OCR -- 文字識別 -- 實踐篇
OCR -- 文字識別 -- 理論篇
本章將詳細介紹如何基於PaddleOCR完成CRNN文字識別模型的搭建、訓練、評估和預測。資料集採用 icdar 2015,其中訓練集有4468張,測試集有2077張。
CRNN是基於CTC的演演算法,CRNN是較早被提出也是目前工業界應用較多的方法。主要用於識別規則文字,有效快的預測速度,並且因為序列不對齊,不受長度的影響,所以在長文字上有很好的預測效果,中文演演算法裡的首選
預測原理詳解
2. 預測原理詳解
第一節中 paddleocr 載入訓練好的 CRNN 識別模型進行預測,本節將詳細介紹 CRNN 的原理及流程。
2.1 所屬類別
CRNN 是基於CTC的演演算法,在理論部分介紹的分類圖中,處在如下位置。可以看出CRNN主要用於解決規則文字,基於CTC的演演算法有較快的預測速度並且很好的適用長文字。因此CRNN是PPOCR選擇的中文識別演演算法。
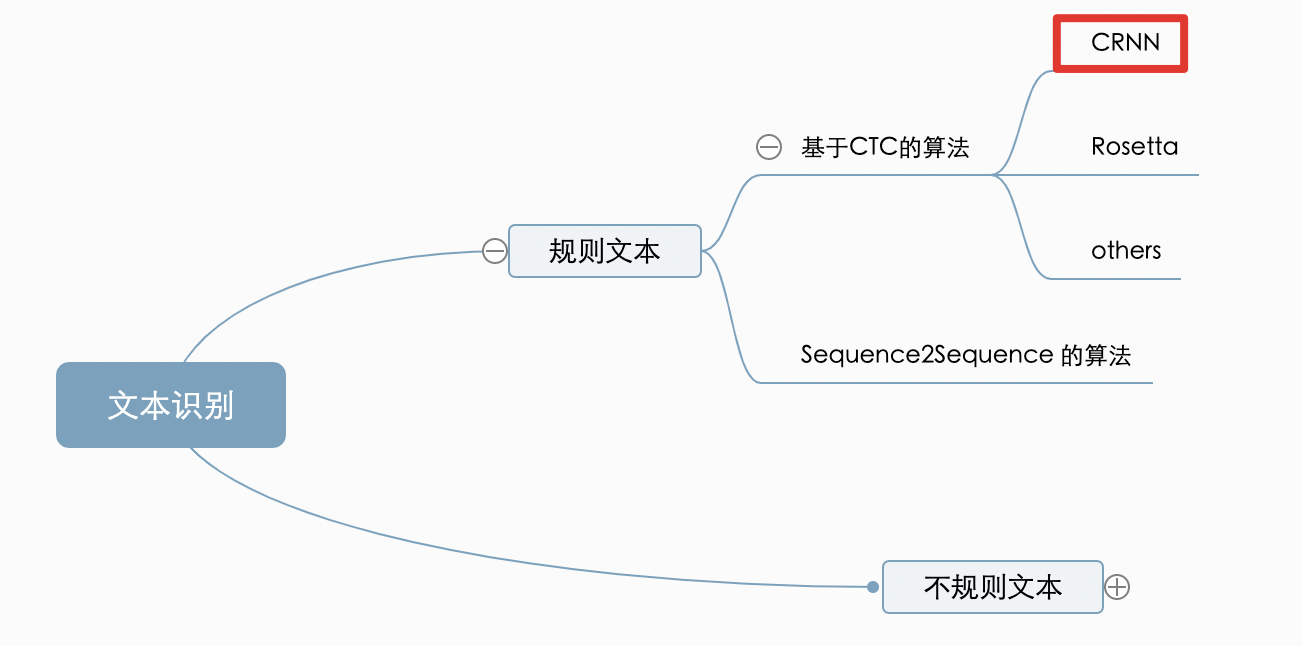
2.2 演演算法詳解
CRNN 的網路結構體系如下所示,從下往上分別為折積層、遞迴層和轉錄層三部分:
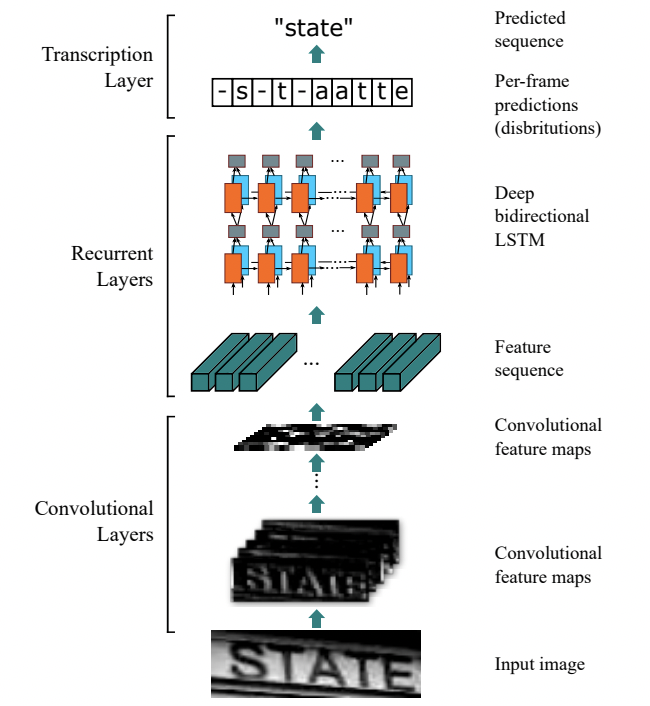
1)backbone:
折積網路作為底層的骨幹網路,用於從輸入影象中提取特徵序列。由於 conv、max-pooling、elementwise 和啟用函數都作用在區域性區域上,所以它們是平移不變的。因此,特徵對映的每一列對應於原始影象的一個矩形區域(稱為感受野),並且這些矩形區域與它們在特徵對映上對應的列從左到右的順序相同。由於CNN需要將輸入的影象縮放到固定的尺寸以滿足其固定的輸入維數,因此它不適合長度變化很大的序列物件。為了更好的支援變長序列,CRNN將backbone最後一層輸出的特徵向量送到了RNN層,轉換為序列特徵。
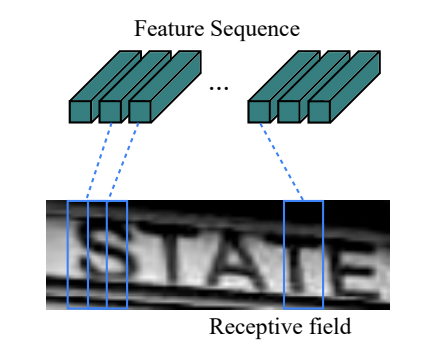
2)neck:
遞迴層,在折積網路的基礎上,構建遞迴網路,將影象特徵轉換為序列特徵,預測每個幀的標籤分佈。
RNN具有很強的捕獲序列上下文資訊的能力。使用上下文線索進行基於影象的序列識別比單獨處理每個畫素更有效。以場景文字識別為例,寬字元可能需要幾個連續的幀來充分描述。此外,有些歧義字元在觀察其上下文時更容易區分。其次,RNN可以將誤差差分反向傳播回折積層,使網路可以統一訓練。第三,RNN能夠對任意長度的序列進行操作,解決了文字圖片變長的問題。CRNN使用雙層LSTM作為遞迴層,解決了長序列訓練過程中的梯度消失和梯度爆炸問題。
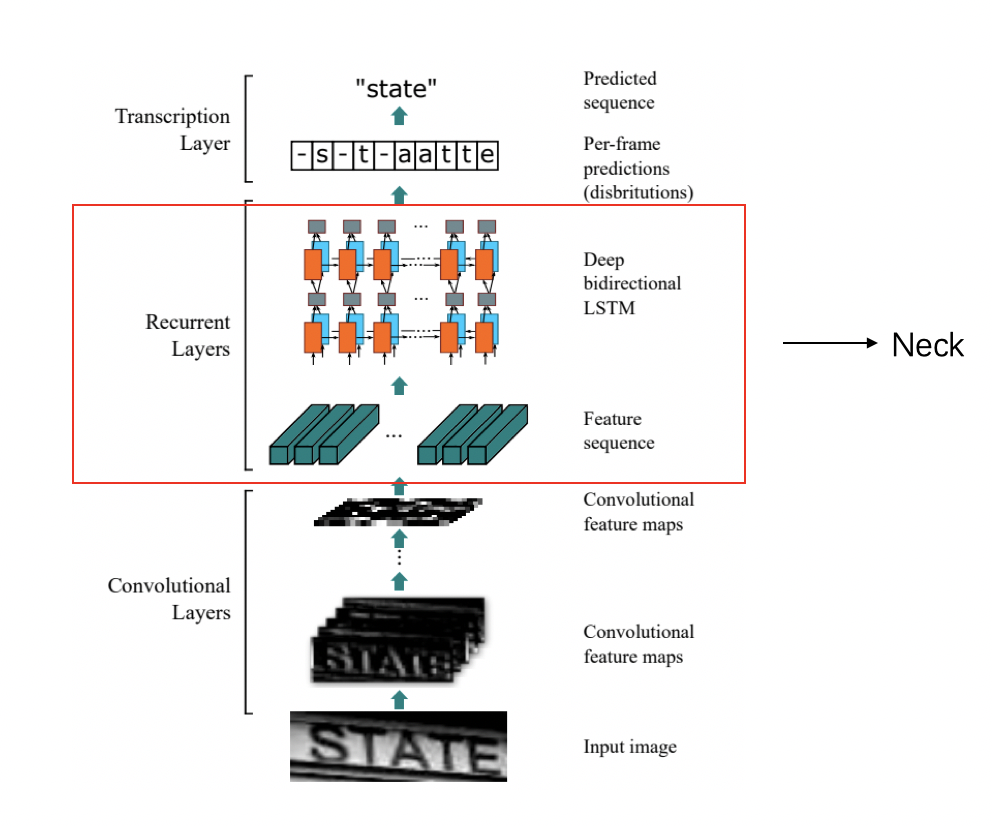
3)head:
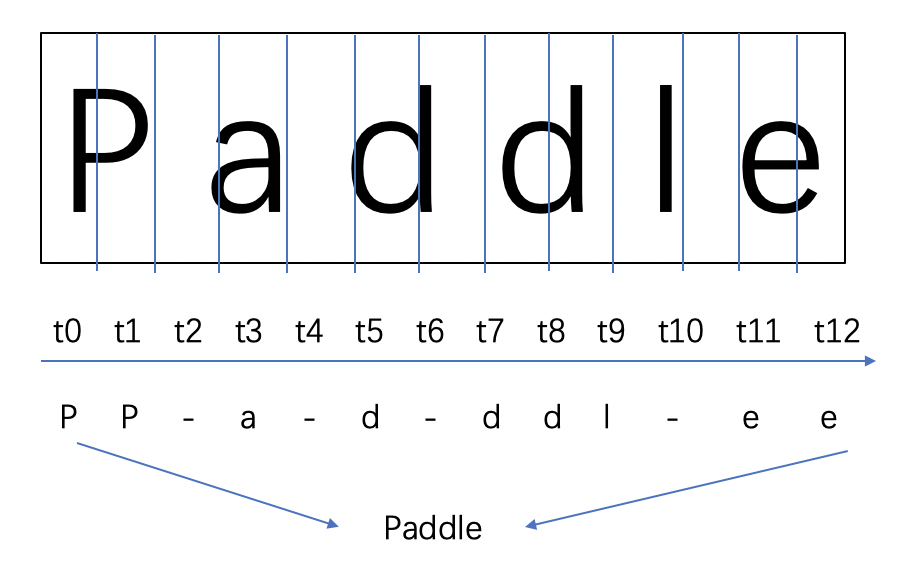
