Java的Atomic原子類
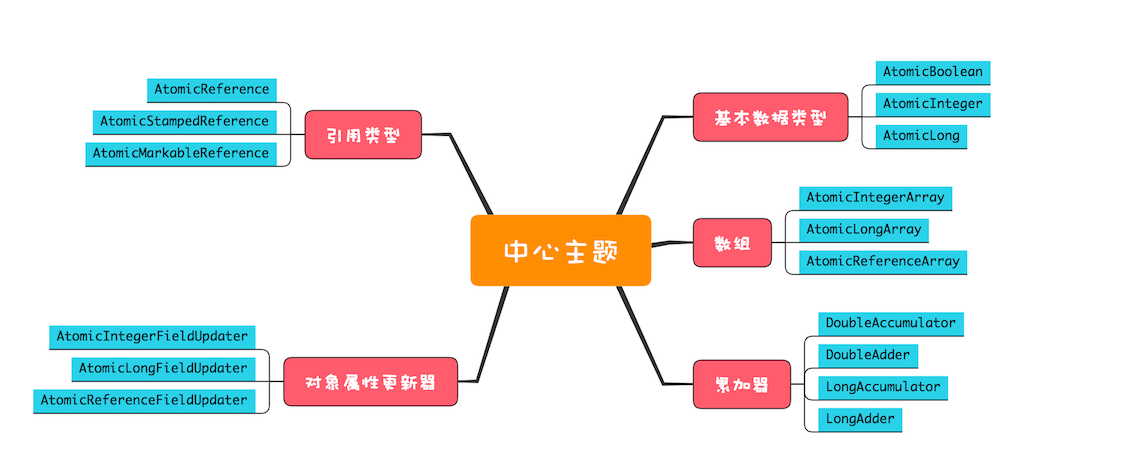
Java SDK 並行包裡提供了豐富的原子類,我們可以將其分為五個類別,這五個類別提供的方法基本上是相似的,並且每個類別都有若干原子類。
- 對基本資料型別的變數值進行原子更新;
- 對物件變數的指向進行原子更新;
- 對陣列裡面的的元素進行原子更新;
- 原子化的物件屬性更新器;
- 原子化的累加器。
基本資料型別
AtomicBoolean、AtomicLong、AtomicInteger 這三個類提供了一些對基本資料型別的變數值進行原子更新的方法。
這些類提供的方法是相似的,主要有(以 AtomicLong 為例):
// 原子化的 i++
long getAndIncrement()
// 原子化的 i--
long getAndDecrement()
// 原子化的 ++i
long incrementAndGet()
// 原子化的 --i
long decrementAndGet()
// 原子化的 i+=delta,返回值為+=前的i值
long getAndAdd(long delta)
// 原子化的 i+=delta,返回值為+=後的i值
long addAndGet(delta)
// CAS操作。如果寫回成功返回true,否則返回false
boolean compareAndSet(long expect, long update)
// 以下四個方法新值可以通過傳入函數式介面(func函數)來計算
long getAndUpdate(LongUnaryOperator updateFunction)
long updateAndGet(LongUnaryOperator updateFunction)
long getAndAccumulate(long x, LongBinaryOperator accumulatorFunction)
long accumulateAndGet(long x, LongBinaryOperator accumulatorFunction)
// 演示 getAndUpdate() 方法的使用
public static void main(String[] args) {
AtomicLong atomicLong = new AtomicLong(0);
long result = atomicLong.getAndUpdate(new LongUnaryOperator() {
@Override
public long applyAsLong(long operand) {
return operand + 1;
}
});
}
物件參照型別
AtomicReference、AtomicStampedReference、AtomicMarkableReference 這三個類提供了一些對物件變數的指向進行原子更新的方法。如果需要對物件的屬性進行原子更像,那麼可以使用原子化的物件屬性更新器。
public class ClassName {
AtomicReference<Employee> employeeAR = new AtomicReference<>(new Employee("小明"));
public void methodName() {
Employee oldVal = employeeAR.get();
Employee newVal = new Employee(oldVal.getName());
employeeAR.compareAndSet(oldVal, newVal);
}
}
物件參照的原子化更新需要重點關注 ABA 問題。當一個執行緒在進行 CAS 操作時,另一個執行緒可能會在此期間修改了同一個共用變數的值,然後又將其改回原來的值。這種情況下,CAS 操作就無法檢測到共用變數值的變化,從而導致 ABA 問題。如果我們僅僅在寫回資料前判斷數值是 A,可能導致不合理的寫回操作。AtomicStampedReference 和 AtomicMarkableReference 這兩個原子類可以解決 ABA 問題。
- AtomicStampedReference 通過為物件參照建立類似版本號(stamp)的方式,來解決 ABA 問題。AtomicStampedReference 實現的 CAS 方法增加了版本號引數
- AtomicMarkableReference 的實現機制則更簡單,將版本號簡化成了一個 Boolean 值
boolean compareAndSet(V expectedReference, V newReference,
int expectedStamp, int newStamp)
boolean compareAndSet(V expectedReference, V newReference,
boolean expectedMark, boolean newMark)
陣列
AtomicIntegerArray、AtomicLongArray、AtomicReferenceArray 這三個類提供了一些對陣列裡面的的元素進行原子更新的方法。
public class ClassName {
AtomicLongArray atomicLongArray = new AtomicLongArray(new long[]{0, 1});
public void methodName() {
int index = 0;
