Parallel 與 ConcurrentBag<T> 這對兒黃金搭檔(C#)
〇、前言
日常開發中經常會遇到資料統計,特別是關於報表的專案。資料處理的效率和準確度當然是首要關注點。
本文主要介紹,如何通過 Parallel 來並行處理資料,並組合 ConcurrentBag<T> 集合,來將處理效率達到高點的同時,也能確保資料的準確。
一、ConcurrentBag<T> 簡介
1、簡介與原始碼
ConcurrentBag<T>,表示物件的執行緒安全的無序集合。ConcurrentBag 內部將資料按執行緒的標識獨立進行儲存,程式可以在同一個執行緒中插入、刪除元素,所以每個執行緒對其資料的操作是非常快的。
下面是原始碼供參考:
點選展開 ConcurrentBag 原始碼
// System.Collections.Concurrent, Version=5.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b03f5f7f11d50a3a
// System.Collections.Concurrent.ConcurrentBag<T>
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Concurrent;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Diagnostics.CodeAnalysis;
using System.Threading;
[DebuggerTypeProxy(typeof(System.Collections.Concurrent.IProducerConsumerCollectionDebugView<>))]
[DebuggerDisplay("Count = {Count}")]
public class ConcurrentBag<T> : IProducerConsumerCollection<T>, IEnumerable<T>, IEnumerable, ICollection, IReadOnlyCollection<T>
{
private sealed class WorkStealingQueue
{
private volatile int _headIndex;
private volatile int _tailIndex;
private volatile T[] _array = new T[32];
private volatile int _mask = 31;
private int _addTakeCount;
private int _stealCount;
internal volatile int _currentOp;
internal bool _frozen;
internal readonly WorkStealingQueue _nextQueue;
internal readonly int _ownerThreadId;
internal bool IsEmpty => _headIndex - _tailIndex >= 0;
internal int DangerousCount
{
get
{
int stealCount = _stealCount;
int addTakeCount = _addTakeCount;
return addTakeCount - stealCount;
}
}
internal WorkStealingQueue(WorkStealingQueue nextQueue)
{
_ownerThreadId = Environment.CurrentManagedThreadId;
_nextQueue = nextQueue;
}
internal void LocalPush(T item, ref long emptyToNonEmptyListTransitionCount)
{
bool lockTaken = false;
try
{
Interlocked.Exchange(ref _currentOp, 1);
int num = _tailIndex;
if (num == int.MaxValue)
{
_currentOp = 0;
lock (this)
{
_headIndex &= _mask;
num = (_tailIndex = num & _mask);
Interlocked.Exchange(ref _currentOp, 1);
}
}
int headIndex = _headIndex;
if (!_frozen && headIndex - (num - 1) < 0 && num - (headIndex + _mask) < 0)
{
_array[num & _mask] = item;
_tailIndex = num + 1;
}
else
{
_currentOp = 0;
Monitor.Enter(this, ref lockTaken);
headIndex = _headIndex;
int num2 = num - headIndex;
if (num2 >= _mask)
{
T[] array = new T[_array.Length << 1];
int num3 = headIndex & _mask;
if (num3 == 0)
{
Array.Copy(_array, array, _array.Length);
}
else
{
Array.Copy(_array, num3, array, 0, _array.Length - num3);
Array.Copy(_array, 0, array, _array.Length - num3, num3);
}
_array = array;
_headIndex = 0;
num = (_tailIndex = num2);
_mask = (_mask << 1) | 1;
}
_array[num & _mask] = item;
_tailIndex = num + 1;
if (num2 == 0)
{
Interlocked.Increment(ref emptyToNonEmptyListTransitionCount);
}
_addTakeCount -= _stealCount;
_stealCount = 0;
}
checked
{
_addTakeCount++;
}
}
finally
{
_currentOp = 0;
if (lockTaken)
{
Monitor.Exit(this);
}
}
}
internal void LocalClear()
{
lock (this)
{
if (_headIndex - _tailIndex < 0)
{
_headIndex = (_tailIndex = 0);
_addTakeCount = (_stealCount = 0);
Array.Clear(_array, 0, _array.Length);
}
}
}
internal bool TryLocalPop([MaybeNullWhen(false)] out T result)
{
int tailIndex = _tailIndex;
if (_headIndex - tailIndex >= 0)
{
result = default(T);
return false;
}
bool lockTaken = false;
try
{
_currentOp = 2;
Interlocked.Exchange(ref _tailIndex, --tailIndex);
if (!_frozen && _headIndex - tailIndex < 0)
{
int num = tailIndex & _mask;
result = _array[num];
_array[num] = default(T);
_addTakeCount--;
return true;
}
_currentOp = 0;
Monitor.Enter(this, ref lockTaken);
if (_headIndex - tailIndex <= 0)
{
int num2 = tailIndex & _mask;
result = _array[num2];
_array[num2] = default(T);
_addTakeCount--;
return true;
}
_tailIndex = tailIndex + 1;
result = default(T);
return false;
}
finally
{
_currentOp = 0;
if (lockTaken)
{
Monitor.Exit(this);
}
}
}
internal bool TryLocalPeek([MaybeNullWhen(false)] out T result)
{
int tailIndex = _tailIndex;
if (_headIndex - tailIndex < 0)
{
lock (this)
{
if (_headIndex - tailIndex < 0)
{
result = _array[(tailIndex - 1) & _mask];
return true;
}
}
}
result = default(T);
return false;
}
internal bool TrySteal([MaybeNullWhen(false)] out T result, bool take)
{
lock (this)
{
int headIndex = _headIndex;
if (take)
{
if (headIndex - (_tailIndex - 2) >= 0 && _currentOp == 1)
{
SpinWait spinWait = default(SpinWait);
