基於Sentinel自研元件的系統限流、降級、負載保護最佳實踐探索
作者:京東物流 楊建民
一、Sentinel簡介
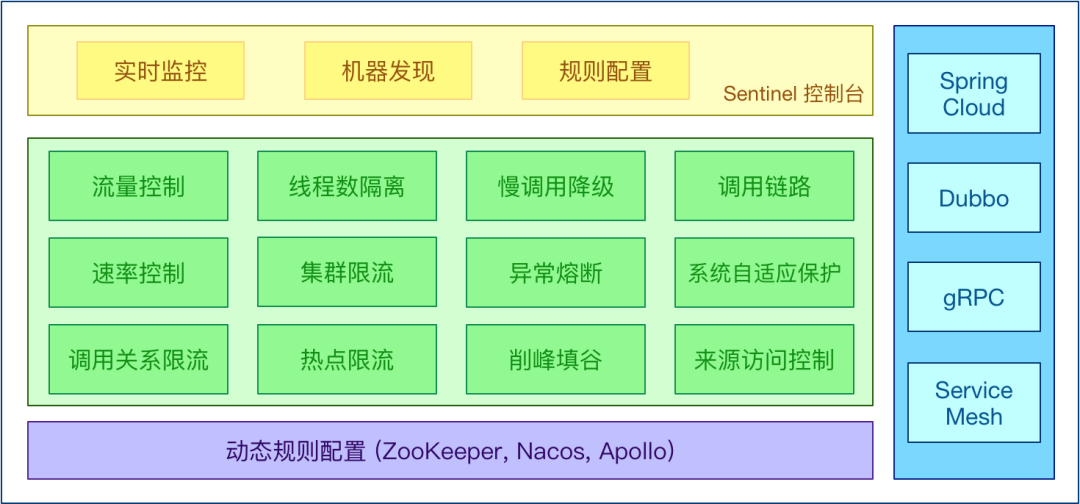
Sentinel 以流量為切入點,從流量控制、熔斷降級、系統負載保護等多個維度保護服務的穩定性。
Sentinel 具有以下特徵:
- 豐富的應用場景:秒殺(即突發流量控制在系統容量可以承受的範圍)、訊息削峰填谷、叢集流量控制、實時熔斷下游不可用應用等。
- 完備的實時監控:Sentinel 同時提供實時的監控功能。您可以在控制檯中看到接入應用的單臺機器秒級資料,甚至 500 臺以下規模的叢集的彙總執行情況。
- 廣泛的開源生態:Sentinel 提供開箱即用的與其它開源框架/庫的整合模組,例如與 Spring Cloud、Apache Dubbo、gRPC、Quarkus 的整合。您只需要引入相應的依賴並進行簡單的設定即可快速地接入 Sentinel。同時 Sentinel 提供 Java/Go/C++ 等多語言的原生實現。
- 完善的 SPI 擴充套件機制:Sentinel 提供簡單易用、完善的 SPI 擴充套件介面。您可以通過實現擴充套件介面來快速地客製化邏輯。例如客製化規則管理、適配動態資料來源等
有關Sentinel的詳細介紹以及和Hystrix的區別可以自行網上檢索,推薦一篇文章:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Q7Xv8cypQFrrOQhbd9BOXw
本次主要使用了Sentinel的降級、限流、系統負載保護功能
二、Sentinel關鍵技術原始碼解析
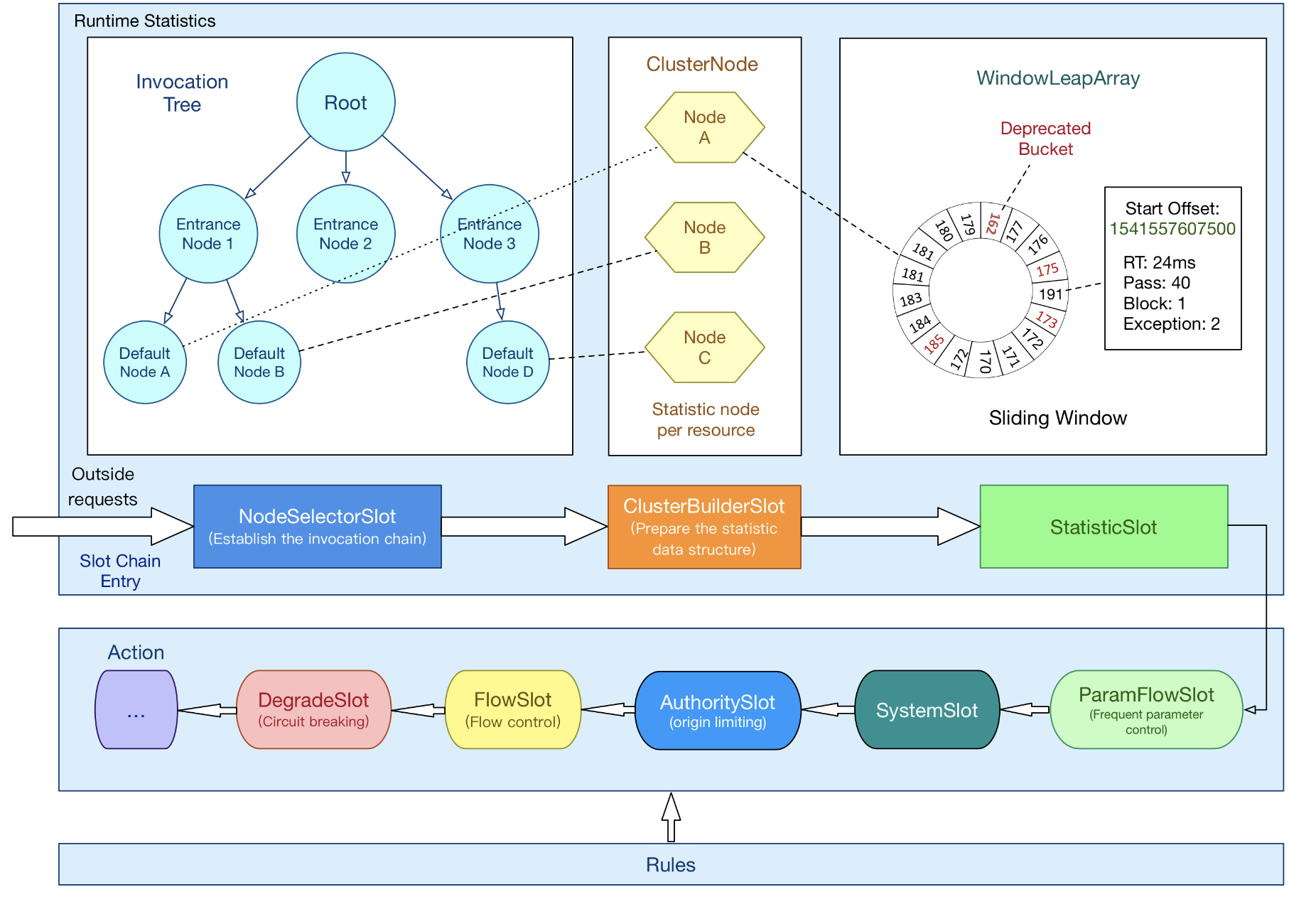
無論是限流、降級、負載等控制手段,大致流程如下:
•StatisticSlot 則用於記錄、統計不同維度的 runtime 指標監控資訊
•責任鏈依次觸發後續 slot 的 entry 方法,如 SystemSlot、FlowSlot、DegradeSlot 等的規則校驗;
•當後續的 slot 通過,沒有丟擲 BlockException 異常,說明該資源被成功呼叫,則增加執行執行緒數和通過的請求數等資訊。
關於資料統計,主要會牽扯到 ArrayMetric、BucketLeapArray、MetricBucket、WindowWrap 等類。
專案結構
以下主要分析core包裡的內容
2.1註解入口
