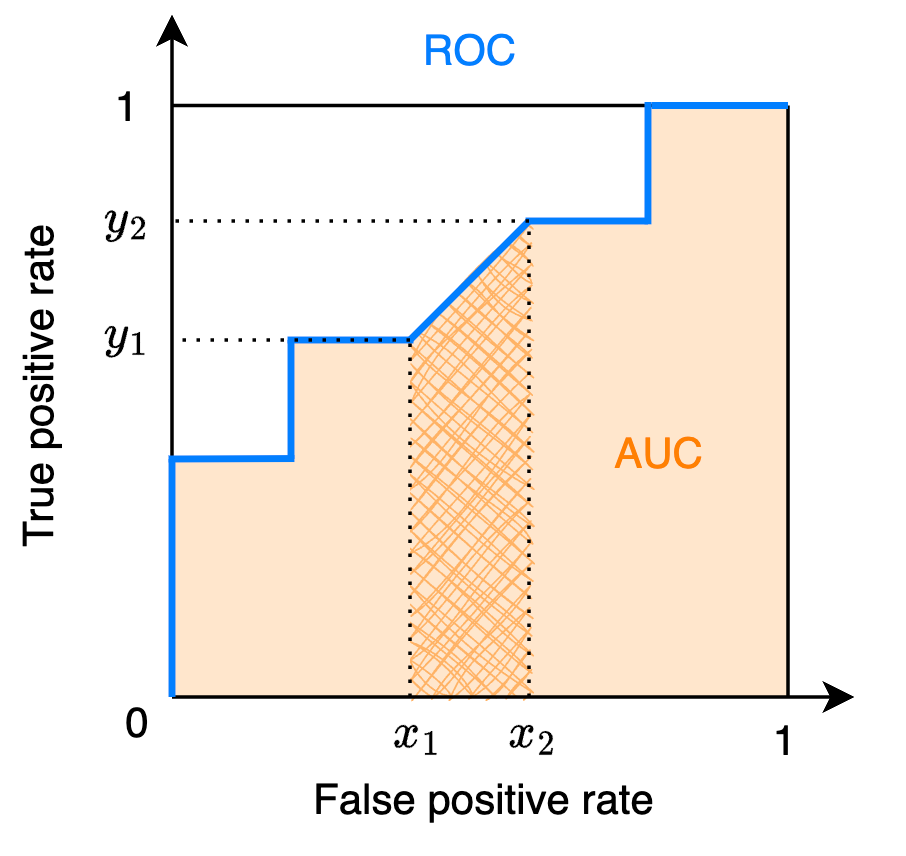
下面是對應的 Python 程式碼
def auc_from_roc(fpr, tpr):
"""
計算ROC面積
fpr: 從小到大排序的fpr座標
tpr: 從小到大排序的tpr座標
"""
area = 0
for i in range(len(fpr) - 1):
area += trapezoid_area(fpr[i], fpr[i + 1], tpr[i], tpr[i + 1])
return area
def trapezoid_area(x1, x2, y1, y2):
"""
計算梯形面積
x1, x2: 橫座標 (x1 <= x2)
y1, y2: 縱座標 (y1 <= y2)
"""
base = x2 - x1
height_avg = (y1 + y2) / 2
return base * height_avg
也可以直接從真實標籤和模型預測分數中計算 ROC,演演算法的時間複雜度為\(O(n\log n)\),參考文獻 1 中的演演算法 2
# import numpy as np
def auc_binary(y_true, y_score, pos_label):
"""
y_true:真實標籤
y_score:模型預測分數
pos_label:正樣本標籤,如「1」
"""
num_positive_examples = (y_true == pos_label).sum()
num_negtive_examples = len(y_true) - num_positive_examples
tp, fp, tp_prev, fp_prev, area = 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
score = -np.inf
for i in np.flip(np.argsort(y_score)):
if y_score[i] != score:
area += trapezoid_area(fp_prev, fp, tp_prev, tp)
score = y_score[i]
fp_prev = fp
tp_prev = tp
if y_true[i] == pos_label:
tp += 1
else:
fp += 1
area += trapezoid_area(fp_prev, fp, tp_prev, tp)
area /= num_positive_examples * num_negtive_examples
return area
多分類 AUC
現在考慮多分類的情況,假設類別數為\(C\)。
一種想法是將某一類別設為正樣本類別,其餘類別設為負樣本類別,然後計算二分類下的 AUC。這種方法叫做一對多,即 One-Vs-Rest (OVR)。可以得到\(C\)個二分類的 AUC,然後計算平均數得到多分類的 AUC。
另一種想法是將某一類別設為正樣本類別,另外一個類別(非自身)設為負樣本類別計算二分類的 AUC。這種方法叫做一對一,即 One-Vs-One (OVO)。可以得到\(C(C-1)\)個二分類的 AUC,然後計算平均數。
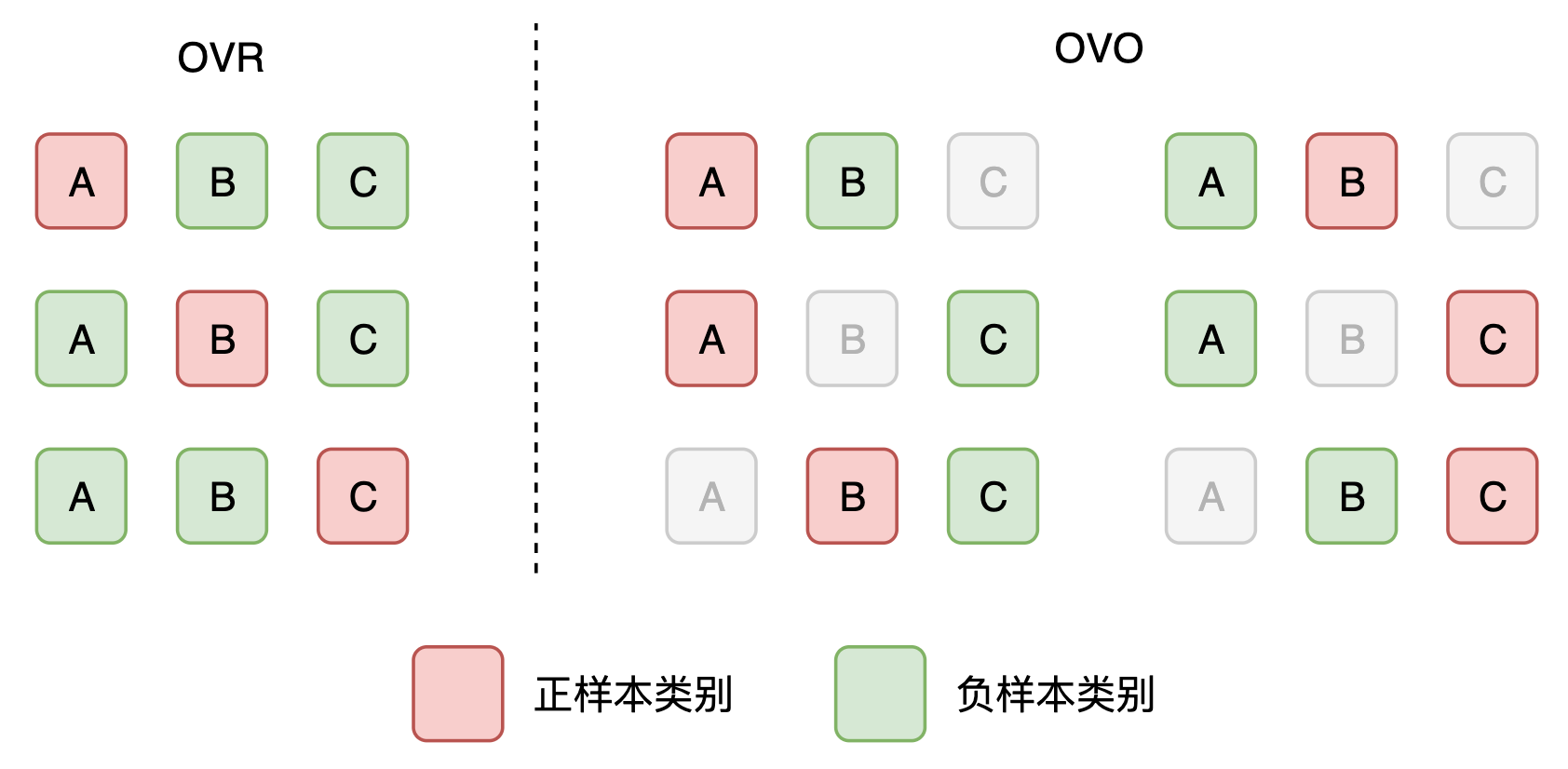