long oldVal = atomicLongArray.get(index);
long newVal = oldVal + 1;
atomicLongArray.compareAndSet(index, oldVal, newVal);
}
}
原子化的物件屬性更新器
原子化的物件屬性更新器有:AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater、AtomicLongFieldUpdater、AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater。
這三個類提供了一些對物件的屬性進行原子更新的方法。這些方法是利用反射機制實現的。
public class ClassName {
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<Employee> fieldUpdater =
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(Employee.class, "salary");
Employee employee = new Employee("小明", 1000);
public void methodName() {
int oldVal = employee.getSalary();
int newVal = oldVal + 1000;
fieldUpdater.compareAndSet(employee, oldVal, newVal);
}
}
需要注意的是:
- 物件屬性的型別必須是基本資料型別,不能是基本資料型別對應的包裝類。如果物件屬性的型別不是基本資料型別,newUpdater() 方法會丟擲 IllegalArgumentException 執行時異常。
- 物件的屬性必須是 volatile 型別的,只有這樣才能保證可見性。如果物件的屬性不是 volatile 型別的,newUpdater() 方法會丟擲 IllegalArgumentException 執行時異常。
// AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater 類中的程式碼
if (field.getType() != int.class) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Must be integer type");
}
if (!Modifier.isVolatile(modifiers)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Must be volatile type");
}
原子化的累加器
原子化的累加器有:LongAdder、DoubleAdder、LongAccumulator、DoubleAccumulator。這四個類僅僅用來在多執行緒環境下,執行累加操作。
相比原子化的基本資料型別,原子化的累加器的速度更快,但是它(原子化的累加器)不支援 compareAndSet() 方法。如果僅僅需要累加操作,使用原子化的累加器效能會更好。
原子化的累加器的本質是空間換時間。
LongAdder 的使用範例如下所示:
public static void main(String[] args) {
LongAdder adder = new LongAdder();
// 初始化
adder.add(1);
// 累加
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
adder.increment();
}
long sum = adder.sum();
}
LongAccumulator 與 LongAdder 類似,但 LongAccumulator 提供了更加靈活的累加操作,可以自定義累加函數。
使用範例如下所示。在使用範例中,我們建立了一個 LongAccumulator 物件,初始值為1,累加函數為 (x, y) -> x * y,即每次累加都將之前的結果與新的值相乘。然後,我們累加了三個數值,最後輸出累加結果。由於累加函數是(x, y) -> x * y,所以最終的累加結果為1 * 5 * 10 * 20 = 1000。
public static void main(String[] args) {
LongAccumulator accumulator = new LongAccumulator(new LongBinaryOperator() {
@Override
public long applyAsLong(long left, long right) {
return left * right;
}
}, 1);
// 初始值為1,累加函數為(x, y) -> x * y
accumulator.accumulate(5);
accumulator.accumulate(10);
accumulator.accumulate(20);
// 累加結果為 1 * 5 * 10 * 20 = 1000
long result = accumulator.get();
}
參考資料
本文來自部落格園,作者:真正的飛魚,轉載請註明原文連結:https://www.cnblogs.com/feiyu2/p/atomic.html