【Python】資料視覺化利器PyCharts在測試工作中的應用
PyCharts 簡介
PyCharts 是一個基於 Python 的資料視覺化庫,它支援多種圖表型別,如折線圖、柱狀圖、餅圖等。PyCharts 提供了簡潔的 API,使得使用者能夠輕鬆地建立各種圖表,同時支援個性化的設定,以滿足不同需求。PyCharts 的底層依賴於 ECharts,這使得它在功能和效能上都具有很高的優勢。
PyCharts 的安裝
PyCharts 的安裝非常簡單,只需在命令列中輸入以下命令:
pip install pyecharts
安裝完成後,即可在 Python 程式碼中匯入 PyCharts 庫並開始使用。
作為軟體測試工程師,我們經常需要處理測試過程中的資料。文不如表、表不如圖,通過 PyCharts,我們可以輕鬆的將這些資料以直觀的形式展示出來,從而更好地分析問題、彙報進度。
缺陷統計
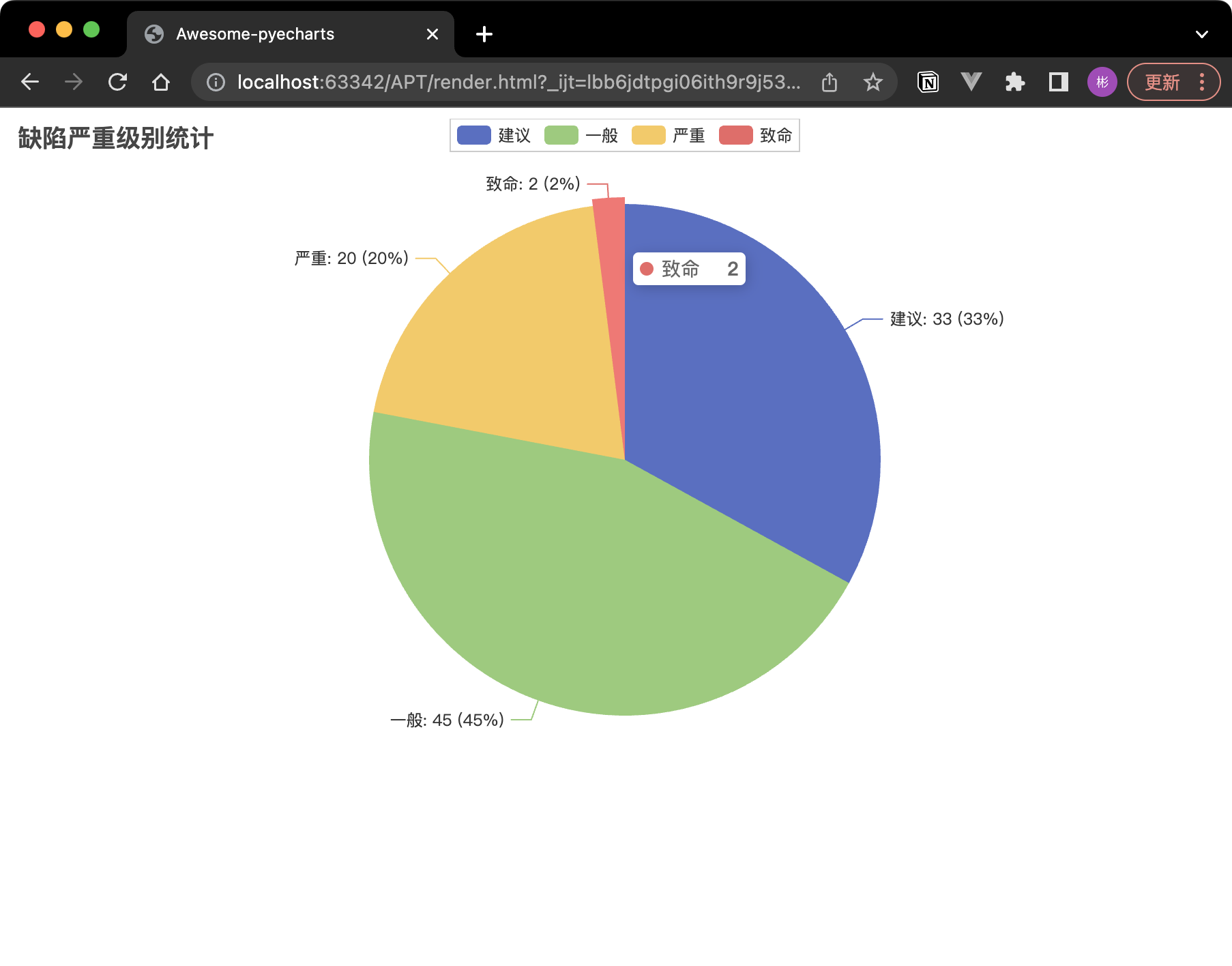
在軟體測試過程中,我們需要對發現的缺陷進行統計和分析。以下程式碼演示瞭如何使用 PyCharts 建立一個餅圖,展示各個嚴重級別的缺陷數量:
from pyecharts.charts import Pie
from pyecharts import options as opts
pie = Pie()
pie.add("", [("建議", 33), ("一般", 45), ("嚴重", 20), ("致命", 2)])
pie.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="缺陷嚴重級別統計"))
pie.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(formatter="{b}: {c} ({d}%)"))
pie.render()
執行上面的程式碼會自動的在同級目錄生成一個 render.xml 檔案,使用瀏覽器開啟就可以看到展示了不同嚴重級別的缺陷數量及其佔比的餅圖。我們可以依據這個圖更好地制定測試策略和優先順序。
當然,我們也可以在 render 之前加上下面這段程式碼來指定顏色,得到下面這張圖:
