怎樣優雅地增刪查改(一):從0開始搭建Volo.Abp專案
@
軟體系統中資料庫或者持久層的基本操作功能可以用Curd描述,Curd即 增加(Create)、更新(Update)、讀取查詢(Retrieve)和刪除(Delete), 這4個單詞的首字母。
在常見的業務系統中,對資料的大部分操作都是Curd,在實踐的過程中對資料的篩選、排序、分頁、關聯查詢等功能抽象和封裝。
本系列博文將從0開始,逐步搭建一個基於Volo.Abp + Vue 的前後端分離的,具有Curd通用查詢功能的專案。
-
怎樣優雅地增刪查改(二):擴充套件身份管理模組
專案介紹
本專案是基於一個簡單的使用者健康資料管理系統,我們將對業務常用的查詢功能進行擴充套件,抽象這些業務並封裝成介面,稱之為通用查詢介面(GeneralCurdInterfaces),本專案關注的是基礎設施層,但大部分實現還是圍繞業務,對於普適性有待研究,所以我還是決定以Sample為名。
模組化
Abp模組是可以供主模組重用的獨立功能單元,每個模組可以包含應用服務、領域層、資料存取層、Web API等,模組可以被其他模組參照,也可以被主模組參照。
本專案模組化的目的除了可重用,更多是為微服務架構做準備。微服務架構不在本博文的討論範圍,為了簡化,還是使用單體應用架構。
由框架實現的
Volo.Abp 為我們實現了CrudAppService,(在舊版本的AbpBoilerplate中稱Crud為Curd,在我看來兩者沒有什麼區別,本專案還是以Curd命名)
CrudAppService為我們提供了基本的增刪改查,以及分頁、排序的實現
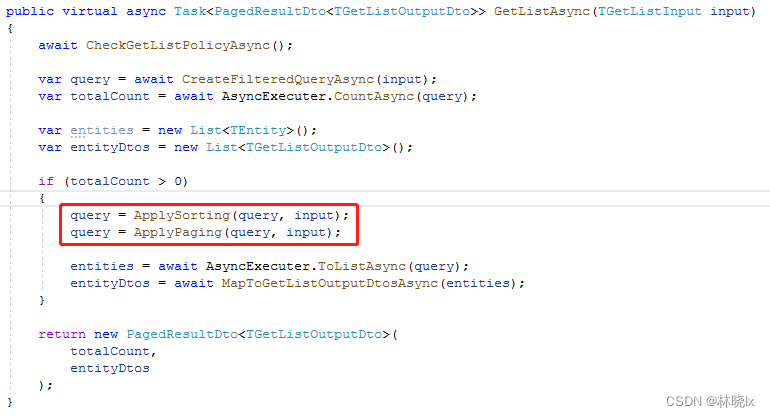
需要實現的
-
按任意欄位關鍵字查詢
-
按任意欄位排序
-
按組織架構查詢
-
按使用者查詢
-
按使用者關係查詢
-
按建立日期查詢(起始日期,結束日期)
本專案雖然是用Volo.Abp實現,但對於舊版本的AbpBoilerplate仍然可以方便的移植,可以看我之前的博文:[Volo.Abp升級筆記]使用舊版Api規則替換RESTful Api以相容老程式,如何以最大限度保持介面的相容性。
建立專案
建立空白資料夾,在資料夾內開啟命令列
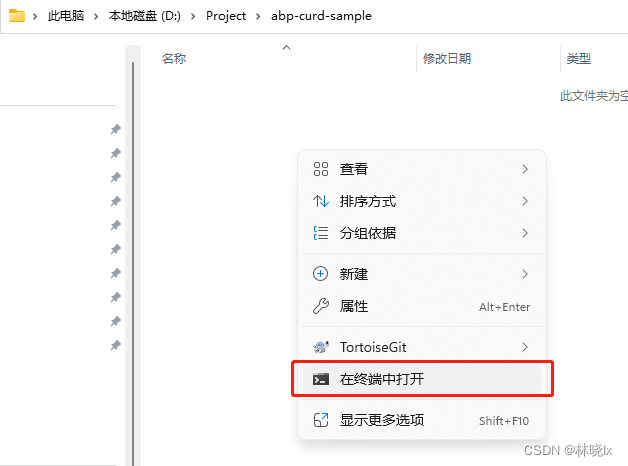
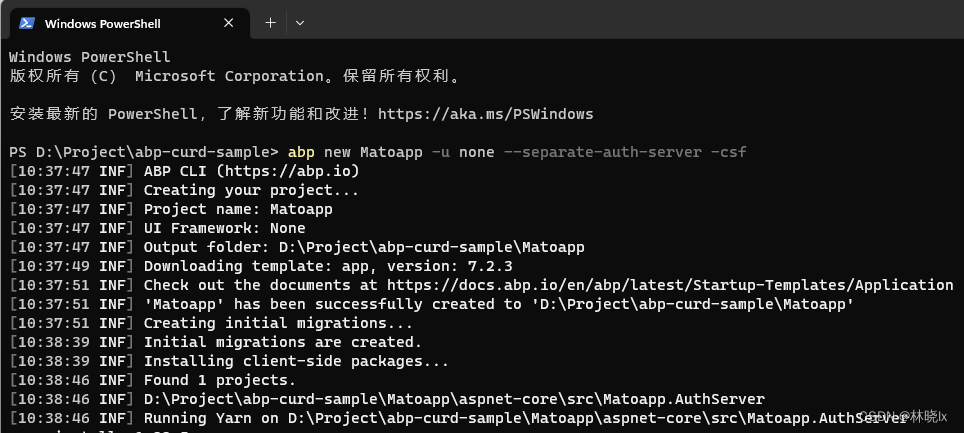
使用AbpCli建立一個無UI的專案 拆分Auth Server,執行以下命令
abp new Matoapp -u none --separate-auth-server -csf