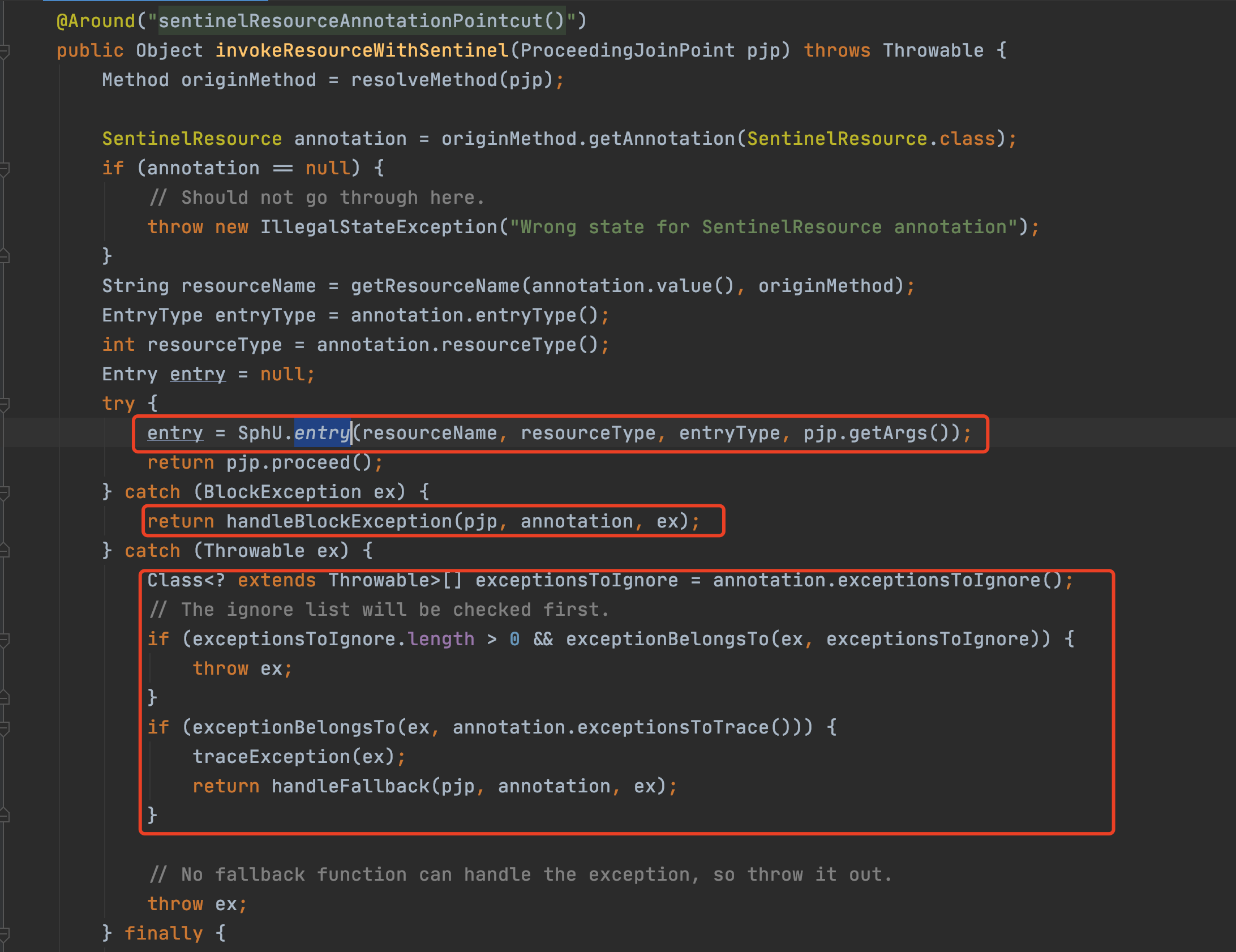

2.1.1 Entry、Context、Node
SphU門面類的方法出參都是Entry,Entry可以理解為每次進入資源的一個憑證,如果呼叫SphO.entry()或者SphU.entry()能獲取Entry物件,代表獲取了憑證,沒有被限流,否則丟擲一個BlockException。
Entry中持有本次對資源呼叫的相關資訊:
•createTime:建立該Entry的時間戳。
•curNode:Entry當前是在哪個節點。
•orginNode:Entry的呼叫源節點。
•resourceWrapper:Entry關聯的資源資訊。
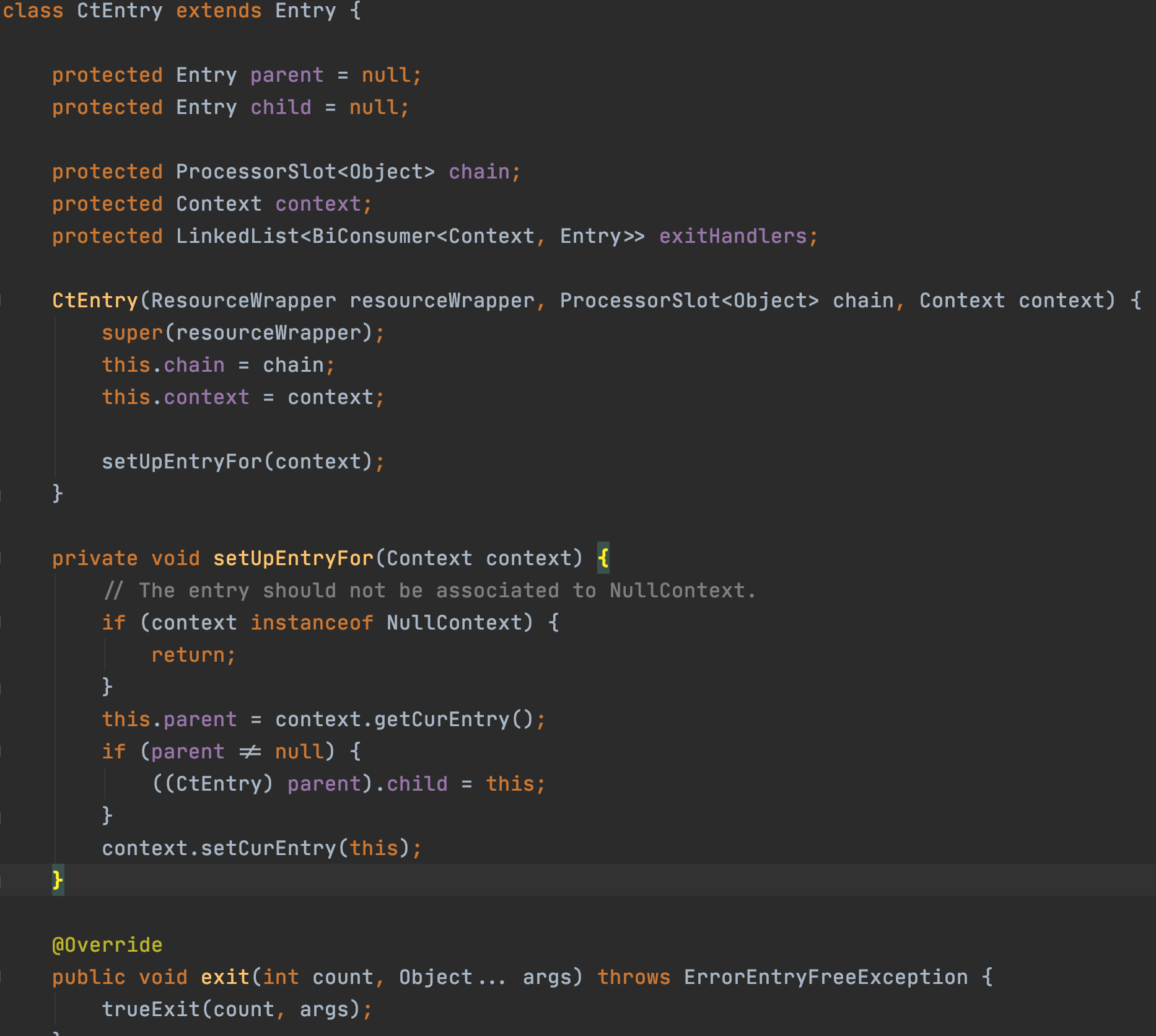
Entry是一個抽象類,CtEntry是Entry的實現,CtEntry持有Context和呼叫鏈的資訊
Context的原始碼註釋如下,
This class holds metadata of current invocation
Node的原始碼註釋
Holds real-time statistics for resources
Node中儲存了對資源的實時資料的統計,Sentinel中的限流或者降級等功能就是通過Node中的資料進行判斷的。Node是一個介面,裡面定義了各種操作request、exception、rt、qps、thread的方法。
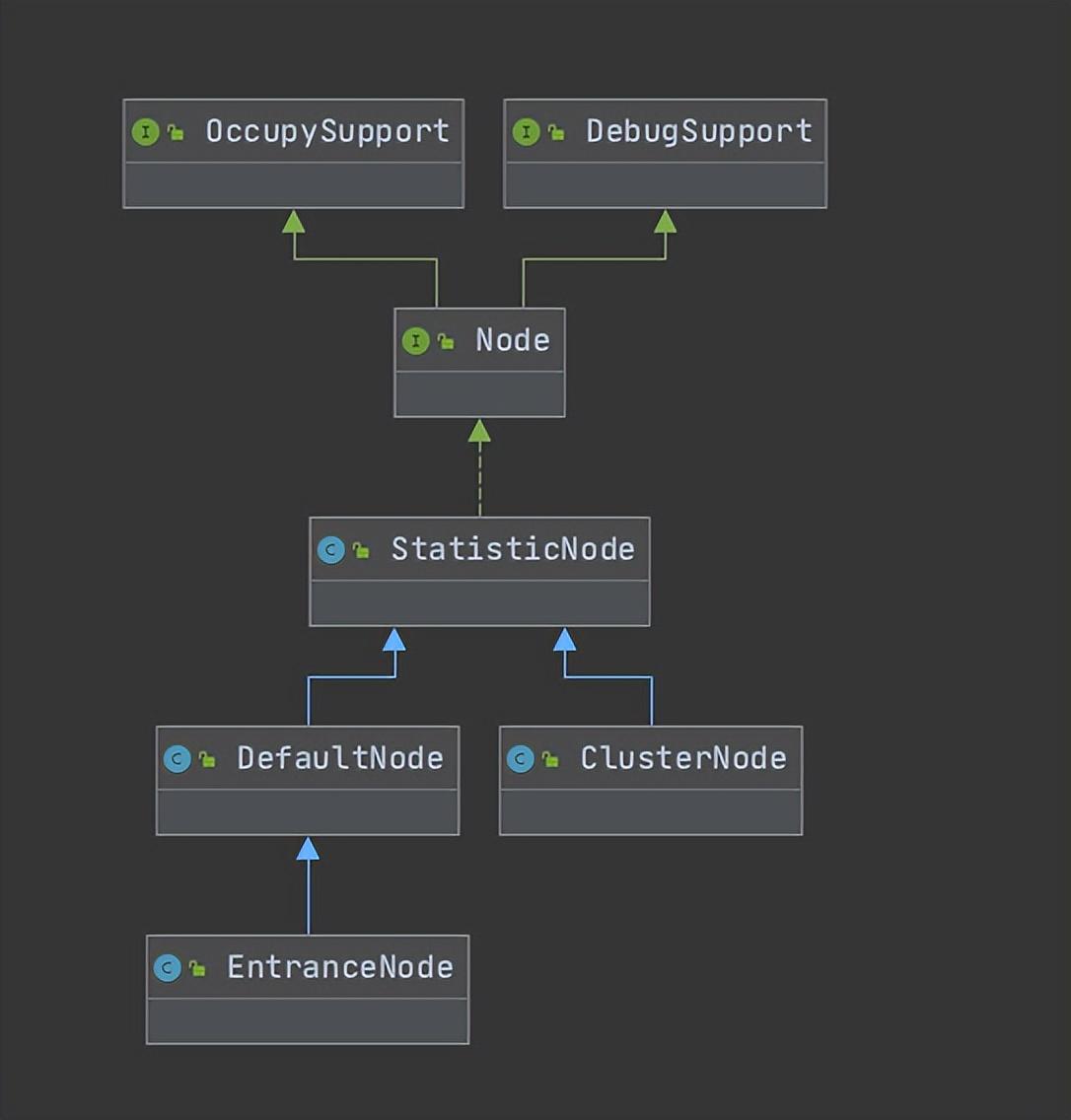
在細看Node實現時,不難發現LongAddr的使用,關於LongAddr和DoubleAddr都是java8 java.util.concurrent.atomic裡的內容,感興趣的小夥伴可以再深入研究一下,這兩個是高並行下計數功能非常優秀的資料結構,實際應用場景裡需要計數時可以考慮使用。
關於Node的介紹後續還會深入,此處大致先提一下這個概念。
2.2 初始化
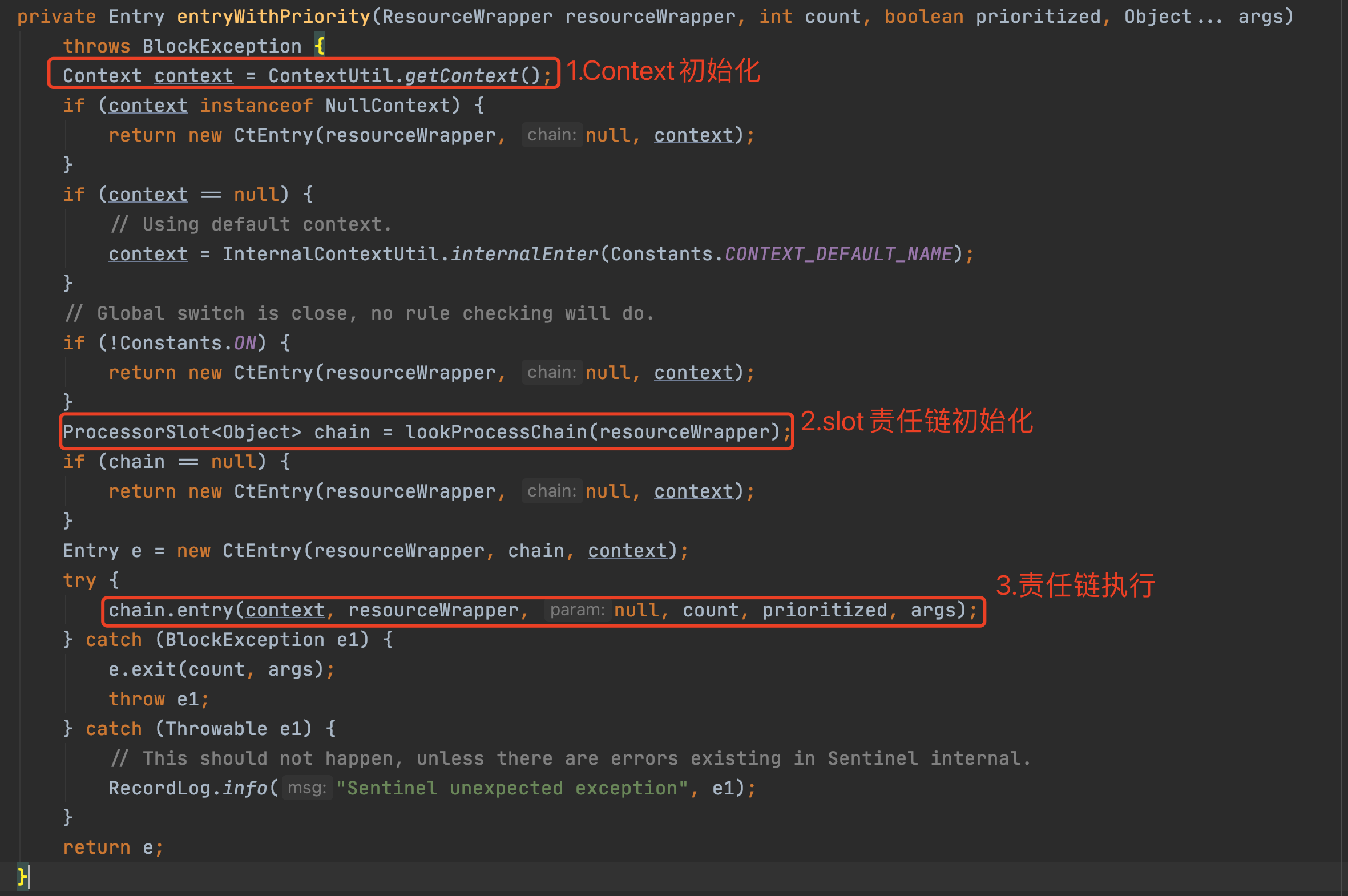
2.2.1 Context初始化
在初始化slot責任鏈部分前,還執行了context的初始化,裡面涉及幾個重要概念,需要解釋一下:
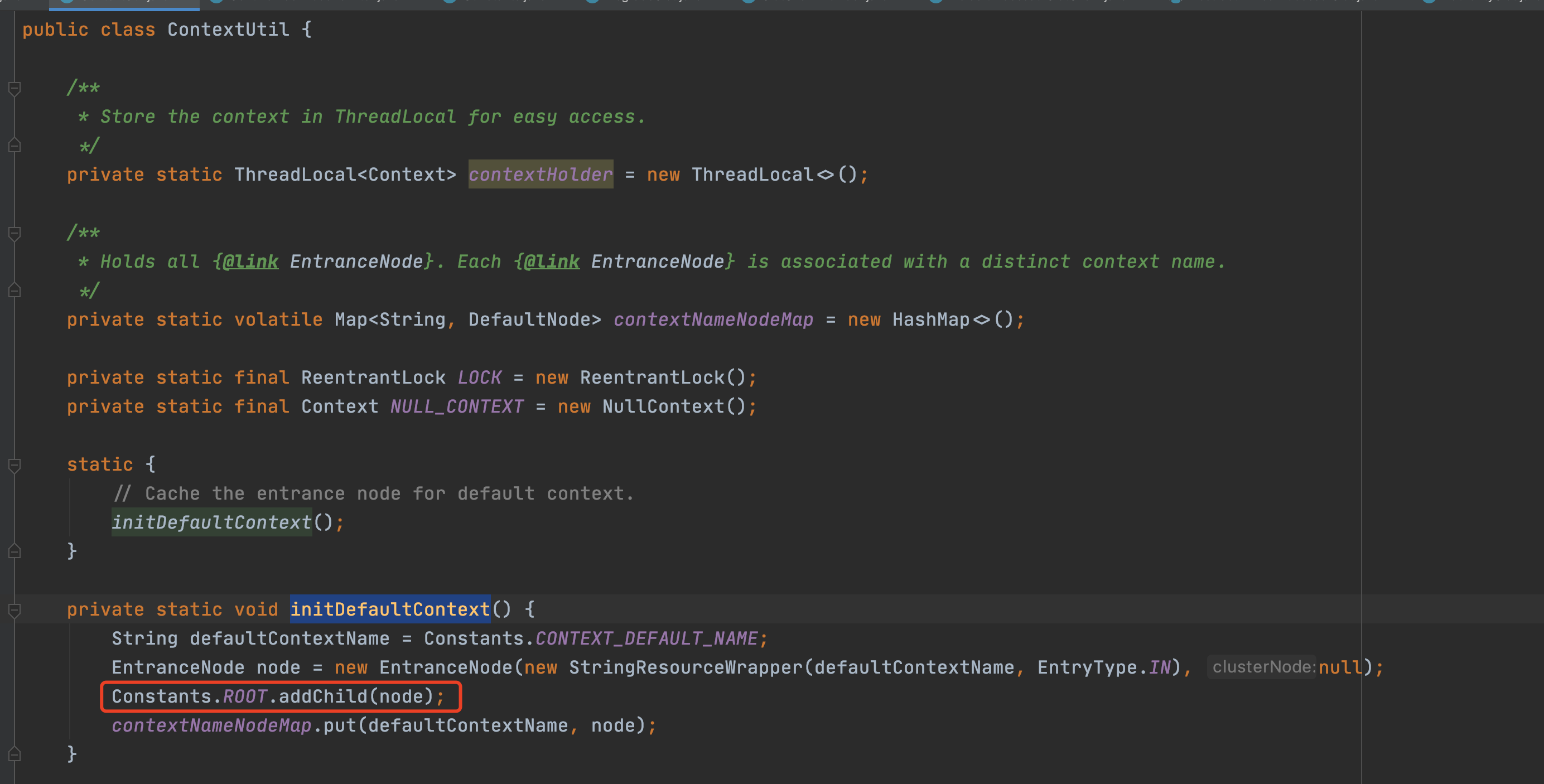
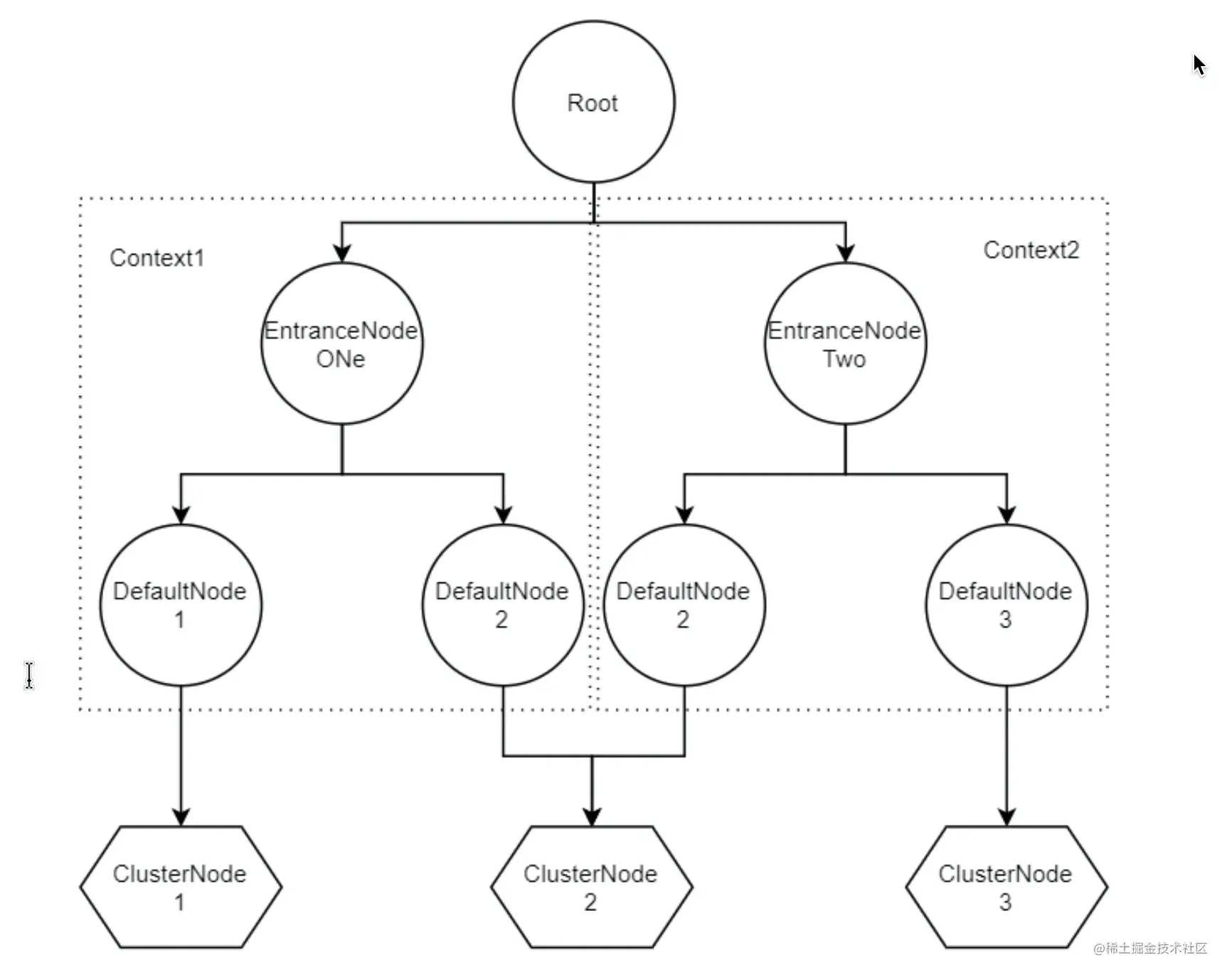