do
{
spinWait.SpinOnce();
}
while (_currentOp == 1);
}
Interlocked.Exchange(ref _headIndex, headIndex + 1);
if (headIndex < _tailIndex)
{
int num = headIndex & _mask;
result = _array[num];
_array[num] = default(T);
_stealCount++;
return true;
}
_headIndex = headIndex;
}
else if (headIndex < _tailIndex)
{
result = _array[headIndex & _mask];
return true;
}
}
result = default(T);
return false;
}
internal int DangerousCopyTo(T[] array, int arrayIndex)
{
int headIndex = _headIndex;
int dangerousCount = DangerousCount;
for (int num = arrayIndex + dangerousCount - 1; num >= arrayIndex; num--)
{
array[num] = _array[headIndex++ & _mask];
}
return dangerousCount;
}
}
private sealed class Enumerator : IEnumerator<T>, IDisposable, IEnumerator
{
private readonly T[] _array;
private T _current;
private int _index;
public T Current => _current;
object IEnumerator.Current
{
get
{
if (_index == 0 || _index == _array.Length + 1)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(System.SR.ConcurrentBag_Enumerator_EnumerationNotStartedOrAlreadyFinished);
}
return Current;
}
}
public Enumerator(T[] array)
{
_array = array;
}
public bool MoveNext()
{
if (_index < _array.Length)
{
_current = _array[_index++];
return true;
}
_index = _array.Length + 1;
return false;
}
public void Reset()
{
_index = 0;
_current = default(T);
}
public void Dispose()
{
}
}
private readonly ThreadLocal<WorkStealingQueue> _locals;
private volatile WorkStealingQueue _workStealingQueues;
private long _emptyToNonEmptyListTransitionCount;
public int Count
{
get
{
if (_workStealingQueues == null)
{
return 0;
}
bool lockTaken = false;
try
{
FreezeBag(ref lockTaken);
return DangerousCount;
}
finally
{
UnfreezeBag(lockTaken);
}
}
}
private int DangerousCount
{
get
{
int num = 0;
for (WorkStealingQueue workStealingQueue = _workStealingQueues; workStealingQueue != null; workStealingQueue = workStealingQueue._nextQueue)
{
num = checked(num + workStealingQueue.DangerousCount);
}
return num;
}
}
public bool IsEmpty
{
get
{
WorkStealingQueue currentThreadWorkStealingQueue = GetCurrentThreadWorkStealingQueue(forceCreate: false);
if (currentThreadWorkStealingQueue != null)
{
if (!currentThreadWorkStealingQueue.IsEmpty)
{
return false;
}
if (currentThreadWorkStealingQueue._nextQueue == null && currentThreadWorkStealingQueue == _workStealingQueues)
{
return true;
}
}
bool lockTaken = false;
try
{
FreezeBag(ref lockTaken);
for (WorkStealingQueue workStealingQueue = _workStealingQueues; workStealingQueue != null; workStealingQueue = workStealingQueue._nextQueue)
{
if (!workStealingQueue.IsEmpty)
{
return false;
}
}
}
finally
{
UnfreezeBag(lockTaken);
}
return true;
}
}
bool ICollection.IsSynchronized => false;
object ICollection.SyncRoot
{
get
{
throw new NotSupportedException(System.SR.ConcurrentCollection_SyncRoot_NotSupported);
}
}
private object GlobalQueuesLock => _locals;
public ConcurrentBag()
{
_locals = new ThreadLocal<WorkStealingQueue>();
}
public ConcurrentBag(IEnumerable<T> collection)
{
if (collection == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("collection", System.SR.ConcurrentBag_Ctor_ArgumentNullException);
}
_locals = new ThreadLocal<WorkStealingQueue>();
WorkStealingQueue currentThreadWorkStealingQueue = GetCurrentThreadWorkStealingQueue(forceCreate: true);
foreach (T item in collection)
{
currentThreadWorkStealingQueue.LocalPush(item, ref _emptyToNonEmptyListTransitionCount);
}
}
public void Add(T item)
{
GetCurrentThreadWorkStealingQueue(forceCreate: true).LocalPush(item, ref _emptyToNonEmptyListTransitionCount);
}
bool IProducerConsumerCollection<T>.TryAdd(T item)
{
Add(item);
return true;
}
public bool TryTake([MaybeNullWhen(false)] out T result)
{
WorkStealingQueue currentThreadWorkStealingQueue = GetCurrentThreadWorkStealingQueue(forceCreate: false);
if (currentThreadWorkStealingQueue == null || !currentThreadWorkStealingQueue.TryLocalPop(out result))
{
return TrySteal(out result, take: true);
}
return true;
}
public bool TryPeek([MaybeNullWhen(false)] out T result)
{
WorkStealingQueue currentThreadWorkStealingQueue = GetCurrentThreadWorkStealingQueue(forceCreate: false);
if (currentThreadWorkStealingQueue == null || !currentThreadWorkStealingQueue.TryLocalPeek(out result))
{
return TrySteal(out result, take: false);
}
return true;
}
