ATtiny88初體驗(七):TWI
2023-09-12 18:01:32
ATtiny88初體驗(七):TWI
TWI模組介紹
ATtiny88的TWI模組相容Phillips I2C以及SMBus,支援主從模式,支援7bit地址,最大允許128個不同的從機地址。在多主機模式下,支援匯流排仲裁。從機模式下的資料速率高達400kHz,且從機地址可程式化。在睡眠模式下,支援地址識別喚醒。
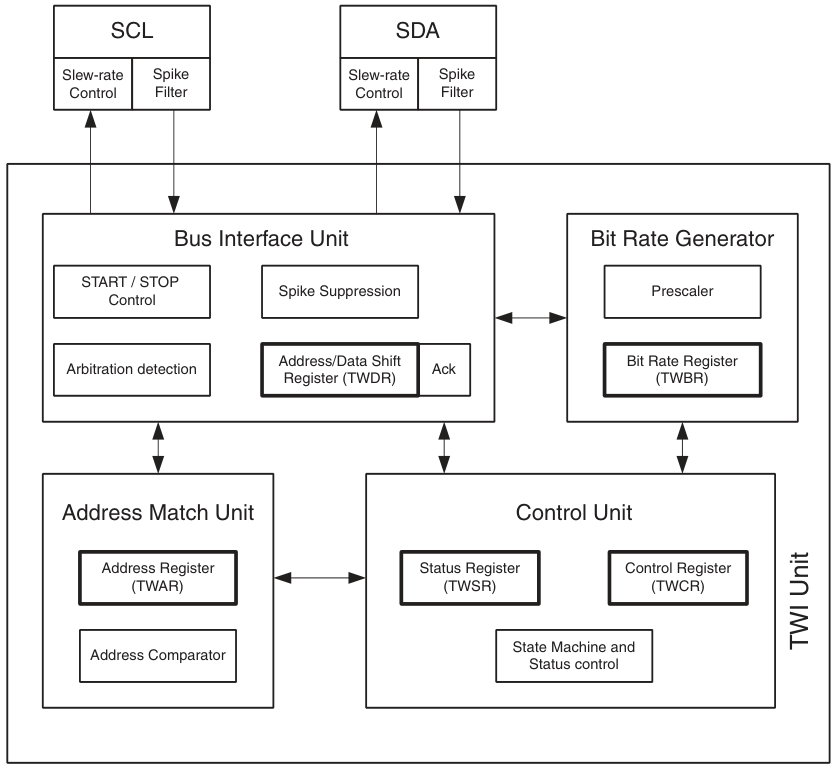
注意:為了使用TWI模組, PRR 暫存器中的 PRTWI 位必須設為0。
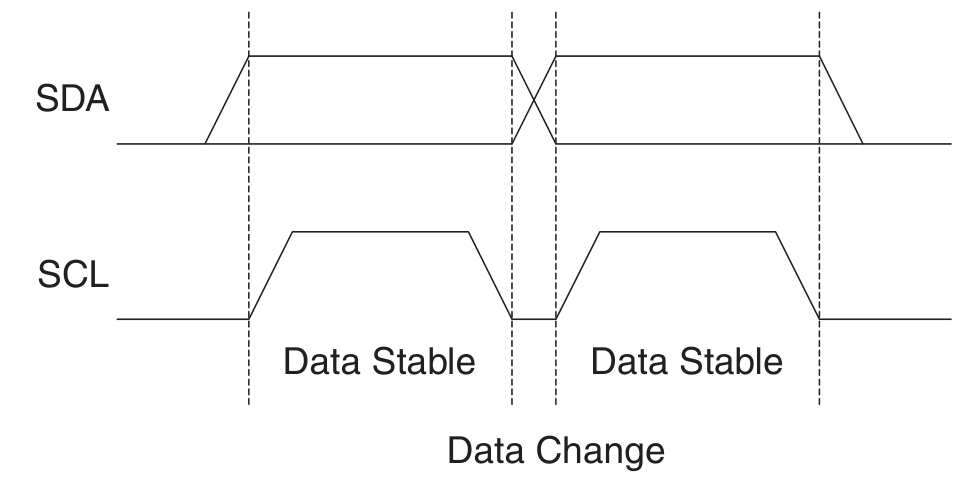
資料位傳輸:
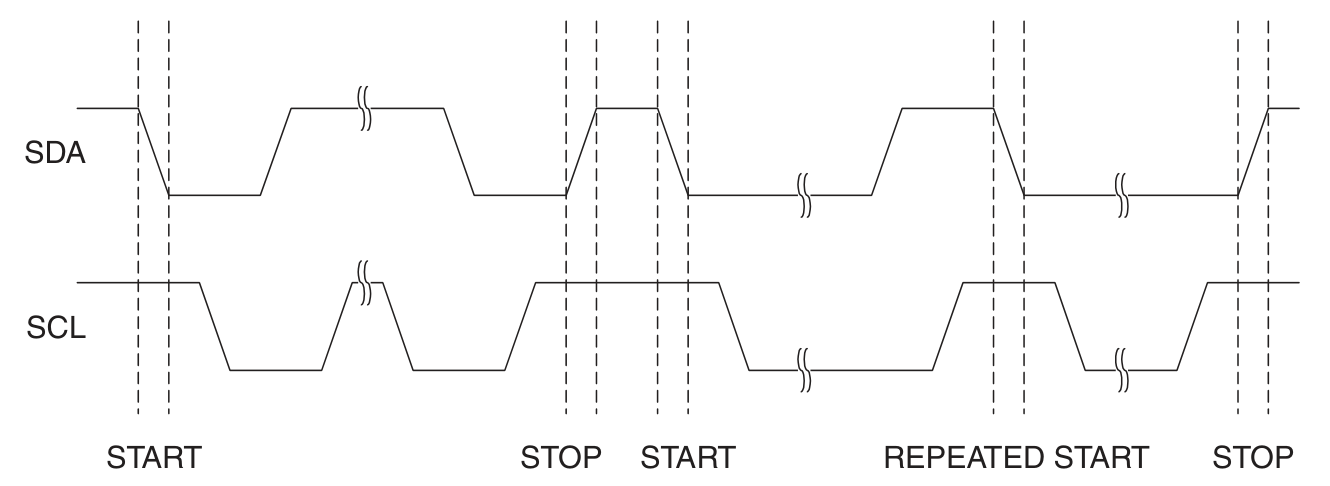
開始和停止條件:
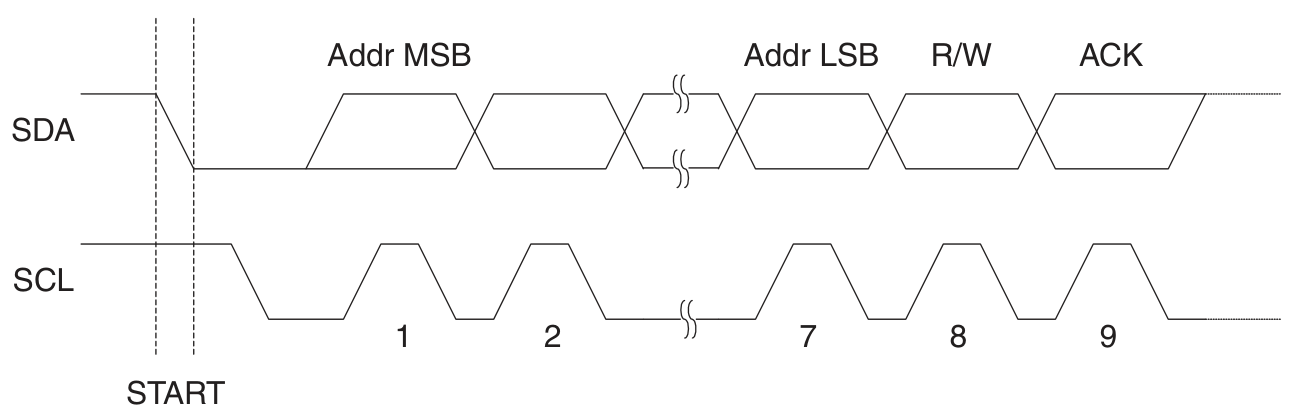
地址幀格式:
資料框格式:
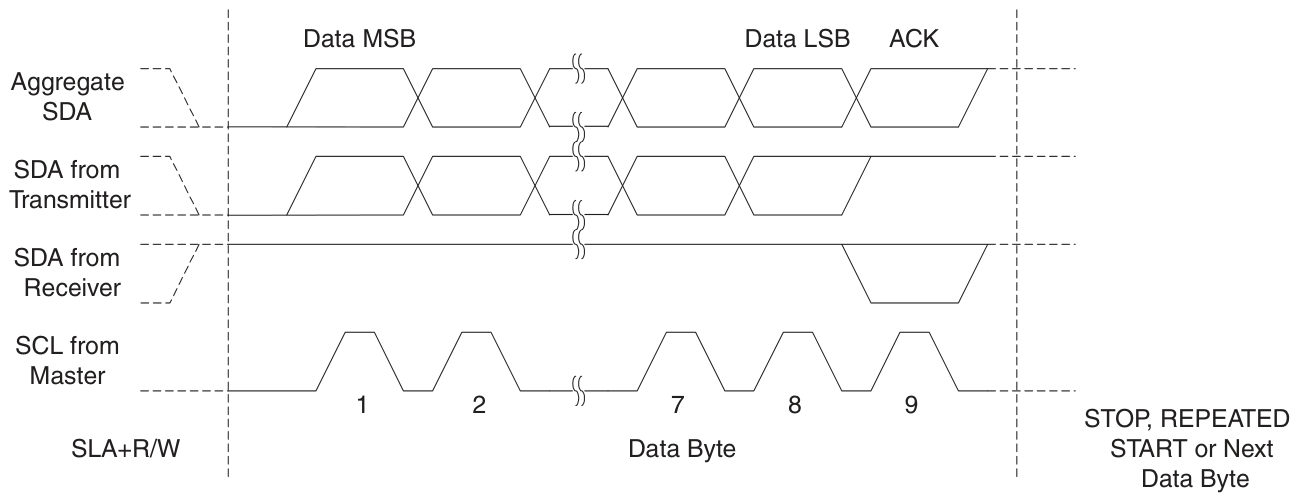
完整的傳輸過程:
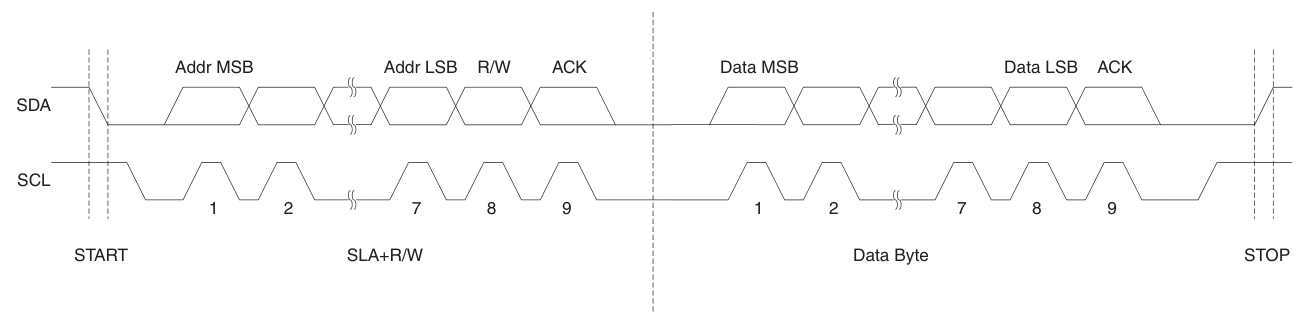
普通模式時脈頻率:
\[f_{SCL} = \frac{clk_{I/O}}{16 + (2 \times TWBR \times TWPS)}
