【調變解調】DSB 雙邊帶調幅
說明
學習數位訊號處理演演算法時整理的學習筆記。同系列文章目錄可見 《DSP 學習之路》目錄,程式碼已上傳到 Github - ModulationAndDemodulation。本篇介紹 DSB 雙邊帶調幅訊號的調變與解調,內附全套 MATLAB 程式碼。
1. DSB 調變演演算法
1.1 演演算法描述
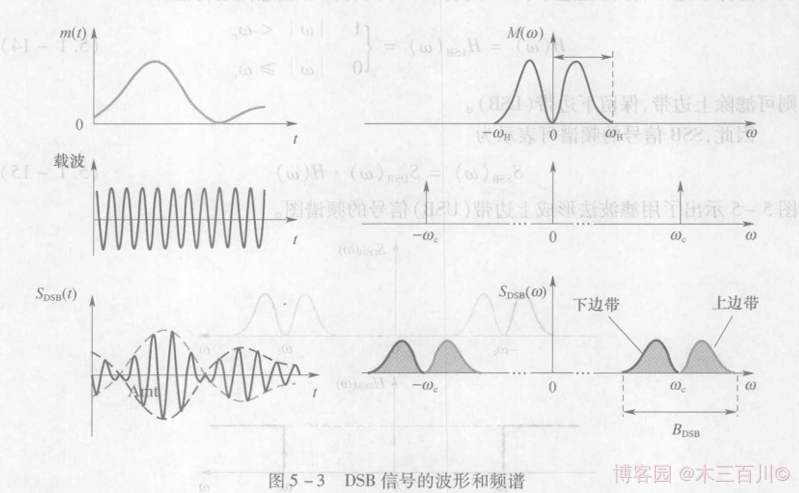
在 AM 調幅訊號中,載波分量並不攜帶資訊,資訊完全由邊帶傳送。如果在 AM 調變模型中將直流 \(A_0\) 去掉,即可得到一種高調變效率的調變方式——抑制載波雙邊帶訊號(DSB - SC, Double Side Band with Suppressed Carrier),簡稱雙邊帶訊號(DSB),其時域表示式為:
式中:\(m(t)\) 是調變訊號(攜帶要發出去的資訊),它可以是確知訊號,也可以是隨機訊號,其均值通常為 0;\(cos{\omega_ct}\) 是載波,\(\omega_c\) 是載波角頻率,與載波頻率 \(f_c\) 之間的關係為 \(\omega_c=2{\pi}f_c\)。DSB 的頻譜與 AM 頻譜相近,只是沒有了在 \(\pm\omega_c\) 處的 \(\delta\) 函數,對式 \((1)\) 進行傅立葉變換,得到 DSB 訊號的頻譜(幅度譜)表示式:
式中,\(M(\omega)\) 是調變訊號 \(m(t)\) 的頻譜。DSB 訊號的特性如下:
-
DSB 訊號的頻譜由上邊帶與下邊帶兩部分組成,不存在載波分量,它的頻寬仍是基頻訊號(調變訊號)頻寬 \(f_H\) 的 2 倍,即 \(B_{DSB}=2f_{H}\),與 AM 訊號頻寬相同。
-
由於不存在載波分量,有用功率 \(P_s\) 就是訊號總功率 \(P_{DSB}\),即 \(P_s=P_{DSB}\),全部功率都用於資訊傳輸,調變效率 \({\eta_{DSB}}=100\%\)。
1.2 DSB 訊號調變範例
調變訊號 \(m(t)\) 可以是確知訊號,也可以是隨機訊號。當 \(m(t)\) 是確知訊號時,不妨假設 \(m(t)\) 的時域表示式如下:
各調變引數取值:\(f_m=2500Hz\),\(f_c=20000Hz\)。訊號取樣率 \(f_s=8{f_c}\),模擬總時長為 \(2s\)。DSB 調變效果如下圖所示(為了美觀,時域只顯示前 500 個點),調變訊號 \(m(t)\) 雙邊幅度譜有四根離散譜線(\({\pm}2500Hz\)、\({\pm}1250Hz\)),載波 \(c(t)\) 的雙邊幅度譜有兩根離散譜線(\({\pm}20000Hz\)),DSB 訊號有八根離散譜線(\(\pm17500Hz\)、\(\pm18750Hz\)、\(\pm21250Hz\)、\(\pm22500Hz\)),程式碼詳見附錄 main_modDSB_example.m 與 mod_dsb.m。