# 指定顏色
colors = ["#0000FF", "#4169E1", "#1E90FF", "#00BFFF"]
pie.set_colors(colors)

測試用例執行情況
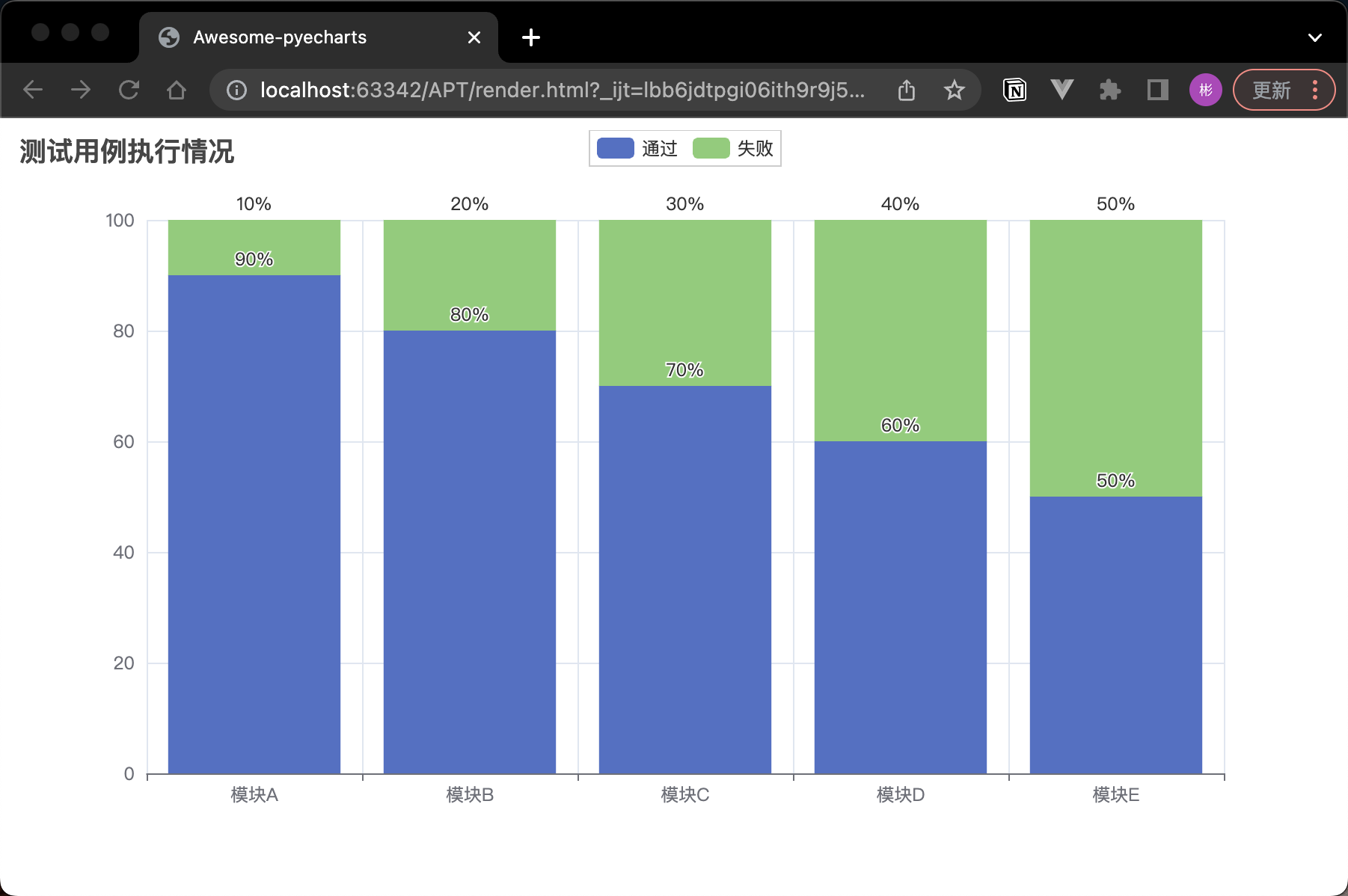
在執行測試用例時,我們需要關注測試用例的執行情況,如通過率、失敗率等。以下程式碼演示瞭如何使用 PyCharts 建立一個堆疊柱狀圖,展示各個模組的測試用例執行情況:
from pyecharts.charts import Bar
from pyecharts import options as opts
bar = Bar()
bar.add_xaxis(["模組A", "模組B", "模組C", "模組D", "模組E"])
# 新增通過和失敗的資料,並設定為堆疊模式
bar.add_yaxis("通過", [90, 80, 70, 60, 50], stack="總量")
bar.add_yaxis("失敗", [10, 20, 30, 40, 50], stack="總量")
# 設定全域性選項,包括標題
bar.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="測試用例執行情況"),)
# 設定系列選項,包括標籤格式
bar.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=True, position="outside", formatter="{c}%")) # 顯示百分比的標籤格式
bar.render()
這段程式碼建立了一個堆疊柱狀圖,展示了各個模組的測試用例通過和失敗數量。通過這樣的圖表,我們可以直觀地瞭解到各個模組的測試情況,從而更好地調整測試計劃和資源分配。
使用JavaScript情況
因為pycharts 底層基於 ECharts,所以 JavaScript程式碼也可以在指令碼中使用。
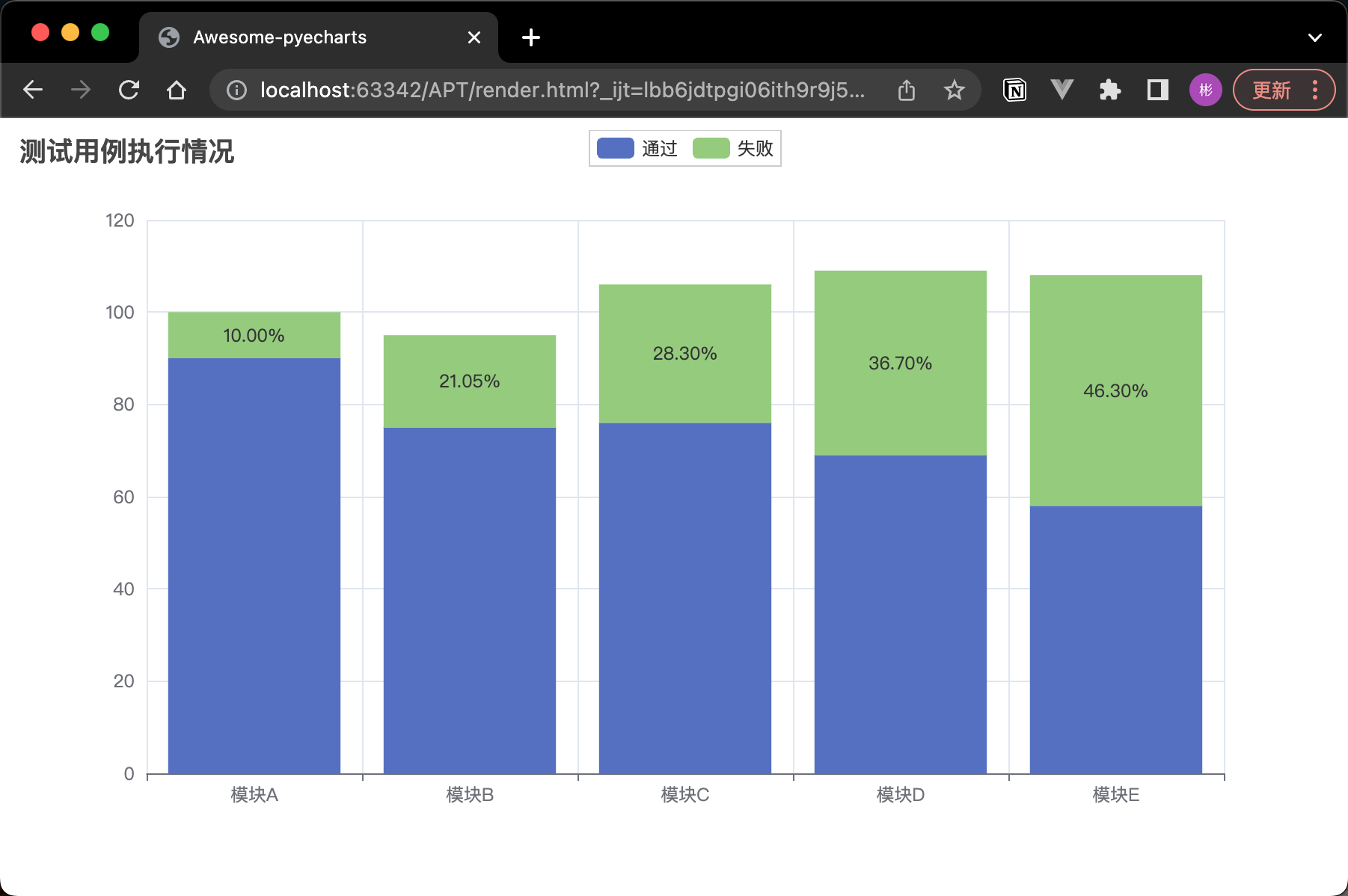
在 Python 中呼叫 JavaScript 程式碼:
from pyecharts.charts import Bar
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.commons.utils import JsCode
