K8s部署輕量級紀錄檔收集系統EFK(elasticsearch + filebeat + kibana)
K8s部署EFK(elasticsearch + filebeat + kibana)紀錄檔收集
一.準備映象
# 在本機拉取映象
docker pull docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:7.17.2
docker pull docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:7.17.2
docker pull docker.elastic.co/beats/filebeat:7.17.2
# 對映象重打標籤 將${harbor_url}和${harbor_project}換成自己的harbor私服地址和目錄
docker tag docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:7.17.2 ${harbor_url}/${harbor_project}/elasticsearch:7.17.2
docker tag docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:7.17.2 ${harbor_url}/${harbor_project}/kibana:7.17.2
docker tag docker.elastic.co/beats/filebeat:7.17.2 ${harbor_url}/${harbor_project}/filebeat:7.17.2
# 登陸自己的harbor伺服器
docker login -u admin -p ${password} ${harbor_url}
# 上傳至harbor倉庫
docker push ${harbor_url}/${harbor_project}/elasticsearch:7.17.2
docker push ${harbor_url}/${harbor_project}/kibana:7.17.2
docker push ${harbor_url}/${harbor_project}/filebeat:7.17.2
此處的目的是避免某些伺服器從docker外網倉庫拉取不了映象,從而導致pod一直執行不了,當然也可以不用這一步,可以直接使用官方的映象地址
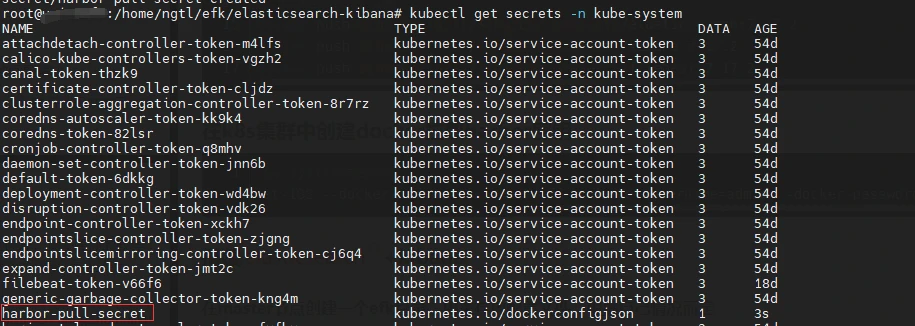
如果此處的Harbor目錄是私有的,則需要在k8s叢集中建立docker拉取harbor私庫的金鑰
# -n 後是指定的空間,根據自己的情況去更改,不加-n,預設是default空間,因為本次EFK安裝在kube-system名稱空間下,所以-n為kube-system。
kubectl create secret docker-registry harbor-pull-secret --docker-server=${harbor_url} --docker-username=admin --docker-password=${password} -n kube-system
kube-system為叢集預設存在的空間,不用手動建立
#檢查金鑰是否建立成功
kubectl get secrets -n kube-system
二.搭建Elasticsearch + kibana
1.在可執行kubectl命令的伺服器準備安裝的yml檔案
2.在elasticsearch-kibana目錄下建立組態檔elasticsearch.yml
cluster.name: my-es
node.name: "node-1"
path.data: /usr/share/elasticsearch/data
#path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch
bootstrap.memory_lock: false
network.host: 0.0.0.0
http.port: 9200
discovery.seed_hosts: ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"]
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1"]
#增加引數,使head外掛可以存取es
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
http.cors.allow-headers: Authorization,X-Requested-With,Content-Length,Content-Type
xpack.monitoring.collection.enabled: true