2. DSB 解調演演算法
解調是調變的逆過程,其作用是從接收的已調訊號中恢復原基頻訊號(即調變訊號)。DSB 訊號的包絡不再與調變訊號 \(m(t)\) 的變化規律一致,因而不能採用簡單的包絡檢波來恢復調變訊號,通常採用相干解調的方法來進行解調。另一種方法是,插入很強的載波,使其成為或近似為 AM 訊號,則可利用包絡檢波器恢復調變訊號,這種方法被稱為插入載波包絡檢波法,為了保證檢波質量,插入的載波振幅應遠大於訊號的振幅,同時也要求插入的載波與調變載波同頻同相。下面介紹三種解調方法並對 1.2 節中的 DSB 訊號進行解調。
2.1 插入載波包絡檢波法
插入幅值為 \(A_0\) 的載波,得到:
其中 \(A_0 \geq {\lvert}{m(t)}{\rvert}_{max}\),這樣就得到了一個 AM 訊號,使用 AM 解調器進行解調即可,步驟如下:
- 第一步:加上載波 \({A_0}cos{\omega_ct}\),其中 \(A_0 \geq {\lvert}{m(t)}{\rvert}_{max}\),獲得 AM 訊號。
- 第二步:使用 AM 解調器進行解調。
對 1.2 節中的 DSB 訊號,設定訊雜比 \(SNR=50dB\),解調效果如下,計算誤差,有:\(\sqrt{\sum{{\lvert}m(t_i)-\hat{m}(t_i){\rvert}^2}}/\sqrt{\sum{{\lvert}m(t_i){\rvert}^2}}\approx0.0022\)。更改插入載波的初始相位為 \({\phi_0}=\pi/4,\pi/2\),或者更改插入載波的中心頻率為 \(0.8f_c,1.2f_c\) 後,解調效果變差,說明這種方法對插入載波同頻同相的要求較高。
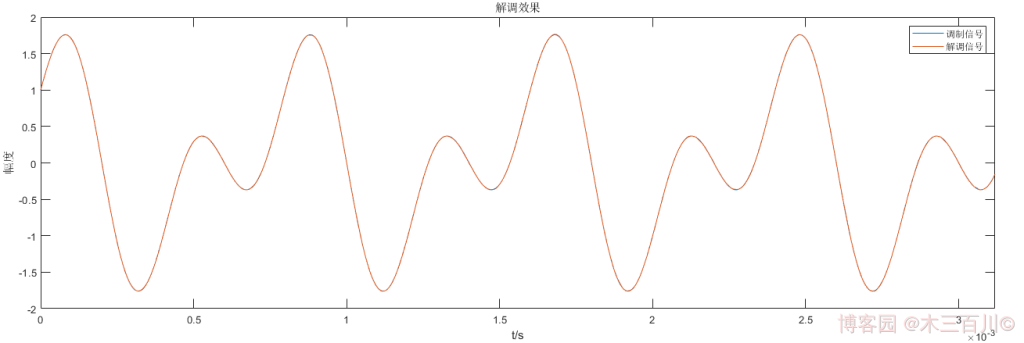
程式碼詳見 demod_dsb_method1.m 和 main_demodDSB_example1.m。AM 解調器詳見本人同系列部落格 【調變解調】AM 調幅。
2.2 相干解調(同步檢測)
將 DSB 訊號與同頻同相的相干載波相乘,得到:
然後通過一個低通濾波器即可獲得解調結果,步驟如下:
- 第一步:乘以相干載波(即乘以 \(2cos({\omega_ct}+{\phi_0})\),前面的 2 被用來做幅度補償。
- 第二步:低通濾波器濾除高頻載波,濾除 \(2{\omega}_c\)。
對 1.2 節中的 DSB 訊號,設定訊雜比 \(SNR=50dB\),解調效果如下,計算誤差,有:\(\sqrt{\sum{{\lvert}m(t_i)-\hat{m}(t_i){\rvert}^2}}/\sqrt{\sum{{\lvert}m(t_i){\rvert}^2}}\approx0.0016\)。更改相干載波的初始相位為 \({\phi_0}=\pi/4,\pi/2\) 後,解調幅值發生失真,當與真實相位相差 \(\pi/2\) 時幅值失真最大;但更改相干載波的中心頻率為 \(0.8f_c,1.2f_c\) 後,解調效果變得很差,波形完全失真,說明這種方法對相干載波同頻同相的要求也較高。
