驅動開發:核心PE結構VA與FOA轉換
本章將繼續探索核心中解析PE檔案的相關內容,PE檔案中FOA與VA,RVA之間的轉換也是很重要的,所謂的FOA是檔案中的地址,VA則是記憶體裝入後的虛擬地址,RVA是記憶體基址與當前地址的相對偏移,本章還是需要用到《驅動開發:核心解析PE結構匯出表》中所封裝的KernelMapFile()對映函數,在對映後對其PE格式進行相應的解析,並實現轉換函數。
首先先來演示一下記憶體VA地址與FOA地址互相轉換的方式,通過使用WinHEX開啟一個二進位制檔案,開啟後我們只需要關注如下藍色註釋為映像建議裝入基址,黃色註釋為映像裝入後的RVA偏移。
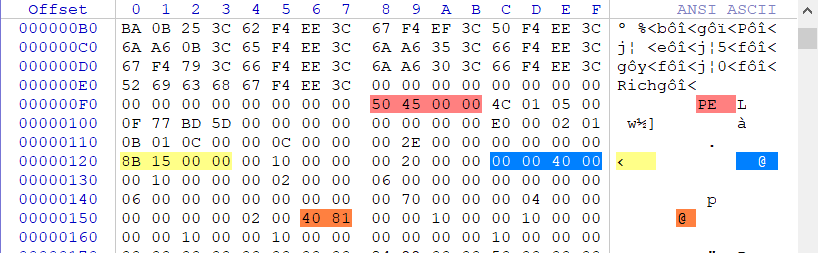
通過上方的截圖結合PE檔案結構圖我們可得知0000158B為映像裝入記憶體後的RVA偏移,緊隨其後的00400000則是映像的建議裝入基址,為什麼是建議而不是絕對?別急後面慢來來解釋。
通過上方的已知條件我們就可以計算出程式實際裝入記憶體後的入口地址了,公式如下:
VA(實際裝入地址) = ImageBase(基址) + RVA(偏移) => 00400000 + 0000158B = 0040158B
找到了程式的OEP以後,接著我們來判斷一下這個0040158B屬於那個節區,以.text節區為例,下圖我們通過觀察區段可知,第一處橙色位置00000B44 (節區尺寸),第二處紫色位置00001000 (節區RVA),第三處00000C00 (檔案對齊尺寸),第四處00000400 (檔案中的偏移),第五處60000020 (節區屬性)。
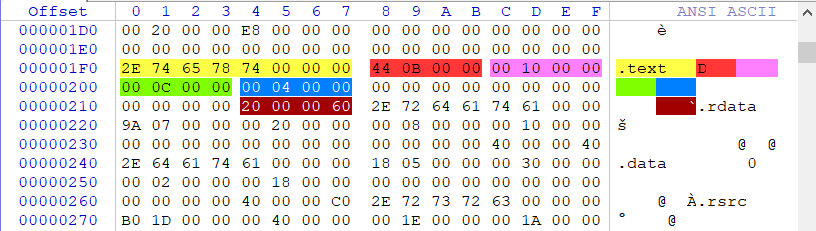
得到了上方text節的相關資料,我們就可以判斷程式的OEP到底落在了那個節區中,這裡以.text節為例子,計算公式如下:
虛擬地址開始位置:節區基地址 + 節區RVA => 00400000 + 00001000 = 00401000
虛擬地址結束位置:text節地址 + 節區尺寸 => 00401000 + 00000B44 = 00401B44
經過計算得知 .text 節所在區間(401000 - 401B44) 你的裝入VA地址0040158B只要在區間裡面就證明在本節區中,此處的VA地址是在401000 - 401B44區間內的,則說明它屬於.text節。
經過上面的公式計算我們知道了程式的OEP位置是落在了.text節,此時你興致勃勃的開啟x64DBG想去驗證一下公式是否計算正確不料,這地址根本不是400000開頭啊,這是什麼鬼?