3.建立kibana組態檔kibana.yml
server.port: 5601
server.host: "0.0.0.0"
elasticsearch.hosts: "http://es-kibana-0.es-kibana.kube-system:9200"
kibana.index: ".kibana"
i18n.locale: "zh-CN"
monitoring.ui.elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://es-kibana-0.es-kibana.kube-system:9200"]
monitoring.ui.enabled: true
其中elasticsearch.hosts的地址構成為pod名:es-kibana-0,service名:es-kibana,名稱空間:kube-system,以及service中設定的埠號9200
4.在k8s中建立elasticsearch和kibana的組態檔configmap
#在編寫yml組態檔的目錄執行該命令
kubectl create configmap es-config -n kube-system --from-file=elasticsearch.yml
kubectl create configmap kibana-config -n kube-system --from-file=kibana.yml
5.檢查是否有StorageClass
kubectl get sc
#如下圖所示是有StorageClass的

如果有則跳過第三步,沒有則需要按照第三步設定NFS伺服器
建立es儲存pvc,pv組態檔:es-pvc.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: es-pv-claim
namespace: kube-system
labels:
app: es
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
storageClassName: "nfs-storage"
resources:
requests:
storage: 20Gi
kubectl apply -f es-pvc.yaml
6.建立es-kibana的yaml組態檔: es-statefulset.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
labels:
app: es-kibana
name: es-kibana
namespace: kube-system
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: es-kibana
serviceName: "es-kibana"
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: es-kibana
spec:
containers:
- image: [Harbor私庫地址]/elasticsearch:7.17.2
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: elasticsearch
resources:
requests:
memory: "800Mi"
cpu: "800m"
limits:
memory: "1Gi"
cpu: "1000m"
volumeMounts:
- name: es-config
mountPath: /usr/share/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml
subPath: elasticsearch.yml
- name: es-persistent-storage
mountPath: /usr/share/elasticsearch/data
env:
- name: TZ
value: Asia/Shanghai
- image: [Harbor私庫地址]/kibana:7.17.2
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: kibana
env:
- name: TZ
value: Asia/Shanghai
volumeMounts:
- name: kibana-config
mountPath: /usr/share/kibana/config/kibana.yml
subPath: kibana.yml
volumes:
- name: es-config
configMap:
name: es-config
- name: kibana-config
configMap:
name: kibana-config