\]
高速模式時脈頻率:
\[f_{SCL} = \frac{clk_{TWIHS}}{16 + (2 \times TWBR \times TWPS)}
\]
其中, \(clk_{I/O}\) 為分頻後的系統時鐘, \(clk_{TWIHS}\) 為系統時鐘。
注意:主機模式下, TWBR 值不能低於10。
下圖展現了一個典型傳輸過程中,應用程式如何與TWI模組互動的。
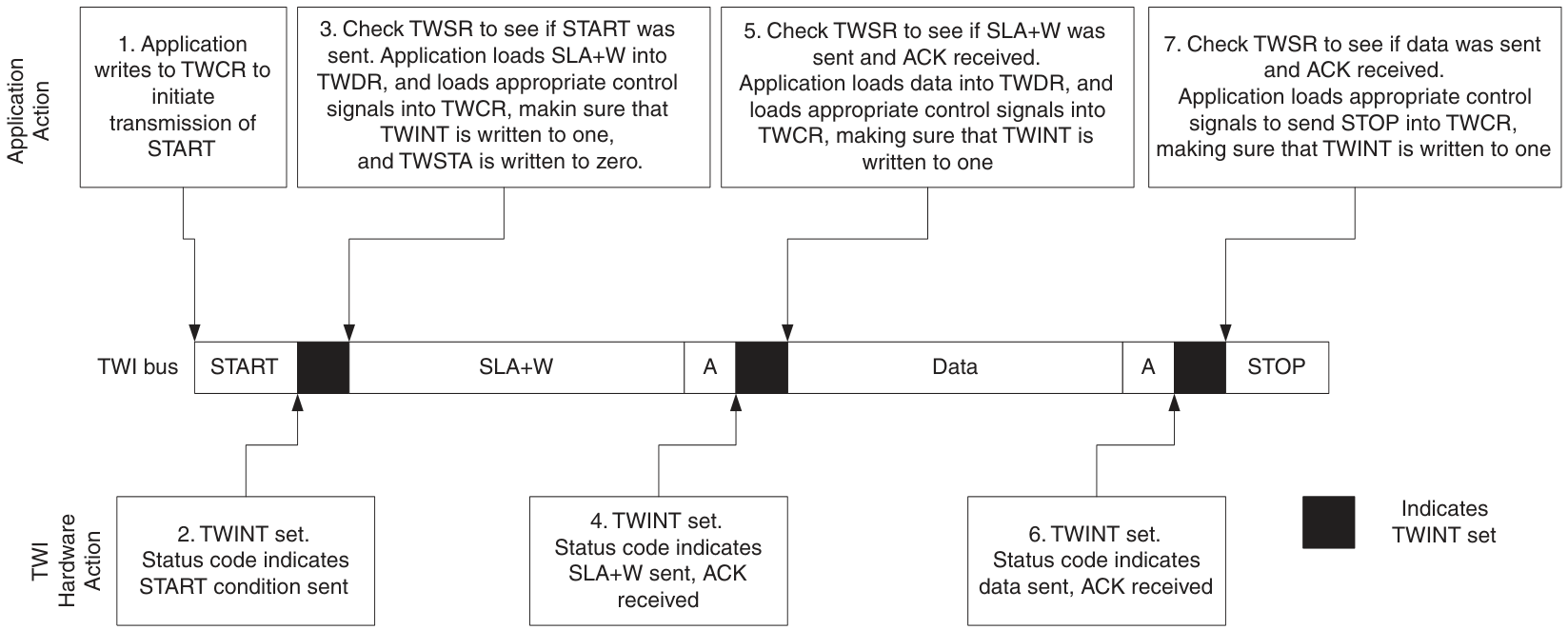
ATtiny88的TWI擁有四種模式:Master Transmitter、Master Receiver、Slave Transmitter、Slave Receiver。
Master Transmitter模式下的狀態碼:

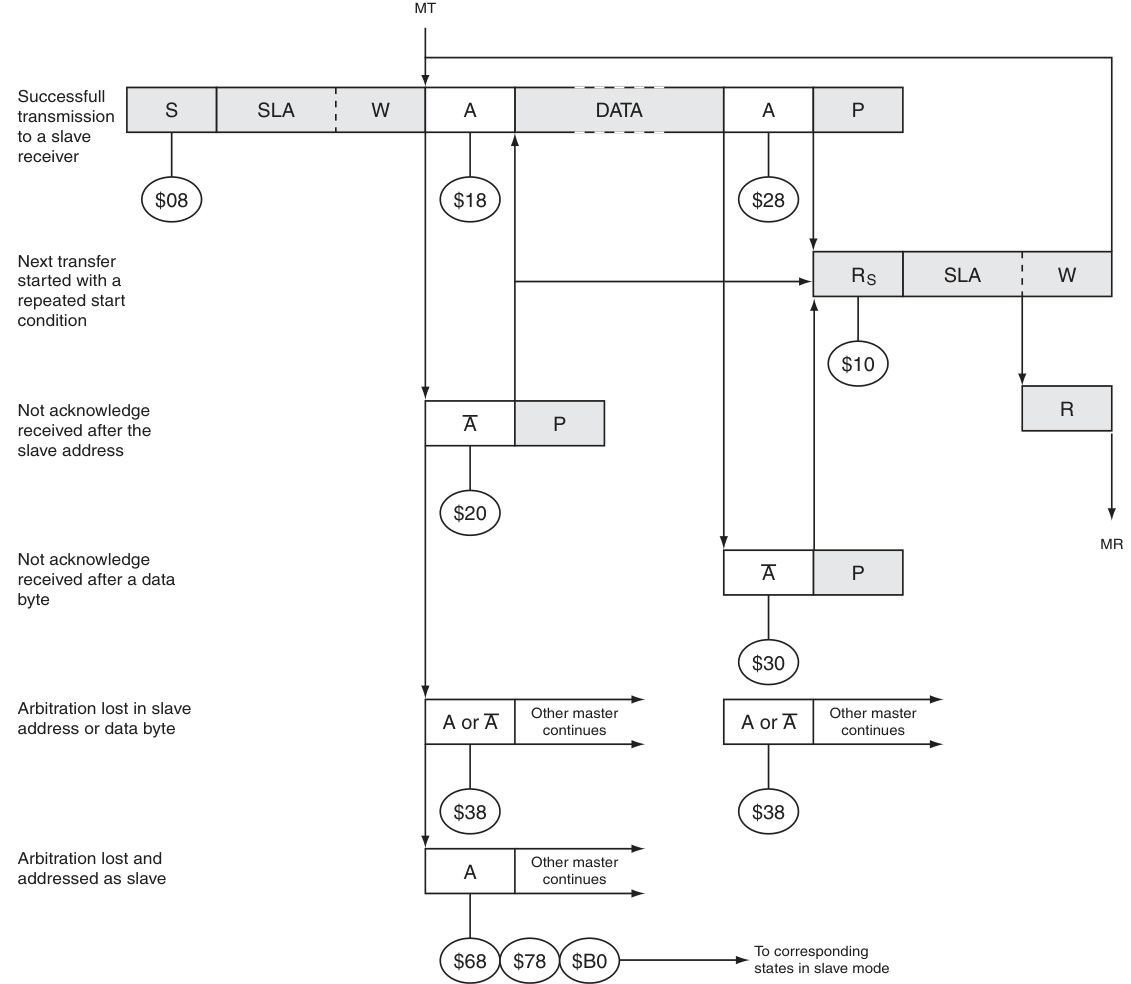
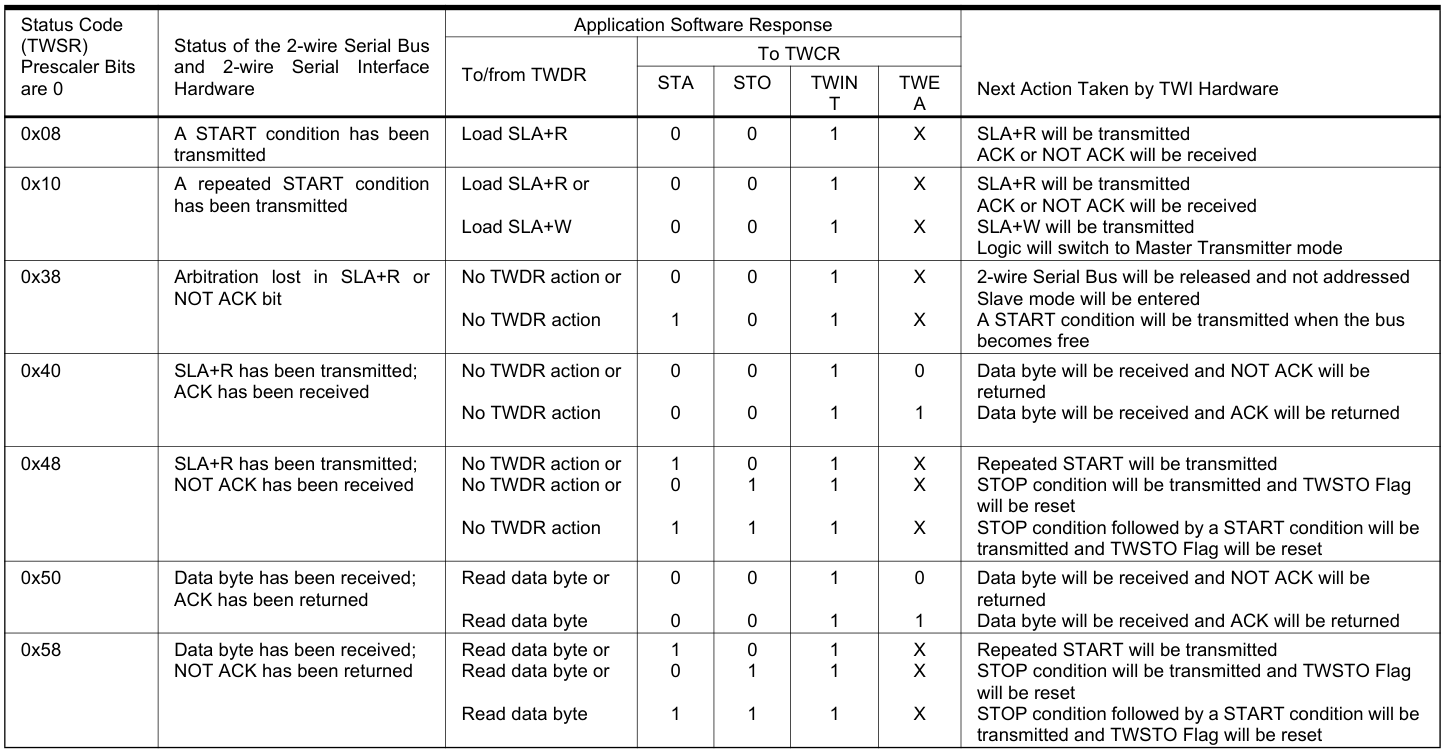
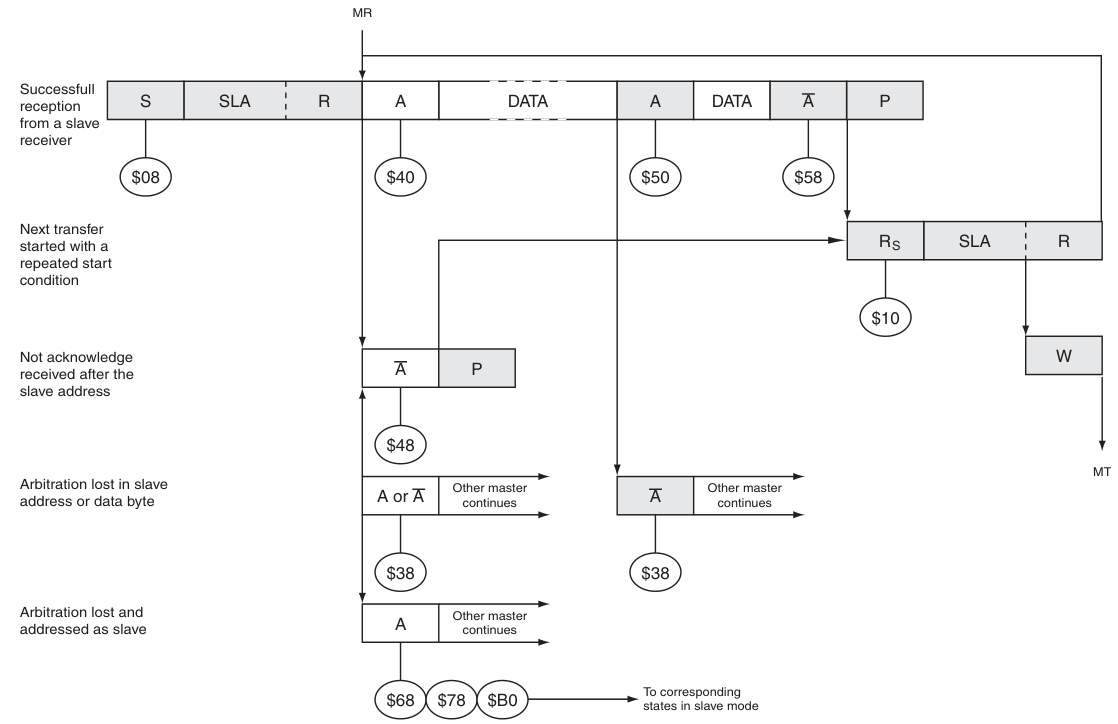
Master Receiver模式下的狀態碼:
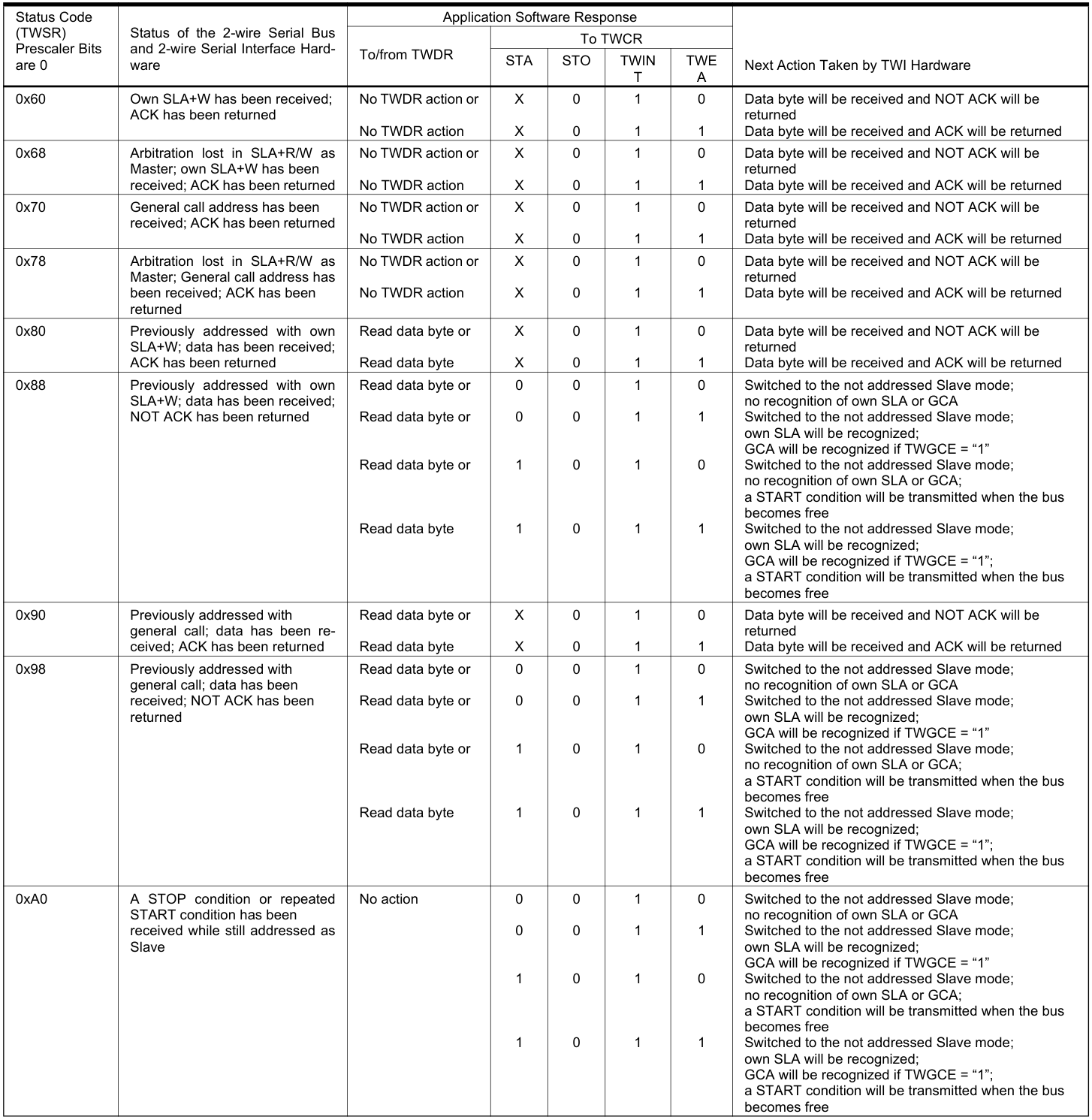
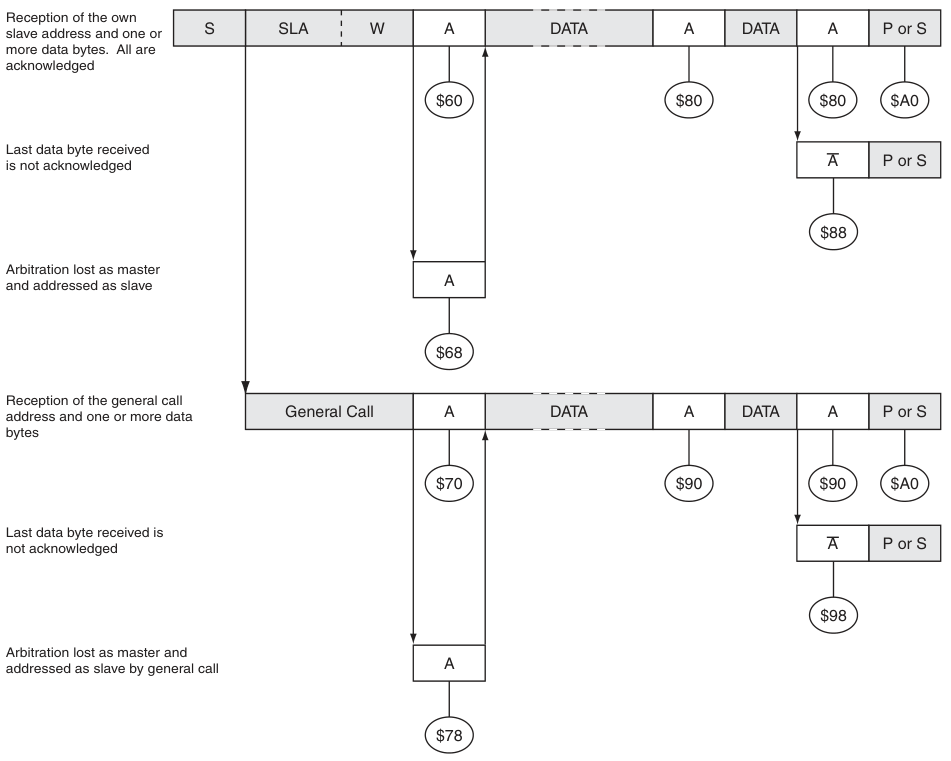