private WorkStealingQueue GetCurrentThreadWorkStealingQueue(bool forceCreate)
{
WorkStealingQueue workStealingQueue = _locals.Value;
if (workStealingQueue == null)
{
if (!forceCreate)
{
return null;
}
workStealingQueue = CreateWorkStealingQueueForCurrentThread();
}
return workStealingQueue;
}
private WorkStealingQueue CreateWorkStealingQueueForCurrentThread()
{
lock (GlobalQueuesLock)
{
WorkStealingQueue workStealingQueues = _workStealingQueues;
WorkStealingQueue workStealingQueue = ((workStealingQueues != null) ? GetUnownedWorkStealingQueue() : null);
if (workStealingQueue == null)
{
workStealingQueue = (_workStealingQueues = new WorkStealingQueue(workStealingQueues));
}
_locals.Value = workStealingQueue;
return workStealingQueue;
}
}
private WorkStealingQueue GetUnownedWorkStealingQueue()
{
int currentManagedThreadId = Environment.CurrentManagedThreadId;
for (WorkStealingQueue workStealingQueue = _workStealingQueues; workStealingQueue != null; workStealingQueue = workStealingQueue._nextQueue)
{
if (workStealingQueue._ownerThreadId == currentManagedThreadId)
{
return workStealingQueue;
}
}
return null;
}
private bool TrySteal([MaybeNullWhen(false)] out T result, bool take)
{
if (CDSCollectionETWBCLProvider.Log.IsEnabled())
{
if (take)
{
CDSCollectionETWBCLProvider.Log.ConcurrentBag_TryTakeSteals();
}
else
{
CDSCollectionETWBCLProvider.Log.ConcurrentBag_TryPeekSteals();
}
}
while (true)
{
long num = Interlocked.Read(ref _emptyToNonEmptyListTransitionCount);
WorkStealingQueue currentThreadWorkStealingQueue = GetCurrentThreadWorkStealingQueue(forceCreate: false);
bool num2;
if (currentThreadWorkStealingQueue != null)
{
if (TryStealFromTo(currentThreadWorkStealingQueue._nextQueue, null, out result, take))
{
goto IL_0078;
}
num2 = TryStealFromTo(_workStealingQueues, currentThreadWorkStealingQueue, out result, take);
}
else
{
num2 = TryStealFromTo(_workStealingQueues, null, out result, take);
}
if (!num2)
{
if (Interlocked.Read(ref _emptyToNonEmptyListTransitionCount) == num)
{
break;
}
continue;
}
goto IL_0078;
IL_0078:
return true;
}
return false;
}
private bool TryStealFromTo(WorkStealingQueue startInclusive, WorkStealingQueue endExclusive, [MaybeNullWhen(false)] out T result, bool take)
{
for (WorkStealingQueue workStealingQueue = startInclusive; workStealingQueue != endExclusive; workStealingQueue = workStealingQueue._nextQueue)
{
if (workStealingQueue.TrySteal(out result, take))
{
return true;
}
}
result = default(T);
return false;
}
public void CopyTo(T[] array, int index)
{
if (array == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("array", System.SR.ConcurrentBag_CopyTo_ArgumentNullException);
}
if (index < 0)
{
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("index", System.SR.Collection_CopyTo_ArgumentOutOfRangeException);
}
if (_workStealingQueues == null)
{
return;
}
bool lockTaken = false;
try
{
FreezeBag(ref lockTaken);
int dangerousCount = DangerousCount;
if (index > array.Length - dangerousCount)
{
throw new ArgumentException(System.SR.Collection_CopyTo_TooManyElems, "index");
}
try
{
int num = CopyFromEachQueueToArray(array, index);
}
catch (ArrayTypeMismatchException ex)
{
throw new InvalidCastException(ex.Message, ex);
}
}
finally
{
UnfreezeBag(lockTaken);
}
}
private int CopyFromEachQueueToArray(T[] array, int index)
{
int num = index;
for (WorkStealingQueue workStealingQueue = _workStealingQueues; workStealingQueue != null; workStealingQueue = workStealingQueue._nextQueue)
{
num += workStealingQueue.DangerousCopyTo(array, num);
}
return num - index;
}
void ICollection.CopyTo(Array array, int index)
{
if (array is T[] array2)
{
CopyTo(array2, index);
return;
}
if (array == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("array", System.SR.ConcurrentBag_CopyTo_ArgumentNullException);
}
ToArray().CopyTo(array, index);
}
public T[] ToArray()
{
if (_workStealingQueues != null)
{
bool lockTaken = false;
try
{
FreezeBag(ref lockTaken);
int dangerousCount = DangerousCount;
if (dangerousCount > 0)
{
T[] array = new T[dangerousCount];
int num = CopyFromEachQueueToArray(array, 0);
return array;
}
}
finally
{
UnfreezeBag(lockTaken);
}
}
return Array.Empty<T>();
}
public void Clear()
{
if (_workStealingQueues == null)
{
return;
}
WorkStealingQueue currentThreadWorkStealingQueue = GetCurrentThreadWorkStealingQueue(forceCreate: false);