- name: es-persistent-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: es-pv-claim
#hostNetwork: true
#dnsPolicy: ClusterFirstWithHostNet
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/hostname: k8s-uni-node3
#建立pod
kubectl create -f es-statefulset.yaml
# 檢視
kubectl get pod -o wide -n kube-system|grep es
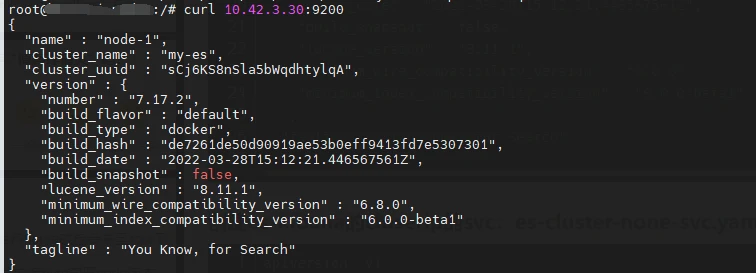
# 使用curl命令測試elasticsearch是否正常
kubectl get pod -o wide -n kube-system|grep es

然後在叢集內部伺服器上測試是否能通訊
當然也可以在Rancher上檢視pod是否執行成功
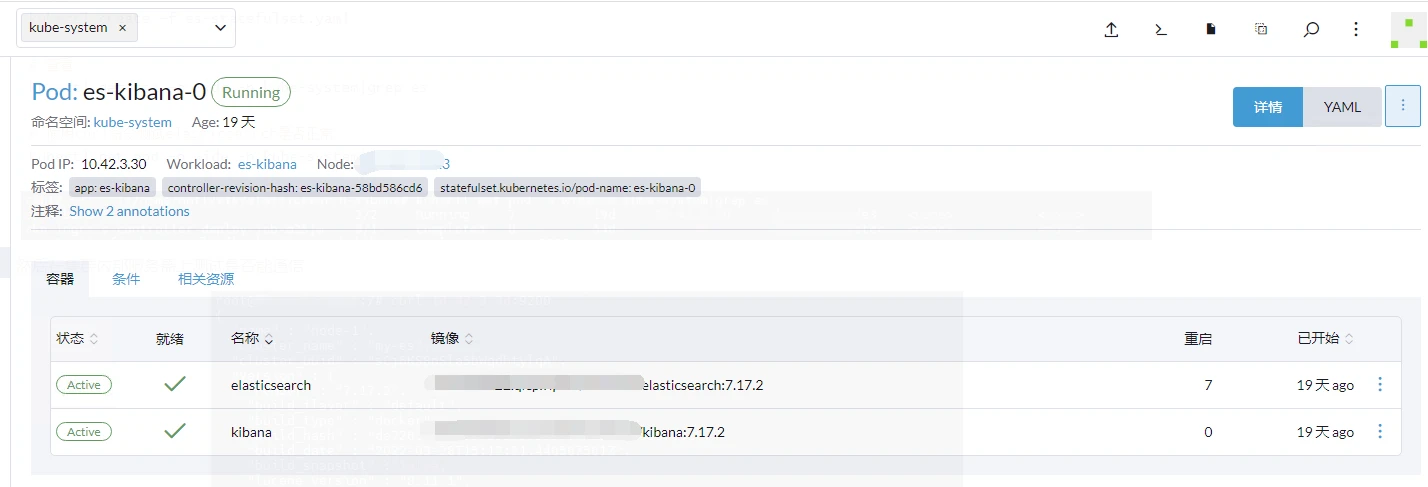
這個pod一次執行了兩個容器,分別是kibanah和elasticsearch,並且把elasticsearch容器中的/usr/share/elasticsearch/data目錄下的內容,掛載到了es-pv-claim下,我們可以在第三步中的NFS伺服器共用目錄中找到掛載的資料。

7.建立es-kibana cluserip的svc
vi es-cluster-none-svc.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: es-kibana
name: es-kibana
namespace: kube-system
spec:
ports:
- name: es9200
port: 9200
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 9200
- name: es9300
port: 9300
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 9300
clusterIP: None
selector:
app: es-kibana
type: ClusterIP
kubectl apply -f es-cluster-none-svc.yaml
這個組態檔描述了一個名為
es-kibana的 Kubernetes Service,該 Service 不分配 Cluster IP(ClusterIP: None),它會將流量路由到具有特定標籤app: es-kibana的 Pod,這些 Pod 的埠 9200 和 9300 將被公開,並且可以通過相應的targetPort進行存取。用於叢集內部存取
8.建立es-kibana的nodeport型別的svc
vi es-nodeport-svc.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: es-kibana
name: es-kibana-nodeport-svc
namespace: kube-system
spec:
ports:
- name: 9200-9200
port: 9200
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 9200
#nodePort: 9200
- name: 5601-5601
port: 5601
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 5601
#nodePort: 5601
selector:
app: es-kibana
type: NodePort
kubectl apply -f es-nodeport-svc.yaml
這個組態檔建立了一個名為 "es-kibana-nodeport-svc" 的 Kubernetes Service。該 Service 使用 NodePort 型別,允許從叢集外部存取服務。Service 公開了兩個埠,9200 和 5601,分別將流量路由到具有相應標籤的 Pod 的對應埠。Pod 的選擇基於標籤
app: es-kibana。用於暴露埠,從叢集外部存取es和kibana
外網暴露的埠是k8s隨機分配的,有兩種辦法可以檢視
#在伺服器使用命令檢視
kubectl get svc -n kube-system|grep es-kibana

Rancher上檢視
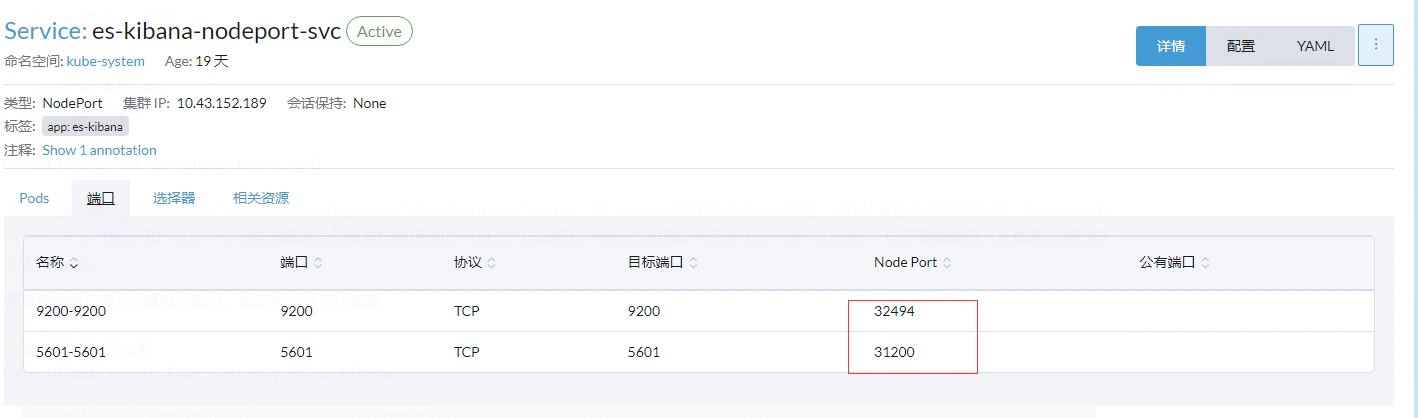
可以看到Kibana的埠為31200,然後就能使用nodeip+port存取
檢查es是否註冊上Kibana,點選側邊欄找到堆疊檢測,然後點Nodes