可以發現在Context初始化的過程中,會把EntranceNode加入到Root子節點中(實際Root本身是一個特殊的EntranceNode),並把EntranceNode放到contextNameNodeMap中。
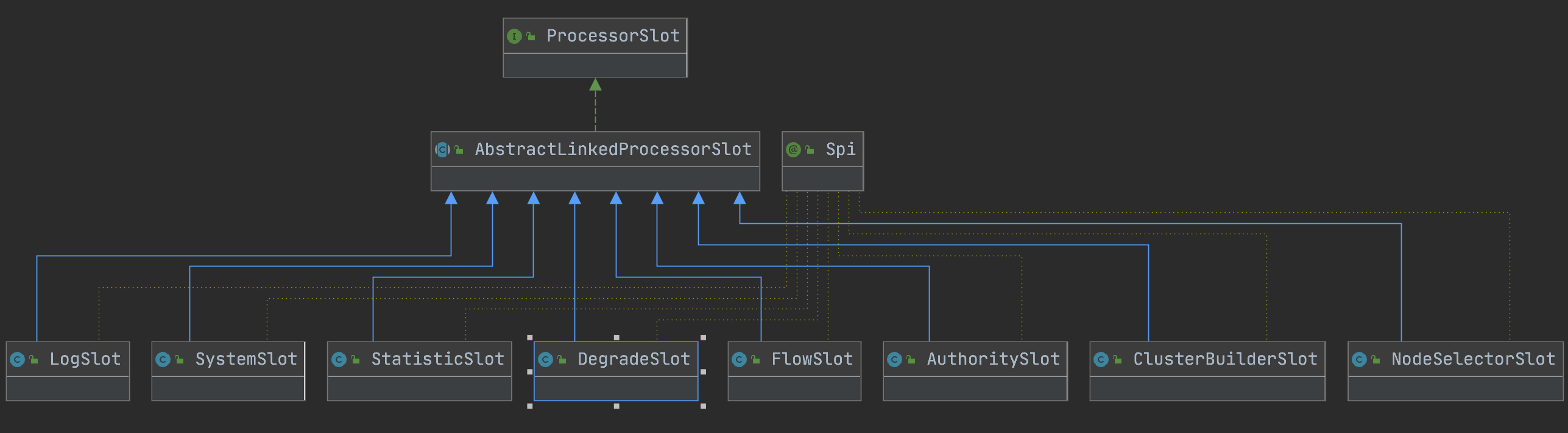
之前簡單提到過Node,是用來統計資料用的,不同Node功能如下:
•Node:用於完成資料統計的介面
•StatisticNode:統計節點,是Node介面的實現類,用於完成資料統計
•EntranceNode:入口節點,一個Context會有一個入口節點,用於統計當前Context的總體流量資料
•DefaultNode:預設節點,用於統計一個資源在當前Context中的流量資料
•ClusterNode:叢集節點,用於統計一個資源在所有Context中的總體流量資料
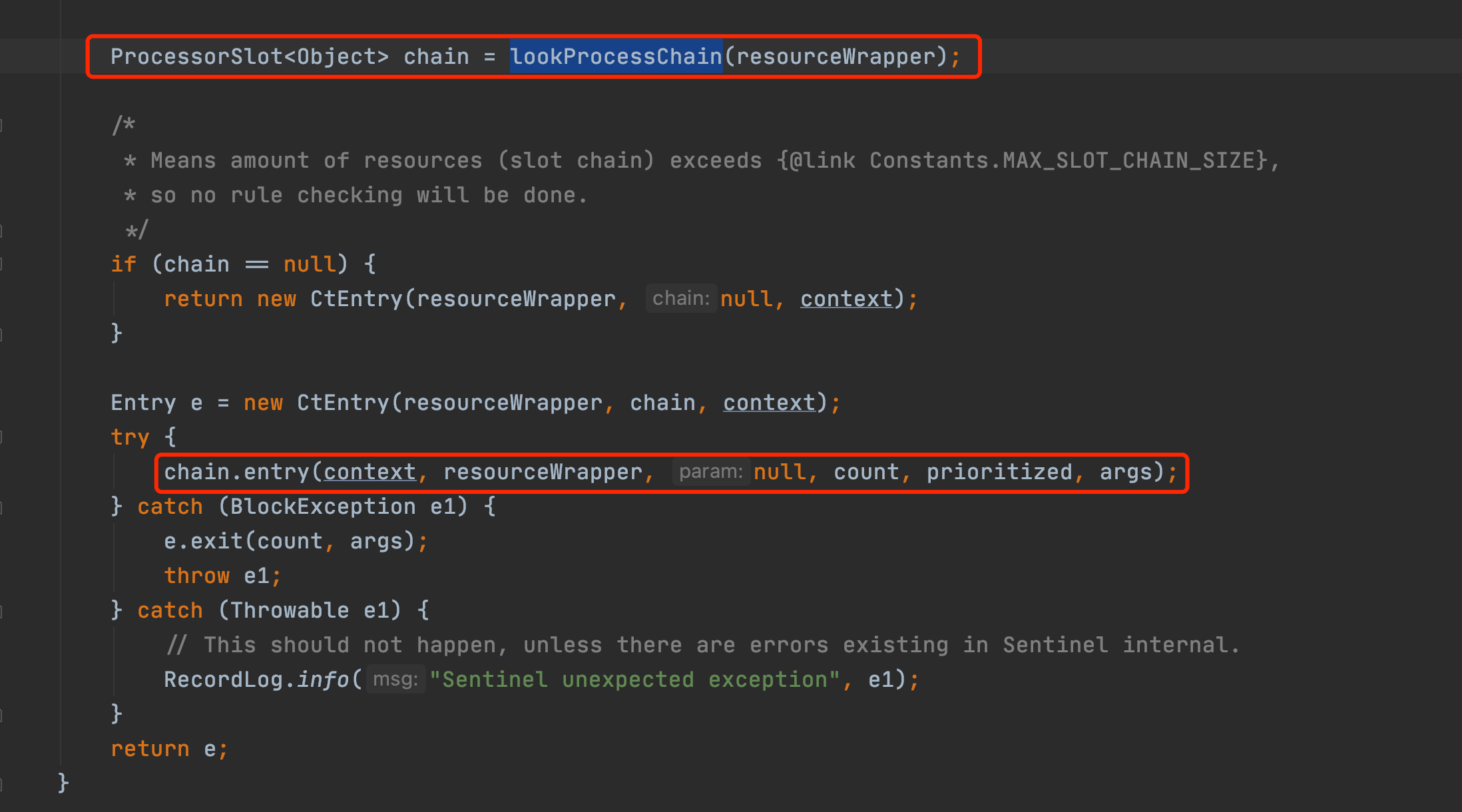
protected static Context trueEnter(String name, String origin) {
Context context = contextHolder.get();
if (context == null) {
Map<String, DefaultNode> localCacheNameMap = contextNameNodeMap;
DefaultNode node = localCacheNameMap.get(name);
if (node == null) {
if (localCacheNameMap.size() > Constants.MAX_CONTEXT_NAME_SIZE) {
setNullContext();
return NULL_CONTEXT;
} else {
LOCK.lock();
try {
node = contextNameNodeMap.get(name);
if (node == null) {
if (contextNameNodeMap.size() > Constants.MAX_CONTEXT_NAME_SIZE) {
setNullContext();
return NULL_CONTEXT;
} else {
node = new EntranceNode(new StringResourceWrapper(name, EntryType.IN), null);
// Add entrance node.