Slave Receiver模式下的狀態碼:
Slave Transmitter模式下的狀態碼:
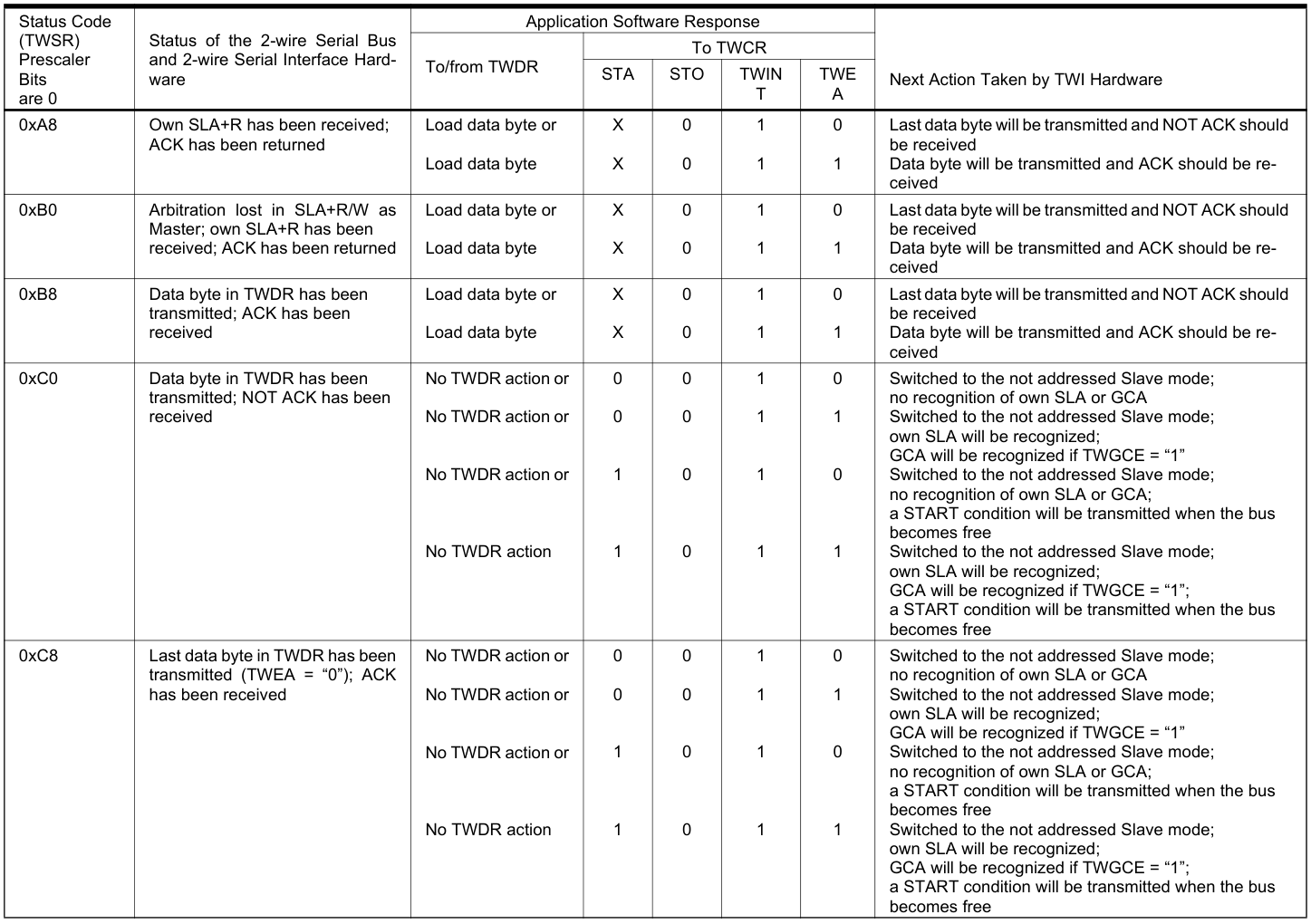
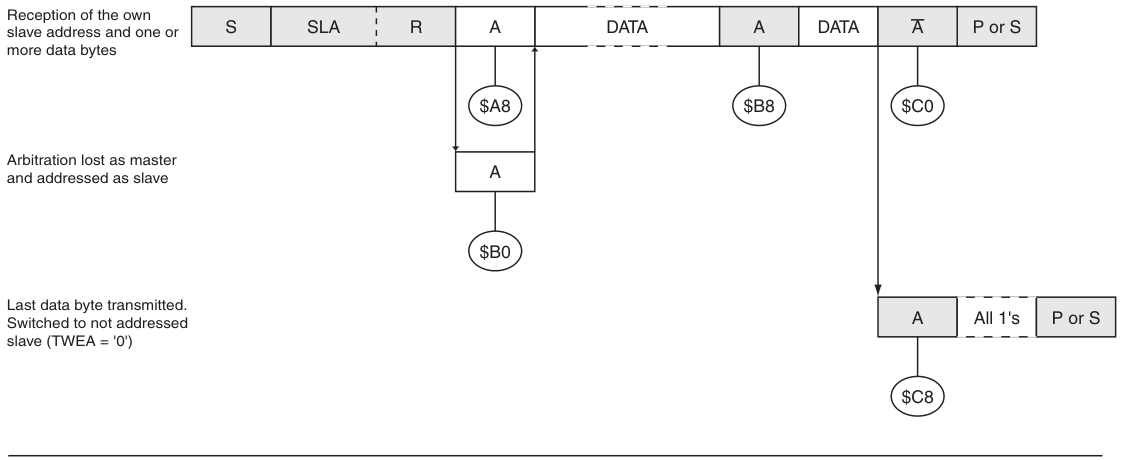
其他狀態碼:
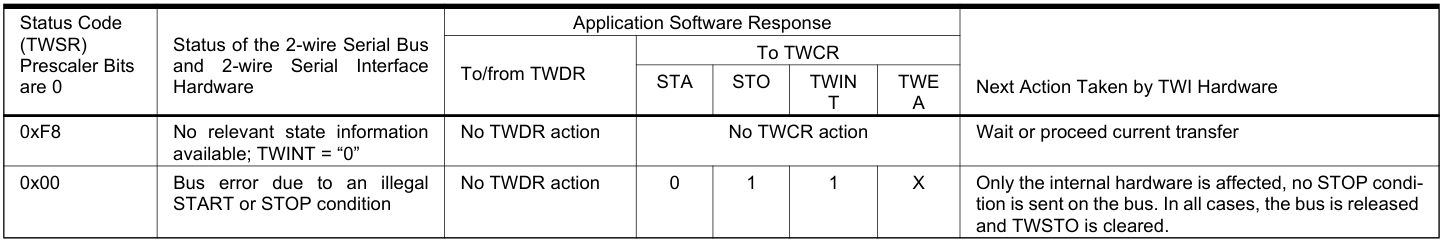
多主機仲裁過程及狀態碼:
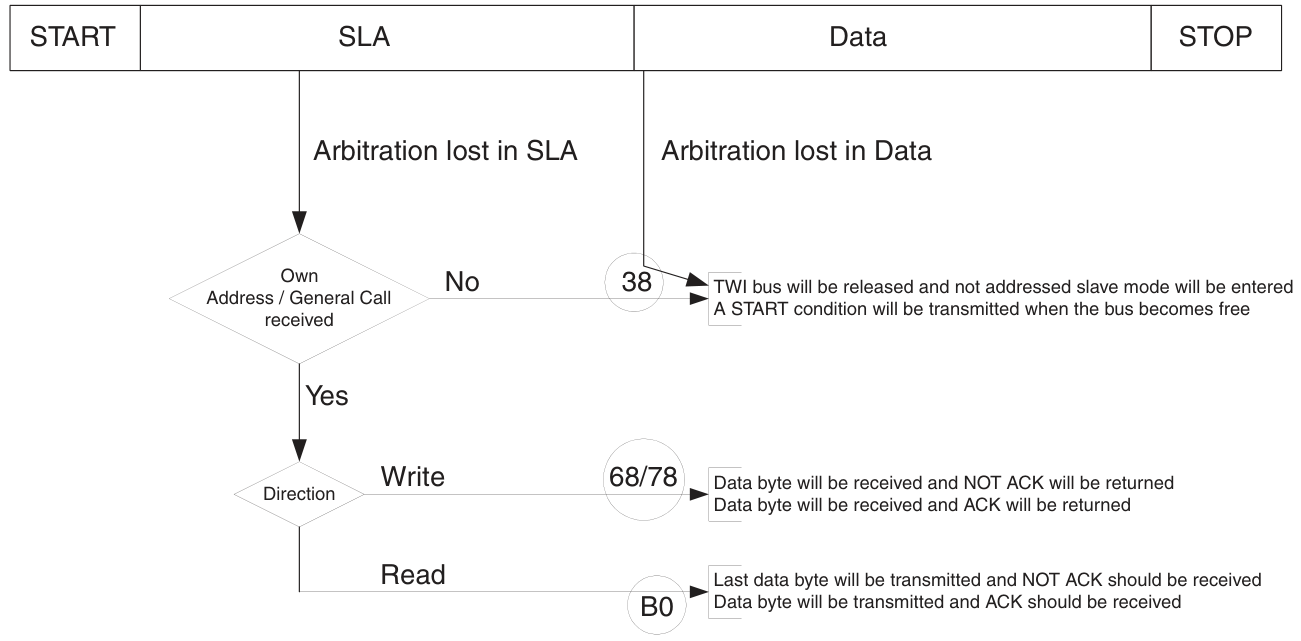
暫存器
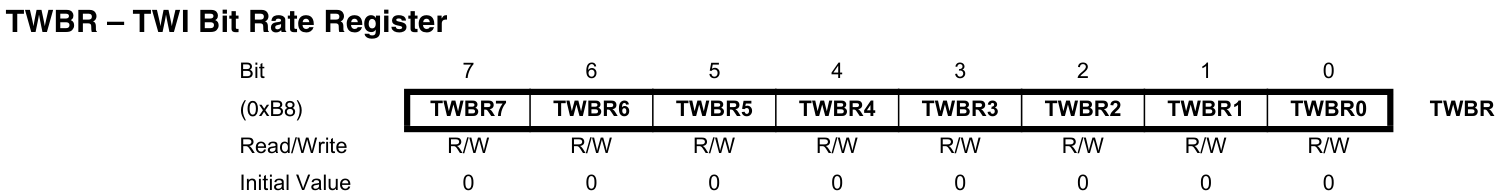
TWBR[7:0]:分頻係數,在主機模式下不能低於10。
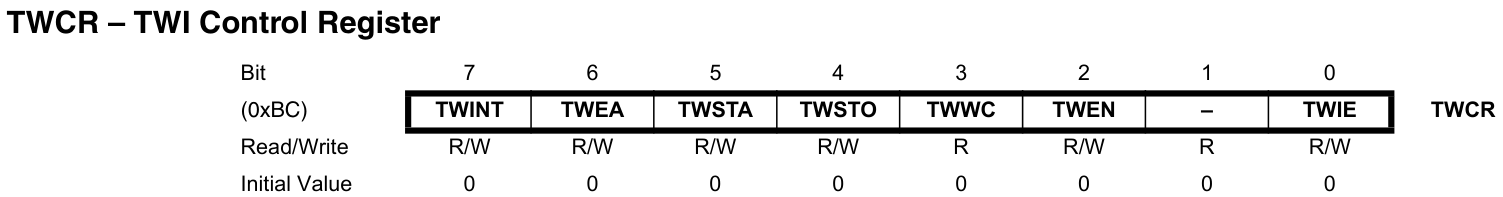
TWINT:TWI中斷標誌,必須寫1清除(不會執行完中斷自動清除),在清除前,必須完成對TWAR暫存器、TWSR暫存器、TWDR暫存器的操作。TWINT置位期間,SCL線始終保持低電平。TWEA:寫1使能應答。TWSTA:寫1產生START訊號,在START訊號傳輸完成後必須手動清除該位。TWSTO:寫1產生STOP訊號,該位會自動清除。從機狀態下,設定該位可以從錯誤狀態中恢復。TWWC:寫衝突標誌,在TWINT位為1時寫TWDR暫存器清除。TWEN:寫1使能TWI模組。TWIE:寫1使能TWI中斷。