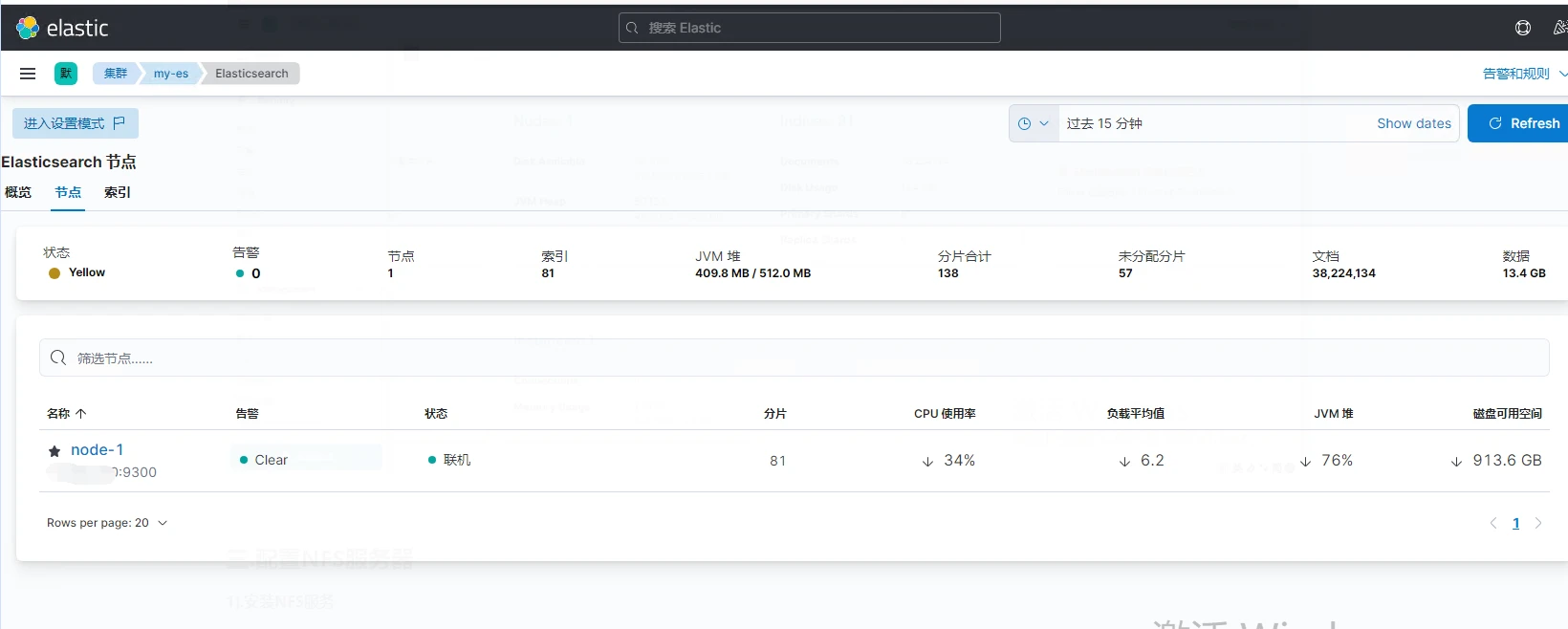
至此,Elasticsearch + kibana已經搭建完成,可以進行第四步。
三.設定NFS伺服器
1).安裝NFS服務
Ubuntu:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install nfs-kernel-server
Centos:
yum update
yum -y install nfs-utils
# 建立或使用用已有的資料夾作為nfs檔案儲存點
mkdir -p /home/data/nfs/share
vi /etc/exports
寫入如下內容
/home/data/nfs/share *(rw,no_root_squash,sync,no_subtree_check)
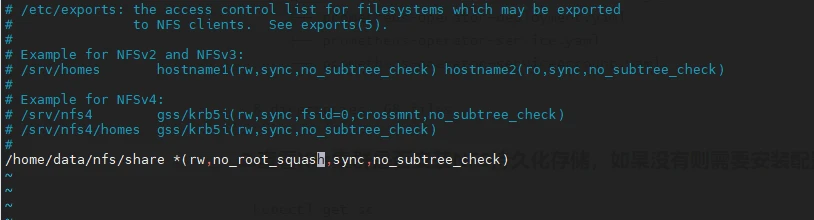
# 設定生效並檢視是否生效
exportfs -r
exportfs

# 啟動rpcbind、nfs服務
#Centos
systemctl restart rpcbind && systemctl enable rpcbind
systemctl restart nfs && systemctl enable nfs
#Ubuntu
systemctl restart rpcbind && systemctl enable rpcbind
systemctl start nfs-kernel-server && systemctl enable nfs-kernel-server
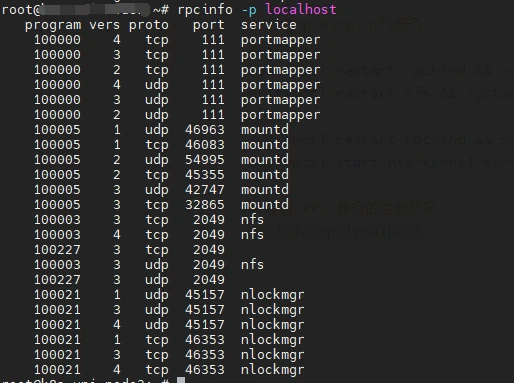
# 檢視 RPC 服務的註冊狀況
rpcinfo -p localhost
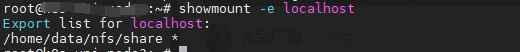
# showmount測試
showmount -e localhost
以上都沒有問題則說明安裝成功
2).k8s註冊nfs服務
新建storageclass-nfs.yaml檔案,貼上如下內容:
## 建立了一個儲存類
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass #儲存類的資源名稱
metadata:
name: nfs-storage #儲存類的名稱,自定義
annotations:
storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "true" #註解,是否是預設的儲存,注意:KubeSphere預設就需要個預設儲存,因此這裡註解要設定為「預設」的儲存系統,表示為"true",代表預設。
provisioner: k8s-sigs.io/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner #儲存分配器的名字,自定義
parameters:
archiveOnDelete: "true" ## 刪除pv的時候,pv的內容是否要備份
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner
labels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 1 #只執行一個副本應用
strategy: #描述瞭如何用新的POD替換現有的POD
type: Recreate #Recreate表示重新建立Pod
selector: #選擇後端Pod
matchLabels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
spec:
serviceAccountName: nfs-client-provisioner #建立賬戶
containers:
- name: nfs-client-provisioner
image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/lfy_k8s_images/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner:v4.0.2 #使用NFS儲存分配器的映象
volumeMounts:
- name: nfs-client-root #定義個儲存卷,
mountPath: /persistentvolumes #表示掛載容器內部的路徑
env:
- name: PROVISIONER_NAME #定義儲存分配器的名稱
value: k8s-sigs.io/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner #需要和上面定義的保持名稱一致
- name: NFS_SERVER #指定NFS伺服器的地址,你需要改成你的NFS伺服器的IP地址