Constants.ROOT.addChild(node);
Map<String, DefaultNode> newMap = new HashMap<>(contextNameNodeMap.size() + 1);
newMap.putAll(contextNameNodeMap);
newMap.put(name, node);
contextNameNodeMap = newMap;
}
}
} finally {
LOCK.unlock();
}
}
}
context = new Context(node, name);
context.setOrigin(origin);
contextHolder.set(context);
}
return context;
}
2.2.2 通過SpiLoader預設初始化8個slot
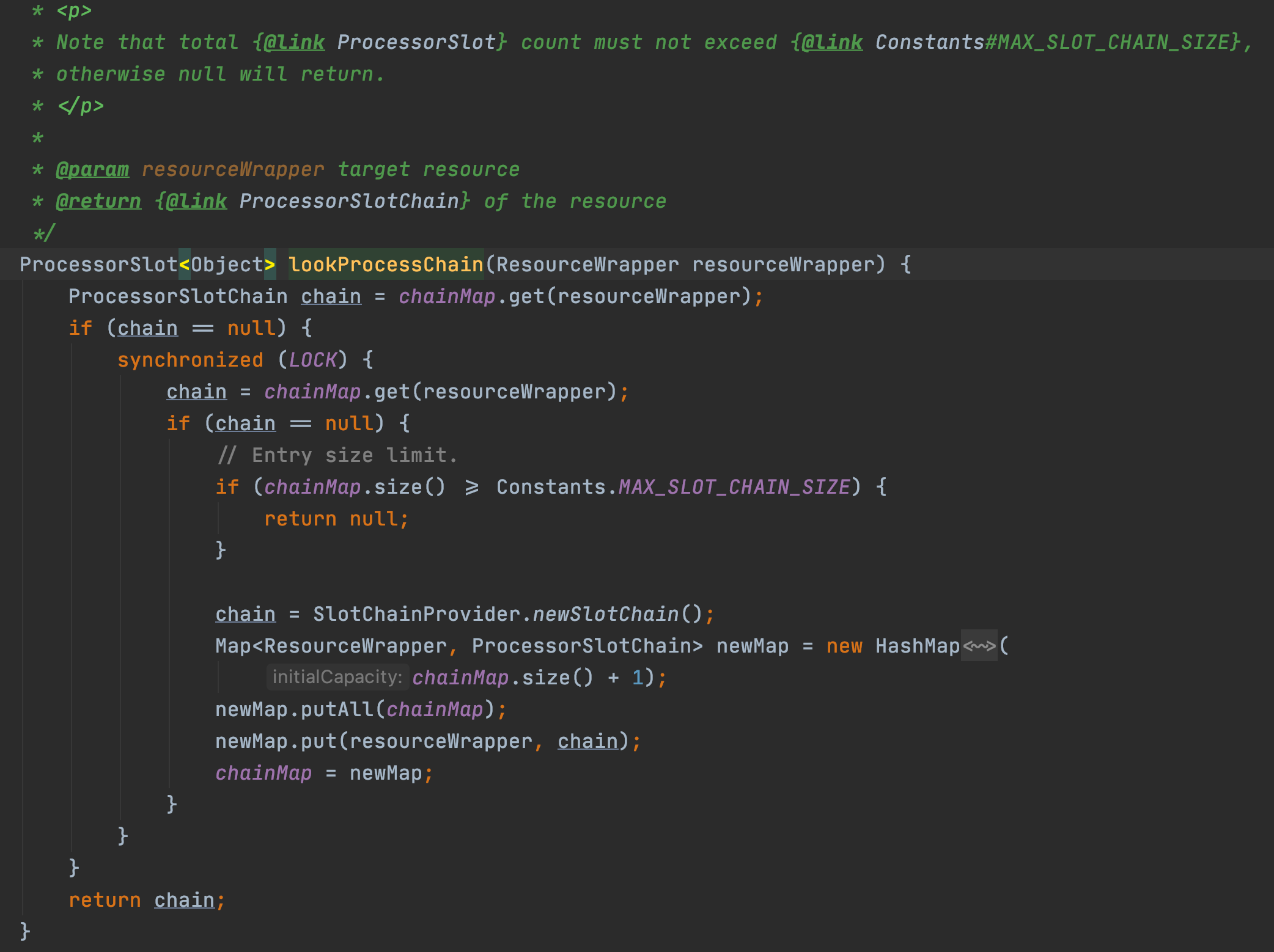
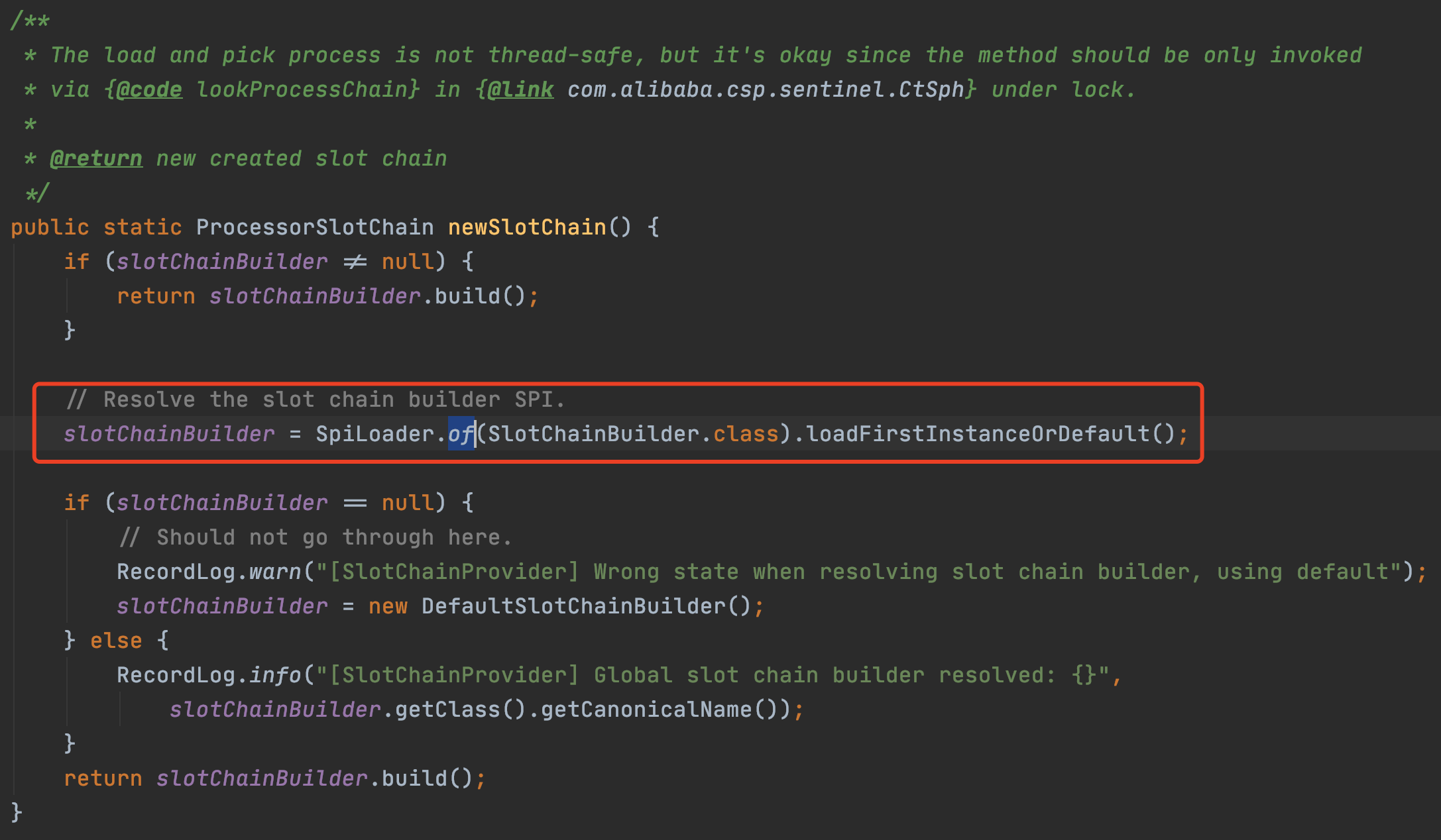
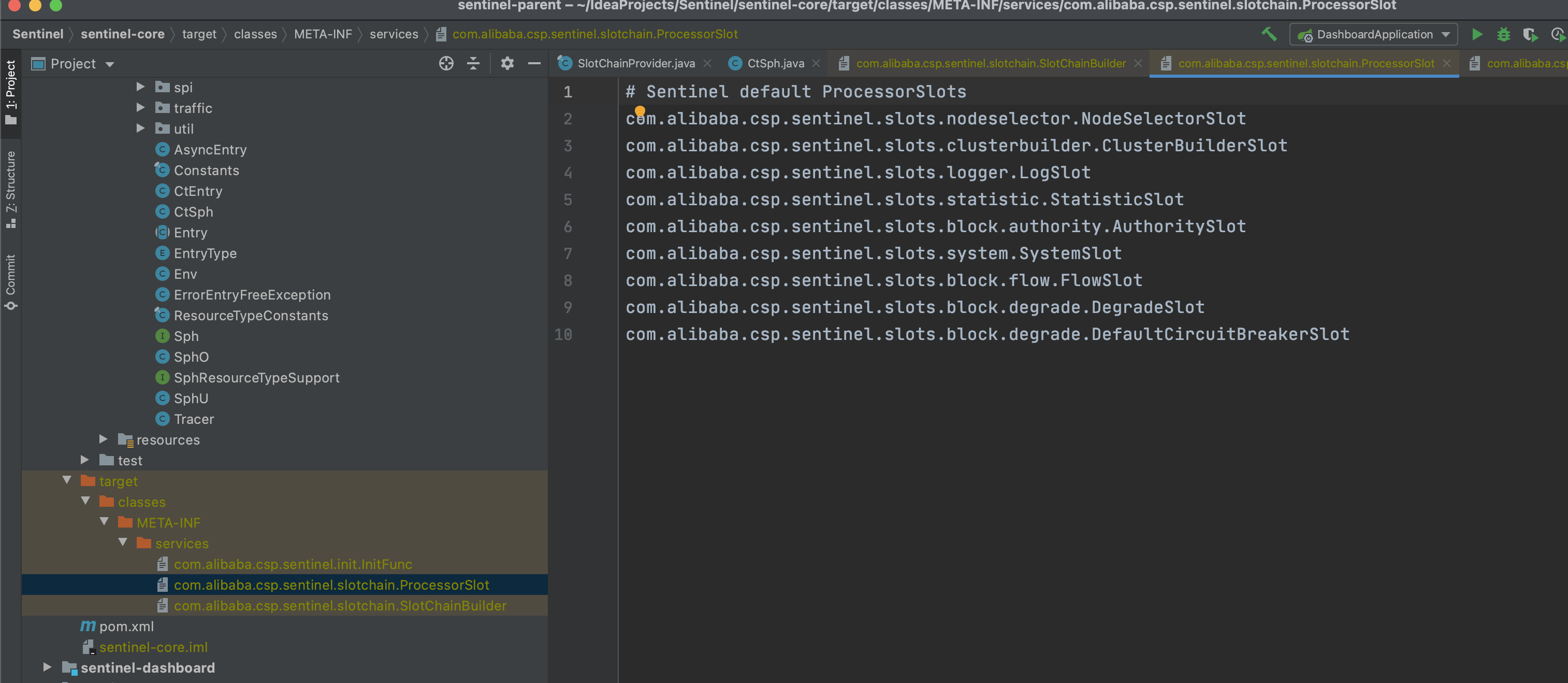
每個slot的主要職責如下:
•NodeSelectorSlot 負責收集資源的路徑,並將這些資源的呼叫路徑,以樹狀結構儲存起來,用於根據呼叫路徑來限流降級;
•ClusterBuilderSlot 則用於儲存資源的統計資訊以及呼叫者資訊,例如該資源的 RT, QPS, thread count 等等,這些資訊將用作為多維度限流,降級的依據;
•StatisticSlot 則用於記錄、統計不同緯度的 runtime 指標監控資訊;
•FlowSlot 則用於根據預設的限流規則以及前面 slot 統計的狀態,來進行流量控制;
•AuthoritySlot 則根據設定的黑白名單和呼叫來源資訊,來做黑白名單控制;
•DegradeSlot 則通過統計資訊以及預設的規則,來做熔斷降級;
•SystemSlot 則通過系統的狀態,例如 叢集QPS、執行緒數、RT、負載 等,來控制總的入口流量;
2.3 StatisticSlot
2.3.1 Node
深入看一下Node,因為統計資訊都在裡面,後面不論是限流、熔斷、負載保護等都是結合規則+統計資訊判斷是否要執行
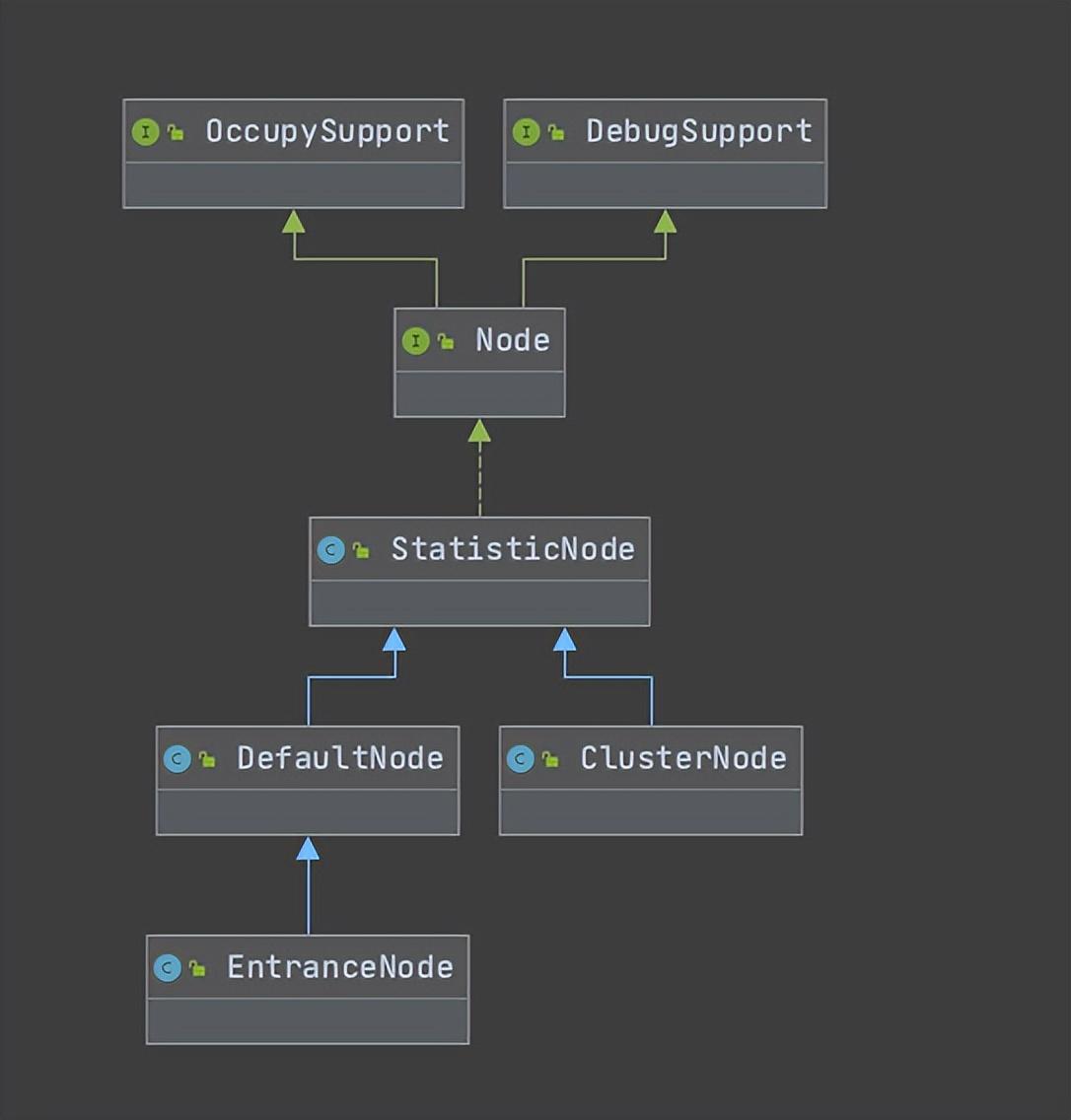
從Node的原始碼註釋看,它會持有資源維度的實時統計資料,以下是介面裡的方法定義,可以看到totalRequest、totalPass、totalSuccess、blockRequest、totalException、passQps等很多request、qps、thread的相關方法:
/**
* Holds real-time statistics for resources.
*
* @author qinan.qn
* @author leyou
* @author Eric Zhao
*/
public interface Node extends OccupySupport, DebugSupport {
long totalRequest();
long totalPass();
long totalSuccess();
long blockRequest();
long totalException();
double passQps();
double blockQps();
double totalQps();
double successQps();
……
}
2.3.2 StatisticNode
我們先從最基礎的StatisticNode開始看,原始碼給出的定位是:
The statistic node keep three kinds of real-time statistics metrics:
metrics in second level ({@code rollingCounterInSecond})
metrics in minute level ({@code rollingCounterInMinute})
thread count
StatisticNode只有四個屬性,除了之前提到過的LongAddr型別的curThreadNum外,還有兩個屬性是Metric物件,通過入參已經屬性命名可以看出,一個用於秒級,一個用於分鐘級統計。接下來我們就要看看Metric
// StatisticNode持有兩個Metric,一個秒級一個分鐘級,由入參可知,秒級統計劃分了兩個時間視窗,視窗程度是500ms
private transient volatile Metric rollingCounterInSecond = new ArrayMetric(SampleCountProperty.SAMPLE_COUNT,
IntervalProperty.INTERVAL);
// 分鐘級統計劃分了60個時間視窗,視窗長度是1000ms
private transient Metric rollingCounterInMinute = new ArrayMetric(60, 60 * 1000, false);
/**
* The counter for thread count.
*/
private LongAdder curThreadNum = new LongAdder();
/**
* The last timestamp when metrics were fetched.
*/
private long lastFetchTime = -1;