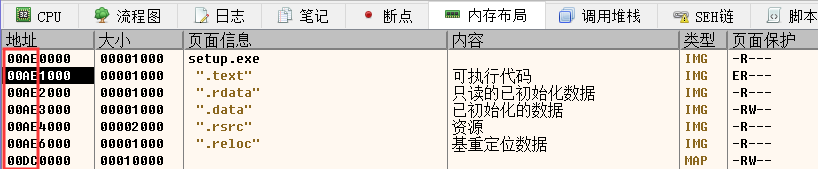
上圖中出現的這種情況就是關於隨機基址的問題,在新版的VS編譯器上存在一個選項是否要啟用隨機基址(預設啟用),至於這個隨機基址的作用,猜測可能是為了防止緩衝區溢位之類的爛七八糟的東西。
為了方便我們偵錯,我們需要手動幹掉它,其對應到PE檔案中的結構為 IMAGE_NT_HEADERS -> IMAGE_OPTIONAL_HEADER -> DllCharacteristics 相對於PE頭的偏移為90位元組,只需要修改這個標誌即可,修改方式 x64:6081 改 2081 相對於 x86:4081 改 0081 以X86程式為例,修改後如下圖所示。
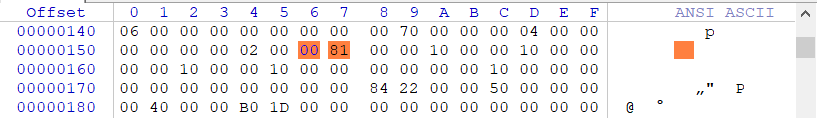
經過上面對標誌位的修改,程式再次載入就能夠停在0040158B的位置,也就是程式的OEP,接下來我們將通過公式計算出該OEP對應到檔案中的位置。
.text(節首地址) = ImageBase + 節區RVA => 00400000 + 00001000 = 00401000
VA(虛擬地址) = ImageBase + RVA(偏移) => 00400000 + 0000158B = 0040158B
RVA(相對偏移) = VA - (.text節首地址) => 0040158B - 00401000 = 58B
FOA(檔案偏移) = RVA + .text節對應到檔案中的偏移 => 58B + 400 = 98B
經過公式的計算,我們找到了虛擬地址0040158B對應到檔案中的位置是98B,通過WinHEX定位過去,即可看到OEP處的機器碼指令了。
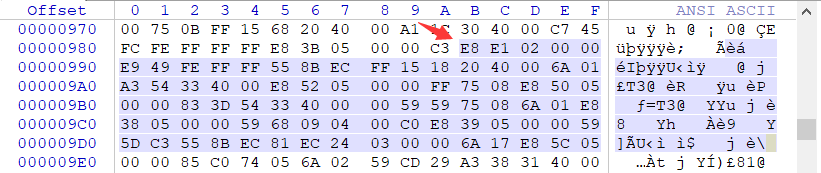
接著我們來計算一下.text節區的結束地址,通過檔案的偏移加上檔案對齊尺寸即可得到.text節的結束地址400+C00= 1000,那麼我們主要就在檔案偏移為(98B - 1000)在該區間中找空白的地方,此處我找到了在檔案偏移為1000之前的位置有一段空白區域,如下圖:
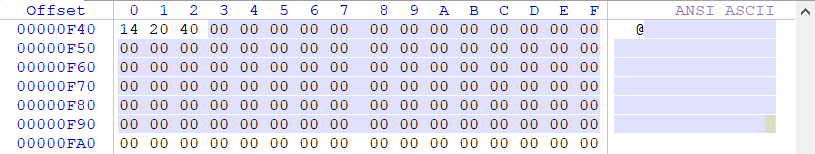
接著我麼通過公式計算一下檔案偏移為0xF43的位置,其對應到VA虛擬地址是多少,公式如下:
.text(節首地址) = ImageBase + 節區RVA => 00400000 + 00001000 = 00401000
VPK(實際大小) = (text節首地址 - ImageBase) - 實際偏移 => 401000-400000-400 = C00
VA(虛擬地址) = FOA(.text節) + ImageBase + VPK => F43+400000+C00 = 401B43
計算後直接X64DBG跳轉過去,我們從00401B44的位置向下全部填充為90(nop),然後直接儲存檔案。
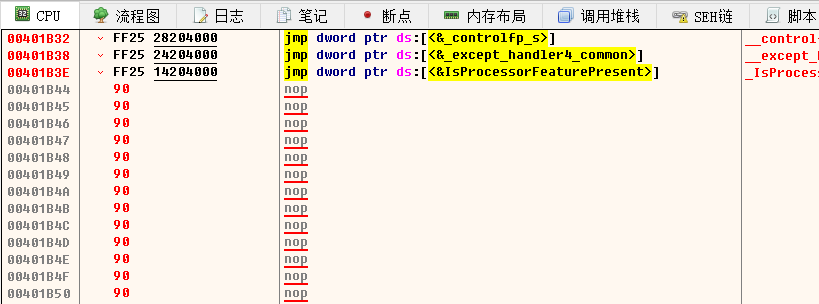
再次使用WinHEX檢視檔案偏移為0xF43的位置,會發現已經全部替換成了90指令,說明計算正確。

到此檔案偏移與虛擬偏移的轉換就結束了,那麼這些功能該如何實現呢,接下來將以此實現這些轉換細節。
FOA轉換為VA: 首先來實現將FOA地址轉換為VA地址,這段程式碼實現起來很簡單,如下所示,此處將dwFOA地址0x84EC00轉換為對應記憶體的虛擬地址。
// 署名權
// right to sign one's name on a piece of work
// PowerBy: LyShark
// Email: [email protected]
NTSTATUS DriverEntry(IN PDRIVER_OBJECT Driver, PUNICODE_STRING RegistryPath)
{
DbgPrint("hello lyshark.com \n");
NTSTATUS status = STATUS_SUCCESS;
HANDLE hFile = NULL;
HANDLE hSection = NULL;
PVOID pBaseAddress = NULL;
UNICODE_STRING FileName = { 0 };
// 初始化字串
