OptiX8入門(一)optixHello
本人初學者,如有錯誤和更好的表述,請指出
環境:CLion+VS2022+CUDA Toolkit 12.0.1+OptiX8
下載好後開啟SDK就可以看到OptiX官方提供的許多例子,CMake設定好後點開自己想看的內容直接開始看。推薦先把GAMES101看完之後再學API。可以看看檔案,但是是英文的
OptiX8是一個基於硬體的光追,主要分為三塊進行理解,管線(Pipeline),加速結構,shader binding table(sbt)(資源組織)。
GPU和CPU之間的區別只需記住,device表示GPU端,host表示CPU端。
管線就是設定整個光追流程,包括硬體部分的函數入口等。
加速結構,一般是BVH或KD-Tree,不懂的話當成黑盒使用即可,暫時不用去管,只要知道是提升光線的遍歷速度的就好。
shader binding table表示裡記錄所有shader的繫結資訊。
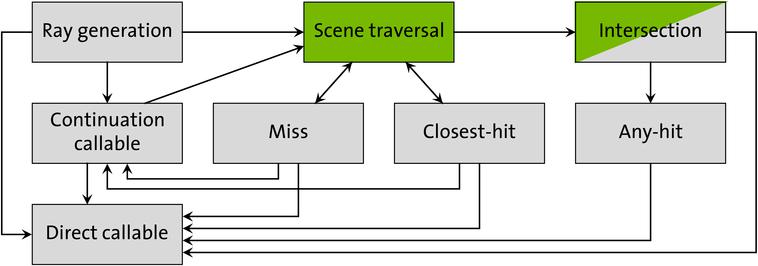
光追中主要存在這麼幾個函數:
Ray generation,可以理解為函數入口(main函數),對每個pixel都執行一遍,一般在這裡進行寫下TraceRay(發出光線)相關函數,具體是optixTrace()。Intersection,這個是光線和幾何體的碰撞,但據說很少用,因為三角形和box的光線交是內建的,一般用於自己定義的可以解析的曲面,例如球。Any hit,射線在任意碰到的交點都會觸發,但是不保證交點的觸發順序(應該是用加速結構的原因),也不保證一條線上所有的交點都會觸發,比如碰到某些點,會更新光線的TMin和TMax,而在[TMin,TMax]之外的點就不會觸發。Closest hit,一條射線上最早碰到的點,可以理解為直射,一般在這裡進行計算資訊,或者可以再發出射線。Miss,沒碰到場景,可以在這裡計算天空資訊,或者再發出射線。
不懂沒關係,看看程式碼,在這裡介紹下基礎的optixHello,這部分主要結果是生成一個帶顏色的畫面。
三個檔案,optixHello.h、draw_solid_color.cu、optixHello.cpp
cpp和h檔案就不說了,cu檔案用於GPU,編譯成ptx檔案後繫結到程式中進行執行,.cu檔案是可以printf進行偵錯的。
看下optixHello.h內容,對比一下draw_solid_color.cu,兩個都是在GPU和CPU通訊的引數。
struct Params
{
uchar4* image; //一維陣列,其中rgb皆為char型,用於填充畫面
unsigned int image_width; //只儲存width就夠了,對於(x,y)的資料用x*width+y就可以定位
};
struct RayGenData
{
float r,g,b; //在cu檔案中作為填充色
};
看下draw_solid_color.cu檔案,這裡的所有函數都要類似__raygen__開頭的命名
extern "C" {
__constant__ Params params; //記錄結果
}
extern "C"
__global__ void __raygen__draw_solid_color()
{
uint3 launch_index = optixGetLaunchIndex(); //獲取當前的pixel座標
RayGenData* rtData = (RayGenData*)optixGetSbtDataPointer(); //獲取sbt記錄的資料,在這裡是顏色,當然這個程式裡直接記錄在params也可以
params.image[launch_index.y * params.image_width + launch_index.x] =
make_color( make_float3( rtData->r, rtData->g, rtData->b ) ); //在image資料中記錄顏色
}
看下optixHello.cpp
建立context
// Initialize CUDA and create OptiX context
OptixDeviceContext context = nullptr;
{
// Initialize CUDA
CUDA_CHECK( cudaFree( 0 ) );
CUcontext cuCtx = 0; // zero means take the current context
OPTIX_CHECK( optixInit() );
OptixDeviceContextOptions options = {};
options.logCallbackFunction = &context_log_cb;
options.logCallbackLevel = 4;
OPTIX_CHECK( optixDeviceContextCreate( cuCtx, &options, &context ) );