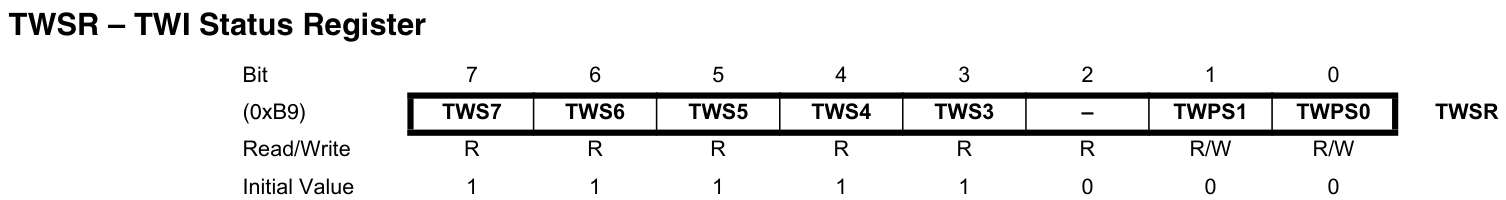
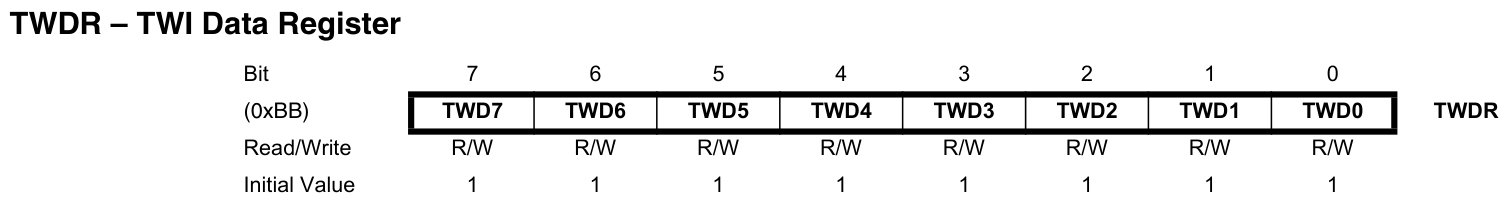
TWS:TWI狀態碼。TWPS:TWI分頻。
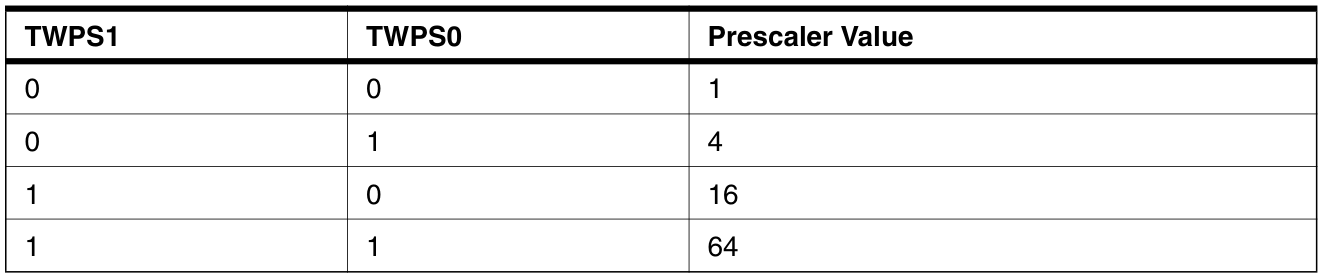
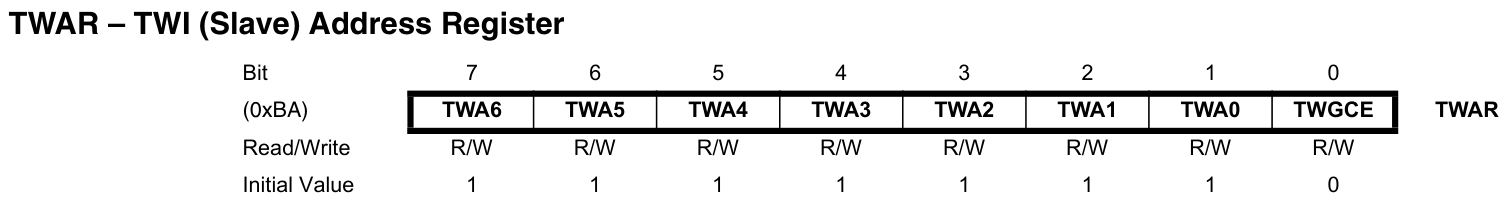
TWA[6:0]:TWI從機地址。TWGCE:寫1使能General Call。
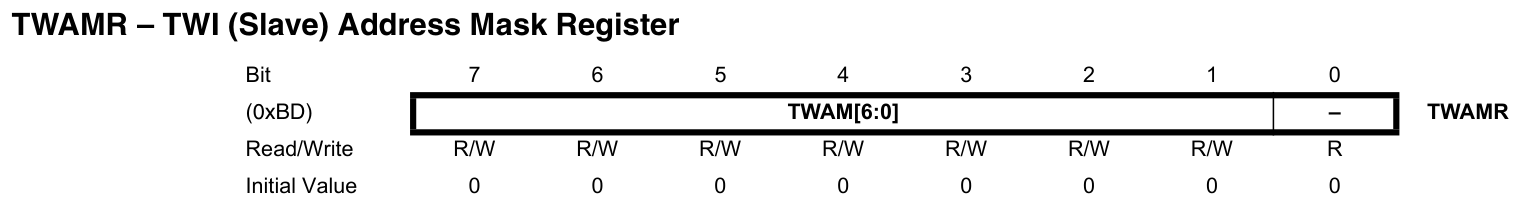
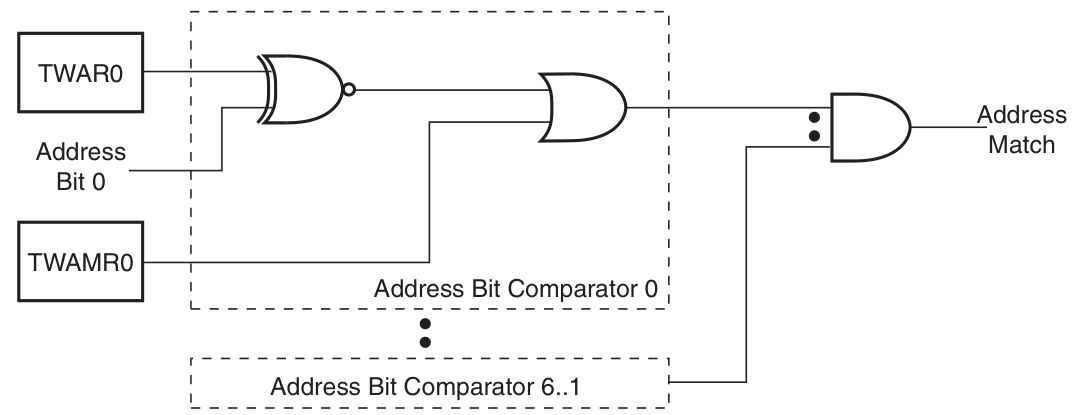
TWAM[6:0]:TWI地址掩碼,設為1將忽略對應位的匹配。
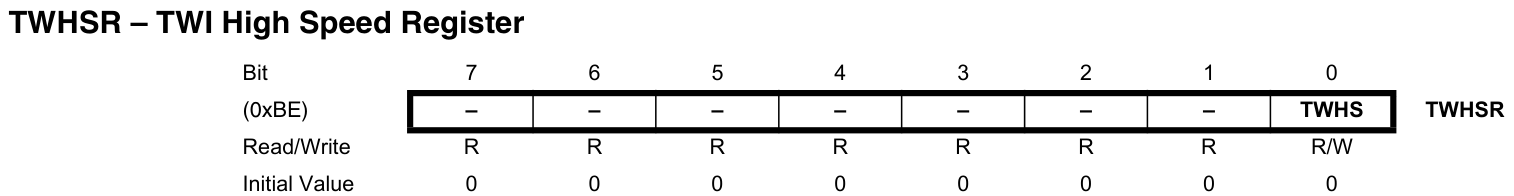
TWHS:寫1使能TWI高速模式。
程式碼
下面的程式碼展示瞭如何使用ATtiny88的TWI模組與SSD1306 OLED進行通訊刷屏。
原始檔的組織結構如下:
.
├── Makefile
├── inc
│ ├── serial.h
│ └── serial_stdio.h
└── src