value: 192.168.0.0 ## 指定自己nfs伺服器地址
- name: NFS_PATH
value: /home/data/nfs/share ## nfs伺服器共用的目錄 #指定NFS伺服器共用的目錄
volumes:
- name: nfs-client-root #儲存卷的名稱,和前面定義的保持一致
nfs:
server: 192.168.0.0 #NFS伺服器的地址,和上面保持一致,這裡需要改為你的IP地址
path: /home/data/nfs/share #NFS共用的儲存目錄,和上面保持一致
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount #建立個SA賬號
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner #和上面的SA賬號保持一致
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: default
---
#以下就是ClusterRole,ClusterRoleBinding,Role,RoleBinding都是許可權繫結設定,不在解釋。直接複製即可。
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner-runner
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["nodes"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["persistentvolumes"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "delete"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["persistentvolumeclaims"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "update"]
- apiGroups: ["storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["storageclasses"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["events"]
verbs: ["create", "update", "patch"]
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: run-nfs-client-provisioner
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: default
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: nfs-client-provisioner-runner
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: default
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["endpoints"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch"]
---
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: default
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: default
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
需要修改的就只有伺服器地址和共用的目錄
建立StorageClass
kubectl apply -f storageclass-nfs.yaml
# 檢視是否存在
kubectl get sc

四.建立filebeat服務
1.建立filebeat主組態檔filebeat.settings.configmap.yml
vi filebeat.settings.configmap.yml
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
namespace: kube-system
name: filebeat-config
labels:
app: filebeat
data:
filebeat.yml: |-
filebeat.inputs:
- type: container