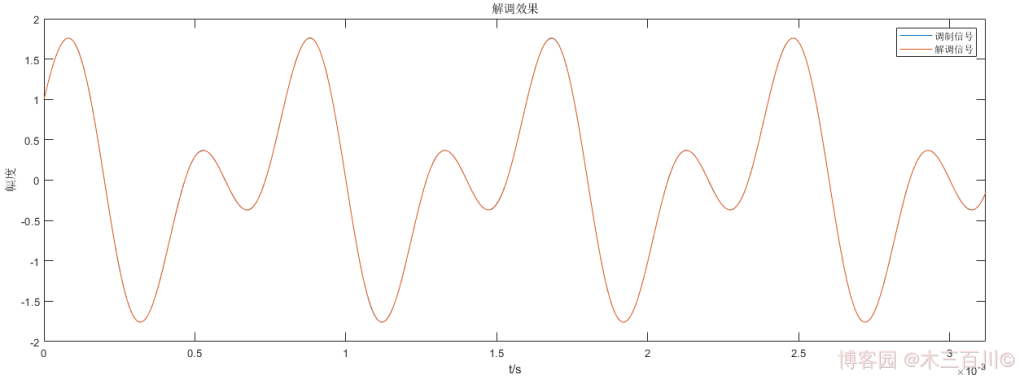
程式碼詳見 lpf_filter.m、demod_dsb_method2.m 和 main_demodDSB_example2.m。
2.3 數位正交解調
DSB 數位正交解調一般有以下兩個步驟,它與相干解調(同步檢測)法是等效的:
- 第一步:乘以正交相干載波得到 \({s_I}(t)\) 與 \({s_Q}(t)\),即 \({s_I}(t)=2s(t)cos({\omega_ct}+{\phi_0})\),\({s_Q}(t)=-2s(t)sin({\omega_ct}+{\phi_0})\),前面的 2 被用來做幅度補償。
- 第二步:低通濾波器濾除 \({s_I}(t)\) 與 \({s_Q}(t)\) 中的高頻分量,所得的 \(s_I(t)\) 即為解調結果。
對 1.2 節中的 DSB 訊號,設定訊雜比 \(SNR=50dB\),解調效果如下,計算誤差,有:\(\sqrt{\sum{{\lvert}m(t_i)-\hat{m}(t_i){\rvert}^2}}/\sqrt{\sum{{\lvert}m(t_i){\rvert}^2}}\approx0.0016\)。與相干解調(同步檢測)一樣,這種方法對相干載波同頻同相的要求較高。

程式碼詳見 lpf_filter.m、demod_dsb_method3.m 和 main_demodDSB_example3.m。
3. DSB 模擬(MATLAB Communications Toolbox)
MATLAB 的 Communications Toolbox 中提供了 AM 調變函數 ammod,高斯白噪聲函數 awgn,以及 AM 解調函數 amdemod,可以很方便地完成 DSB 訊號模擬,設定 ammod 與 amdemod 的輸入引數 carramp = 0 即為 DSB 的調變與解調(carramp 引數的預設值就是 0,不顯式設定這個引數也可以)。使用這三個函數實現上面 1.2 節中確知訊號 \(m(t)\) 的 DSB 調變解調,調變後加噪聲的效果如下:
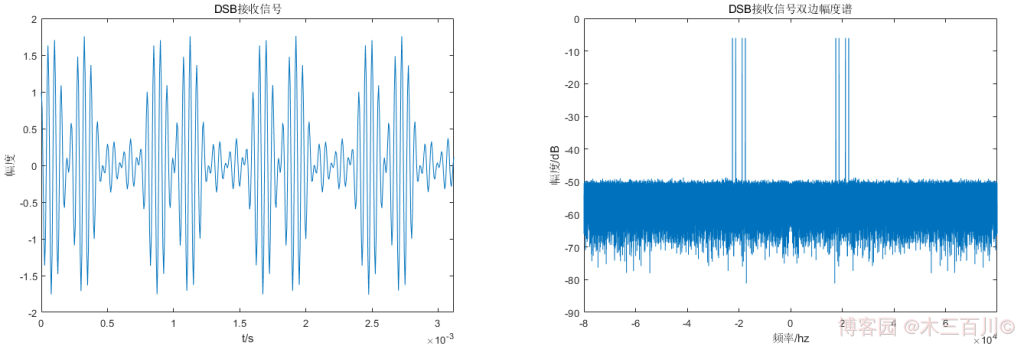
解調效果如下:

解調訊號與調變訊號波形基本重回,計算誤差,有:\(\sqrt{\sum{{\lvert}m(t_i)-\hat{m}(t_i){\rvert}^2}}/\sqrt{\sum{{\lvert}m(t_i){\rvert}^2}}\approx0.0025\)。程式碼詳見附錄 main_CommDSB_example.m。
參考資料
[1] 樓才義,徐建良,楊小牛.軟體無線電原理與應用[M].電子工業出版社,2014.