等待專案建立成功
建立業務模組
作為名稱空間字首,Matoapp是一個虛構的企業名稱。
在解決方案目錄中建立新目錄src/modules,在該目錄下建立員工健康管理模組Health,公共業務模組Common,以及擴充套件了Volo.Abp.Indentity的Identity模組
在modules目錄下開啟命令列,分別執行以下命令
abp new Matoapp.Health -t module --no-ui
abp new Matoapp.Common -t module --no-ui
abp new Matoapp.Identity -t module --no-ui
等待模組建立完成
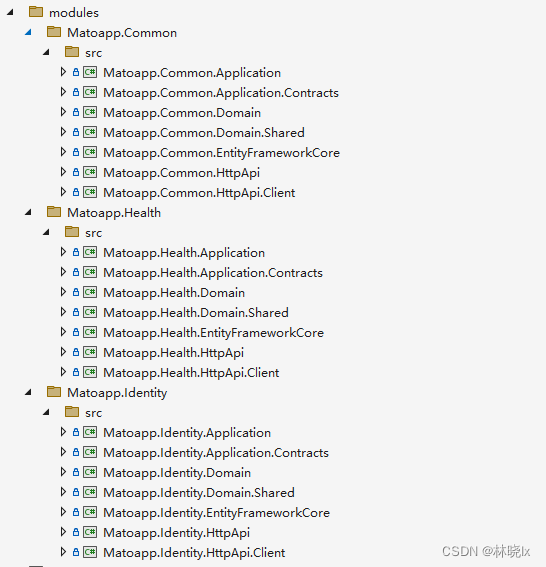
開啟解決方案,將業務模組中的各個專案新增到解決方案中,我們只需要新增各模組的Application,Application.Contracts,Domain,Domain.Shared,EntityFrameworkCore,HttpApi以及HttpApi.Client。
新增完成後的解決方案結構看上去像這樣:
設定參照和依賴
將Volo.Abp.Identity.Application新增到Application專案的參照中
dotnet add package Volo.Abp.Identity.Application
將Volo.Abp.Identity.Application.Contracts新增到Application.Contracts專案的參照中
dotnet add package Volo.Abp.Identity.Application.Contracts
將Volo.Abp.Identity.Domain,Volo.Abp.PermissionManagement.Domain新增到Domain專案的參照中
dotnet add package Volo.Abp.Identity.Domain
dotnet add package Volo.Abp.PermissionManagement.Domain
將Volo.Abp.Identity.EntityFrameworkCore新增到EntityFrameworkCore專案的參照中
dotnet add package Volo.Abp.Identity.EntityFrameworkCore
Application層
Application層新增對各模組的參照,
ApplicationModule中新增對各模組的依賴
[DependsOn(
...