}
建立module,在這裡繫結變數和cu檔案
// Create module
OptixModule module = nullptr;
OptixPipelineCompileOptions pipeline_compile_options = {};
{
OptixModuleCompileOptions module_compile_options = {};
#if !defined(NDEBUG)
module_compile_options.optLevel = OPTIX_COMPILE_OPTIMIZATION_LEVEL_0;
module_compile_options.debugLevel = OPTIX_COMPILE_DEBUG_LEVEL_FULL;
#endif
pipeline_compile_options.usesMotionBlur = false;
pipeline_compile_options.traversableGraphFlags = OPTIX_TRAVERSABLE_GRAPH_FLAG_ALLOW_SINGLE_LEVEL_INSTANCING;
pipeline_compile_options.numPayloadValues = 2;
pipeline_compile_options.numAttributeValues = 2;
pipeline_compile_options.exceptionFlags = OPTIX_EXCEPTION_FLAG_NONE; // TODO: should be OPTIX_EXCEPTION_FLAG_STACK_OVERFLOW;
pipeline_compile_options.pipelineLaunchParamsVariableName = "params"; //這裡繫結cu檔案的params變數
size_t inputSize = 0;
const char* input = sutil::getInputData( OPTIX_SAMPLE_NAME, OPTIX_SAMPLE_DIR, "draw_solid_color.cu", inputSize ); //這裡繫結cu檔案
OPTIX_CHECK_LOG( optixModuleCreate(
context,
&module_compile_options,
&pipeline_compile_options,
input,
inputSize,
LOG, &LOG_SIZE,
&module
) );
}
建立program groups,在這裡繫結函數
// Create program groups, including NULL miss and hitgroups
OptixProgramGroup raygen_prog_group = nullptr;
OptixProgramGroup miss_prog_group = nullptr;
{
OptixProgramGroupOptions program_group_options = {}; // Initialize to zeros
OptixProgramGroupDesc raygen_prog_group_desc = {}; //
raygen_prog_group_desc.kind = OPTIX_PROGRAM_GROUP_KIND_RAYGEN;
raygen_prog_group_desc.raygen.module = module;
raygen_prog_group_desc.raygen.entryFunctionName = "__raygen__draw_solid_color"; //看這裡繫結入口函數
OPTIX_CHECK_LOG( optixProgramGroupCreate(
context,
&raygen_prog_group_desc,
1, // num program groups
&program_group_options,
LOG, &LOG_SIZE,
&raygen_prog_group
) );
// Leave miss group's module and entryfunc name null
OptixProgramGroupDesc miss_prog_group_desc = {}; //這個是miss相關的,在這個程式裡暫時沒用
miss_prog_group_desc.kind = OPTIX_PROGRAM_GROUP_KIND_MISS;
OPTIX_CHECK_LOG( optixProgramGroupCreate(
context,
&miss_prog_group_desc,
1, // num program groups
&program_group_options,