轉錄層,通過全連線網路和softmax啟用函數,將每幀的預測轉換為最終的標籤序列。最後使用 CTC Loss 在無需序列對齊的情況下,完成CNN和RNN的聯合訓練。CTC 有一套特別的合併序列機制,LSTM輸出序列後,需要在時序上分類得到預測結果。可能存在多個時間步對應同一個類別,因此需要對相同結果進行合併。為避免合併本身存在的重複字元,CTC 引入了一個 blank 字元插入在重複字元之間。
2.2 程式碼實現
整個網路結構非常簡潔,程式碼實現也相對簡單,可以跟隨預測流程依次搭建模組。本節需要完成:資料輸入、backbone搭建、neck搭建、head搭建。
【資料輸入】
資料送入網路前需要縮放到統一尺寸(3,32,320)【英文一般是(3,32,100),高度 32 效果比較好,】,並完成歸一化處理。這裡省略掉訓練時需要的資料增強部分,以單張圖為例展示預處理的必須步驟(原始碼位置):
中文字元,長、寬比,1:1, 10倍 320,
import cv2
import math
import numpy as np
def resize_norm_img(img):
"""
資料縮放和歸一化
:param img: 輸入圖片
"""
# 預設輸入尺寸 英文為 (3,32,100)
imgC = 3
imgH = 32 # 高度 32 效果比較好
imgW = 320 # 中文每個字長寬比為1:1,防止長寬比在resize後被壓縮過小或拉伸過大,識別大概10個字左右,所以寬度 10倍 = 320
# 圖片的真實高寬
h, w = img.shape[:2]
# 圖片真實長寬比
ratio = w / float(h)
# 按比例縮放
if math.ceil(imgH * ratio) > imgW:
# 如大於預設寬度,則寬度為imgW
resized_w = imgW
else:
# 如小於預設寬度則以圖片真實寬為準
resized_w = int(math.ceil(imgH * ratio))
# 縮放
resized_image = cv2.resize(img, (resized_w, imgH))
resized_image = resized_image.astype('float32')
# 歸一化
resized_image = resized_image.transpose((2, 0, 1)) / 255
resized_image -= 0.5
resized_image /= 0.5
# 對寬度不足的位置,補0
padding_im = np.zeros((imgC, imgH, imgW), dtype=np.float32)
padding_im[:, :, 0:resized_w] = resized_image
# 轉置 padding 後的圖片用於視覺化
draw_img = padding_im.transpose((1,2,0))