bar = Bar()
bar.add_xaxis(["模組A", "模組B", "模組C", "模組D", "模組E"])
passed_cases = [90, 75, 76, 69, 58]
# 新增通過和失敗的資料,並設定為堆疊模式
bar.add_yaxis(
"通過",
passed_cases,
stack="總量",
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False) # 隱藏通過用例的標籤
)
# 使用回撥函數計算失敗用例的百分比
failure_percentage = f"""
function(params) {{
var passed_cases = {passed_cases};
var total = params.value + passed_cases[params.dataIndex];
var percentage = (params.value / total) * 100;
return percentage.toFixed(2) + '%';
}}
"""
bar.add_yaxis(
"失敗",
[10, 20, 30, 40, 50],
stack="總量",
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(
is_show=True, position="inside", formatter=JsCode(failure_percentage)
) # 顯示失敗用例的標籤
)
# 設定全域性選項,包括標題
bar.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="測試用例執行情況"),
)
bar.render()
缺陷趨勢分析
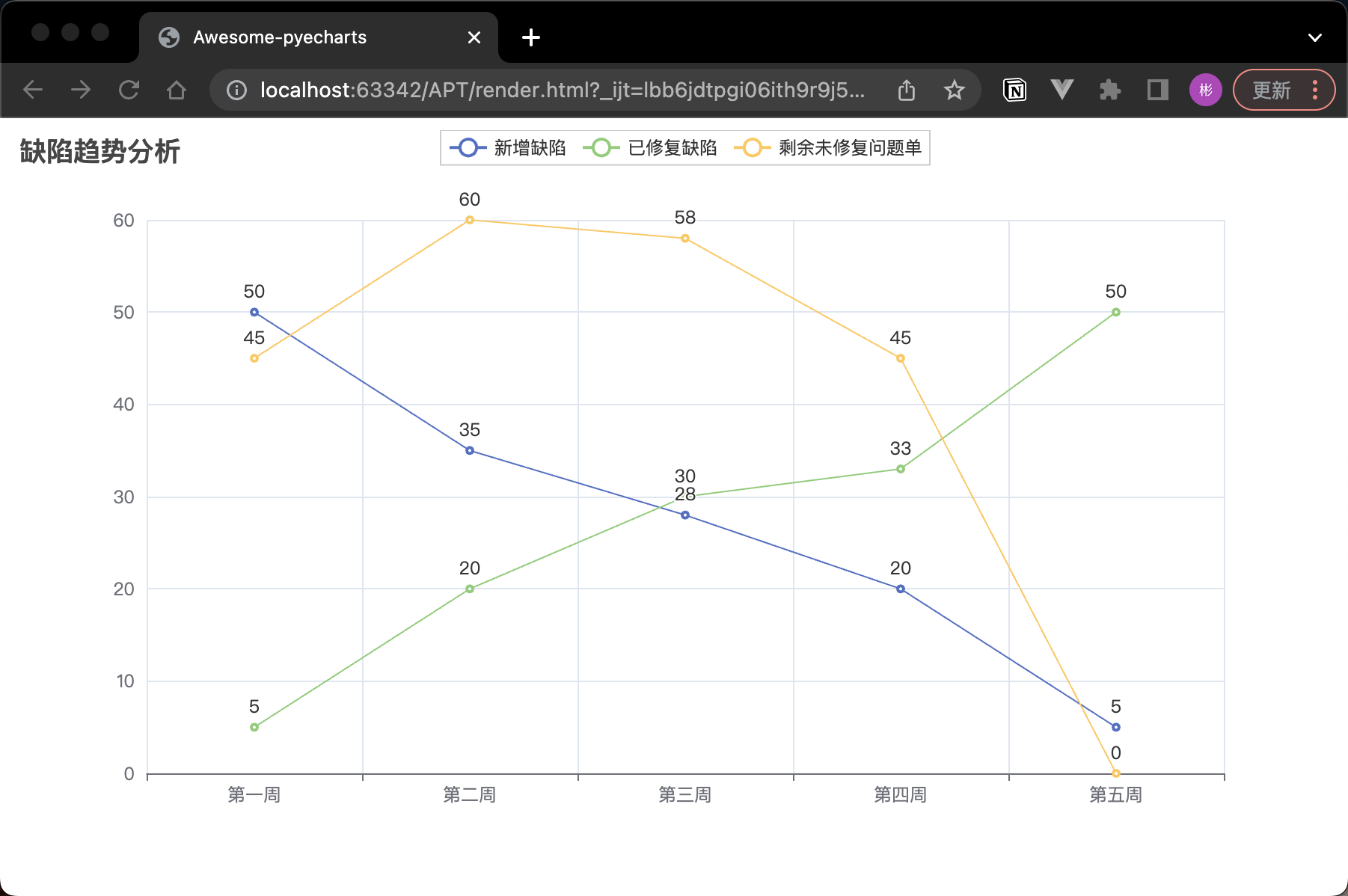
在專案進展過程中,我們需要關注缺陷的趨勢,以評估專案質量和進度。以下程式碼演示瞭如何使用 PyCharts 建立一個折線圖,展示專案中缺陷的趨勢變化:
from pyecharts.charts import Line
from pyecharts import options as opts