typeof(CommonApplicationModule),
typeof(HealthApplicationModule),
typeof(IdentityApplicationModule)
)]
public class MatoappApplicationModule : AbpModule
{
}
AuthServer新增Identity資料存取層參照,並設定依賴關係
[DependsOn(
...
typeof(IdentityDomainModule),
typeof(IdentityEntityFrameworkCoreModule)
)]
public class MatoappAuthServerModule : AbpModule
{
}
HttpApi層新增對各模組的參照,
HttpApiModule中新增對各模組的依賴
[DependsOn(
...
typeof(CommonHttpApiModule),
typeof(HealthHttpApiModule),
typeof(IdentityHttpApiModule)
)]
public class MatoappHttpApiModule : AbpModule
{
}
設定DbContext
用CodeFirst方式建立一些業務表,比如員工表,客戶表,報警表等,這些表都是在Health模組中建立的,
Tag相關的表放入Common模組中,Relation表放入Identity模組中。
這些業務表按照業務模組的劃分,放入各自的DbContext中。
public interface IIdentityDbContext : IEfCoreDbContext
{
DbSet<Relation.Relation> Relation { get; set; }
}
public interface IHealthDbContext : IEfCoreDbContext
{
DbSet<Client.Client> Client { get; set; }
DbSet<Employee.Employee> Employee { get; set; }
DbSet<Alarm.Alarm> Alarm { get; set; }
DbSet<SimpleValueRecord> SimpleValueRecord { get; set; }
}
public interface ICommonDbContext : IEfCoreDbContext
{
DbSet<DataEnum.DataEnum> DataEnum { get; set; }
DbSet<DataEnumCategory.DataEnumCategory> DataEnumCategory { get; set; }
DbSet<Tag.Tag> Tag { get; set; }
}
各業務模組的DbContextModelCreatingExtensions中新增對各表的欄位,約束,索引等的設定。以便在DbContext的OnModelCreating中呼叫
builder.ConfigureCommon();
builder.ConfigureHealth();
builder.ConfigureMatoIdentity();
EntityFrameworkCore層中改寫MatoappDbContext如下:
[ReplaceDbContext(typeof(Matoapp.Identity.EntityFrameworkCore.IIdentityDbContext))]
[ReplaceDbContext(typeof(IHealthDbContext))]
[ReplaceDbContext(typeof(ICommonDbContext))]
[ReplaceDbContext(typeof(ITenantManagementDbContext))]
[ConnectionStringName("Default")]
public class MatoappDbContext :
AbpDbContext<MatoappDbContext>,
Matoapp.Identity.EntityFrameworkCore.IIdentityDbContext,
IHealthDbContext,
ICommonDbContext,
ITenantManagementDbContext
{
#region Entities from the modules
public DbSet<Relation> Relation { get; set; }
// Tenant Management
public DbSet<Tenant> Tenants { get; set; }
public DbSet<TenantConnectionString> TenantConnectionStrings { get; set; }
public DbSet<Client> Client { get; set; }
public DbSet<Employee> Employee { get; set; }
public DbSet<Alarm> Alarm { get; set; }
public DbSet<SimpleValueRecord> SimpleValueRecord { get; set; }
public DbSet<DataEnum> DataEnum { get; set; }
public DbSet<DataEnumCategory> DataEnumCategory { get; set; }
public DbSet<Tag> Tag { get; set; }
#endregion
public MatoappDbContext(DbContextOptions<MatoappDbContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder builder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(builder);
/* Include modules to your migration db context */
builder.ConfigurePermissionManagement();
builder.ConfigureSettingManagement();
builder.ConfigureBackgroundJobs();
builder.ConfigureAuditLogging();
builder.ConfigureIdentity();
builder.ConfigureOpenIddict();
builder.ConfigureFeatureManagement();
builder.ConfigureTenantManagement();
builder.ConfigureCommon();
builder.ConfigureHealth();
builder.ConfigureMatoIdentity();
/* Configure your own tables/entities inside here */
//builder.Entity<YourEntity>(b =>
//{
// b.ToTable(MatoappConsts.DbTablePrefix + "YourEntities", MatoappConsts.DbSchema);
// b.ConfigureByConvention(); //auto configure for the base class props
// //...