[2] 樊昌信,曹麗娜.通訊原理.第7版[M].國防工業出版社,2012.
[3] CSDN - 通訊原理之模擬幅度調變(線性調變)詳解。
附錄程式碼
附.1 檔案 mod_dsb.m
function [ sig_dsb ] = mod_dsb(fc, fs, mt, t)
% MOD_DSB DSB 雙邊帶調幅
% 輸入引數:
% fc 載波中心頻率
% fs 訊號取樣率
% mt 調變訊號
% t 取樣時間
% 輸出引數:
% sig_dsb DSB 雙邊帶調幅實訊號
% @author 木三百川
% 生成訊號
ct = cos(2*pi*fc*t);
sig_dsb = mt.*ct; % DSB 雙邊帶調幅訊號
% 繪圖
nfft = length(sig_dsb);
freq = (-nfft/2:nfft/2-1).'*(fs/nfft);
figure;set(gcf,'color','w');
plot_length = min(500, length(sig_dsb));
subplot(3,2,1);
plot(t(1:plot_length), mt(1:plot_length));xlim([t(1),t(plot_length)]);
xlabel('t/s');ylabel('幅度');title('調變訊號m(t)');
subplot(3,2,2);
plot(freq, 10*log10(fftshift(abs(fft(mt,nfft)/nfft))+eps));xlim([freq(1),freq(end)]);
xlabel('頻率/hz');ylabel('幅度/dB');title('調變訊號m(t)雙邊幅度譜');
subplot(3,2,3);
plot(t(1:plot_length), ct(1:plot_length));xlim([t(1),t(plot_length)]);
xlabel('t/s');ylabel('幅度');title('載波c(t)');
subplot(3,2,4);
plot(freq, 10*log10(fftshift(abs(fft(ct,nfft)/nfft))+eps));xlim([freq(1),freq(end)]);
xlabel('頻率/hz');ylabel('幅度/dB');title('載波c(t)雙邊幅度譜');
subplot(3,2,5);
plot(t(1:plot_length), sig_dsb(1:plot_length));xlim([t(1),t(plot_length)]);
xlabel('t/s');ylabel('幅度');title('DSB雙邊帶調幅訊號s(t)');
subplot(3,2,6);
plot(freq, 10*log10(fftshift(abs(fft(sig_dsb,nfft)/nfft))+eps));xlim([freq(1),freq(end)]);
xlabel('頻率/hz');ylabel('幅度/dB');title('DSB雙邊帶調幅訊號s(t)雙邊幅度譜');
end
附.2 檔案 main_modDSB_example.m
clc;
clear;
close all;
% DSB 調變模擬(調變訊號為確知訊號)
% @author 木三百川
% 調變引數
fm = 2500; % 調變訊號引數
fc = 20000; % 載波頻率
fs = 8*fc; % 取樣率
total_time = 2; % 模擬時長,單位:秒
% 取樣時間
t = 0:1/fs:total_time-1/fs;
% 調變訊號為確知訊號
mt = sin(2*pi*fm*t)+cos(pi*fm*t);
% DSB 調變
[ sig_dsb ] = mod_dsb(fc, fs, mt, t);
附.3 檔案 demod_dsb_method1.m
function [ sig_dsb_demod ] = demod_dsb_method1(sig_dsb_receive, fc, fs, t, phi0)
% DEMOD_DSB_METHOD1 DSB 插入載波包絡檢波法
% 輸入引數:
% sig_dsb_receive DSB 接收訊號,行向量
% fc 載波中心頻率
% fs 訊號取樣率
% t 取樣時間
% phi0 載波初始相位
% 輸出引數:
% sig_dsb_demod 解調結果,與 sig_dsb_receive 等長
% @author 木三百川
% 第一步:插入載波
A0 = max(abs(sig_dsb_receive))/0.8;
sig_dsb2am = sig_dsb_receive + A0*cos(2*pi*fc*t+phi0);
% 第二步:使用 AM 解調器進行解調
[ sig_dsb_demod ] = demod_am_method4(sig_dsb2am, fs, t);
end
附.4 檔案 main_demodDSB_example1.m
clc;
clear;
close all;
% DSB 解調模擬(調變訊號為確知訊號,插入載波包絡檢波法)
% @author 木三百川
% 調變引數
fm = 2500; % 調變訊號引數
fc = 20000; % 載波頻率
fs = 8*fc; % 取樣率