enabled: true
paths:
- /var/log/containers/*.log
multiline:
pattern: ^\d{4}-\d{1,2}-\d{1,2}\s\d{1,2}:\d{1,2}:\d{1,2}
negate: true
match: after
processors:
- add_kubernetes_metadata:
in_cluster: true
host: ${NODE_NAME}
matchers:
- logs_path:
logs_path: "/var/log/containers/"
- add_cloud_metadata:
- add_kubernetes_metadata:
matchers:
- logs_path:
logs_path: "/var/log/containers/"
- add_docker_metadata:
output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ["http://[節點IP]:32494"]
indices:
- index: "filebeat-demo-%{+yyyy.MM.dd}"
setup.ilm:
policy_file: /etc/indice-lifecycle.json
#執行
kubectl apply -f filebeat.settings.configmap.yml
filebeat.inputs: 定義輸入設定,這裡設定了從容器紀錄檔中收集資料。
type: 定義輸入型別為 container,表示從容器紀錄檔中收集資料。
enabled: 啟用該輸入設定。
paths: 指定要監視的紀錄檔檔案路徑,這裡是容器紀錄檔路徑。k8s容器的紀錄檔預設是儲存在在伺服器的/var/log/containers/下的。
multiline: 多行紀錄檔設定,用於將多行紀錄檔合併為單個事件。正則表示如果前面幾個數位不是4個數位開頭,那麼就會合併到一行,解決Java堆疊錯誤紀錄檔收集問題
processors: 定義處理器,用於新增後設資料。add_kubernetes_metadata:為紀錄檔事件新增 Kubernetes 相關的後設資料資訊,例如 Pod 名稱、名稱空間、標籤等。
output.elasticsearch: 定義輸出設定,將收集到的紀錄檔傳送到 Elasticsearch。
hosts: 指定 Elasticsearch 節點的地址和埠。埠號為第二步安裝es時,nodeport暴露的埠號。indices: 定義索引模式,這裡以日期為字尾,建立每日索引。
setup.ilm: 設定索引生命週期管理 (ILM),用於管理索引的生命週期。
- policy_file:後面定義的是生命週期組態檔的地址
2.建立Filebeat索引生命週期策略組態檔
為了防止大量的資料儲存,可以利用 indice 的生命週期來設定資料保留。 如下所示的檔案中,設定成每天或每次超過5GB的時候就對 indice 進行輪轉,並刪除所有超過30天的 indice 檔案。
vi filebeat.indice-lifecycle.configmap.yml
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
namespace: kube-system
name: filebeat-indice-lifecycle
labels:
app: filebeat
data:
indice-lifecycle.json: |-
{
"policy": {
"phases": {
"hot": {
"actions": {
"rollover": {
"max_size": "5GB" ,
"max_age": "1d"
}
}
},
"delete": {
"min_age": "30d",
"actions": {
"delete": {}
}
}
}
}
}
#執行
kubectl apply -f filebeat.indice-lifecycle.configmap.yml
3.Filebeat操作許可權
vi filebeat.permission.yml
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: filebeat
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources:
- namespaces
- pods
- nodes
verbs:
- get
- watch
- list
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: filebeat
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: filebeat