if (currentThreadWorkStealingQueue != null)
{
currentThreadWorkStealingQueue.LocalClear();
if (currentThreadWorkStealingQueue._nextQueue == null && currentThreadWorkStealingQueue == _workStealingQueues)
{
return;
}
}
bool lockTaken = false;
try
{
FreezeBag(ref lockTaken);
for (WorkStealingQueue workStealingQueue = _workStealingQueues; workStealingQueue != null; workStealingQueue = workStealingQueue._nextQueue)
{
T result;
while (workStealingQueue.TrySteal(out result, take: true))
{
}
}
}
finally
{
UnfreezeBag(lockTaken);
}
}
public IEnumerator<T> GetEnumerator()
{
return new Enumerator(ToArray());
}
IEnumerator IEnumerable.GetEnumerator()
{
return GetEnumerator();
}
private void FreezeBag(ref bool lockTaken)
{
Monitor.Enter(GlobalQueuesLock, ref lockTaken);
WorkStealingQueue workStealingQueues = _workStealingQueues;
for (WorkStealingQueue workStealingQueue = workStealingQueues; workStealingQueue != null; workStealingQueue = workStealingQueue._nextQueue)
{
Monitor.Enter(workStealingQueue, ref workStealingQueue._frozen);
}
Interlocked.MemoryBarrier();
for (WorkStealingQueue workStealingQueue2 = workStealingQueues; workStealingQueue2 != null; workStealingQueue2 = workStealingQueue2._nextQueue)
{
if (workStealingQueue2._currentOp != 0)
{
SpinWait spinWait = default(SpinWait);
do
{
spinWait.SpinOnce();
}
while (workStealingQueue2._currentOp != 0);
}
}
}
private void UnfreezeBag(bool lockTaken)
{
if (!lockTaken)
{
return;
}
for (WorkStealingQueue workStealingQueue = _workStealingQueues; workStealingQueue != null; workStealingQueue = workStealingQueue._nextQueue)
{
if (workStealingQueue._frozen)
{
workStealingQueue._frozen = false;
Monitor.Exit(workStealingQueue);
}
}
Monitor.Exit(GlobalQueuesLock);
}
}2、屬性
Count
獲取 ConcurrentBag<T> 中包含的元素數
IsEmpty
獲取一個值,該值指示 ConcurrentBag<T> 是否為空
3、方法
Add(T)
將物件新增到 ConcurrentBag<T> 中。
Clear()
從 ConcurrentBag<T> 中刪除所有值。
CopyTo(T[], Int32)
從指定陣列索引開始將 ConcurrentBag<T> 元素複製到現有一維 Array 中。以下範例程式碼:
ConcurrentBag<TempModel> tempModels = new ConcurrentBag<TempModel>();
tempModels.Add(new TempModel() { Code = "1", Name = "一" });
tempModels.Add(new TempModel() { Code = "2", Name = "二" });
tempModels.Add(new TempModel() { Code = "3", Name = "三" });
TempModel[] temparr = new TempModel[5];
tempModels.CopyTo(temparr, 1);輸出結果為:
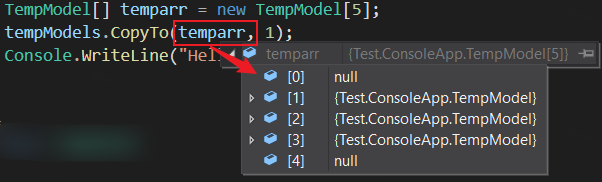
TryPeek(T)
嘗試從 ConcurrentBag<T> 返回一個物件但不移除該物件。
TryTake(T)
嘗試從 ConcurrentBag<T> 中移除和返回一個物件。
ToString()
返回表示當前物件的字串。測試值:System.Collections.Concurrent.ConcurrentBag`1[Test.ConsoleApp.TempModel]
ToArray()
將 ConcurrentBag<T> 元素複製到新陣列。
GetEnumerator()
獲取當前時間的列舉元。 呼叫後不影響集合的任何更新。列舉元可以安全地與讀取、寫入 ConcurrentBag<T> 同時使用。
GetHashCode()
獲取集合的雜湊值。
4、List<T> 和 ConcurrentBag<T> 對比
眾所周知,List<T> 集合是非執行緒安全的,所以我們採用並行程式設計時會發生丟資料的情況。比如我們通過多執行緒將一千個物件加入 List<T>,我們最終得到的集合中元素數就會小於一千。
如下測試程式碼,通過多工物件 Task 實現將一千個物件加入到 List<T> 中,新增了一千次,但實際上最終的 objects.Count() 值為 913,小於 1000。 但如果將集合名稱改成 ConcurrentBag<T>,結果就不會丟失,最終為等於 1000。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
// List<MyObject> objects = new List<MyObject>();
ConcurrentBag<MyObject> objects = new ConcurrentBag<MyObject>();
Task[] tasks = new Task[1000];
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
tasks[i] = Task.Run(() =>
objects.Add(new MyObject() { Name = "1", Threadnum = Thread.GetCurrentProcessorId() }));
}
Task.WaitAll(tasks); // 等待所有任務完成
Console.WriteLine(objects.Count()); // List<T>:913; ConcurrentBag<T>:1000
Console.ReadLine();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
}
}
public class MyObject
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Threadnum { get; set; }
}二、Parallel 的使用
任務並行庫(TPL)支援通過 System.Threading.Tasks.Parallel 類實現資料操作的並行。Parallel.For 或 Parallel.ForEach 編寫的迴圈邏輯與常見的 for 和 foreach 類似,只是增加並行邏輯,來提升效率。TPL 省去了使用者端建立執行緒或列工作項,同時在基本回圈中,不需要加鎖,TPL 會處理所有低階別的工作。
常用的方法有 Parallel.For、Parallel.ForEach、Parallel.Invoke 等,下面將一一例舉。
1、Parallel.For()
1.1 過載一:Parallel.For(Int32, Int32, Action<Int32>)
// fromInclusive:開始索引(含) toExclusive:結束索引(不含) body:不允許為 null
public static System.Threading.Tasks.ParallelLoopResult For (int fromInclusive, int toExclusive, Action<int> body);以下範例使用 For 方法呼叫 100 個委託,該委託生成隨機 Byte 值,並計算其總和:
ParallelLoopResult result = Parallel.For(0, 100,
ctr =>
{
//Random rnd = new Random(ctr * 100000); // public Random(int Seed); // 亂數的種子,若種子相同,多次生成的亂數序列值相同
Random rnd = new Random();