├── main.c
├── serial.c
└── serial_stdio.c
src/main.c 原始檔的內容如下:
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <avr/io.h>
#include <avr/interrupt.h>
#include <serial_stdio.h>
#define OLED_ADDR 0x3C
#define oled_write_command(cmd) oled_write_byte(0, cmd)
#define oled_write_data(data) oled_write_byte(1, data)
static void oled_setup(void);
static void oled_write_byte(uint8_t dc, uint8_t data);
static void oled_fill(uint8_t color);
int main(void)
{
cli();
stdio_setup(); // initialize stdio and redirect it to serial
oled_setup(); // initialize oled
sei();
static const uint8_t colors[] = {
0x01, 0x02, 0x04, 0x08, 0x10, 0x20, 0x40,
0x80, 0x40, 0x20, 0x10, 0x08, 0x04, 0x02
};
uint8_t i = 0;
for (;;) {
oled_fill(colors[i]);
i = (i + 1) % sizeof(colors);
}
}
static void oled_setup(void)
{
static const uint8_t cmds[] = {
0xAE, 0xD5, 0x80, 0xA8, 0x3F,
0xD3, 0x00, 0x40, 0x8D, 0x14,
0x20, 0x00, 0xA1, 0xC8, 0xDA,
0x12, 0x81, 0xEF, 0xD9, 0xF1,
0xDB, 0x30, 0xA4, 0xA6, 0xAF
};
TWSR = 0x00; // TWPS = 1
TWBR = 12; // TWBR = 12, freq = 16MHz / (16 + 2 * 12 * 1) = 400KHz
TWHSR = 0x00; // disable high speed mode