ArrayMetric只有一個屬性LeapArray
//以分鐘級的統計屬性為例,看一下時間視窗初始化過程
private transient Metric rollingCounterInMinute = new ArrayMetric(60, 60 * 1000, false);
public LeapArray(int sampleCount, int intervalInMs) {
AssertUtil.isTrue(sampleCount > 0, "bucket count is invalid: " + sampleCount);
AssertUtil.isTrue(intervalInMs > 0, "total time interval of the sliding window should be positive");
AssertUtil.isTrue(intervalInMs % sampleCount == 0, "time span needs to be evenly divided");
// windowLengthInMs = 60*1000 / 60 = 1000 滑動視窗時間長度,可見sentinel預設將單位時間分為了60個滑動視窗進行資料統計
this.windowLengthInMs = intervalInMs / sampleCount;
// 60*1000
this.intervalInMs = intervalInMs;
// 60
this.intervalInSecond = intervalInMs / 1000.0;
// 60
this.sampleCount = sampleCount;
// 陣列長度60
this.array = new AtomicReferenceArray<>(sampleCount);
}
/**
* Get bucket item at provided timestamp.
*
* @param timeMillis a valid timestamp in milliseconds
* @return current bucket item at provided timestamp if the time is valid; null if time is invalid
*/
public WindowWrap<T> currentWindow(long timeMillis) {
if (timeMillis < 0) {
return null;
}
// 根據當前時間戳算一個陣列索引
int idx = calculateTimeIdx(timeMillis);
// Calculate current bucket start time.
// timeMillis % 1000
long windowStart = calculateWindowStart(timeMillis);
/*
* Get bucket item at given time from the array.
*
* (1) Bucket is absent, then just create a new bucket and CAS update to circular array.
* (2) Bucket is up-to-date, then just return the bucket.
* (3) Bucket is deprecated, then reset current bucket.
*/
while (true) {
WindowWrap<T> old = array.get(idx);
if (old == null) {
/*
* B0 B1 B2 NULL B4
* ||_______|_______|_______|_______|_______||___
* 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 timestamp
* ^
* time=888
* bucket is empty, so create new and update
*
* If the old bucket is absent, then we create a new bucket at {@code windowStart},
* then try to update circular array via a CAS operation. Only one thread can
* succeed to update, while other threads yield its time slice.
*/
// newEmptyBucket 方法重寫,秒級和分鐘級統計物件實現不同
WindowWrap<T> window = new WindowWrap<T>(windowLengthInMs, windowStart, newEmptyBucket(timeMillis));
if (array.compareAndSet(idx, null, window)) {
// Successfully updated, return the created bucket.
return window;
} else {
// Contention failed, the thread will yield its time slice to wait for bucket available.