namespace: kube-system
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: filebeat
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
namespace: kube-system
name: filebeat
#執行
kubectl apply -f filebeat.permission.yml
- ClusterRole:
- 作用:定義了一個 ClusterRole,它是一種許可權集合,指定了 Filebeat 在叢集範圍內可以執行的操作,如獲取(get)、監視(watch)、列出(list)等。
- 許可權:
- 可以對名稱空間執行 get、watch、list 操作。
- 可以對 Pod 執行 get、watch、list 操作。
- 可以對節點執行 get、watch、list 操作。
- ClusterRoleBinding:
- 作用:定義了一個 ClusterRoleBinding,將 ClusterRole (
filebeat) 繫結到特定的 ServiceAccount (filebeat)。- 意義:將 ClusterRole 與 ServiceAccount 繫結,以使 Filebeat 具有在 Kubernetes 中執行相應操作的許可權。
- ServiceAccount:
- 作用:定義了一個 ServiceAccount (
filebeat),它是 Kubernetes 中用於身份驗證和授權的實體。- 意義:建立了一個用於 Filebeat 的身份實體,使得 Filebeat 在 Kubernetes 中能夠以其身份執行。
4.Filebeat Daemonset組態檔
vi filebeat.daemonset.yml
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
namespace: kube-system
name: filebeat
labels:
app: filebeat
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: filebeat
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: filebeat
spec:
serviceAccountName: filebeat
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
containers:
- name: filebeat
image: [Harbor私服地址]/filebeat:7.17.2
args: [
"-c", "/etc/filebeat.yml",
"-e",
]
env:
- name: NODE_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: spec.nodeName
securityContext:
runAsUser: 0
resources:
limits:
memory: 200Mi
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 100Mi
volumeMounts:
- name: config
mountPath: /etc/filebeat.yml
readOnly: true
subPath: filebeat.yml
- name: filebeat-indice-lifecycle
mountPath: /etc/indice-lifecycle.json
readOnly: true
subPath: indice-lifecycle.json
- name: data
mountPath: /usr/share/filebeat/data
- name: varlog
mountPath: /var/log
readOnly: true
- name: varlibdockercontainers
mountPath: /var/lib/docker/containers
readOnly: true
- name: dockersock
mountPath: /var/run/docker.sock
volumes:
- name: config
configMap:
defaultMode: 0600
name: filebeat-config
- name: filebeat-indice-lifecycle
configMap:
defaultMode: 0600
name: filebeat-indice-lifecycle
- name: varlog
hostPath:
path: /var/log
- name: varlibdockercontainers