Byte[] bytes = new Byte[100]; // Byte 陣列,每個值的範圍為 0~255
rnd.NextBytes(bytes); // 生成 100 個 Byte 數值
int sum = 0;
foreach (var byt in bytes) // 再將生成的 100 個數值相加
sum += byt;
Console.WriteLine("Iteration {0,2}: {1:N0}", ctr, sum);
});
Console.WriteLine("Result: Completed Normally");1.2 比較執行效率 Parallel.For() 和 for()
Paraller.For() 方法類似於 for 迴圈語句,也是根據入參多次執行同一邏輯操作。使用 Paraller.For() 方法,可以無序的並行執行迭代,而 for 迴圈只能根據既定的順序序列執行。
如下範例,對比 Parallel.For() 和 for() 迴圈的執行效率進行比較:
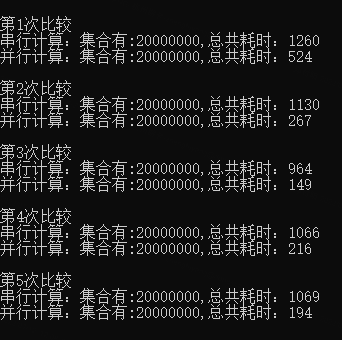
// 進行 5 此對比
for (int j = 1; j < 6; j++)
{
// for()
Console.WriteLine($"\n第{j}次比較");
ConcurrentBag<int> bag = new ConcurrentBag<int>();
var watch = Stopwatch.StartNew();
watch.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < 20000000; i++)
{
bag.Add(i);
}
watch.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"序列計算:集合有:{bag.Count},總共耗時:{watch.ElapsedMilliseconds}");
// Parallel.For()
bag = new ConcurrentBag<int>();
watch = Stopwatch.StartNew();
watch.Start();
Parallel.For(0, 20000000, i => // i 為整數序列號
{
bag.Add(i);
});
watch.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"平行計算:集合有:{bag.Count},總共耗時:{watch.ElapsedMilliseconds}");
}程式碼總共執行了五次對比,如下圖中的耗時比較,很明顯,採用並行的 Parallel.For() 遠比序列的 for() 效率要高許多。
1.3 過載二:Parallel.For(Int32, Int32, Action<Int32,ParallelLoopState>)
// fromInclusive:開始索引(含) toExclusive:結束索引(不含) body:不允許為 null
public static ParallelLoopResult For (int fromInclusive, int toExclusive, Action<int, ParallelLoopState> body);此過載增加了 System.Threading.Tasks.ParallelLoopState 迴圈狀態引數,從而使得我們可以通過迴圈狀態來控制並行迴圈的執行。
以下範例,執行 100 次迭代,在亂數 breakIndex 指示的一次迭代時進行中斷操作,呼叫完 Break() 方法後,迴圈狀態的 ShouldExitCurrentIteration 屬性值就是 true,然後進入判斷if (state.LowestBreakIteration < i),當當前迭代序號大於中斷時的序號,就直接返回,不再進行後續操作。
var rnd = new Random();
int breakIndex = rnd.Next(1, 11);
Console.WriteLine($"Will call Break at iteration {breakIndex}\n");
var result = Parallel.For(1, 101, (i, state) => // 實際執行的是 1 ~ 100,不包含 101
{
Console.WriteLine($"Beginning iteration {i} {Thread.GetCurrentProcessorId()}");
int delay;
lock (rnd)
delay = rnd.Next(1, 1001);
Thread.Sleep(delay);
if (state.ShouldExitCurrentIteration)
{
if (state.LowestBreakIteration < i)
return;
}
if (i == breakIndex) // 8
{
Console.WriteLine($"Break in iteration {i}");
state.Break();
}
Console.WriteLine($"Completed iteration {i} {Thread.GetCurrentProcessorId()}");
});
if (result.LowestBreakIteration.HasValue)
Console.WriteLine($"\nLowest Break Iteration: {result.LowestBreakIteration}");
else
Console.WriteLine($"\nNo lowest break iteration.");如下是當索引值為 9 時的處理過程:(當迭代序號為 9 時,執行 Break(),此之前已經開始迭代執行的大於 9 的迭代,均直接退出,只有開始沒有結束)

1.4 過載三:Parallel.For(Int32, Int32, ParallelOptions, Action<Int32,ParallelLoopState>)
// fromInclusive:開始索引(含) toExclusive:結束索引(不含) body:不允許為 null
public static ParallelLoopResult For (int fromInclusive, int toExclusive, ParallelOptions parallelOptions, Action<int, ParallelLoopState> body);此過載在執行 for 迴圈時,可以設定迴圈選項 ParallelOptions。
下邊是一個範例,通過設定 ParallelOptions 的 CancellationToken 屬性,使得迴圈支援手動取消:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
CancellationTokenSource cancellationSource = new CancellationTokenSource();
ParallelOptions options = new ParallelOptions();
options.CancellationToken = cancellationSource.Token;
try
{
ParallelLoopResult loopResult = Parallel.For( 0, 10, options,
(i, loopState) =>
{
Console.WriteLine("Start Thread={0}, i={1}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId, i);
if (i == 5) // 模擬某次迭代執行時,取消迴圈
{
cancellationSource.Cancel();
}
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++)
{
Thread.Sleep(1 * 200); // 模擬耗時任務
if (loopState.ShouldExitCurrentIteration) // 判斷迴圈是否已經取消執行
return;
}
Console.WriteLine($"Finish Thread={Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}, i={i}");
}
);
if (loopResult.IsCompleted)
{
Console.WriteLine("All iterations completed successfully. THIS WAS NOT EXPECTED.");
}
}
catch (AggregateException aex) // 注意:AggregateException 為並行中專用的異常資訊集合
{
Console.WriteLine($"Parallel.For has thrown an AggregateException. THIS WAS NOT EXPECTED.\n{aex}");
//foreach (var item in aex.InnerExceptions) // 可以通過迴圈將全部資訊記錄下來
//{
// Console.WriteLine(item.InnerException.Message + " " + item.GetType().Name);
//}
//aex.Handle(p => // 如果想往上級拋,需要使用 Handle 方法處理一下
//{
// if (p.InnerException.Message == "my god!Exception from childTask1 happend!")