Thread.yield();
}
} else if (windowStart == old.windowStart()) {
/*
* B0 B1 B2 B3 B4
* ||_______|_______|_______|_______|_______||___
* 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 timestamp
* ^
* time=888
* startTime of Bucket 3: 800, so it's up-to-date
*
* If current {@code windowStart} is equal to the start timestamp of old bucket,
* that means the time is within the bucket, so directly return the bucket.
*/
return old;
} else if (windowStart > old.windowStart()) {
/*
* (old)
* B0 B1 B2 NULL B4
* |_______||_______|_______|_______|_______|_______||___
* ... 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000 2200 timestamp
* ^
* time=1676
* startTime of Bucket 2: 400, deprecated, should be reset
*
* If the start timestamp of old bucket is behind provided time, that means
* the bucket is deprecated. We have to reset the bucket to current {@code windowStart}.
* Note that the reset and clean-up operations are hard to be atomic,
* so we need a update lock to guarantee the correctness of bucket update.
*
* The update lock is conditional (tiny scope) and will take effect only when
* bucket is deprecated, so in most cases it won't lead to performance loss.
*/
if (updateLock.tryLock()) {
try {
// Successfully get the update lock, now we reset the bucket.
return resetWindowTo(old, windowStart);
} finally {
updateLock.unlock();
}
} else {
// Contention failed, the thread will yield its time slice to wait for bucket available.
Thread.yield();
}
} else if (windowStart < old.windowStart()) {
// Should not go through here, as the provided time is already behind.
return new WindowWrap<T>(windowLengthInMs, windowStart, newEmptyBucket(timeMillis));
}
}
}
// 持有一個時間視窗物件的資料,會根據當前時間戳除以時間視窗長度然後雜湊到陣列中
private int calculateTimeIdx(/*@Valid*/ long timeMillis) {
long timeId = timeMillis / windowLengthInMs;
// Calculate current index so we can map the timestamp to the leap array.
return (int)(timeId % array.length());
}
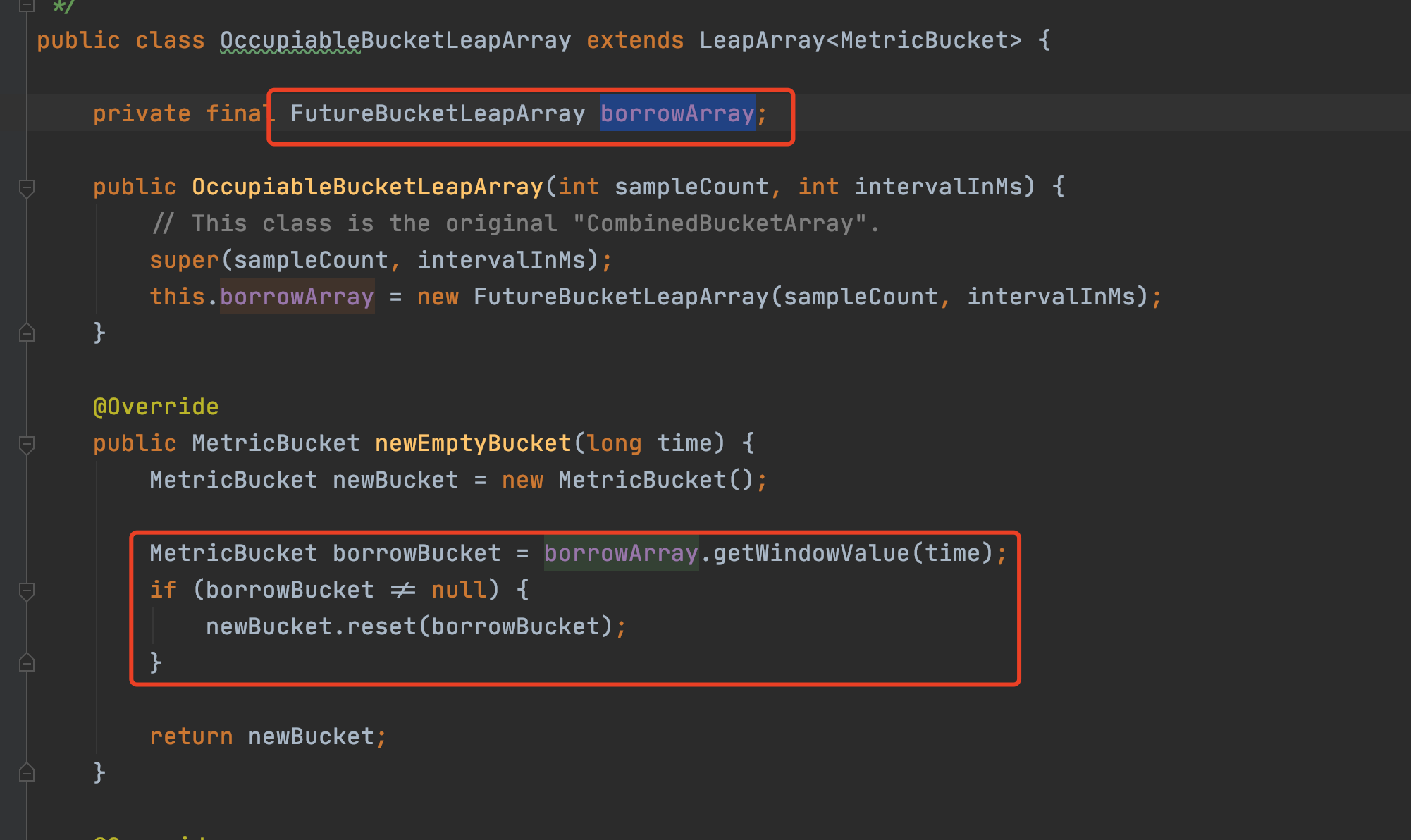
WindowWrap持有了windowLengthInMs, windowStart和LeapArray(分鐘統計實現是BucketLeapArray,秒級統計實現是OccupiableBucketLeapArray),對於分鐘級別的統計,MetricBucket維護了一個longAddr陣列和一個設定的minRT
/**
* The fundamental data structure for metric statistics in a time span.
*
* @author jialiang.linjl
* @author Eric Zhao
* @see LeapArray
*/
public class BucketLeapArray extends LeapArray<MetricBucket> {
public BucketLeapArray(int sampleCount, int intervalInMs) {
super(sampleCount, intervalInMs);
}
@Override
public MetricBucket newEmptyBucket(long time) {
return new MetricBucket();
}
@Override
protected WindowWrap<MetricBucket> resetWindowTo(WindowWrap<MetricBucket> w, long startTime) {