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < sizeof(cmds); i++) {
oled_write_command(cmds[i]);
}
oled_fill(0x00);
}
static void oled_write_byte(uint8_t dc, uint8_t data)
{
// transmit START condition
TWCR = _BV(TWINT) | _BV(TWSTA) | _BV(TWEN);
while (!(TWCR & _BV(TWINT)));
// transmit SLA+W
TWDR = OLED_ADDR << 1;
TWCR = _BV(TWINT) | _BV(TWEN);
while (!(TWCR & _BV(TWINT)));
// transmit control byte
TWDR = dc ? 0x40 : 0x00;
TWCR = _BV(TWINT) | _BV(TWEN);
while (!(TWCR & _BV(TWINT)));
// transmit data byte
TWDR = data;
TWCR = _BV(TWINT) | _BV(TWEN);
while (!(TWCR & _BV(TWINT)));
// transmit STOP condition
TWCR = _BV(TWINT) | _BV(TWSTO) | _BV(TWEN);
// Note that TWINT is NOT set after a STOP condition has been transmitted
}
static void oled_fill(uint8_t color)
{
oled_write_command(0x21);
oled_write_command(0x00);
oled_write_command(0x7F);
oled_write_command(0x22);
oled_write_command(0x00);
oled_write_command(0x07);
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 128; i++) {
for (uint8_t j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
oled_write_data(color);
}
}
}
參考資料
本文來自部落格園,作者:chinjinyu,轉載請註明原文連結:https://www.cnblogs.com/chinjinyu/p/17696396.html