total_time = 2; % 模擬時長,單位:秒
% 取樣時間
t = 0:1/fs:total_time-1/fs;
% 調變訊號為確知訊號
mt = sin(2*pi*fm*t)+cos(pi*fm*t);
% DSB 調變
[ sig_dsb_send ] = mod_dsb(fc, fs, mt, t);
% 加噪聲
snr = 50; % 訊雜比
sig_dsb_receive = awgn(sig_dsb_send, snr, 'measured');
% 插入載波包絡檢波法
phi0 = 0;
[ sig_dsb_demod ] = demod_dsb_method1(sig_dsb_receive, fc, fs, t, phi0);
% 繪圖
nfft = length(sig_dsb_receive);
freq = (-nfft/2:nfft/2-1).'*(fs/nfft);
figure;set(gcf,'color','w');
plot_length = min(500, length(sig_dsb_receive));
subplot(1,2,1);
plot(t(1:plot_length), sig_dsb_receive(1:plot_length));xlim([t(1),t(plot_length)]);
xlabel('t/s');ylabel('幅度');title('DSB接收訊號');
subplot(1,2,2);
plot(freq, 10*log10(fftshift(abs(fft(sig_dsb_receive,nfft)/nfft))+eps));xlim([freq(1),freq(end)]);
xlabel('頻率/hz');ylabel('幅度/dB');title('DSB接收訊號雙邊幅度譜');
figure;set(gcf,'color','w');
plot(t(1:plot_length), mt(1:plot_length));xlim([t(1),t(plot_length)]);
hold on;
plot(t(1:plot_length), sig_dsb_demod(1:plot_length));xlim([t(1),t(plot_length)]);
xlabel('t/s');ylabel('幅度');title('解調效果');
legend('調變訊號','解調訊號');
coef = mean(abs(mt))/mean(abs(sig_dsb_demod));
fprintf('norm(調變訊號 - %.2f * 解調訊號)/norm(調變訊號) = %.4f.\n', coef, norm(mt-coef*sig_dsb_demod)/norm(mt));
附.5 檔案 lpf_filter.m
function sig_lpf = lpf_filter(sig_data, cutfre)
% LPF_FILTER 自定義理想低通濾波器
% 輸入引數:
% sig_data 待濾波資料
% cutfre 截止頻率,範圍 (0,1)
% 輸出引數:
% sig_lpf 低通濾波結果
% @author 木三百川
nfft = length(sig_data);
lidx = round(nfft/2-cutfre*nfft/2);
ridx = nfft - lidx;
sig_fft_lpf = fftshift(fft(sig_data));
sig_fft_lpf([1:lidx,ridx:nfft]) = 0;
sig_lpf = real(ifft(fftshift(sig_fft_lpf)));
end
附.6 檔案 demod_dsb_method2.m
function [ sig_dsb_demod ] = demod_dsb_method2(sig_dsb_receive, fc, fs, t, phi0)
% DEMOD_DSB_METHOD2 DSB 相干解調(同步檢測)
% 輸入引數:
% sig_dsb_receive DSB 接收訊號,行向量
% fc 載波中心頻率
% fs 訊號取樣率
% t 取樣時間
% phi0 載波初始相位
% 輸出引數:
% sig_dsb_demod 解調結果,與 sig_dsb_receive 等長
% @author 木三百川
% 第一步:乘以相干載波
sig_dsbct = 2*sig_dsb_receive.*cos(2*pi*fc*t+phi0);
% 第二步:低通濾波
sig_dsb_demod = lpf_filter(sig_dsbct, fc/(fs/2));
end
附.7 檔案 main_demodDSB_example2.m
clc;
clear;
close all;
% DSB 解調模擬(調變訊號為確知訊號,相干解調(同步檢測))
% @author 木三百川
% 調變引數
fm = 2500; % 調變訊號引數
fc = 20000; % 載波頻率
fs = 8*fc; % 取樣率
total_time = 2; % 模擬時長,單位:秒
% 取樣時間
t = 0:1/fs:total_time-1/fs;
% 調變訊號為確知訊號
mt = sin(2*pi*fm*t)+cos(pi*fm*t);
% DSB 調變