return padding_im, draw_img
【網路結構】
- backbone
PaddleOCR 使用 MobileNetV3 作為骨幹網路,組網順序與網路結構一致,首先定義網路中的公共模組(原始碼位置):ConvBNLayer、ResidualUnit、make_divisible
import paddle
import paddle.nn as nn
import paddle.nn.functional as F
class ConvBNLayer(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self,
in_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size,
stride,
padding,
groups=1,
if_act=True,
act=None):
"""
折積BN層
:param in_channels: 輸入通道數
:param out_channels: 輸出通道數
:param kernel_size: 折積核尺寸
:parma stride: 步長大小
:param padding: 填充大小
:param groups: 二維折積層的組數
:param if_act: 是否新增啟用函數
:param act: 啟用函數
"""
super(ConvBNLayer, self).__init__()
self.if_act = if_act
self.act = act
self.conv = nn.Conv2D(
in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=out_channels,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=stride,
padding=padding,
groups=groups,
bias_attr=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm(num_channels=out_channels, act=None)
def forward(self, x):
# conv層
x = self.conv(x)
# batchnorm層
x = self.bn(x)
# 是否使用啟用函數
if self.if_act:
if self.act == "relu":
x = F.relu(x)
elif self.act == "hardswish":
x = F.hardswish(x)
else:
print("The activation function({}) is selected incorrectly.".