// Update the start time and reset value.
w.resetTo(startTime);
w.value().reset();
return w;
}
}
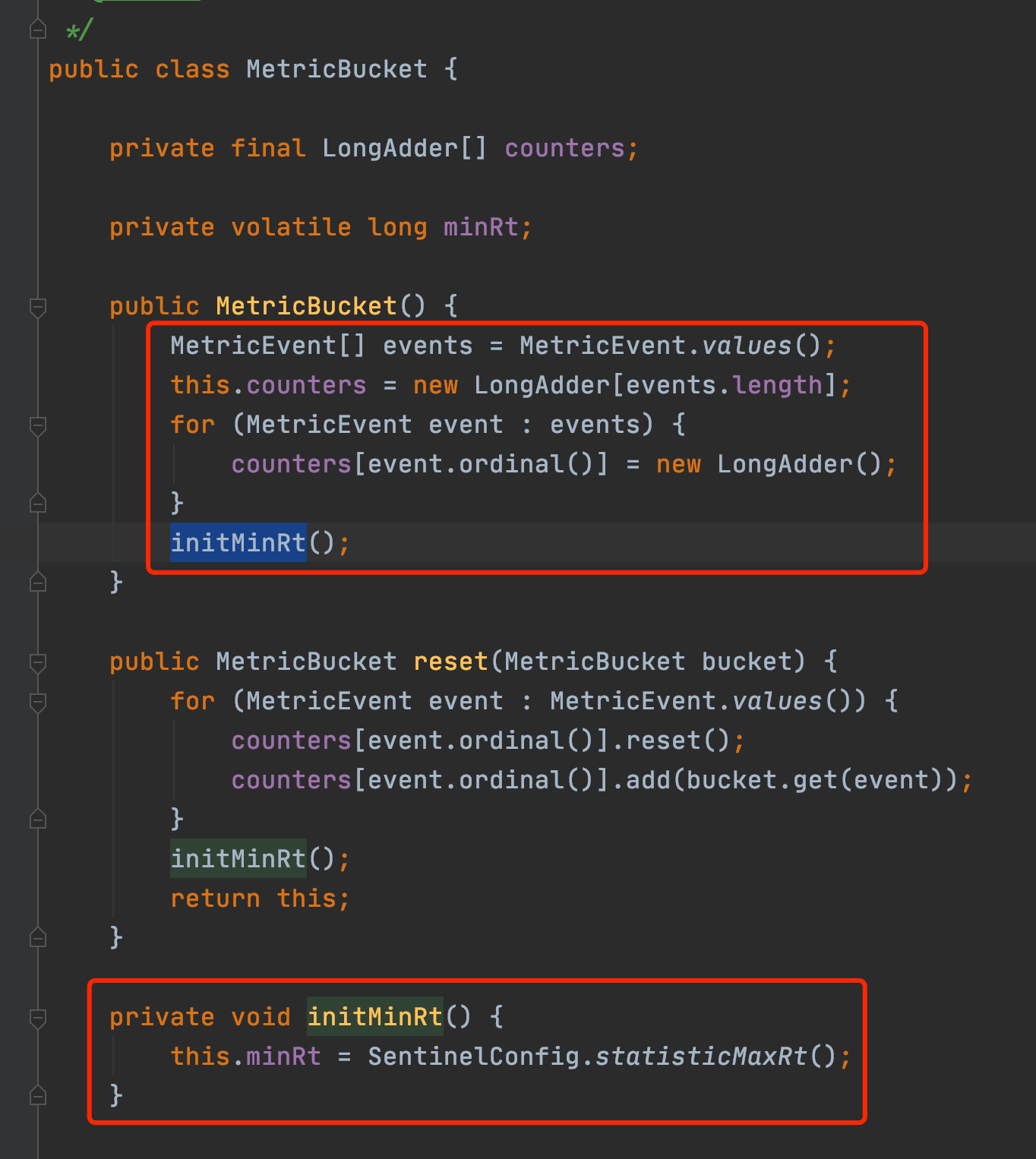
對於秒級統計,QPS=20場景下,如何準確統計的問題,此處用到了另外一個LeapArry實現FutureBucketLeapArray,至於秒級統計如何保證沒有統計誤差,讀者可以再研究一下FutureBucketLeapArray的上下文就好。
2.4 FlowSlot
2.4.1 常見限流演演算法
介紹sentinel限流實現前,先介紹一下常見限流演演算法,基本分為三種:計數器、漏斗、令牌桶。
計數器演演算法
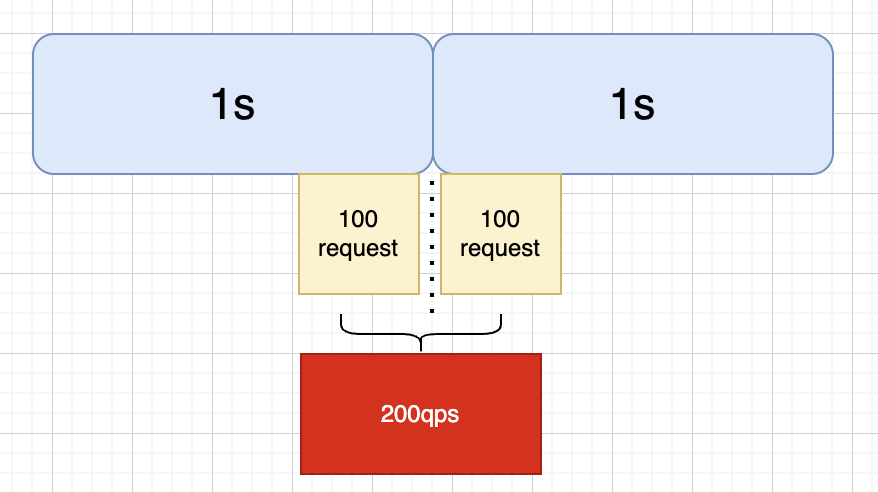
顧名思義,計數器演演算法就是統計某個時間段內的請求,每單位時間加1,然後與設定的限流值(最大QPS)進行比較,如果超出則觸發限流。但是這種演演算法不能做到「平滑限流」,以1s為單位時間,100QPS為限流值為例,如下圖,會出現某時段超出限流值的情況
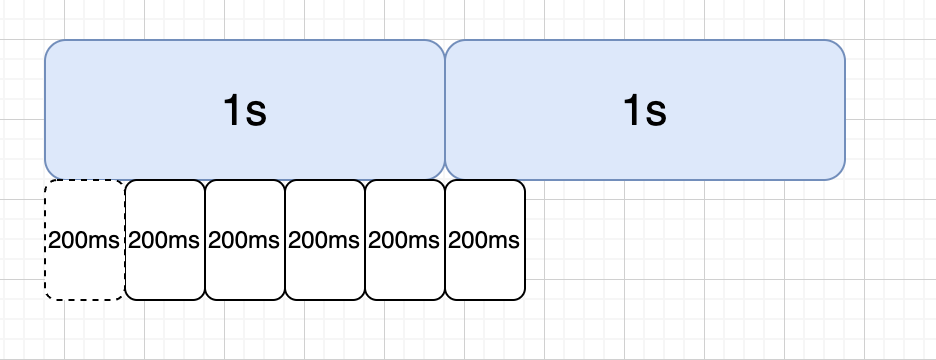
因此在單純計數器演演算法上,又出現了滑動視窗計數器演演算法,我們將統計時間細分,比如將1s統計時長分為5個時間視窗,通過捲動統計所有時間視窗的QPS作為系統實際的QPS的方式,就能解決上述臨界統計問題,後續我們看sentinel原始碼時也能看到類似操作。
漏斗演演算法
不論流量有多大都會先到漏桶中,然後以均勻的速度流出。如何在程式碼中實現這個勻速呢?比如我們想讓勻速為100q/s,那麼我們可以得到每流出一個流量需要消耗10ms,類似一個佇列,每隔10ms從佇列頭部取出流量進行放行,而我們的佇列也就是漏桶,當流量大於佇列的長度的時候,我們就可以拒絕超出的部分。
漏斗演演算法同樣的也有一定的缺點:無法應對突發流量。比如一瞬間來了100個請求,在漏桶演演算法中只能一個一個的過去,當最後一個請求流出的時候時間已經過了一秒了,所以漏斗演演算法比較適合請求到達比較均勻,需要嚴格控制請求速率的場景。
令牌桶演演算法
令牌桶演演算法和漏斗演演算法比較類似,區別是令牌桶存放的是令牌數量不是請求數量,令牌桶可以根據自身需求多樣性得管理令牌的生產和消耗,可以解決突發流量的問題。
2.4.2 單機限流模式
接下來我們看一下Sentinel中的限流實現,相比上述基本限流演演算法,Sentinel限流的第一個特性就是引入「資源」的概念,可以細粒度多樣性的支援特定資源、關聯資源、指定鏈路的限流。
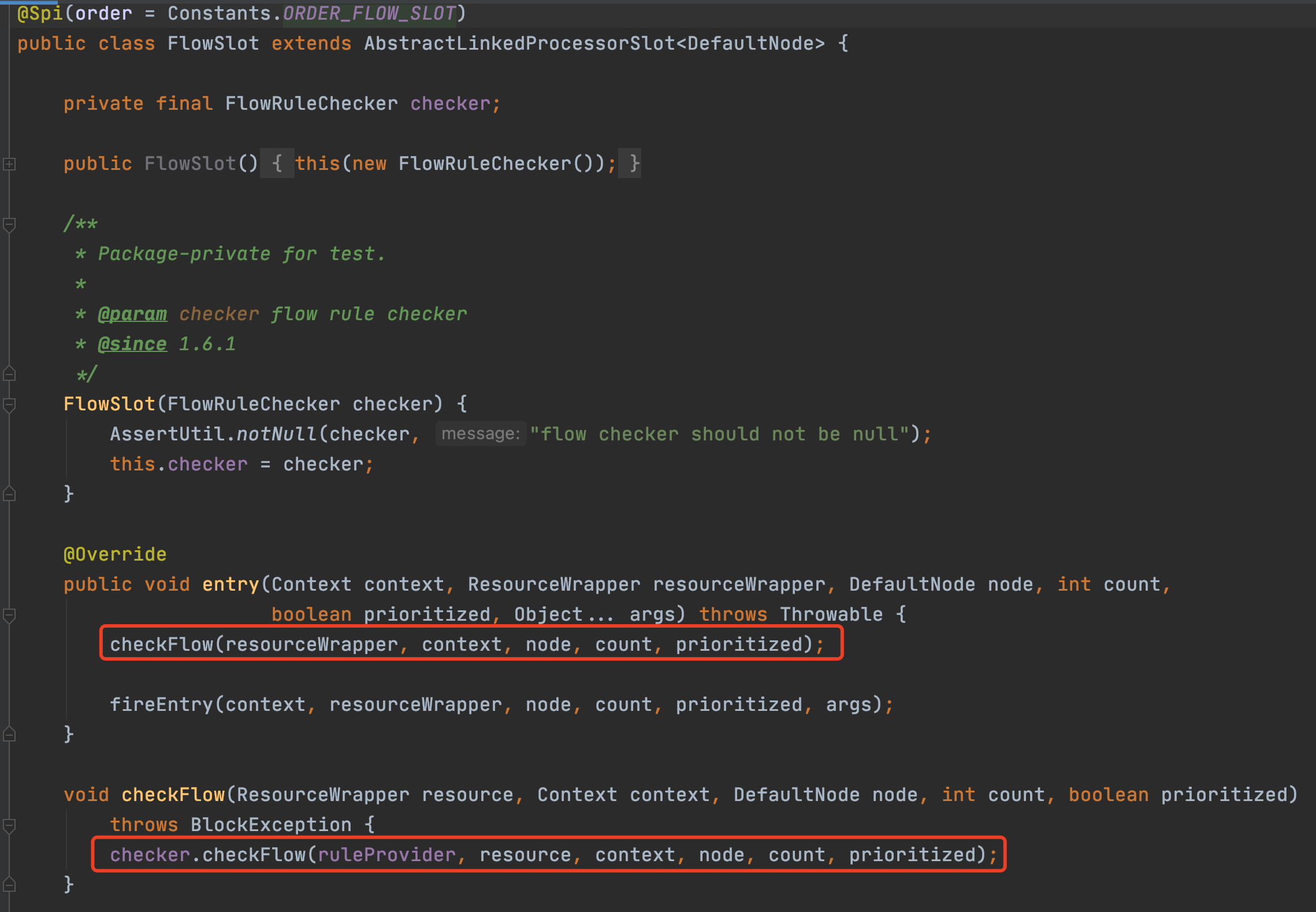
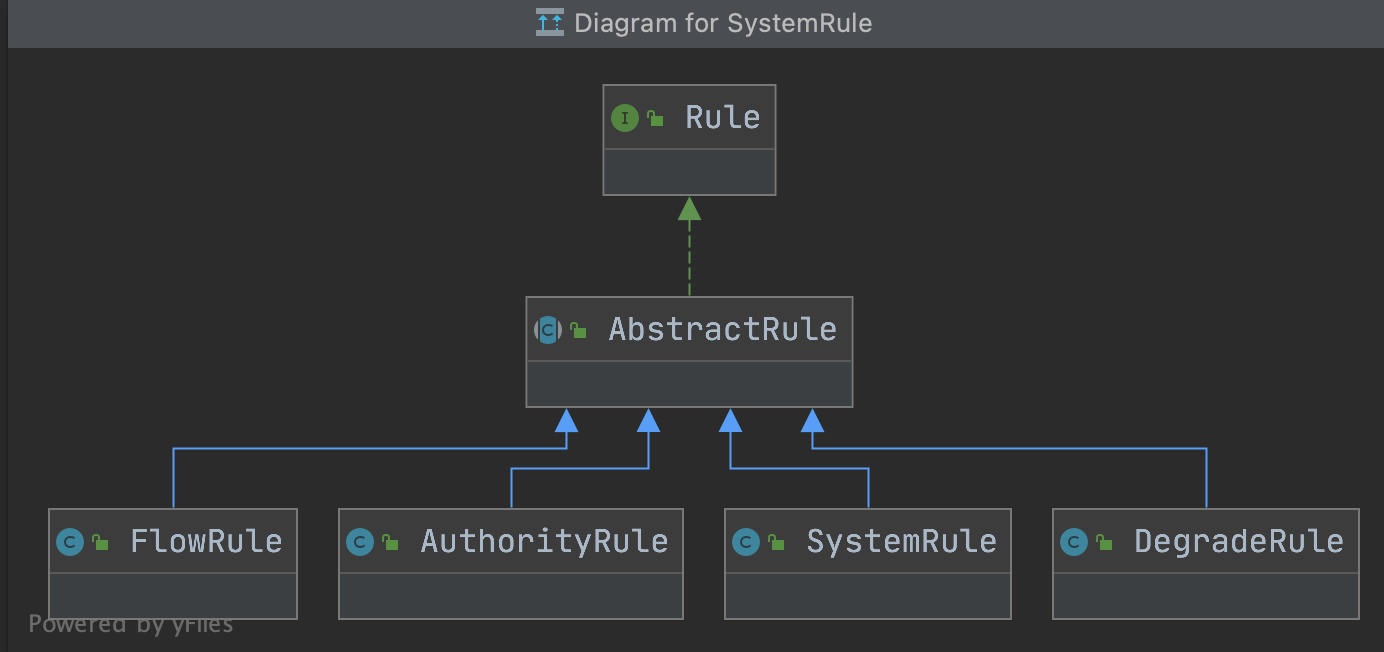
FlowSlot的主要邏輯都在FlowRuleChecker裡,介紹之前,我們先看一下Sentinel關於規則的模型描述,下圖分別是限流、存取控制規則、系統保護規則(Linux負載)、降級規則
/**
* 流量控制兩種模式
* 0: thread count(當呼叫該api的執行緒數達到閾值的時候,進行限流)
* 1: QPS(當呼叫該api的QPS達到閾值的時候,進行限流)
*/
private int grade = RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS;
/**
* 流量控制閾值,值含義與grade有關
*/
private double count;
/**
* 呼叫關係限流策略(可以支援關聯資源或指定鏈路的多樣性限流需求)
* 直接(api 達到限流條件時,直接限流)
* 關聯(當關聯的資源達到限流閾值時,就限流自己)
* 鏈路(只記錄指定鏈路上的流量)
* {@link RuleConstant#STRATEGY_DIRECT} for direct flow control (by origin);
* {@link RuleConstant#STRATEGY_RELATE} for relevant flow control (with relevant resource);
* {@link RuleConstant#STRATEGY_CHAIN} for chain flow control (by entrance resource).
*/
private int strategy = RuleConstant.STRATEGY_DIRECT;
/**
* Reference resource in flow control with relevant resource or context.
*/
private String refResource;
/**
* 流控效果:
* 0. default(reject directly),直接拒絕,拋異常FlowException
* 1. warm up, 慢啟動模式(根據coldFactor(冷載入因子,預設3)的值,從閾值/coldFactor,經過預熱時長,才達到設定的QPS閾值)
* 2. rate limiter 排隊等待
* 3. warm up + rate limiter
*/
private int controlBehavior = RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_DEFAULT;
private int warmUpPeriodSec = 10;
/**
* Max queueing time in rate limiter behavior.
*/
private int maxQueueingTimeMs = 500;
/**
* 是否叢集限流,預設為否
*/
private boolean clusterMode;
/**
* Flow rule config for cluster mode.
*/
private ClusterFlowConfig clusterConfig;
/**
* The traffic shaping (throttling) controller.