# 建立 Line 物件
line = Line()
# 新增 x 軸資料
line.add_xaxis(["第一週", "第二週", "第三週", "第四周", "第五週"])
# 新增問題單和已修復問題單的資料
new_defects = [50, 35, 28, 20, 5]
fixed_defects = [5, 20, 30, 33, 50]
# 計算剩餘未修復的問題單
remaining_defects = []
cumulative_new_defects = 0
cumulative_fixed_defects = 0
# 遍歷新增問題單和已修復問題單的資料
for new, fixed in zip(new_defects, fixed_defects):
# 累積計算新增問題單和已修復問題單的數量
cumulative_new_defects += new
cumulative_fixed_defects += fixed
# 計算剩餘未修復的問題單,並將結果新增到 remaining_defects 列表中
remaining_defects.append(cumulative_new_defects - cumulative_fixed_defects)
# 向圖表中新增 y 軸資料系列
line.add_yaxis("新增缺陷", new_defects)
line.add_yaxis("已修復缺陷", fixed_defects)
line.add_yaxis("剩餘未修復問題單", remaining_defects)
# 設定全域性選項,包括標題
line.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="缺陷趨勢分析"))
# 渲染圖表
line.render()
這段程式碼建立了一個折線圖,展示了專案中新增缺陷和已修復缺陷的數量變化。通過這樣的圖表,我們可以直觀地瞭解到專案的質量趨勢,從而更好地制定測試策略和計劃。
將兩張圖放在一個組合裡(grid)
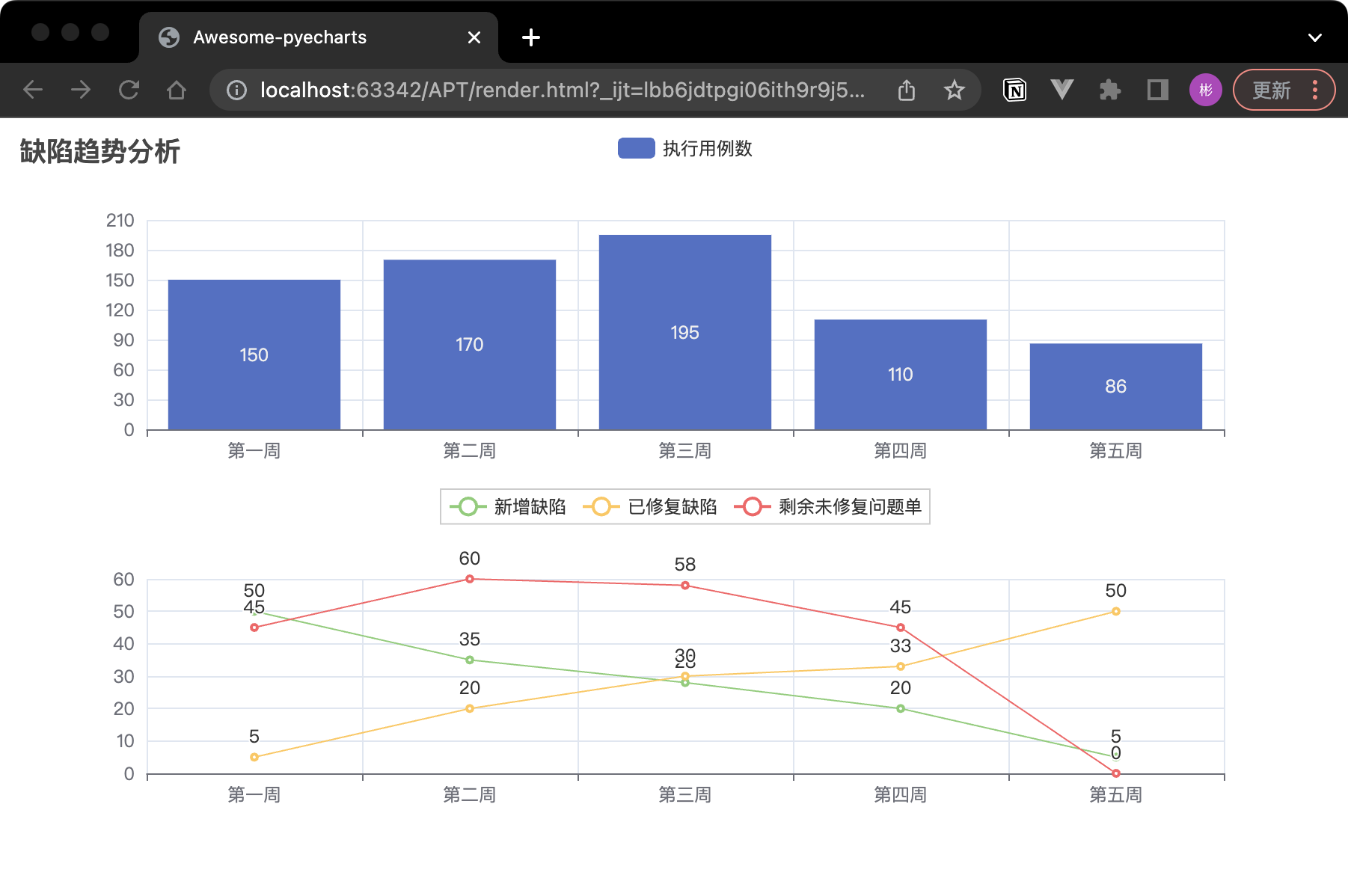
體現隨著時間的變化,執行用例和 bug 情況的變化:
from pyecharts.charts import Line, Bar, Grid