hostPath:
path: /var/lib/docker/containers
- name: dockersock
hostPath:
path: /var/run/docker.sock
- name: data
hostPath:
path: /var/lib/filebeat-data
type: DirectoryOrCreate
#執行
kubectl apply -f filebeat.daemonset.yml
volumeMounts設定示意:
- name: config:
- 作用: 建立一個掛載點,將 ConfigMap 中的
filebeat.yml組態檔掛載到容器中的/etc/filebeat.yml路徑。- readOnly: 設定為 true,表示唯讀存取該組態檔。
- name: filebeat-indice-lifecycle:
- 作用: 建立一個掛載點,將 ConfigMap 中的
indice-lifecycle.json檔案掛載到容器中的/etc/indice-lifecycle.json路徑。- readOnly: 設定為 true,表示唯讀存取該檔案。
- name: data:
- 作用: 建立一個掛載點,將宿主機的
/var/lib/filebeat-data目錄掛載到容器中的/usr/share/filebeat/data路徑。- type: DirectoryOrCreate: 指定掛載型別為目錄,如果該目錄不存在則建立。
- name: varlog:
- 作用: 建立一個掛載點,將宿主機的
/var/log目錄掛載到容器中的/var/log路徑。- readOnly: 設定為 true,表示唯讀存取該目錄。
- name: varlibdockercontainers:
- 作用: 建立一個掛載點,將宿主機的
/var/lib/docker/containers目錄掛載到容器中的/var/lib/docker/containers路徑。- readOnly: 設定為 true,表示唯讀存取該目錄。
- name: dockersock:
- 作用: 建立一個掛載點,將宿主機的 Docker socket 檔案
/var/run/docker.sock掛載到容器中的/var/run/docker.sock路徑。
volumes設定示意:
- name: config:
- 作用: 與volumeMounts中的name: config相對應。
- defaultMode: 0600: 表示只有檔案所有者可讀寫,其他使用者無許可權。
- name:filebeat-config對應第一步建立的filebeat.settings.configmap.yml中的Configmap的名字
- name: filebeat-indice-lifecycle:
- 作用: 與volumeMounts中的filebeat-indice-lifecycle相對應。
- defaultMode: 0600: 表示只有檔案所有者可讀寫,其他使用者無許可權。
- name:filebeat-indice-lifecycle對應第二步建立的filebeat.indice-lifecycle.configmap.yml中的Configmap的名字
- name: data
- 作用:與volumeMounts中的name: data相對應。
- path:需要掛載的目錄路徑
- type:DirectoryOrCreatea表示容器啟動時會檢查宿主機是否存在該目錄,不存在則建立。因為Filebeat在每個節點的宿主機上都會執行,所以直接掛載到宿主機目錄
檢查是否執行成功
kubectl get pod -o wide -n kube-system|grep filebeat
#如下圖,全為Running則表示執行成功
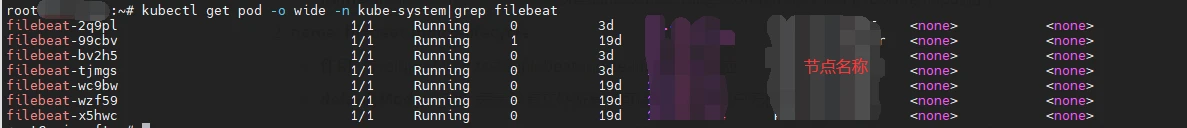
也可以在Rancher上檢視
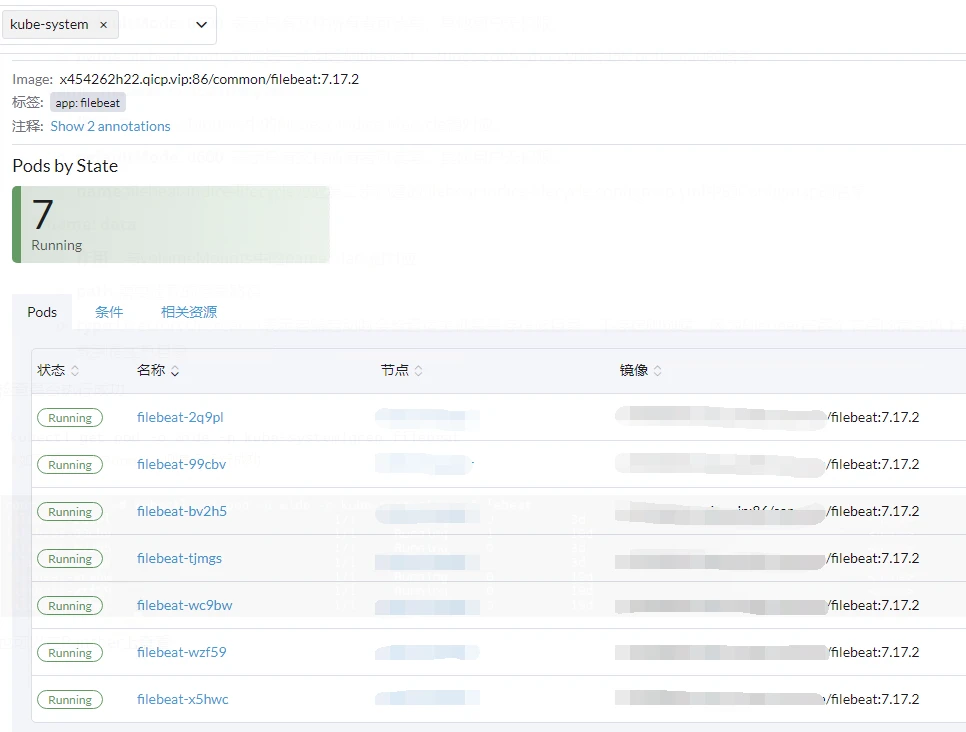
五.檢查File beat與es,Kibana是否設定成功
1.首先在側邊欄找到Stack Management
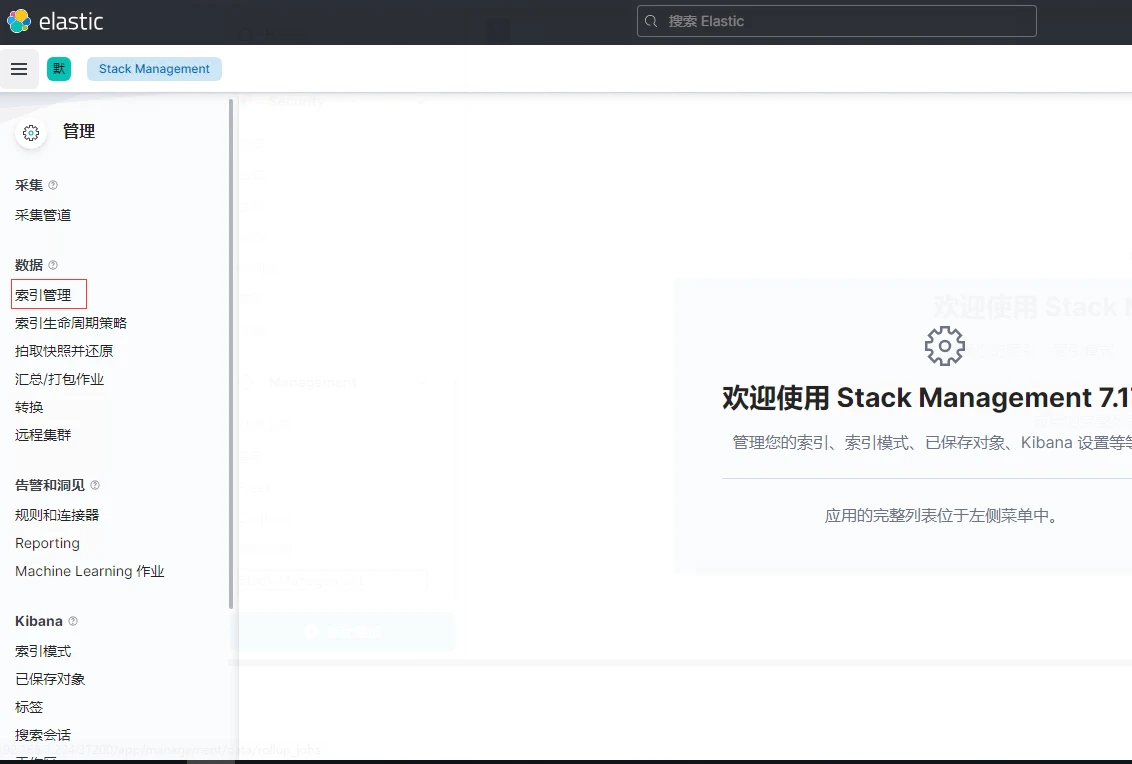
2.選擇索引管理,檢視是否有以filebeat-demo加時間戳為名的索引
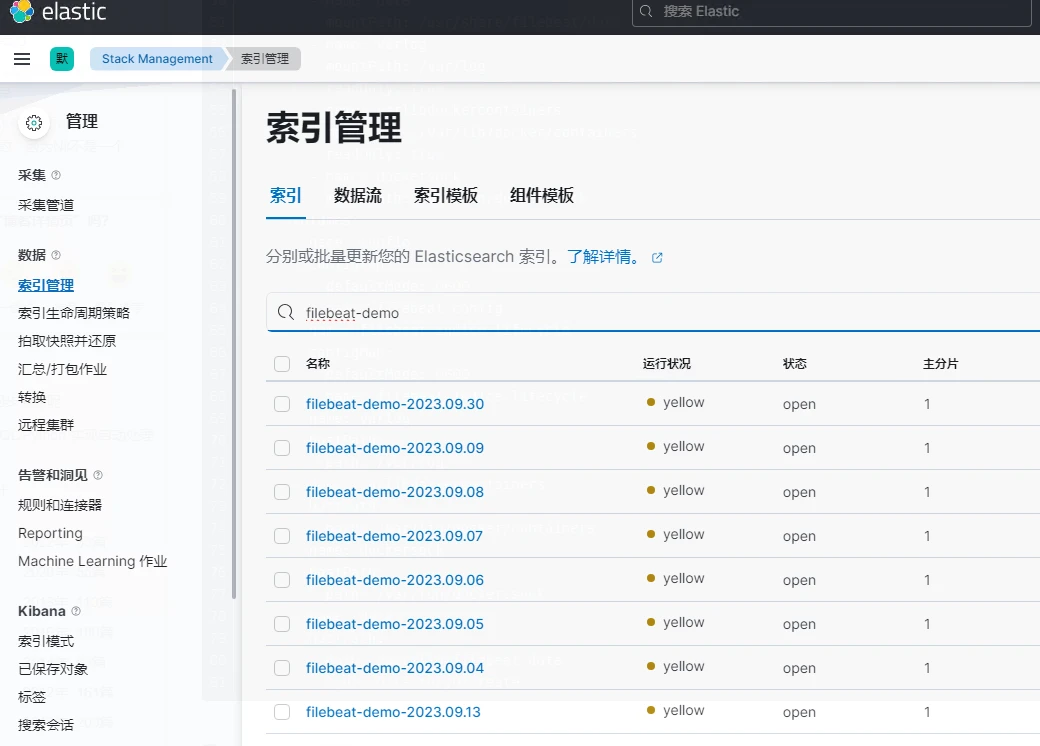
3.建立索引模式
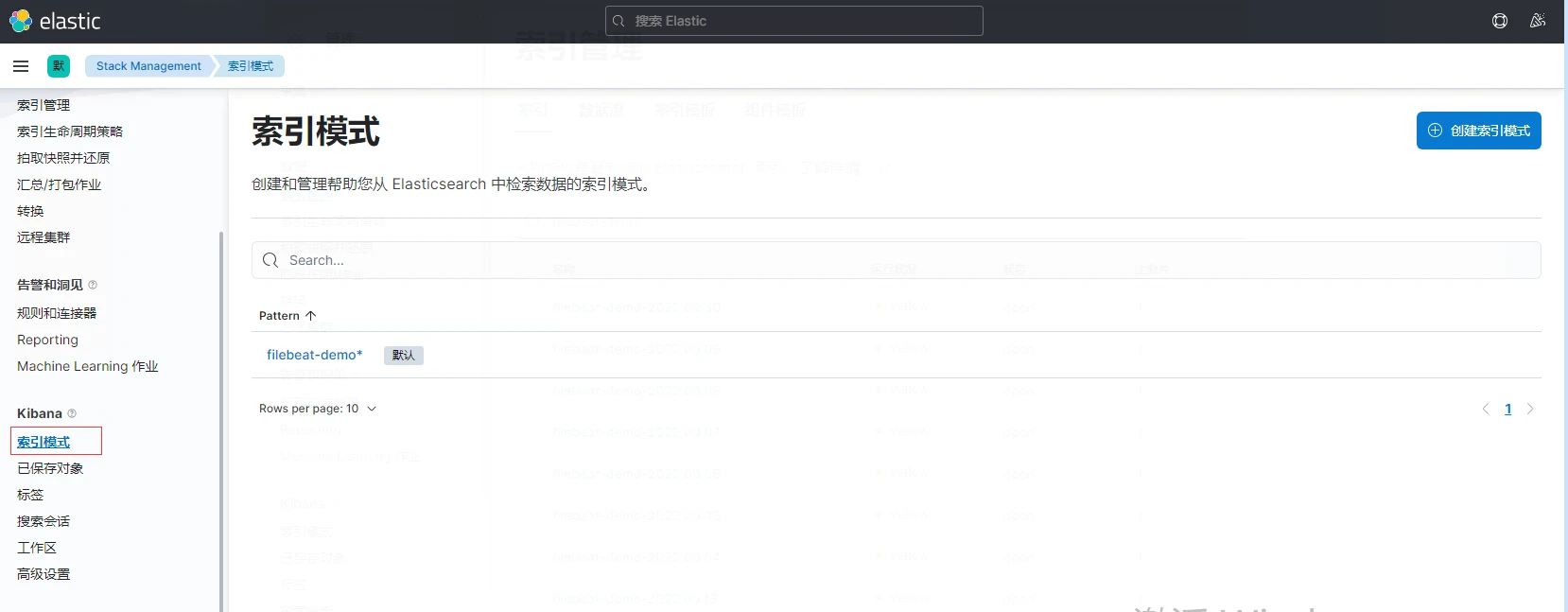
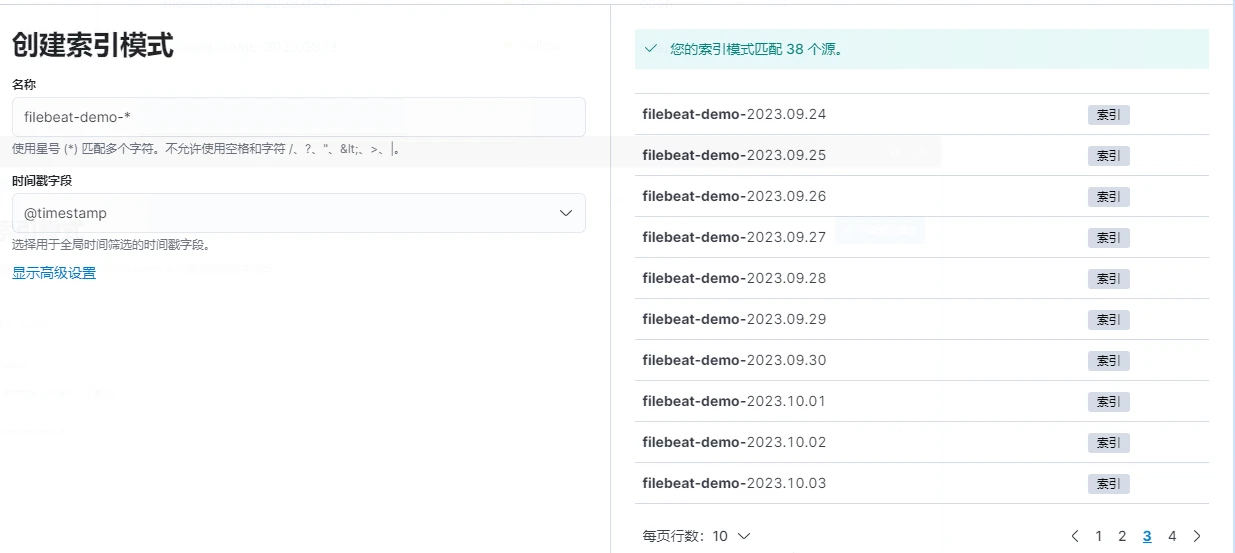
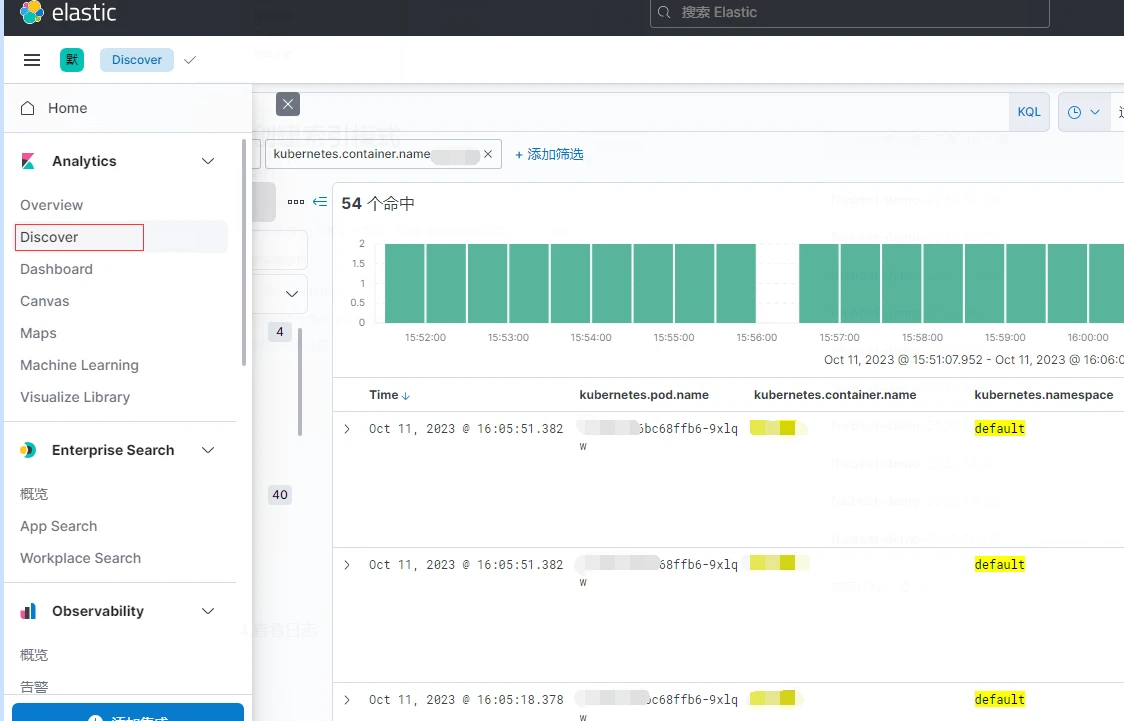
4.檢視紀錄檔
點選側邊欄,選擇discover,就能看到Filebeat收集到的容器紀錄檔,可以按照自己的需求進行紀錄檔篩選