format(self.act))
exit()
return x
class SEModule(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, in_channels, reduction=4):
"""
SE模組
:param in_channels: 輸入通道數
:param reduction: 通道縮放率
"""
super(SEModule, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2D(1)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2D(
in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=in_channels // reduction,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2D(
in_channels=in_channels // reduction,
out_channels=in_channels,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0)
def forward(self, inputs):
# 平均池化
outputs = self.avg_pool(inputs)
# 第一個折積層
outputs = self.conv1(outputs)
# relu啟用函數
outputs = F.relu(outputs)
# 第二個折積層
outputs = self.conv2(outputs)
# hardsigmoid 啟用函數
outputs = F.hardsigmoid(outputs, slope=0.2, offset=0.5)
return inputs * outputs
class ResidualUnit(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self,
in_channels,
mid_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size,
stride,
use_se,
act=None):
"""
殘差層
:param in_channels: 輸入通道數
:param mid_channels: 中間通道數
:param out_channels: 輸出通道數
:param kernel_size: 折積核尺寸
:parma stride: 步長大小
:param use_se: 是否使用se模組
:param act: 啟用函數
"""
super(ResidualUnit, self).__init__()
self.if_shortcut = stride == 1 and in_channels == out_channels
self.if_se = use_se
self.expand_conv = ConvBNLayer(
in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=mid_channels,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0,
if_act=True,
act=act)
self.bottleneck_conv = ConvBNLayer(
in_channels=mid_channels,
out_channels=mid_channels,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=stride,
padding=int((kernel_size - 1) // 2),
groups=mid_channels,
if_act=True,
act=act)
if self.if_se:
self.mid_se = SEModule(mid_channels)
self.linear_conv = ConvBNLayer(
in_channels=mid_channels,
out_channels=out_channels,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0,
if_act=False,
act=None)
def forward(self, inputs):
x = self.expand_conv(inputs)
x = self.bottleneck_conv(x)
if self.if_se:
x = self.mid_se(x)
x = self.linear_conv(x)
if self.if_shortcut:
x = paddle.add(inputs, x)
return x
def make_divisible(v, divisor=8, min_value=None):
"""
確保被8整除
"""
if min_value is None:
min_value = divisor
new_v = max(min_value, int(v + divisor / 2) // divisor * divisor)
if new_v < 0.9 * v:
new_v += divisor
return new_v
利用公共模組搭建骨幹網路
class MobileNetV3(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self,
in_channels=3,
model_name='small',
scale=0.5,
small_stride=None,
disable_se=False,
**kwargs):
super(MobileNetV3, self).__init__()
self.disable_se = disable_se
small_stride = [1, 2, 2, 2]
if model_name == "small":
cfg = [
# k, exp, c, se, nl, s,
[3, 16, 16, True, 'relu', (small_stride[0], 1)],
[3, 72, 24, False, 'relu', (small_stride[1], 1)],
[3, 88, 24, False, 'relu', 1],
[5, 96, 40, True, 'hardswish', (small_stride[2], 1)],
[5, 240, 40, True, 'hardswish', 1],
[5, 240, 40, True, 'hardswish', 1],
[5, 120, 48, True, 'hardswish', 1],
[5, 144, 48, True, 'hardswish', 1],
[5, 288, 96, True, 'hardswish', (small_stride[3], 1)],
[5, 576, 96, True, 'hardswish', 1],
[5, 576, 96, True, 'hardswish', 1],
]
cls_ch_squeeze = 576
else:
raise NotImplementedError("mode[" + model_name +
"_model] is not implemented!")
supported_scale = [0.35, 0.5, 0.75, 1.0, 1.25]
assert scale in supported_scale, \
"supported scales are {} but input scale is {}".format(supported_scale, scale)
inplanes = 16
# conv1
self.conv1 = ConvBNLayer(
in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=make_divisible(inplanes * scale),
kernel_size=3,
stride=2,
padding=1,
groups=1,
if_act=True,
act='hardswish')
i = 0
block_list = []
inplanes = make_divisible(inplanes * scale)
for (k, exp, c, se, nl, s) in cfg:
se = se and not self.disable_se
block_list.append(
ResidualUnit(
in_channels=inplanes,
mid_channels=make_divisible(scale * exp),
out_channels=make_divisible(scale * c),
kernel_size=k,
stride=s,
use_se=se,
act=nl))
inplanes = make_divisible(scale * c)
i += 1
self.blocks = nn.Sequential(*block_list)
self.conv2 = ConvBNLayer(
in_channels=inplanes,
out_channels=make_divisible(scale * cls_ch_squeeze),
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0,
groups=1,
if_act=True,
act='hardswish')
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2D(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0)