當計算平均數時,可以考慮算數平均數(稱為 macro),或者加權平均數(稱為 weighted)。其中,加權為各類別的樣本所佔比例。因此,兩兩組合可以的得到四種計算多分類 AUC 的方法。值得一提的是,知名機器學習庫 scikit-learn 的 roc_auc_score 函數 包含了上述四種方法。
- 一對多 + 算數平均數(OVR + macro)
- 一對多 + 加權平均數(OVR + weighted)
- 一對一 + 算數平均數(OVO + macro)
- 一對一 + 加權平均數(OVO + weighted)
一對多 + 算數平均數
多分類 AUC 的計算公式為
其中\(\text{AUC}(c_i)\)是將類別\(c_i\)作為正樣本類別(剩餘作為負樣本類別),計算的二分類 AUC。
# sklearn.metrics.roc_auc_score(y_true, y_score, average='macro', multi_class='ovr')
def auc_ovr_macro(y_true, y_score):
auc = 0
C = max(y_true) + 1
for i in range(C):
auc += auc_binary(y_true, y_score[:, i], pos_label=i)
return auc / C
一對多 + 加權平均數
多分類 AUC 的計算公式為
其中,權重\(p(c_i)=\frac{\sum\mathbb{I}\{y=c_i\}}{n}\),即標籤為\(c_i\)的樣本所佔比例,權重之和為 1。
# sklearn.metrics.roc_auc_score(y_true, y_score, average='weighted', multi_class='ovr')
def auc_ovr_weighted(y_true, y_score):
auc = 0
C = max(y_true) + 1
n = len(y_true)
for i in range(C):
p = sum(y_true == i) / n
auc += auc_binary(y_true, y_score[:, i], pos_label=i) * p
return auc
一對一 + 算數平均數
多分類 AUC 的計算公式為
其中,\(\text{AUC}(c_i,c_j)=\frac{\text{AUC}(c_i|c_j)+\text{AUC}(c_j|c_i )}{2}\)。即將\(c_i\)作為正樣本類別、\(c_j\)作為負樣本類別計算二分類\(\text{AUC}(c_i|c_j)\);然後將\(c_j\)作為正樣本類別、\(c_i\)作為負樣本類別計算二分類\(\text{AUC}(c_j|c_i)\)。\(\text{AUC}(c_i,c_j)\)為其計算的算數平均值。由於將\(c_i\)和\(c_j\)組合計算,共得到\(C(C-1)/2\) 個二分類 AUC。
# sklearn.metrics.roc_auc_score(y_true, y_score, average='macro', multi_class='ovo')
def auc_ovo_macro(y_true, y_score):
auc = 0
C = max(y_true) + 1
for i in range(C - 1):
i_index = np.where(y_true == i)[0]
for j in range(i + 1, C):
j_index = np.where(y_true == j)[0]