// return true;
// else
// return false; // 返回 false 表示往上繼續丟擲異常
//});
}
catch (OperationCanceledException ocex) // 專門用於取消迴圈異常的捕捉
{
Console.WriteLine($"An iteration has triggered a cancellation. THIS WAS EXPECTED.\n{ocex}");
}
finally
{
cancellationSource.Dispose();
}
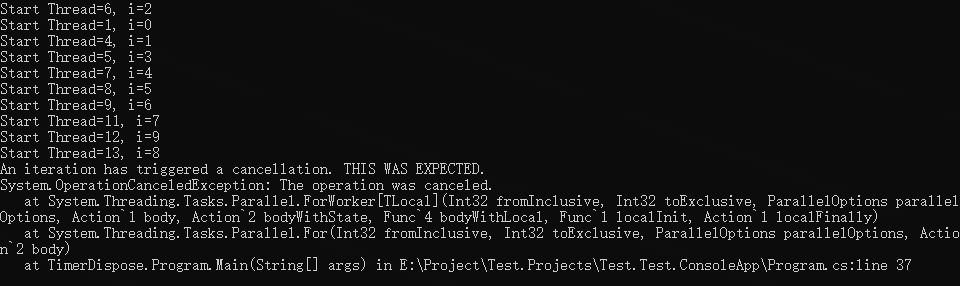
} 如下圖中的輸出,所有迭代任務都未完成,主要是因為耗時操作執行完成之前,迴圈就取消了,在if (loopState.ShouldExitCurrentIteration)判斷時,均為 true 就直接返回了。
1.5 過載四:For<TLocal>(Int32, Int32, ParallelOptions, Func<TLocal>, Func<Int32,ParallelLoopState,TLocal,TLocal>, Action<TLocal>)
public static ParallelLoopResult For<TLocal> (int fromInclusive, int toExclusive,
ParallelOptions parallelOptions,
Func<TLocal> localInit,
Func<int,ParallelLoopState,TLocal,TLocal> body,
Action<TLocal> localFinally);以下範例使用執行緒區域性變數來計算許多冗長操作的結果之和。 此範例將並行度限制為 4。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int result = 0;
int N = 1000000;
Parallel.For(
0, N,
// 限制最多 4 個並行任務
new ParallelOptions { MaxDegreeOfParallelism = 4 },
// Func<TLocal> 初始化本地變數,本地變數是執行緒獨立變數
() => 0,
// Func<Int32,ParallelLoopState,TLocal,TLocal> 迭代操作
(i, loop, localState) =>
{
for (int ii = 0; ii < 10000; ii++) ;
return localState + 1;
},
localState =>
Interlocked.Add(ref result, localState)
);
Console.WriteLine("實際運算結果: {0}. 目標值: 1000000", result);
Console.ReadLine();
}如下圖輸出結果:
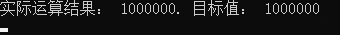
參考:https://learn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/dotnet/api/system.threading.tasks.parallel.for?view=net-7.0
關於 ParallelOptions 詳見:https://learn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/dotnet/api/system.threading.tasks.paralleloptions?view=net-7.0
2、Parallel.ForEach()
2.1 過載一:Parallel.ForEach<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource>, Action<TSource>)
public static ParallelLoopResult ForEach<TSource> (IEnumerable<TSource> source, Action<TSource> body);執行 ForEach 操作,在處理關於 IEnumerable 集合的任務時,可並行執行迭代。
如下程式碼塊,簡單的將一個整數陣列,輸出到控制檯:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] ints = { 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19 };
ParallelLoopResult result = Parallel.ForEach(ints,
i =>
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
});
Console.ReadLine();
}從輸出結果看,ForEach 操作是無序的:

2.2 過載二:ForEach<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource>, ParallelOptions, Action<TSource,ParallelLoopState,Int64>)
public static ParallelLoopResult ForEach<TSource> (IEnumerable<TSource> source, ParallelOptions parallelOptions, Action<TSource,ParallelLoopState,long> body);執行具有 64 位索引(標識待迴圈集合的順序)的 foreach 操作,其中在 IEnumerable 上可能會並行執行迭代,而且可以設定迴圈選項,可以監視和操作迴圈的狀態。
如下範例程式碼,設定並行任務數為 5,在索引為 6 的任務執行過程中中斷迴圈,看下輸出結果:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 建立一個集合,其中包含一些數位
var numbers = new int[] { 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19 };
// 使用 ParallelOptions 選項設定並行處理的行為
var parallelOptions = new ParallelOptions
{
MaxDegreeOfParallelism = 5
};
Parallel.ForEach(numbers, parallelOptions, (source, loopState, index) => // index:集合中物件的從 0 開始的序號
{
// 在此處編寫並行處理邏輯
Console.WriteLine($"開始--Index: {index}, Value: {source}, ThreadId: {Thread.GetCurrentProcessorId()}");
if (loopState.ShouldExitCurrentIteration)
return;
Thread.Sleep(200);
if (index == 6)
loopState.Break();
Console.WriteLine($"結束++Index: {index}, Value: {source}, ThreadId: {Thread.GetCurrentProcessorId()}");
});
Console.ReadLine();
}如下圖輸出結果,一次性開始 5 個並行任務,當第 6 個任務進入時,中斷迴圈。
由於操作是無序的,所以在中斷之前可能索引在 6 之後的已經開始或者已經執行完成,如下圖 8、9 已經執行完畢,7尚未執行。
注意,若允許並行的任務數少時,可能 6 之後的任務都還沒來得及開始,另外,每次執行的結果不同。

2.3 過載三:Parallel.ForEach<TSource>(Partitioner<TSource>, Action<TSource>)