self.out_channels = make_divisible(scale * cls_ch_squeeze)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.blocks(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.pool(x)
return x
# 圖片輸入骨幹網路
backbone = MobileNetV3()
# 將numpy資料轉換為Tensor
input_data = paddle.to_tensor([padding_im])
# 骨幹網路輸出
feature = backbone(input_data)
# 檢視feature map的緯度
print("backbone output:", feature.shape)
- neck
neck 部分將backbone輸出的視覺特徵圖轉換為1維向量輸入送到 LSTM 網路中,輸出序列特徵( 原始碼位置 ):
class Im2Seq(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, in_channels, **kwargs):
"""
影象特徵轉換為序列特徵
:param in_channels: 輸入通道數
"""
super().__init__()
self.out_channels = in_channels
def forward(self, x):
B, C, H, W = x.shape
assert H == 1
x = x.squeeze(axis=2)
x = x.transpose([0, 2, 1]) # (NWC)(batch, width, channels)
return x
class EncoderWithRNN(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, in_channels, hidden_size):
super(EncoderWithRNN, self).__init__()
self.out_channels = hidden_size * 2
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(
in_channels, hidden_size, direction='bidirectional', num_layers=2)
def forward(self, x):
x, _ = self.lstm(x)
return x
class SequenceEncoder(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, in_channels, hidden_size=48, **kwargs):
"""
序列編碼
:param in_channels: 輸入通道數
:param hidden_size: 隱藏層size
"""
super(SequenceEncoder, self).__init__()
self.encoder_reshape = Im2Seq(in_channels)
self.encoder = EncoderWithRNN(
self.encoder_reshape.out_channels, hidden_size)
self.out_channels = self.encoder.out_channels
def forward(self, x):
x = self.encoder_reshape(x)
x = self.encoder(x)
return x
neck = SequenceEncoder(in_channels=288)
sequence = neck(feature)
print("sequence shape:", sequence.shape) # sequence shape:[1, 80, 96] 96 = hidden_size=48 * 2
- head
預測頭部分由全連線層和softmax組成,用於計算序列特徵時間步上的標籤概率分佈,本範例僅支援模型識別小寫英文字母和數位(26+10)36個類別(原始碼位置):
class CTCHead(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self,
in_channels,
out_channels,
**kwargs):
"""
CTC 預測層
:param in_channels: 輸入通道數
:param out_channels: 輸出通道數
"""
super(CTCHead, self).__init__()
self.fc = nn.Linear(
in_channels,
out_channels)
# 思考:out_channels 應該等於多少? fc(x) 的 out_channels = 37 因為有一個空字元 = (26+10)36個類別 + 1 = 37
self.out_channels = out_channels
def forward(self, x):
predicts = self.fc(x)
result = predicts
if not self.training:
predicts = F.softmax(predicts, axis=2)
result = predicts
return result
在網路隨機初始化的情況下,輸出結果是無序的,經過SoftMax之後,可以得到各時間步上的概率最大的預測結果,其中:pred_id 代表預測的標籤ID,pre_scores 代表預測結果的置信度:
ctc_head = CTCHead(in_channels=96, out_channels=37)
predict = ctc_head(sequence)
print("predict shape:", predict.shape)
result = F.softmax(predict, axis=2)
pred_id = paddle.argmax(result, axis=2)
pred_socres = paddle.max(result, axis=2)
print("pred_id:", pred_id)
print("pred_scores:", pred_socres)
- 後處理
識別網路最終返回的結果是各個時間步上的最大索引值,最終期望的輸出是對應的文字結果,因此CRNN的後處理是一個解碼過程,主要邏輯如下:
def decode(text_index, text_prob=None, is_remove_duplicate=False):
""" convert text-index into text-label. """
character = "-0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz" # 沒有從字典取字元,因為比較簡單,就直接寫在這了
result_list = []
# 忽略tokens [0] 代表ctc中的blank位
ignored_tokens = [0]
batch_size = len(text_index)
for batch_idx in range(batch_size):
char_list = []
conf_list = []
for idx in range(len(text_index[batch_idx])):
if text_index[batch_idx][idx] in ignored_tokens:
continue
# 合併blank之間相同的字元
if is_remove_duplicate:
# only for predict
if idx > 0 and text_index[batch_idx][idx - 1] == text_index[
batch_idx][idx]:
continue
# 將解碼結果存在char_list內
char_list.append(character[int(text_index[batch_idx][
idx])])
# 記錄置信度
if text_prob is not None:
conf_list.append(text_prob[batch_idx][idx])
else:
conf_list.append(1)
text = ''.join(char_list)
# 輸出結果
result_list.append((text, np.mean(conf_list)))
return result_list
以 head 部分隨機初始化預測出的結果為例,進行解碼得到:
pred_id = paddle.argmax(result, axis=2)
pred_socres = paddle.max(result, axis=2)
print(pred_id)
decode_out = decode(pred_id, pred_socres)
print("decode out:", decode_out)
上述步驟完成了網路的搭建,也實現了一個簡單的前向預測過程。
沒有經過訓練的網路無法正確預測結果,因此需要定義損失函數、優化策略,將整個網路run起來,下面將詳細介紹網路訓練原理。
3. 訓練原理詳解
3.1 準備訓練資料
PaddleOCR 支援兩種資料格式:
lmdb用於訓練以lmdb格式儲存的資料集(LMDBDataSet);通用資料用於訓練以文字檔案儲存的資料集(SimpleDataSet);
本次只介紹通用資料格式讀取
訓練資料的預設儲存路徑是 ./train_data, 執行以下命令解壓資料:
cd /home/aistudio/work/train_data/ && tar xf ic15_data.tar
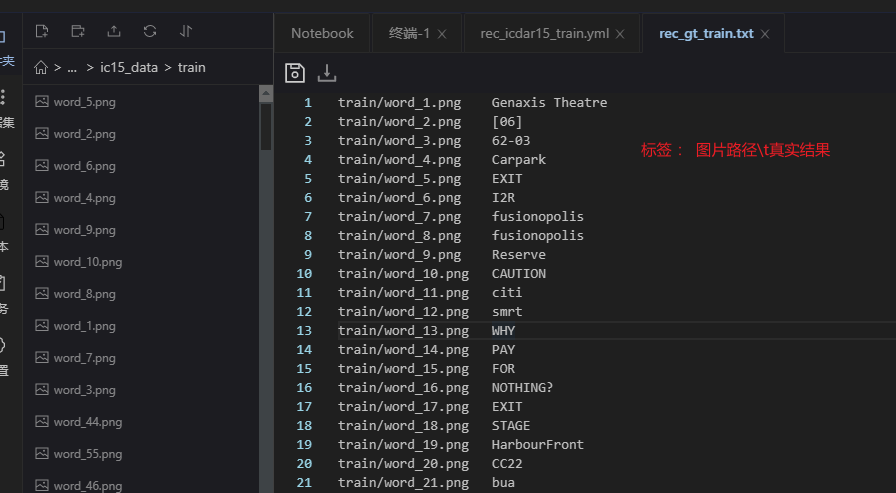
解壓完成後,訓練圖片都在同一個資料夾內,並有一個txt檔案(rec_gt_train.txt)記錄圖片路徑和標籤,txt檔案裡的內容如下:
" 影象檔名 影象標註資訊 "
train/word_1.png Genaxis Theatre
train/word_2.png [06]
...