[ sig_dsb_send ] = mod_dsb(fc, fs, mt, t);
% 加噪聲
snr = 50; % 訊雜比
sig_dsb_receive = awgn(sig_dsb_send, snr, 'measured');
% 相干解調(同步檢測)
phi0 = 0;
[ sig_dsb_demod ] = demod_dsb_method2(sig_dsb_receive, fc, fs, t, phi0);
% 繪圖
nfft = length(sig_dsb_receive);
freq = (-nfft/2:nfft/2-1).'*(fs/nfft);
figure;set(gcf,'color','w');
plot_length = min(500, length(sig_dsb_receive));
subplot(1,2,1);
plot(t(1:plot_length), sig_dsb_receive(1:plot_length));xlim([t(1),t(plot_length)]);
xlabel('t/s');ylabel('幅度');title('DSB接收訊號');
subplot(1,2,2);
plot(freq, 10*log10(fftshift(abs(fft(sig_dsb_receive,nfft)/nfft))+eps));xlim([freq(1),freq(end)]);
xlabel('頻率/hz');ylabel('幅度/dB');title('DSB接收訊號雙邊幅度譜');
figure;set(gcf,'color','w');
plot(t(1:plot_length), mt(1:plot_length));xlim([t(1),t(plot_length)]);
hold on;
plot(t(1:plot_length), sig_dsb_demod(1:plot_length));xlim([t(1),t(plot_length)]);
xlabel('t/s');ylabel('幅度');title('解調效果');
legend('調變訊號','解調訊號');
coef = mean(abs(mt))/mean(abs(sig_dsb_demod));
fprintf('norm(調變訊號 - %.2f * 解調訊號)/norm(調變訊號) = %.4f.\n', coef, norm(mt-coef*sig_dsb_demod)/norm(mt));
附.8 檔案 demod_dsb_method3.m
function [ sig_dsb_demod ] = demod_dsb_method3(sig_dsb_receive, fc, fs, t, phi0)
% DEMOD_DSB_METHOD3 DSB 數位正交解調,與相干解調(同步檢測)是等效的
% 輸入引數:
% sig_dsb_receive DSB 接收訊號,行向量
% fc 載波中心頻率
% fs 訊號取樣率
% t 取樣時間
% phi0 載波初始相位
% 輸出引數:
% sig_dsb_demod 解調結果,與 sig_dsb_receive 等長
% @author 木三百川
% 第一步:乘以正交相干載波
sig_dsb_i = 2*sig_dsb_receive.*cos(2*pi*fc*t+phi0);
sig_dsb_q = -2*sig_dsb_receive.*sin(2*pi*fc*t+phi0);
% 第二步:低通濾波
sig_dsb_i_lpf = lpf_filter(sig_dsb_i, fc/(fs/2));
sig_dsb_q_lpf = lpf_filter(sig_dsb_q, fc/(fs/2));
sig_dsb_demod = sig_dsb_i_lpf;
end
附.9 檔案 main_demodDSB_example3.m
clc;
clear;
close all;
% DSB 解調模擬(調變訊號為確知訊號,數位正交解調)
% @author 木三百川
% 調變引數
fm = 2500; % 調變訊號引數
fc = 20000; % 載波頻率
fs = 8*fc; % 取樣率
total_time = 2; % 模擬時長,單位:秒
% 取樣時間
t = 0:1/fs:total_time-1/fs;
% 調變訊號為確知訊號
mt = sin(2*pi*fm*t)+cos(pi*fm*t);
% DSB 調變
[ sig_dsb_send ] = mod_dsb(fc, fs, mt, t);
% 加噪聲
snr = 50; % 訊雜比
sig_dsb_receive = awgn(sig_dsb_send, snr, 'measured');
% 數位正交解調
phi0 = 0;
[ sig_dsb_demod ] = demod_dsb_method3(sig_dsb_receive, fc, fs, t, phi0);
% 繪圖
nfft = length(sig_dsb_receive);
freq = (-nfft/2:nfft/2-1).'*(fs/nfft);
figure;set(gcf,'color','w');
plot_length = min(500, length(sig_dsb_receive));