public static ParallelLoopResult ForEach<TSource> (System.Collections.Concurrent.Partitioner<TSource> source, Action<TSource> body);此過載的獨到之處,就是可以將資料進行分割區,每一個小區內實現序列計算,分割區採用 Partitioner.Create() 實現。
long sum = 0;
long sumtop = 10000000;
Stopwatch sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
Parallel.ForEach(Partitioner.Create(0, sumtop), (range) =>
{
long local = 0;
for (long i = range.Item1; i < range.Item2; i++)
local += i;
Interlocked.Add(ref sum, local); // Interlocked:為由多個執行緒共用的變數提供原子操作 Add():求和後替換原來的數值,相當於 +=
});
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"Partitioner.Create() 分割區方式執行效率: result = {sum}, time = {sw.ElapsedMilliseconds} ms");
// 輸出:
// Partitioner.Create() 分割區方式執行效率: result = 49999995000000, time = 8 ms關於分割區的建立方法 Partitioner.Create(0, Int64)
- 指定了分割區的範圍,就是 0 ~ Int64;
- 引數中並沒有指定分多少個區,預設是系統自動判斷執行的。
- 還可以指定分割區,做法就是
Partitioner.Create(0, 3000000, Environment.ProcessorCount),其中 Environment.ProcessorCount 引數,就對應當前計算機邏輯處理器的數量。
2.4 過載四:ForEach<TSource,TLocal>(IEnumerable<TSource>, Func<TLocal>, Func<TSource,ParallelLoopState,TLocal,TLocal>, Action<TLocal>)
執行具有執行緒本地資料的 foreach 操作,其中在 IEnumerable 上可能會並行執行迭代,而且可以監視和操作迴圈的狀態。
public static ParallelLoopResult ForEach<TSource,TLocal> (IEnumerable<TSource> source,
Func<TLocal> localInit,
Func<TSource,ParallelLoopState,TLocal,TLocal> body,
Action<TLocal> localFinally);如下範例,將全部整數逐個輸出並且最後在輸出他們之和:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 全部值的和為 40
int[] input = { 4, 1, 6, 2, 9, 5, 10, 3 };
int sum = 0;
try
{
Parallel.ForEach(
// IEnumerable<TSource> 可列舉的資料來源
input,
// Func<TLocal> 用於返回每個任務的【本地資料的初始狀態】的函數委託
// 本範例中的目的就是將 TLocal localSum 的值在每次迭代都賦值為 0
() => 0,
// Func<TSource,ParallelLoopState,TLocal,TLocal> 將為每個迭代呼叫一次的委託
(n, loopState, localSum) =>
{
localSum += n;
Console.WriteLine($"Thread={Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}, n={n}, localSum={localSum}");
return localSum;
},
// Action<TLocal> 用於對每個任務的本地狀態執行一個最終操作的委託
// 此範例中的作用是將每個值逐一求和,並返回 sum
(localSum) =>
Interlocked.Add(ref sum, localSum)
);
Console.WriteLine("\nSum={0}", sum);
}
catch (AggregateException e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Parallel.ForEach has thrown an exception. This was not expected.\n{0}", e);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}如下輸出結果,其中 localSum 在每個執行緒中初始值都是 0,在其他執行緒中參與的求和運算,不影響當前執行緒。
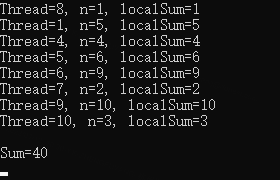
2.5 比較執行效率 for、Parallel.For()、Parallel.For()+TLocal、Parallel.ForEach(Partitioner.Create(), Action<TSource>)
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Stopwatch sw = null;
long sum = 0;
long sumtop = 10000000;
// 常規 for 迴圈
sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
for (long i = 0; i < sumtop; i++)
sum += i;
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"result = {sum}, time = {sw.ElapsedMilliseconds} ms --常規 for 迴圈");
// Parallel.For() 方式
sum = 0;
sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
Parallel.For(0L, sumtop,
(item) => Interlocked.Add(ref sum, item));
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"result = {sum}, time = {sw.ElapsedMilliseconds} ms --Parallel.For() 方式");
// Parallel.For() + TLocal
sum = 0;
sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
Parallel.For(
0L, sumtop,
() => 0L,
(item, state, prevLocal) =>
prevLocal + item,
local =>
Interlocked.Add(ref sum, local));
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"result = {sum}, time = {sw.ElapsedMilliseconds} ms --Parallel.For() + locals 方式");
// Partitioner.Create() 分割區方式
sum = 0;
sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
Parallel.ForEach(Partitioner.Create(0L, sumtop), (range) =>
{
long local = 0;
for (long i = range.Item1; i < range.Item2; i++)
local += i;