注意: txt檔案中預設將圖片路徑和圖片標籤用 \t 分割,如用其他方式分割將造成訓練報錯。
資料集應有如下檔案結構:
|-train_data
|-ic15_data
|- rec_gt_train.txt
|- train
|- word_001.png
|- word_002.jpg
|- word_003.jpg
| ...
|- rec_gt_test.txt
|- test
|- word_001.png
|- word_002.jpg
|- word_003.jpg
| ...
確認組態檔中的資料路徑是否正確,以 rec_icdar15_train.yml為例:
Train:
dataset:
name: SimpleDataSet
# 訓練資料根目錄
data_dir: ./train_data/ic15_data/
# 訓練資料標籤
label_file_list: ["./train_data/ic15_data/rec_gt_train.txt"]
transforms:
- DecodeImage: # load image
img_mode: BGR
channel_first: False
- CTCLabelEncode: # Class handling label
- RecResizeImg:
image_shape: [3, 32, 100] # [3,32,320]
- KeepKeys:
keep_keys: ['image', 'label', 'length'] # dataloader will return list in this order
loader:
shuffle: True
batch_size_per_card: 256 # 第一次偵錯可以改小一點。防止一起來就崩了
drop_last: True
num_workers: 8
use_shared_memory: False
Eval:
dataset:
name: SimpleDataSet
# 評估資料根目錄
data_dir: ./train_data/ic15_data
# 評估資料標籤
label_file_list: ["./train_data/ic15_data/rec_gt_test.txt"]
transforms:
- DecodeImage: # load image
img_mode: BGR
channel_first: False
- CTCLabelEncode: # Class handling label
- RecResizeImg:
image_shape: [3, 32, 100] # 要得訓練的設定值一致
- KeepKeys:
keep_keys: ['image', 'label', 'length'] # dataloader will return list in this order
loader:
shuffle: False
drop_last: False
batch_size_per_card: 256
num_workers: 4
use_shared_memory: False
3.2 資料預處理
送入網路的訓練資料,需要保證一個batch內維度一致,同時為了不同維度之間的特徵在數值上有一定的比較性,需要對資料做統一尺度縮放和歸一化。
為了增加模型的魯棒性,抑制過擬合提升泛化效能,需要實現一定的資料增廣。
- 縮放和歸一化
第二節中已經介紹了相關內容,這是圖片送入網路之前的最後一步操作。呼叫 resize_norm_img 完成圖片縮放、padding和歸一化。
- 資料增廣
PaddleOCR中實現了多種資料增廣方式,如:顏色反轉、隨機切割、仿射變化、隨機噪聲等等,這裡以簡單的隨機切割為例,更多增廣方式可參考:rec_img_aug.py
def get_crop(image):
"""
random crop
"""
import random
h, w, _ = image.shape
top_min = 1
top_max = 8
top_crop = int(random.randint(top_min, top_max))
top_crop = min(top_crop, h - 1)
crop_img = image.copy()
ratio = random.randint(0, 1)
if ratio:
crop_img = crop_img[top_crop:h, :, :]
else:
crop_img = crop_img[0:h - top_crop, :, :]
return crop_img
# 讀圖
raw_img = cv2.imread("/home/aistudio/work/word_1.png")
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(2,1,1)
# 視覺化原圖
plt.imshow(raw_img)
# 隨機切割
crop_img = get_crop(raw_img)
plt.subplot(2,1,2)
# 視覺化增廣圖
plt.imshow(crop_img)
plt.show()

3.3 訓練主程式
模型訓練的入口程式碼是 train.py,它展示了訓練中所需的各個模組: build dataloader, build post process, build model , build loss, build optim, build metric,將各部分串聯後即可開始訓練:
- 構建 dataloader
訓練模型需要將資料組成指定數目的 batch ,並在訓練過程中依次 yield 出來,本例中呼叫了 PaddleOCR 中實現的 SimpleDataSet
基於原始程式碼稍作修改,其返回單條資料的主要邏輯如下
def __getitem__(data_line, data_dir):
import os
mode = "train"
delimiter = '\t' # label 設定的時候,前面是圖片的路徑,所以要 \t 進行分隔後面真實的標籤
try:
substr = data_line.strip("\n").split(delimiter)
file_name = substr[0]
label = substr[1]
img_path = os.path.join(data_dir, file_name)
data = {'img_path': img_path, 'label': label}
if not os.path.exists(img_path):
raise Exception("{} does not exist!".format(img_path))
with open(data['img_path'], 'rb') as f:
img = f.read()
data['image'] = img
# 預處理操作,先註釋掉
# outs = transform(data, self.ops)
outs = data
except Exception as e:
print("When parsing line {}, error happened with msg: {}".format(
data_line, e))
outs = None
return outs
假設當前輸入的標籤為 train/word_1.png Genaxis Theatre, 訓練資料的路徑為 /home/aistudio/work/train_data/ic15_data/, 解析出的結果是一個字典,裡面包含 img_path label image 三個欄位:
data_line = "train/word_1.png Genaxis Theatre"
data_dir = "/home/aistudio/work/train_data/ic15_data/"
item = __getitem__(data_line, data_dir)
print(item)
實現完單條資料返回邏輯後,呼叫 padde.io.Dataloader 即可把資料組合成batch,具體可參考 build_dataloader
-
build model