index = np.concatenate((i_index, j_index))
auc_i_j = auc_binary(y_true[index], y_score[index, i], pos_label=i)
auc_j_i = auc_binary(y_true[index], y_score[index, j], pos_label=j)
auc += (auc_i_j + auc_j_i) / 2
return auc * 2 / (C * (C - 1))
一對一 + 加權平均數
多分類 AUC 的計算公式為
其中,權重\(p(c_i,c_j)=\frac{\sum\mathbb{I}\{y=c_i\}+\sum\mathbb{I}\{y=c_j\}}{(C-1)n}\),即標籤為\(c_i\)和\(c_j\)的樣本所佔比例,分母中的係數\(C-1\)使得權重之和為 1。
# sklearn.metrics.roc_auc_score(y_true, y_score, average='weighted', multi_class='ovo')
def auc_ovo_weighted(y_true, y_score):
auc = 0
C = max(y_true) + 1
n = len(y_true)
for i in range(C - 1):
i_index = np.where(y_true == i)[0]
for j in range(i + 1, C):
j_index = np.where(y_true == j)[0]
index = np.concatenate((i_index, j_index))
p = len(index) / n / (C - 1)
auc_i_j = auc_binary(y_true[index], y_score[index, i], pos_label=i)
auc_j_i = auc_binary(y_true[index], y_score[index, j], pos_label=j)
auc += (auc_i_j + auc_j_i) / 2 * p
return auc
參考文獻
- Fawcett, Tom. "An introduction to ROC analysis." Pattern recognition letters 27, no. 8 (2006): 861-874. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Tom-Fawcett/publication/222511520_Introduction_to_ROC_analysis/links/5ac7844ca6fdcc8bfc7fa47e/Introduction-to-ROC-analysis.pdf
- Hand, David J., and Robert J. Till. "A simple generalisation of the area under the ROC curve for multiple class classification problems." Machine learning 45 (2001): 171-186. https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1023/A:1010920819831.pdf
作者:PrimiHub-Kevin