RtlInitUnicodeString(&FileName, L"\\??\\C:\\Windows\\System32\\ntoskrnl.exe");
// 記憶體對映檔案
status = KernelMapFile(FileName, &hFile, &hSection, &pBaseAddress);
if (!NT_SUCCESS(status))
{
return 0;
}
// 獲取PE頭資料集
PIMAGE_DOS_HEADER pDosHeader = (PIMAGE_DOS_HEADER)pBaseAddress;
PIMAGE_NT_HEADERS pNtHeaders = (PIMAGE_NT_HEADERS)((PUCHAR)pDosHeader + pDosHeader->e_lfanew);
PIMAGE_SECTION_HEADER pSection = IMAGE_FIRST_SECTION(pNtHeaders);
PIMAGE_FILE_HEADER pFileHeader = &pNtHeaders->FileHeader;
DWORD64 dwFOA = 0x84EC00;
DWORD64 ImageBase = pNtHeaders->OptionalHeader.ImageBase;
DWORD NumberOfSectinsCount = pNtHeaders->FileHeader.NumberOfSections;
DbgPrint("映象基址 = %p | 節表數量 = %d \n", ImageBase, NumberOfSectinsCount);
for (int each = 0; each < NumberOfSectinsCount; each++)
{
DWORD64 PointerRawStart = pSection[each].PointerToRawData; // 檔案偏移開始位置
DWORD64 PointerRawEnds = pSection[each].PointerToRawData + pSection[each].SizeOfRawData; // 檔案偏移結束位置
// DbgPrint("檔案開始偏移 = %p | 檔案結束偏移 = %p \n", PointerRawStart, PointerRawEnds);
if (dwFOA >= PointerRawStart && dwFOA <= PointerRawEnds)
{
DWORD64 RVA = pSection[each].VirtualAddress + (dwFOA - pSection[each].PointerToRawData); // 計算出RVA
DWORD64 VA = RVA + pNtHeaders->OptionalHeader.ImageBase; // 計算出VA
DbgPrint("FOA偏移 [ %p ] --> 對應VA地址 [ %p ] \n", dwFOA, VA);
}
}
ZwUnmapViewOfSection(NtCurrentProcess(), pBaseAddress);
ZwClose(hSection);
ZwClose(hFile);
Driver->DriverUnload = UnDriver;
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
執行效果如下所示,此處之所以出現兩個結果是因為沒有及時返回,一般我們取第一個結果就是最準確的;
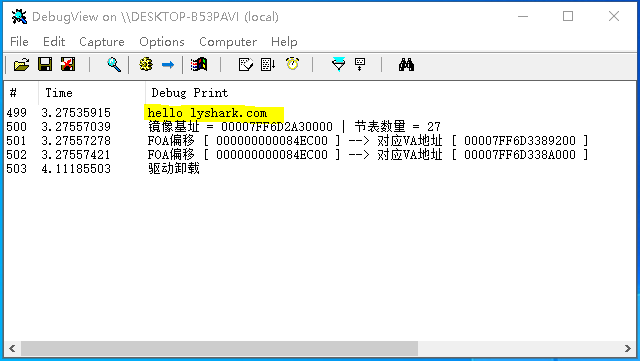
VA轉換為FOA: 將VA記憶體地址轉換為FOA檔案偏移,程式碼與如上基本保持一致。
// 署名權
// right to sign one's name on a piece of work
// PowerBy: LyShark
// Email: [email protected]
NTSTATUS DriverEntry(IN PDRIVER_OBJECT Driver, PUNICODE_STRING RegistryPath)
{
DbgPrint("hello lyshark.com \n");