from pyecharts import options as opts
# 建立 Line 物件
new_defects = [50, 35, 28, 20, 5]
fixed_defects = [5, 20, 30, 33, 50]
remaining_defects = []
cumulative_new_defects = 0
cumulative_fixed_defects = 0
for new, fixed in zip(new_defects, fixed_defects):
cumulative_new_defects += new
cumulative_fixed_defects += fixed
remaining_defects.append(cumulative_new_defects - cumulative_fixed_defects)
line = (Line().add_xaxis(["第一週", "第二週", "第三週", "第四周", "第五週"]).add_yaxis("新增缺陷", new_defects)
.add_yaxis("已修復缺陷", fixed_defects)
.add_yaxis("剩餘未修復問題單", remaining_defects)
# 設定全域性選項,包括標題
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="缺陷趨勢分析"),
legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(pos_top="48%"),)
)
# 新增執行用例數的資料
executed_cases = [150, 170, 195, 110, 86]
# 建立 Bar 物件
bar = (Bar().add_xaxis(["第一週", "第二週", "第三週", "第四周", "第五週"])
.add_yaxis("執行用例數", executed_cases)
)
# 建立 Grid 物件,並新增 Line 和 Bar 圖表
grid = (Grid().
add(bar, grid_opts=opts.GridOpts(pos_bottom="60%")).