//});
}
}
在AuthServer建立AuthServerDbContextFactory,AuthServerDbContext。
AuthServerDbContext.cs程式碼如下
public class AuthServerDbContext : AbpDbContext<AuthServerDbContext>
{
public AuthServerDbContext(DbContextOptions<AuthServerDbContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
modelBuilder.ConfigureIdentity();
modelBuilder.ConfigureIdentityServer();
modelBuilder.ConfigureAuditLogging();
modelBuilder.ConfigurePermissionManagement();
modelBuilder.ConfigureSettingManagement();
modelBuilder.ConfigureTenantManagement();
modelBuilder.ConfigureFeatureManagement();
modelBuilder.ConfigureMatoIdentity();
}
}
建立實體和Dto
在各業務模組中建立實體類,以及對應的Dto類
此處以Health模組為例,建立以下實體類
- Employee 員工
- Client 客戶
- Alarm 報警
- SimpleValueRecord 簡單值記錄
設定AutoMapper
根據實際業務需求,設定AutoMapper,將實體類對映到DTO類。此處以Health模組為例。
public HealthApplicationAutoMapperProfile()
{
CreateMap<Client.Client, ClientDto>().Ignore(c => c.EntityVersion);
CreateMap<Employee.Employee, EmployeeDto>().Ignore(c => c.EntityVersion);
CreateMap<ClientDto, Client.Client>();
CreateMap<EmployeeDto, Employee.Employee>();
CreateMap<Alarm.Alarm, AlarmDto>();
CreateMap<Alarm.Alarm, AlarmBriefDto>();
CreateMap<AlarmDto, Alarm.Alarm>().Ignore(c => c.TenantId)
.Ignore(c => c.ConcurrencyStamp);
CreateMap<CreateAlarmInput, Alarm.Alarm>().IgnoreFullAuditedObjectProperties()
.IgnoreSoftDeleteProperties()
.Ignore(c => c.TenantId)
.Ignore(c => c.User)
.Ignore(c => c.ConcurrencyStamp)
.Ignore(c => c.Id);
CreateMap<UpdateAlarmInput, Alarm.Alarm>().IgnoreFullAuditedObjectProperties()
.IgnoreSoftDeleteProperties()
.Ignore(c => c.TenantId)
.Ignore(c => c.User)
.Ignore(c => c.ConcurrencyStamp);
CreateMap<SimpleValueRecord, SimpleValueRecordBriefDto>();
CreateMap<SimpleValueRecord, SimpleValueRecordDto>();
CreateMap<SimpleValueRecordDto, SimpleValueRecord>().Ignore(c => c.TenantId)
.Ignore(c => c.Alarm)
.Ignore(c => c.ConcurrencyStamp);
CreateMap<CreateClientInput, Client.Client>()
.ForAllMembers(opt => opt.Condition((src, dest, srcMember, destMember) => srcMember != null));
CreateMap<CreateClientWithUserInput, Client.Client>()
.IgnoreFullAuditedObjectProperties()
.IgnoreSoftDeleteProperties()
.Ignore(c => c.LockoutEnabled)
.Ignore(c => c.LockoutEnd)
.Ignore(c => c.TenantId)
.Ignore(c => c.ConcurrencyStamp)
.Ignore(c => c.EmailConfirmed)
.Ignore(c => c.PhoneNumberConfirmed)
.Ignore(c => c.Id)
.ForAllMembers(opt => opt.Condition((src, dest, srcMember, destMember) => srcMember != null));
CreateMap<CreateEmployeeInput, Employee.Employee>()
.ForAllMembers(opt => opt.Condition((src, dest, srcMember, destMember) => srcMember != null));
CreateMap<CreateEmployeeWithUserInput, Employee.Employee>()
.IgnoreFullAuditedObjectProperties()
.IgnoreSoftDeleteProperties()
.Ignore(c => c.LockoutEnabled)
.Ignore(c => c.LockoutEnd)
.Ignore(c => c.TenantId)
.Ignore(c => c.ConcurrencyStamp)
.Ignore(c => c.EmailConfirmed)
.Ignore(c => c.PhoneNumberConfirmed)
.Ignore(c => c.Id)
.ForAllMembers(opt => opt.Condition((src, dest, srcMember, destMember) => srcMember != null));
}
至此,我們有了基礎的資料庫,實體類,Dto類。下一步我們將建立通用Curd應用服務,以及通用查詢介面。
本文來自部落格園,作者:林曉lx,轉載請註明原文連結:https://www.cnblogs.com/jevonsflash/p/17535877.html