NTSTATUS status = STATUS_SUCCESS;
HANDLE hFile = NULL;
HANDLE hSection = NULL;
PVOID pBaseAddress = NULL;
UNICODE_STRING FileName = { 0 };
// 初始化字串
RtlInitUnicodeString(&FileName, L"\\??\\C:\\Windows\\System32\\ntoskrnl.exe");
// 記憶體對映檔案
status = KernelMapFile(FileName, &hFile, &hSection, &pBaseAddress);
if (!NT_SUCCESS(status))
{
return 0;
}
// 獲取PE頭資料集
PIMAGE_DOS_HEADER pDosHeader = (PIMAGE_DOS_HEADER)pBaseAddress;
PIMAGE_NT_HEADERS pNtHeaders = (PIMAGE_NT_HEADERS)((PUCHAR)pDosHeader + pDosHeader->e_lfanew);
PIMAGE_SECTION_HEADER pSection = IMAGE_FIRST_SECTION(pNtHeaders);
PIMAGE_FILE_HEADER pFileHeader = &pNtHeaders->FileHeader;
DWORD64 dwVA = 0x00007FF6D3389200;
DWORD64 ImageBase = pNtHeaders->OptionalHeader.ImageBase;
DWORD NumberOfSectinsCount = pNtHeaders->FileHeader.NumberOfSections;
DbgPrint("映象基址 = %p | 節表數量 = %d \n", ImageBase, NumberOfSectinsCount);
for (DWORD each = 0; each < NumberOfSectinsCount; each++)
{
DWORD Section_Start = ImageBase + pSection[each].VirtualAddress; // 獲取節的開始地址
DWORD Section_Ends = ImageBase + pSection[each].VirtualAddress + pSection[each].Misc.VirtualSize; // 獲取節的結束地址
DbgPrint("Section開始地址 = %p | Section結束地址 = %p \n", Section_Start, Section_Ends);
if (dwVA >= Section_Start && dwVA <= Section_Ends)
{
DWORD RVA = dwVA - pNtHeaders->OptionalHeader.ImageBase; // 計算RVA
DWORD FOA = pSection[each].PointerToRawData + (RVA - pSection[each].VirtualAddress); // 計算FOA
DbgPrint("VA偏移 [ %p ] --> 對應FOA地址 [ %p ] \n", dwVA, FOA);
}
}
ZwUnmapViewOfSection(NtCurrentProcess(), pBaseAddress);
ZwClose(hSection);
ZwClose(hFile);
Driver->DriverUnload = UnDriver;
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
執行效果如下所示,此處沒有出現想要的結果是因為我們當前的VA記憶體地址並非實際裝載地址,僅僅是PE磁碟中的地址,此處如果換成記憶體中的PE則可以提取出正確的結果;
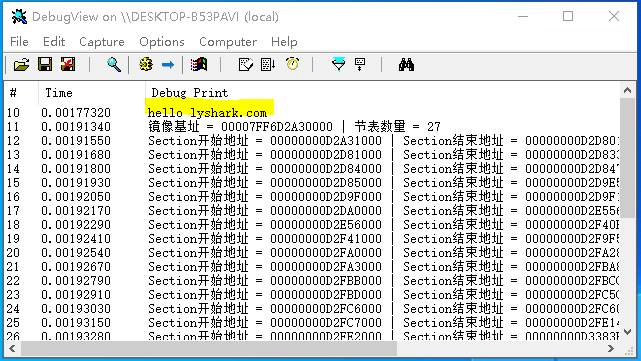
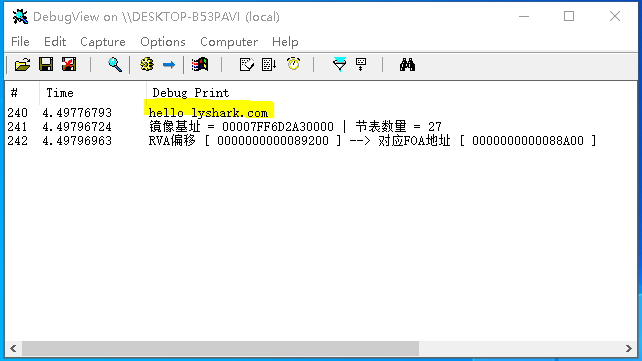