add(line, grid_opts=opts.GridOpts(pos_top="60%")))
# 渲染圖表
grid.render()
將兩張圖重疊成一張圖(overlap)
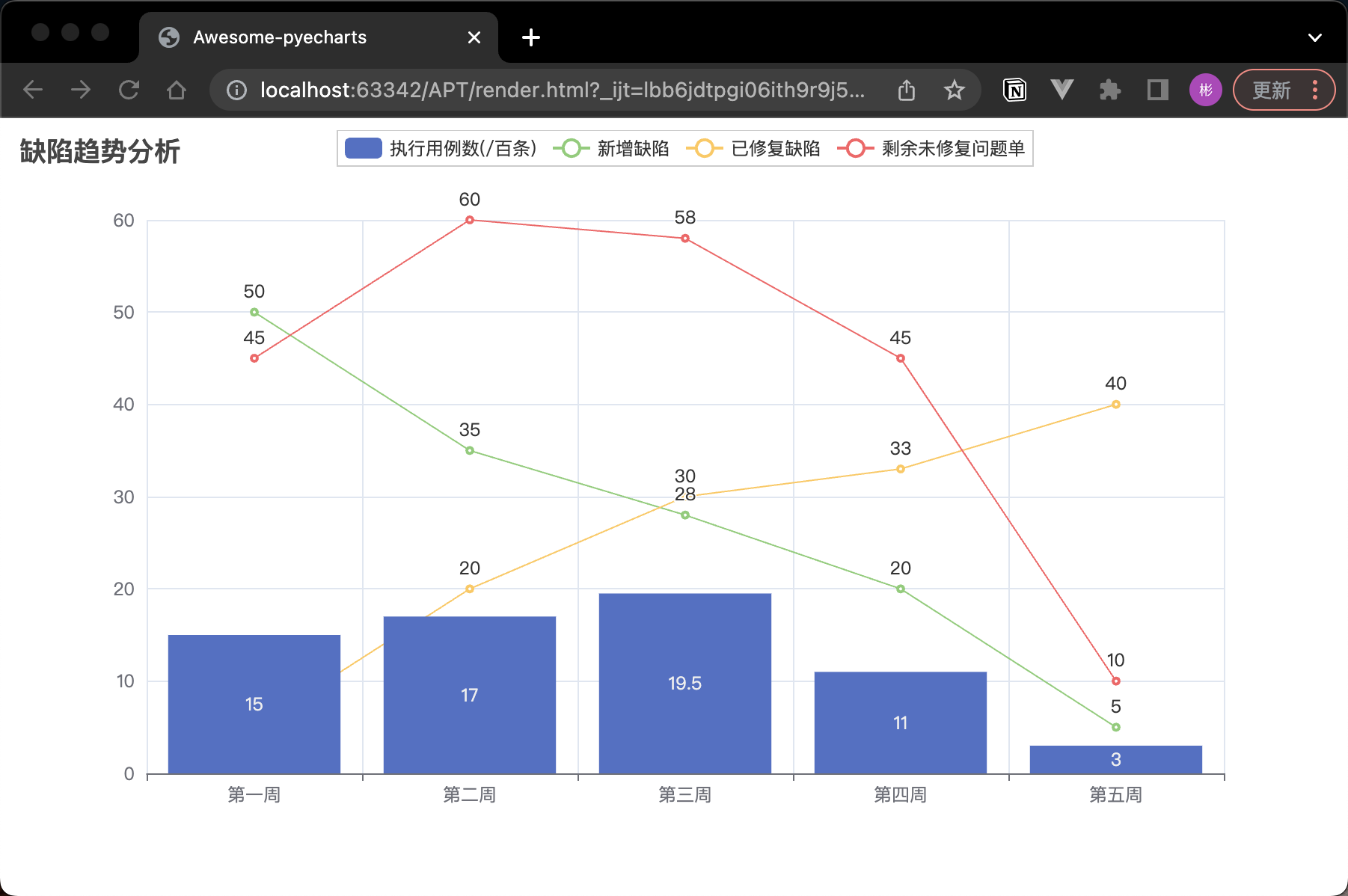
from pyecharts.charts import Line, Bar
from pyecharts import options as opts
# 建立 Bar 物件
bar = Bar()
bar.add_xaxis(["第一週", "第二週", "第三週", "第四周", "第五週"])
# 新增執行用例數的資料
executed_cases = [15, 17, 19.5, 11, 3]
bar.add_yaxis("執行用例數(/百條)", executed_cases)
# 建立 Line 物件
line = Line()
line.add_xaxis(["第一週", "第二週", "第三週", "第四周", "第五週"])
new_defects = [50, 35, 28, 20, 5]
fixed_defects = [5, 20, 30, 33, 40]
remaining_defects = []
cumulative_new_defects = 0
cumulative_fixed_defects = 0
for new, fixed in zip(new_defects, fixed_defects):
cumulative_new_defects += new
cumulative_fixed_defects += fixed
remaining_defects.append(cumulative_new_defects - cumulative_fixed_defects)
# 設定 is_smooth=True 引數使折線平滑顯示
line.add_yaxis("新增缺陷", new_defects)
line.add_yaxis("已修復缺陷", fixed_defects)
line.add_yaxis("剩餘未修復問題單", remaining_defects)
# 使用 overlap() 方法將 Line 圖表疊加到 Bar 圖表中
bar.overlap(line)
# 設定全域性選項,包括標題
bar.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="缺陷趨勢分析"))
# 渲染圖表
bar.render()