LOG, &LOG_SIZE,
&miss_prog_group
) );
}
建立pipeline,這裡繫結program group
// Link pipeline
OptixPipeline pipeline = nullptr;
{
const uint32_t max_trace_depth = 0;
OptixProgramGroup program_groups[] = { raygen_prog_group };
OptixPipelineLinkOptions pipeline_link_options = {};
pipeline_link_options.maxTraceDepth = max_trace_depth;
OPTIX_CHECK_LOG( optixPipelineCreate( //建立pipeline,繫結program group
context,
&pipeline_compile_options,
&pipeline_link_options,
program_groups,
sizeof( program_groups ) / sizeof( program_groups[0] ),
LOG, &LOG_SIZE,
&pipeline
) );
OptixStackSizes stack_sizes = {};
for( auto& prog_group : program_groups )
{
OPTIX_CHECK( optixUtilAccumulateStackSizes( prog_group, &stack_sizes, pipeline ) );
}
uint32_t direct_callable_stack_size_from_traversal;
uint32_t direct_callable_stack_size_from_state;
uint32_t continuation_stack_size;
OPTIX_CHECK( optixUtilComputeStackSizes( &stack_sizes, max_trace_depth,
0, // maxCCDepth
0, // maxDCDEpth
&direct_callable_stack_size_from_traversal,
&direct_callable_stack_size_from_state, &continuation_stack_size ) );
OPTIX_CHECK( optixPipelineSetStackSize( pipeline, direct_callable_stack_size_from_traversal,
direct_callable_stack_size_from_state, continuation_stack_size,
2 // maxTraversableDepth
) );
}
建立sbt,在這裡設定record和傳進去的data,在這裡就是生成的顏色
// Set up shader binding table
OptixShaderBindingTable sbt = {};
{
CUdeviceptr raygen_record;
const size_t raygen_record_size = sizeof( RayGenSbtRecord );
CUDA_CHECK( cudaMalloc( reinterpret_cast<void**>( &raygen_record ), raygen_record_size ) );
RayGenSbtRecord rg_sbt;
OPTIX_CHECK( optixSbtRecordPackHeader( raygen_prog_group, &rg_sbt ) );
rg_sbt.data = {0.462f, 0.725f, 0.f};
CUDA_CHECK( cudaMemcpy(
reinterpret_cast<void*>( raygen_record ),
&rg_sbt,
raygen_record_size,
cudaMemcpyHostToDevice
) );
CUdeviceptr miss_record;
size_t miss_record_size = sizeof( MissSbtRecord );
CUDA_CHECK( cudaMalloc( reinterpret_cast<void**>( &miss_record ), miss_record_size ) );
RayGenSbtRecord ms_sbt;
OPTIX_CHECK( optixSbtRecordPackHeader( miss_prog_group, &ms_sbt ) );
CUDA_CHECK( cudaMemcpy(
reinterpret_cast<void*>( miss_record ),