Interlocked.Add(ref sum, local);
});
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"result = {sum}, time = {sw.ElapsedMilliseconds} ms --Partitioner.Create() 分割區方式");
Console.ReadLine();
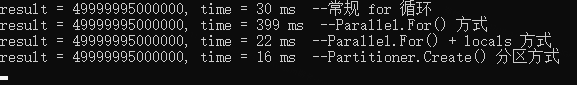
}如下輸出結果,效率最高的顯然是自動分割區的方式,比常規的 for 迴圈塊將近一倍。最慢的是 Parallel.For() 方式,由於加鎖求和導致上下文頻繁切換比較耗時,因此這種求和的計算模式不適用。
參考:https://learn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/dotnet/api/system.threading.tasks.parallel.foreach?view=net-7.0
3、Parallel.ForEachAsync()
Parallel.ForEachAsync() 是在 .NET 6 中新增的一個 API,是 Parallel.ForEach() 的非同步版本。https://learn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/dotnet/api/system.threading.tasks.parallel.foreachasync?view=net-7.0
下面簡單說明一下 Parallel.ForEach() 和 Parallel.ForEachAsync() 的區別。
- Parallel.ForEach() 是在預設多個或指定的個數的執行緒下執行的。而 Parallel.ForEachAsync() 不一定是多執行緒的,強調的是非同步而已。
- 若目標集合必須按照順序執行,則不能選用 Parallel.ForEach() 方法,因為它是無序執行的。
- 當待處理的資料量很大或者執行過程比較耗時,則選用多執行緒執行的 Parallel.ForEach() 方法更好。
下面是一個關於過載 ForEachAsync<TSource>(IAsyncEnumerable<TSource>, ParallelOptions, Func<TSource,CancellationToken,ValueTask>) 的一個簡單範例程式碼:
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
var nums = Enumerable.Range(0, 10).ToArray();
await Parallel.ForEachAsync(
nums,
new ParallelOptions { MaxDegreeOfParallelism = 3 }, // 設定最多同時分配三個執行緒
async (i, token) => // Func<TSource,CancellationToken,ValueTask> // 其中 ValueTask 提供非同步操作的可等待結果,指的是下文 await 的內容
{
Console.WriteLine($"開始迭代任務 {i} ThreadId:{Thread.GetCurrentProcessorId()}");
// public static Task Delay(int millisecondsDelay, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
// 在指定毫秒後,呼叫 token 取消當前任務
await Task.Delay(1000, token);
Console.WriteLine($"完成迭代任務 {i}");
});
Console.WriteLine("Finished!");
Console.ReadLine();
}詳情可參考:https://learn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/dotnet/api/system.threading.tasks.parallel.foreachasync?view=net-7.0 ; https://www.gregbair.dev/posts/parallel-foreachasync/
4、Parallel.Invoke()
儘可能並行執行提供的每個操作。
4.1 兩個過載:Invoke(Action[])、Invoke(ParallelOptions, Action[])
下面是一個運用 Invoke(Action[]) 過載的範例,分別加入了三個操作,然後看執行結果。第二個過載是在第一個過載的基礎上加了並行選項 ParallelOptions 就不在贅述了。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
Parallel.Invoke(
BasicAction, // 第一個操作 - 靜態方法
() => // 第二個操作 - 箭頭函數
{
Console.WriteLine("Method=beta, Thread={0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
},
delegate () // 第三個操作 - 委託函數
{
Console.WriteLine("Method=gamma, Thread={0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
}
);
}
catch (AggregateException e)
{
Console.WriteLine("An action has thrown an exception. THIS WAS UNEXPECTED.\n{0}", e.InnerException.ToString());
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
static void BasicAction()
{
Console.WriteLine("Method=alpha, Thread={0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
}由輸出結果可知,三個操作是無序的、多執行緒執行的。
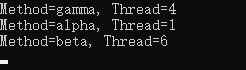
兩個參考:https://learn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/dotnet/api/system.threading.tasks.parallel.invoke?view=net-7.0 Parallel的使用
三、簡單總結一下下
實際上看的資料再多,如果沒用到實際開發當中就是無用功,下邊簡單總結一下吧。
由本文 1.2 比較執行效率 Parallel.For() 和 for() 中可知:
- 對於大批次耗時且順序要求不高的場景可以採用 Parallel.For() 方法,如果對次序有依賴,則只能採用常用的 for 迴圈。
- 對於操作簡單的迴圈操作,Parallel.For() 就不太適合了,因為多執行緒操作涉及到上下文的切換,過多的切換場景會嚴重影響程式執行的效率。
- 由於範例中的操作比較簡單,此時 Parallel.For() 上下文的的切換耗時以及加鎖的缺點就凸現了,效率最差。
- 使用執行緒本地變數(TLocal)的 Parallel.For() 可以避免將大量的存取同步為共用狀態的開銷,所以可以看到效率就高很多。可參考:編寫具有執行緒區域性變數的 Parallel.For 迴圈
- 分割區迴圈操作 Partitioner.Create(0, Int64) 方法的效率最高,因為事先給待處理的任務進行了分割區,分割區內序列,避免了過多的上下文切換耗時。
注:個人整理,歡迎路過的大佬評論區指正和補充。
本文來自部落格園,作者:橙子家,微訊號:zfy1070491745,有任何疑問歡迎溝通,一起成長。
轉載本文請註明原文連結:https://www.cnblogs.com/czzj/p/ParallelAndConcurrentBag.html