將多張圖組合在一個page 中(page)
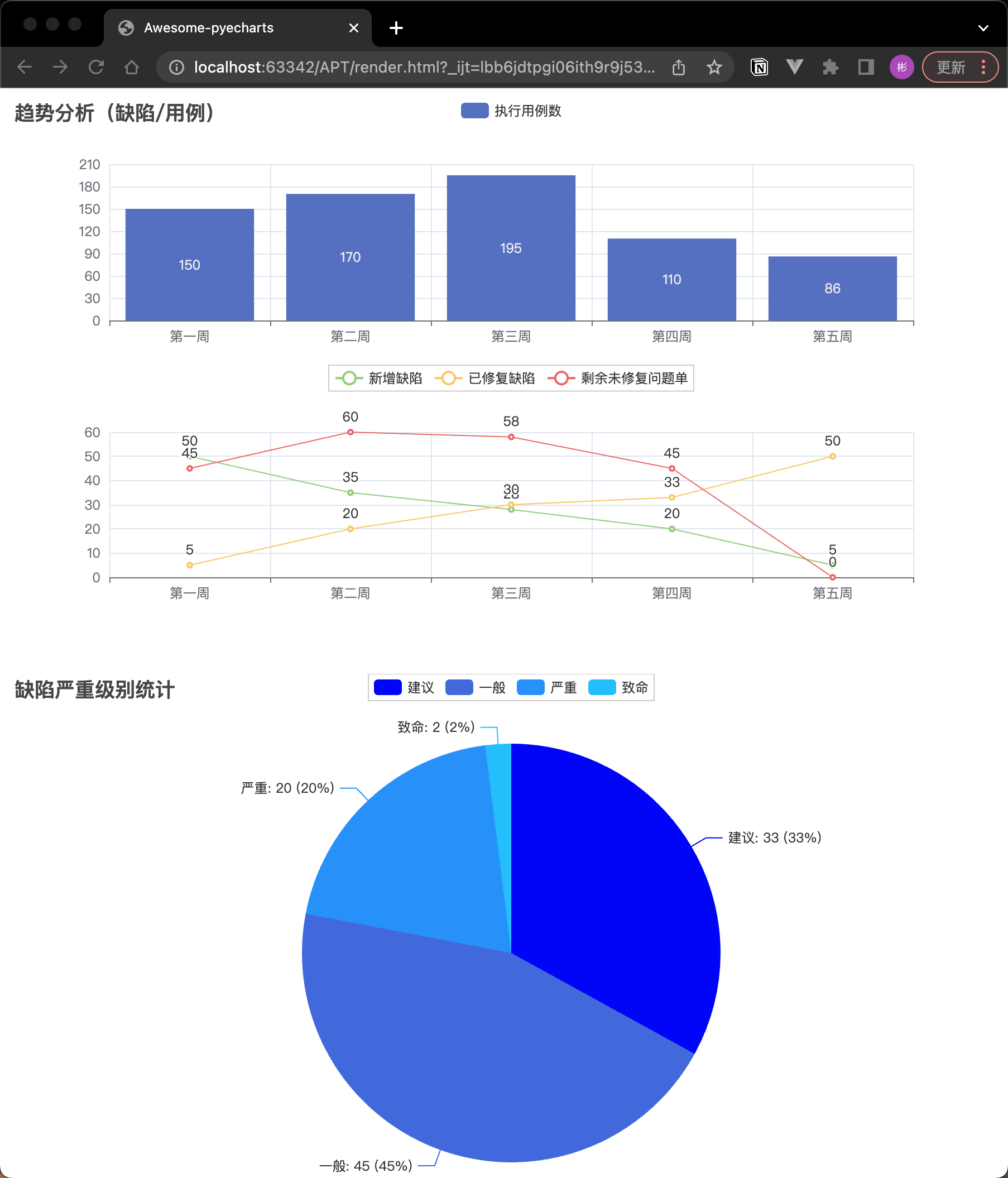
from pyecharts.charts import Line, Bar, Page, Pie, Grid
from pyecharts import options as opts
# 建立 Line 物件
new_defects = [50, 35, 28, 20, 5]
fixed_defects = [5, 20, 30, 33, 50]
remaining_defects = []
cumulative_new_defects = 0
cumulative_fixed_defects = 0
for new, fixed in zip(new_defects, fixed_defects):
cumulative_new_defects += new
cumulative_fixed_defects += fixed
remaining_defects.append(cumulative_new_defects - cumulative_fixed_defects)
line = (Line().add_xaxis(["第一週", "第二週", "第三週", "第四周", "第五週"]).add_yaxis("新增缺陷", new_defects)
.add_yaxis("已修復缺陷", fixed_defects)
.add_yaxis("剩餘未修復問題單", remaining_defects)
# 設定全域性選項,包括標題
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="趨勢分析(缺陷/用例)"),
legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(pos_top="48%"),)
)
# 新增執行用例數的資料
executed_cases = [150, 170, 195, 110, 86]
# 建立 Bar 物件
bar = (Bar().add_xaxis(["第一週", "第二週", "第三週", "第四周", "第五週"])
.add_yaxis("執行用例數", executed_cases)
)
# 建立 Grid 物件,並新增 Line 和 Bar 圖表
grid = (Grid().
add(bar, grid_opts=opts.GridOpts(pos_bottom="60%")).