build model 即搭建主要網路結構,具體細節如《2.3 程式碼實現》所述,本節不做過多介紹,各模組程式碼可參考modeling
-
build loss
CRNN 模型的損失函數為 CTC loss, 飛槳整合了常用的 Loss 函數,只需呼叫實現即可:
import paddle.nn as nn
class CTCLoss(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, use_focal_loss=False, **kwargs):
super(CTCLoss, self).__init__()
# blank 是 ctc 的無意義連線符
self.loss_func = nn.CTCLoss(blank=0, reduction='none')
def forward(self, predicts, batch):
if isinstance(predicts, (list, tuple)):
predicts = predicts[-1]
# 轉置模型 head 層的預測結果,沿channel層排列
predicts = predicts.transpose((1, 0, 2)) #[80,1,37]
N, B, _ = predicts.shape
preds_lengths = paddle.to_tensor([N] * B, dtype='int64')
labels = batch[1].astype("int32")
label_lengths = batch[2].astype('int64')
# 計算損失函數
loss = self.loss_func(predicts, labels, preds_lengths, label_lengths)
loss = loss.mean()
return {'loss': loss}
- build post process
具體細節同樣在《2.3 程式碼實現》有詳細介紹,實現邏輯與之前一致。
- build optim
優化器使用 Adam , 同樣呼叫飛槳API: paddle.optimizer.Adam
- build metric
metric 部分用於計算模型指標,PaddleOCR的文字識別中,將整句預測正確判斷為預測正確,因此準確率計算主要邏輯如下:
def metric(preds, labels):
correct_num = 0
all_num = 0
norm_edit_dis = 0.0
for (pred), (target) in zip(preds, labels):
pred = pred.replace(" ", "") # 如果嚴格預測的話,把這程式碼註釋掉,比較時,空格敏感的預測
target = target.replace(" ", "")
if pred == target:
correct_num += 1
all_num += 1
correct_num += correct_num
all_num += all_num
return {
'acc': correct_num / all_num,
}
preds = ["aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "123", "456"]
labels = ["aaa", "bbb", "ddd", "123", "444"]
acc = metric(preds, labels)
print("acc:", acc)
# 五個預測結果中,完全正確的有3個,因此準確率應為0.6
將以上各部分組合起來,即是完整的訓練流程:
def main(config, device, logger, vdl_writer):
# init dist environment
if config['Global']['distributed']:
dist.init_parallel_env()
global_config = config['Global']
# build dataloader
train_dataloader = build_dataloader(config, 'Train', device, logger)
if len(train_dataloader) == 0:
logger.error(
"No Images in train dataset, please ensure\n" +
"\t1. The images num in the train label_file_list should be larger than or equal with batch size.\n"
+
"\t2. The annotation file and path in the configuration file are provided normally."
)
return
if config['Eval']:
valid_dataloader = build_dataloader(config, 'Eval', device, logger)
else:
valid_dataloader = None
# build post process
post_process_class = build_post_process(config['PostProcess'],
global_config)
# build model
# for rec algorithm
if hasattr(post_process_class, 'character'):
char_num = len(getattr(post_process_class, 'character'))
if config['Architecture']["algorithm"] in ["Distillation",
]: # distillation model
for key in config['Architecture']["Models"]:
config['Architecture']["Models"][key]["Head"][
'out_channels'] = char_num
else: # base rec model
config['Architecture']["Head"]['out_channels'] = char_num
model = build_model(config['Architecture'])
if config['Global']['distributed']:
model = paddle.DataParallel(model)
# build loss
loss_class = build_loss(config['Loss'])
# build optim
optimizer, lr_scheduler = build_optimizer(
config['Optimizer'],
epochs=config['Global']['epoch_num'],
step_each_epoch=len(train_dataloader),
parameters=model.parameters())
# build metric
eval_class = build_metric(config['Metric'])
# load pretrain model
pre_best_model_dict = load_model(config, model, optimizer)
logger.info('train dataloader has {} iters'.format(len(train_dataloader)))
if valid_dataloader is not None:
logger.info('valid dataloader has {} iters'.format(
len(valid_dataloader)))
use_amp = config["Global"].get("use_amp", False)
if use_amp:
AMP_RELATED_FLAGS_SETTING = {
'FLAGS_cudnn_batchnorm_spatial_persistent': 1,