&ms_sbt,
miss_record_size,
cudaMemcpyHostToDevice
) );
sbt.raygenRecord = raygen_record;
sbt.missRecordBase = miss_record;
sbt.missRecordStrideInBytes = sizeof( MissSbtRecord );
sbt.missRecordCount = 1;
}
建立outputbuffer用於接收結果,然後launch,這個launch會在每個pixel中執行一次
sutil::CUDAOutputBuffer<uchar4> output_buffer( sutil::CUDAOutputBufferType::CUDA_DEVICE, width, height );
// launch
{
CUstream stream;
CUDA_CHECK( cudaStreamCreate( &stream ) );
Params params;
params.image = output_buffer.map(); //對應到outputbuffer
params.image_width = width;
CUdeviceptr d_param; //建立一個GPU指標
CUDA_CHECK( cudaMalloc( reinterpret_cast<void**>( &d_param ), sizeof( Params ) ) ); //malloc一個GPU空間存放Params
CUDA_CHECK( cudaMemcpy(
reinterpret_cast<void*>( d_param ),
¶ms, sizeof( params ),
cudaMemcpyHostToDevice
) );
OPTIX_CHECK( optixLaunch( pipeline, stream, d_param, sizeof( Params ), &sbt, width, height, /*depth=*/1 ) );
CUDA_SYNC_CHECK();
output_buffer.unmap();
CUDA_CHECK( cudaFree( reinterpret_cast<void*>( d_param ) ) );
}
顯示影象
//// Display results
{
sutil::ImageBuffer buffer;
buffer.data = output_buffer.getHostPointer(); //這裡要在CPU端展示,因此要轉為CPU端的資料
buffer.width = width;
buffer.height = height;
buffer.pixel_format = sutil::BufferImageFormat::UNSIGNED_BYTE4; //對應uchar4
if( outfile.empty() )
sutil::displayBufferWindow( argv[0], buffer );
else
sutil::saveImage( outfile.c_str(), buffer, false );
}
清理資源,注意正序生成,倒序清理
// Cleanup
{
CUDA_CHECK( cudaFree( reinterpret_cast<void*>( sbt.raygenRecord ) ) );
CUDA_CHECK( cudaFree( reinterpret_cast<void*>( sbt.missRecordBase ) ) );
OPTIX_CHECK( optixPipelineDestroy( pipeline ) );
OPTIX_CHECK( optixProgramGroupDestroy( miss_prog_group ) );
OPTIX_CHECK( optixProgramGroupDestroy( raygen_prog_group ) );
OPTIX_CHECK( optixModuleDestroy( module ) );
OPTIX_CHECK( optixDeviceContextDestroy( context ) );
}
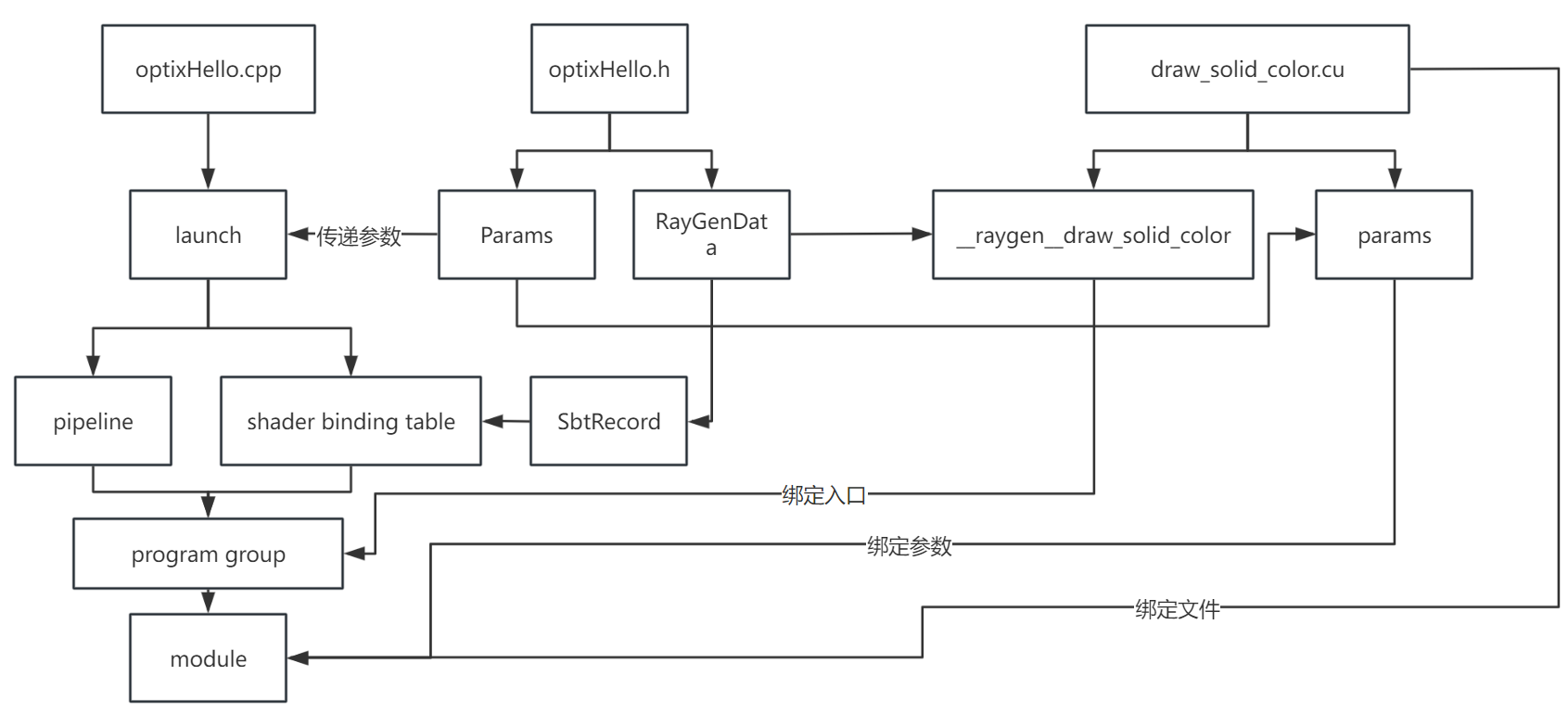
整個程式的大致結構如圖(不保證正確)
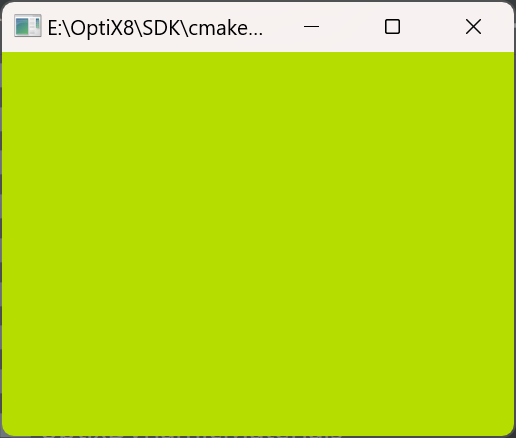
執行結果:
碼字不易,點個贊吧
總結
整個程式流程大致就是:
- 建立加速結構(在這裡沒有)
- 建立
module、program group - 建立
pipeline、sbt launch,顯示影象
每個pixel中執行launch,在這裡就是每個pixel執行__raygen__draw_solid_color函數設定顏色,傳遞形成一個outbuffer一維陣列,形成影象。