RVA轉換為FOA: 將相對偏移地址轉換為FOA檔案偏移地址,此處僅僅只是多了一步pNtHeaders->OptionalHeader.ImageBase + dwRVARVA轉換為VA的過程其轉換結果與VA轉FOA一致。
// 署名權
// right to sign one's name on a piece of work
// PowerBy: LyShark
// Email: [email protected]
NTSTATUS DriverEntry(IN PDRIVER_OBJECT Driver, PUNICODE_STRING RegistryPath)
{
DbgPrint("hello lyshark.com \n");
NTSTATUS status = STATUS_SUCCESS;
HANDLE hFile = NULL;
HANDLE hSection = NULL;
PVOID pBaseAddress = NULL;
UNICODE_STRING FileName = { 0 };
// 初始化字串
RtlInitUnicodeString(&FileName, L"\\??\\C:\\Windows\\System32\\ntoskrnl.exe");
// 記憶體對映檔案
status = KernelMapFile(FileName, &hFile, &hSection, &pBaseAddress);
if (!NT_SUCCESS(status))
{
return 0;
}
// 獲取PE頭資料集
PIMAGE_DOS_HEADER pDosHeader = (PIMAGE_DOS_HEADER)pBaseAddress;
PIMAGE_NT_HEADERS pNtHeaders = (PIMAGE_NT_HEADERS)((PUCHAR)pDosHeader + pDosHeader->e_lfanew);
PIMAGE_SECTION_HEADER pSection = IMAGE_FIRST_SECTION(pNtHeaders);
PIMAGE_FILE_HEADER pFileHeader = &pNtHeaders->FileHeader;
DWORD64 dwRVA = 0x89200;
DWORD64 ImageBase = pNtHeaders->OptionalHeader.ImageBase;
DWORD NumberOfSectinsCount = pNtHeaders->FileHeader.NumberOfSections;
DbgPrint("映象基址 = %p | 節表數量 = %d \n", ImageBase, NumberOfSectinsCount);
for (DWORD each = 0; each < NumberOfSectinsCount; each++)
{
DWORD Section_Start = pSection[each].VirtualAddress; // 計算RVA開始位置
DWORD Section_Ends = pSection[each].VirtualAddress + pSection[each].Misc.VirtualSize; // 計算RVA結束位置
if (dwRVA >= Section_Start && dwRVA <= Section_Ends)
{
DWORD VA = pNtHeaders->OptionalHeader.ImageBase + dwRVA; // 得到VA地址
DWORD FOA = pSection[each].PointerToRawData + (dwRVA - pSection[each].VirtualAddress); // 得到FOA
DbgPrint("RVA偏移 [ %p ] --> 對應FOA地址 [ %p ] \n", dwRVA, FOA);
}
}
ZwUnmapViewOfSection(NtCurrentProcess(), pBaseAddress);
ZwClose(hSection);
ZwClose(hFile);
Driver->DriverUnload = UnDriver;
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
執行效果如下所示;