'FLAGS_max_inplace_grad_add': 8,
}
paddle.fluid.set_flags(AMP_RELATED_FLAGS_SETTING)
scale_loss = config["Global"].get("scale_loss", 1.0)
use_dynamic_loss_scaling = config["Global"].get(
"use_dynamic_loss_scaling", False)
scaler = paddle.amp.GradScaler(
init_loss_scaling=scale_loss,
use_dynamic_loss_scaling=use_dynamic_loss_scaling)
else:
scaler = None
# start train
program.train(config, train_dataloader, valid_dataloader, device, model,
loss_class, optimizer, lr_scheduler, post_process_class,
eval_class, pre_best_model_dict, logger, vdl_writer, scaler)
4. 完整訓練任務
4.1 啟動訓練
PaddleOCR 識別任務與檢測任務類似,是通過組態檔傳輸引數的。
要進行完整的模型訓練,首先需要下載整個專案並安裝相關依賴:
# 克隆PaddleOCR程式碼
#!git clone https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleOCR
# 修改程式碼執行的預設目錄為 /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR
import os
os.chdir("/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR")
# 安裝PaddleOCR第三方依賴
!pip install -r requirements.txt
建立軟鏈,將訓練資料放在PaddleOCR專案下:
!ln -s /home/aistudio/work/train_data/ /home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/
下載預訓練模型:
為了加快收斂速度,建議下載訓練好的模型在 icdar2015 資料上進行 finetune
!cd PaddleOCR/
# 下載MobileNetV3的預訓練模型
!wget -nc -P ./pretrain_models/ https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/en/rec_mv3_none_bilstm_ctc_v2.0_train.tar
# 解壓模型引數
!tar -xf pretrain_models/rec_mv3_none_bilstm_ctc_v2.0_train.tar && rm -rf pretrain_models/rec_mv3_none_bilstm_ctc_v2.0_train.tar
啟動訓練命令很簡單,指定好組態檔即可。另外在命令列中可以通過 -o 修改組態檔中的引數值。啟動訓練命令如下所示
其中:
Global.pretrained_model: 載入的預訓練模型路徑Global.character_dict_path: 字典路徑(這裡只支援26個小寫字母+數位)Global.eval_batch_step: 評估頻率,[0,200] 從第0次開始計算,每200次評估一次Global.epoch_num: 總訓練輪數
# -o 修改預設的引數值,命令列修改優先順序會更高
!python3 tools/train.py -c configs/rec/rec_icdar15_train.yml \
-o Global.pretrained_model=rec_mv3_none_bilstm_ctc_v2.0_train/best_accuracy \
Global.character_dict_path=ppocr/utils/ic15_dict.txt \
Global.eval_batch_step=[0,200] \
Global.epoch_num=40 \
Global.use_gpu=false
根據組態檔中設定的的 save_model_dir 欄位,會有以下幾種引數被儲存下來:
output/rec/ic15
├── best_accuracy.pdopt # 每次評估時,拿到的最優評估結果
├── best_accuracy.pdparams
├── best_accuracy.states
├── config.yml # 命令列修改後的引數(當前訓練的引數)
├── iter_epoch_3.pdopt # 每3個epoch儲存一次,會看到 epoch_3、epoch_6、epoch_9 訓練的中間狀態,可以在組態檔中修改儲存的頻度
├── iter_epoch_3.pdparams
├── iter_epoch_3.states
├── latest.pdopt
├── latest.pdparams
├── latest.states
└── train.log
其中 best_accuracy.* 是評估集上的最優模型;iter_epoch_x.* 是以 save_epoch_step 為間隔儲存下來的模型;latest.* 是最後一個epoch的模型。
總結:
如果需要訓練自己的資料需要修改:
- 訓練和評估資料路徑(必須)
- 字典路徑(必須)
- 預訓練模型 (可選)
- 學習率、image shape、網路結構(可選)
4.2 模型評估
評估資料集可以通過 configs/rec/rec_icdar15_train.yml 修改Eval中的 label_file_path 設定。
這裡預設使用 icdar2015 的評估集,載入剛剛訓練好的模型權重:
!python tools/eval.py -c configs/rec/rec_icdar15_train.yml -o Global.checkpoints=output/rec/ic15/best_accuracy \
Global.character_dict_path=ppocr/utils/ic15_dict.txt
評估後,可以看到訓練模型在驗證集上的精度。
PaddleOCR支援訓練和評估交替進行, 可在 configs/rec/rec_icdar15_train.yml 中修改 eval_batch_step 設定評估頻率,預設每2000個iter評估一次。評估過程中預設將最佳acc模型,儲存為 output/rec/ic15/best_accuracy 。
如果驗證集很大,測試將會比較耗時,建議減少評估次數,或訓練完再進行評估。
4.3 預測
使用 PaddleOCR 訓練好的模型,可以通過以下指令碼進行快速預測。
預測圖片:

預設預測圖片儲存在 infer_img 裡,通過 -o Global.checkpoints 載入訓練好的引數檔案:
!python tools/infer_rec.py -c configs/rec/rec_icdar15_train.yml -o Global.checkpoints=output/rec/ic15/best_accuracy Global.character_dict_path=ppocr/utils/ic15_dict.txt
得到輸入影象的預測結果:
infer_img: doc/imgs_words_en/word_19.png
result: slow 0.8795223
原文:AI Studio學習『動手學OCR·十講』https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/course/introduce/25207?sharedLesson=2077537&sharedType=2&sharedUserId=2631487&ts=1685512885510