add(line, grid_opts=opts.GridOpts(pos_top="60%"))
)
# 渲染圖表
grid.render()
pie = Pie()
pie.add("", [("建議", 33), ("一般", 45), ("嚴重", 20), ("致命", 2)])
pie.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="缺陷嚴重級別統計"))
pie.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(formatter="{b}: {c} ({d}%)"))
# 指定顏色
colors = ["#0000FF", "#4169E1", "#1E90FF", "#00BFFF"]
pie.set_colors(colors)
# 建立 Page 物件,並新增圖表
page = Page()
page.add(grid)
page.add(pie)
# 渲染圖表
page.render()
實際應用:常態化效能壓測資料統計
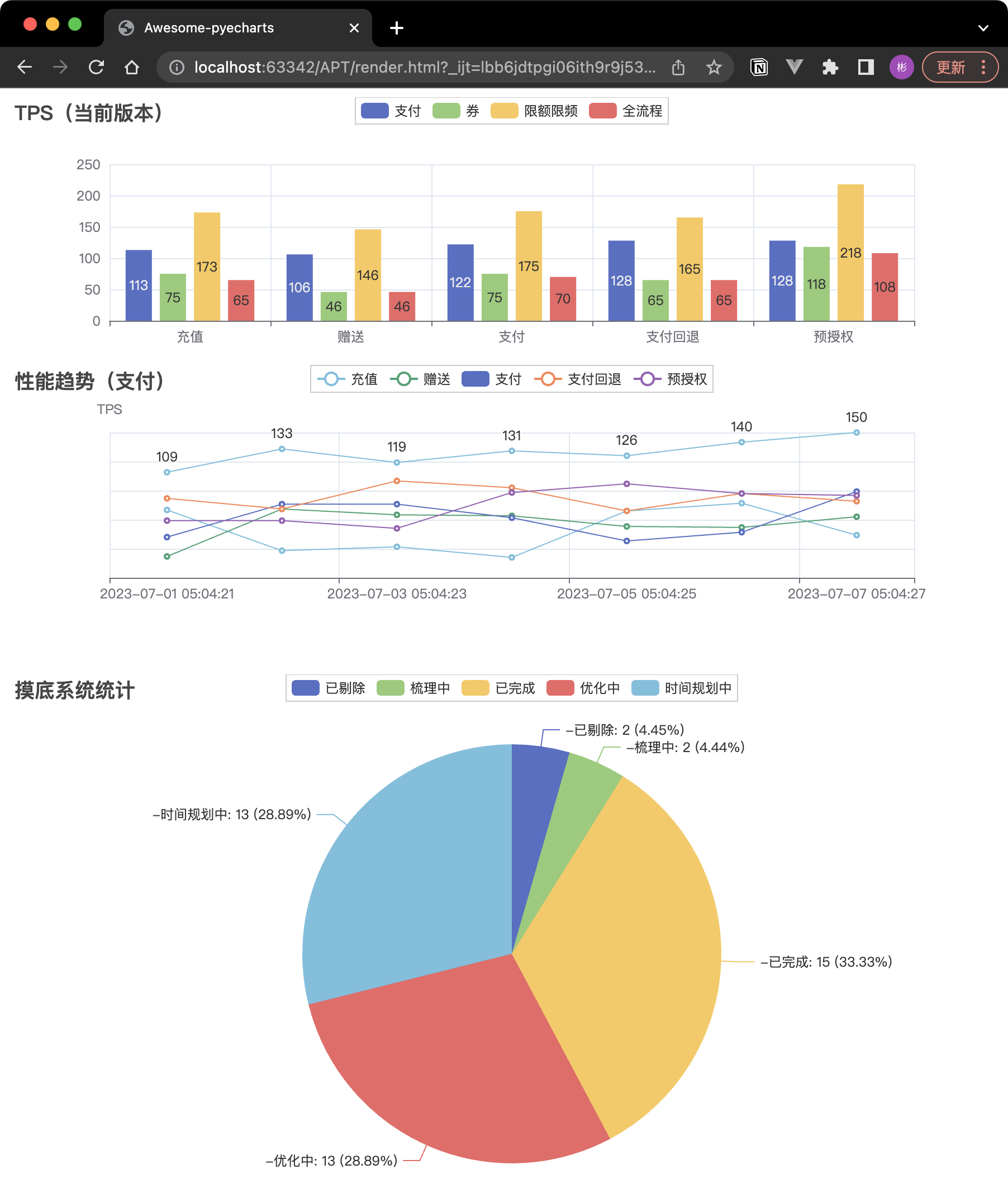
import random
from pyecharts.charts import Line, Bar, Grid, Pie, Page
from pyecharts import options as opts
# 查詢過去 8 次資料
time_range = 8
interface = ['充值', '贈送', '支付', '支付回退', '預授權']
bar = (
Bar()
.add_xaxis(interface)
.add_yaxis("支付", [113, 106, 122, 128, 128, 55, 45])
.add_yaxis("券", [75, 46, 75, 65, 118, 15, 70])
.add_yaxis("限額限頻", [173, 146, 175, 165, 218, 115, 170])
.add_yaxis("全流程", [65, 46, 70, 65, 108, 45, 40])
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="TPS(當前版本)"))
)
line = Line().add_xaxis([f"2023-07-0{i} 05:04:2{i}" for i in range(1, time_range)]). \
add_yaxis(interface[0], [random.randint(100, 150) for _ in range(time_range)])
for i, inter in enumerate(interface):
line.add_yaxis(inter, [random.randint(10 * (i + 1), 100) for _ in range(time_range)],
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False))
line.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="效能趨勢(支付)", pos_top="48%"),
legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(pos_top="48%"),
yaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(
name="TPS",
axislabel_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False), # 設定label_opts引數
)
)
grid = Grid().add(bar, grid_opts=opts.GridOpts(pos_bottom="60%")).add(line, grid_opts=opts.GridOpts(pos_top="60%"))
pie = Pie()
pie.add("-", [("已剔除", 2), ("梳理中", 2), ("已完成", 15), ("優化中", 13), ("時間規劃中", 13)])
pie.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="摸底系統統計"), )
# - `{a}`:表示系列名稱。`{b}`:表示資料類別 `{c}`:表示資料值(如10、25、50和15)。`{d}`:表示資料所佔的百分比。- `{@[index]}`:表示資料陣列中索引為`index`的值。
pie.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(formatter="{a}{b}: {c} ({d}%)"))
page = Page()
page.add(grid)
page.add(pie)
page.render()
總結
PyCharts 是一個功能強大、易於使用的 Python 資料視覺化庫。本文以測試工程師的日常工作中的一些資料舉例,演示瞭如何展示測試資料,從而提高工作效率,更好地服務於專案進展。本文僅介紹了 PyCharts 的基本使用和一些常見的應用場景,實際上 PyCharts 還有更多的功能等待我們去探索。希望本文能對大家的工作帶來幫助。
合抱之木,生於毫末;九層之臺,起於累土;千里之行,始於足下。