subplot(1,2,1);
plot(t(1:plot_length), sig_dsb_receive(1:plot_length));xlim([t(1),t(plot_length)]);
xlabel('t/s');ylabel('幅度');title('DSB接收訊號');
subplot(1,2,2);
plot(freq, 10*log10(fftshift(abs(fft(sig_dsb_receive,nfft)/nfft))+eps));xlim([freq(1),freq(end)]);
xlabel('頻率/hz');ylabel('幅度/dB');title('DSB接收訊號雙邊幅度譜');
figure;set(gcf,'color','w');
plot(t(1:plot_length), mt(1:plot_length));xlim([t(1),t(plot_length)]);
hold on;
plot(t(1:plot_length), sig_dsb_demod(1:plot_length));xlim([t(1),t(plot_length)]);
xlabel('t/s');ylabel('幅度');title('解調效果');
legend('調變訊號','解調訊號');
coef = mean(abs(mt))/mean(abs(sig_dsb_demod));
fprintf('norm(調變訊號 - %.2f * 解調訊號)/norm(調變訊號) = %.4f.\n', coef, norm(mt-coef*sig_dsb_demod)/norm(mt));
附.10 檔案 main_CommDSB_example.m
clc;
clear;
close all;
% DSB 調變解調模擬(使用Communications Toolbox工具箱)
% @author 木三百川
% 調變引數
fm = 2500; % 調變訊號引數
fc = 20000; % 載波頻率
fs = 8*fc; % 取樣率
total_time = 2; % 模擬時長,單位:秒
% 取樣時間
t = 0:1/fs:total_time-1/fs;
% 調變訊號為確知訊號
mt = sin(2*pi*fm*t)+cos(pi*fm*t);
% DSB 調變
ini_phase = 0;
sig_dsb_send = ammod(mt, fc, fs, ini_phase);
% 加噪聲
snr = 50; % 訊雜比
sig_dsb_receive = awgn(sig_dsb_send, snr, 'measured');
% DSB 解調
[ sig_dsb_demod ] = amdemod(sig_dsb_receive, fc, fs, ini_phase);
% 繪圖
nfft = length(sig_dsb_receive);
freq = (-nfft/2:nfft/2-1).'*(fs/nfft);
figure;set(gcf,'color','w');
plot_length = min(500, length(sig_dsb_receive));
subplot(1,2,1);
plot(t(1:plot_length), sig_dsb_receive(1:plot_length));xlim([t(1),t(plot_length)]);
xlabel('t/s');ylabel('幅度');title('DSB接收訊號');
subplot(1,2,2);
plot(freq, 10*log10(fftshift(abs(fft(sig_dsb_receive,nfft)/nfft))+eps));xlim([freq(1),freq(end)]);
xlabel('頻率/hz');ylabel('幅度/dB');title('DSB接收訊號雙邊幅度譜');
figure;set(gcf,'color','w');
plot(t(1:plot_length), mt(1:plot_length));xlim([t(1),t(plot_length)]);
hold on;
plot(t(1:plot_length), sig_dsb_demod(1:plot_length));xlim([t(1),t(plot_length)]);
xlabel('t/s');ylabel('幅度');title('解調效果');
legend('調變訊號','解調訊號');
coef = mean(abs(mt))/mean(abs(sig_dsb_demod));
fprintf('norm(調變訊號 - %.2f * 解調訊號)/norm(調變訊號) = %.4f.\n', coef, norm(mt-coef*sig_dsb_demod)/norm(mt));
本文作者:木三百川
本文連結:https://www.cnblogs.com/young520/p/17542816.html
版權宣告:本文系博主原創文章,著作權歸作者所有。商業轉載請聯絡作者獲得授權,非商業轉載請附上出處連結。遵循 署名-非商業性使用-相同方式共用 4.0 國際版 (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) 版權協定。