*/
private TrafficShapingController controller;
接著我們繼續分析FlowRuleChecker
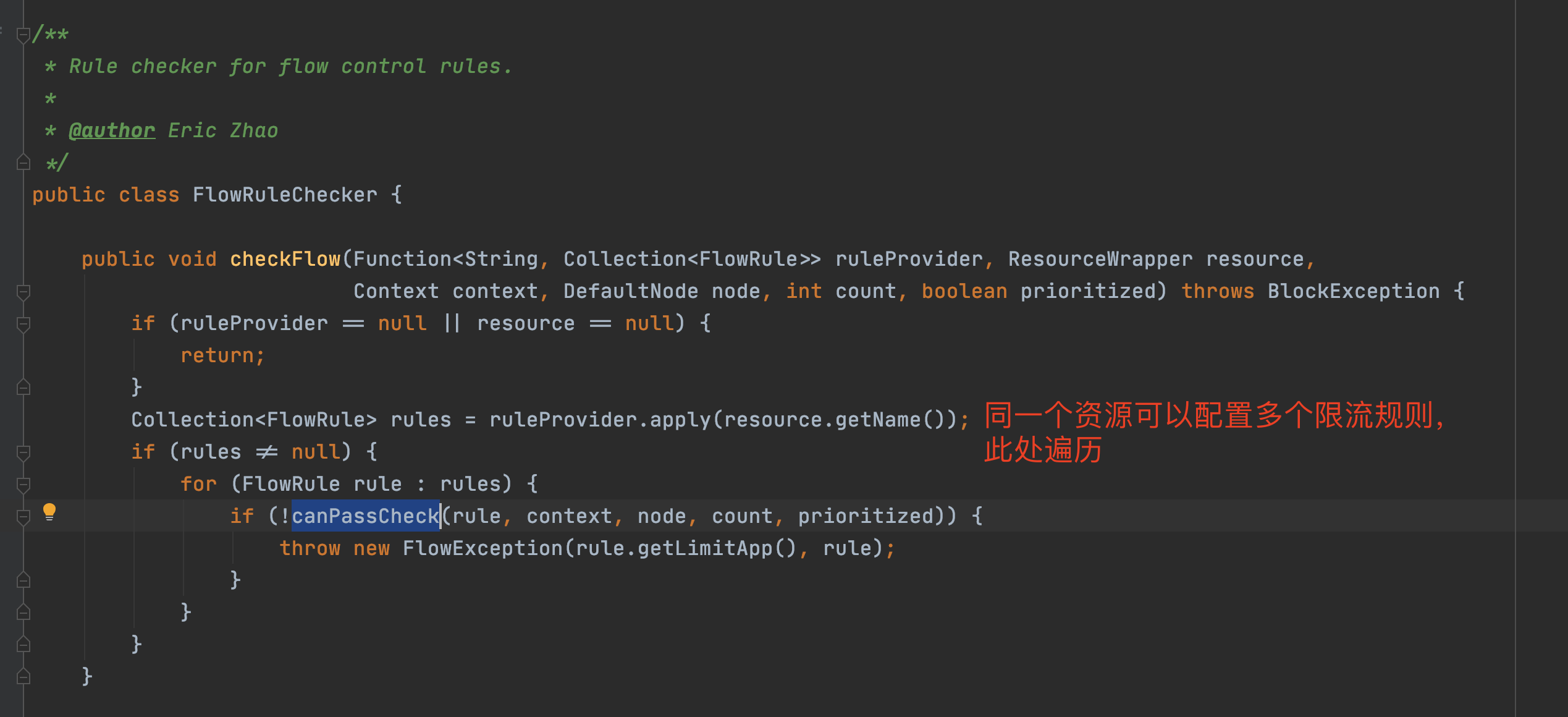
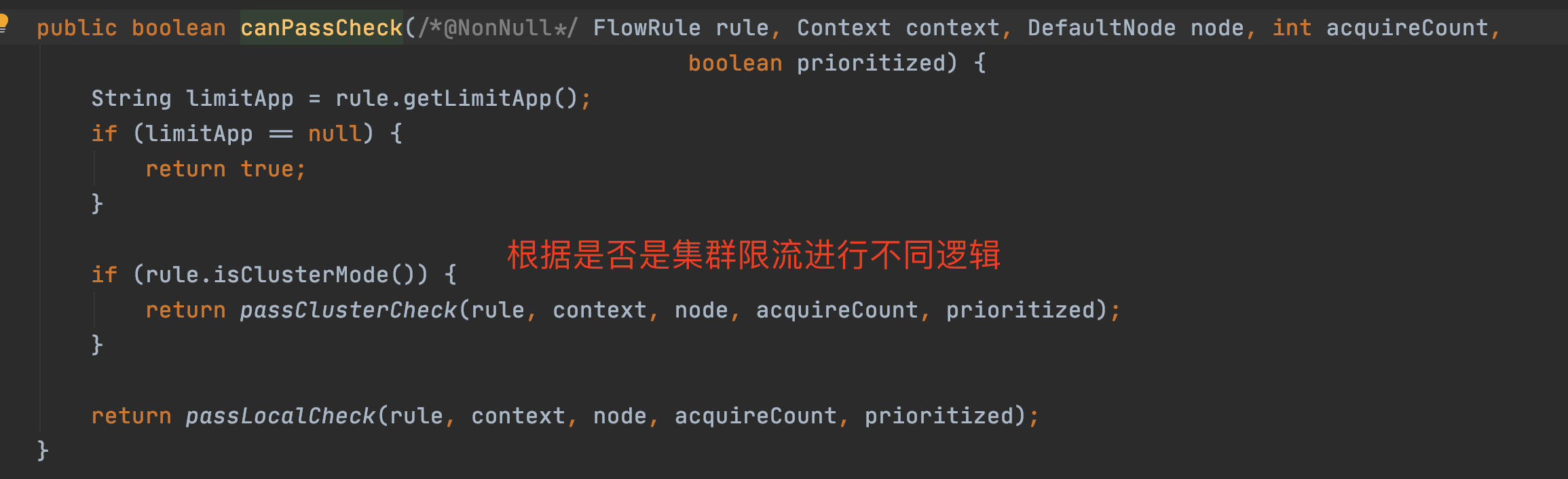
canPassCheck第一步會好看limitApp,這個是結合存取授許可權制規則使用的,預設是所有。
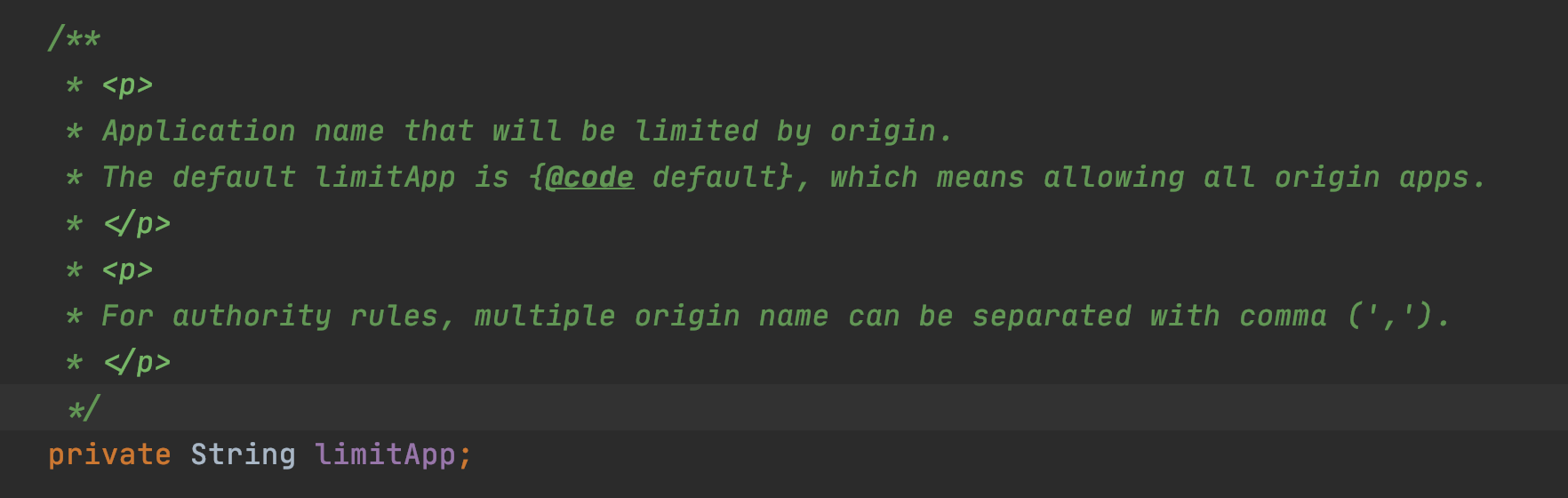
private static boolean passLocalCheck(FlowRule rule, Context context, DefaultNode node, int acquireCount,
boolean prioritized) {
// 根據策略選擇Node來進行統計(可以是本身Node、關聯的Node、指定的鏈路)
Node selectedNode = selectNodeByRequesterAndStrategy(rule, context, node);
if (selectedNode == null) {
return true;
}
return rule.getRater().canPass(selectedNode, acquireCount, prioritized);
}
static Node selectNodeByRequesterAndStrategy(/*@NonNull*/ FlowRule rule, Context context, DefaultNode node) {
// limitApp是存取控制使用的,預設是default,不限制來源
String limitApp = rule.getLimitApp();
// 拿到限流策略
int strategy = rule.getStrategy();
String origin = context.getOrigin();
// 基於呼叫來源做鑑權
if (limitApp.equals(origin) && filterOrigin(origin)) {
if (strategy == RuleConstant.STRATEGY_DIRECT) {
// Matches limit origin, return origin statistic node.
return context.getOriginNode();
}
//
return selectReferenceNode(rule, context, node);
} else if (RuleConstant.LIMIT_APP_DEFAULT.equals(limitApp)) {
if (strategy == RuleConstant.STRATEGY_DIRECT) {
// Return the cluster node.
return node.getClusterNode();
}
return selectReferenceNode(rule, context, node);
} else if (RuleConstant.LIMIT_APP_OTHER.equals(limitApp)
&& FlowRuleManager.isOtherOrigin(origin, rule.getResource())) {
if (strategy == RuleConstant.STRATEGY_DIRECT) {
return context.getOriginNode();
}
return selectReferenceNode(rule, context, node);
}
return null;
}
static Node selectReferenceNode(FlowRule rule, Context context, DefaultNode node) {
String refResource = rule.getRefResource();
int strategy = rule.getStrategy();
if (StringUtil.isEmpty(refResource)) {
return null;
}
if (strategy == RuleConstant.STRATEGY_RELATE) {
return ClusterBuilderSlot.getClusterNode(refResource);
}
if (strategy == RuleConstant.STRATEGY_CHAIN) {
if (!refResource.equals(context.getName())) {
return null;
}
return node;
}
// No node.
return null;
}
// 此程式碼是load限流規則時根據規則初始化流量整形控制器的邏輯,rule.getRater()返回TrafficShapingController
private static TrafficShapingController generateRater(/*@Valid*/ FlowRule rule) {
if (rule.getGrade() == RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS) {
switch (rule.getControlBehavior()) {
// 預熱模式返回WarmUpController
case RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_WARM_UP:
return new WarmUpController(rule.getCount(), rule.getWarmUpPeriodSec(),
ColdFactorProperty.coldFactor);
// 排隊模式返回ThrottlingController
case RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_RATE_LIMITER:
return new ThrottlingController(rule.getMaxQueueingTimeMs(), rule.getCount());
// 預熱+排隊模式返回WarmUpRateLimiterController
case RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_WARM_UP_RATE_LIMITER:
return new WarmUpRateLimiterController(rule.getCount(), rule.getWarmUpPeriodSec(),
rule.getMaxQueueingTimeMs(), ColdFactorProperty.coldFactor);
case RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_DEFAULT:
default:
// Default mode or unknown mode: default traffic shaping controller (fast-reject).
}
}
// 預設是DefaultController
return new DefaultController(rule.getCount(), rule.getGrade());
}
Sentinel單機限流演演算法
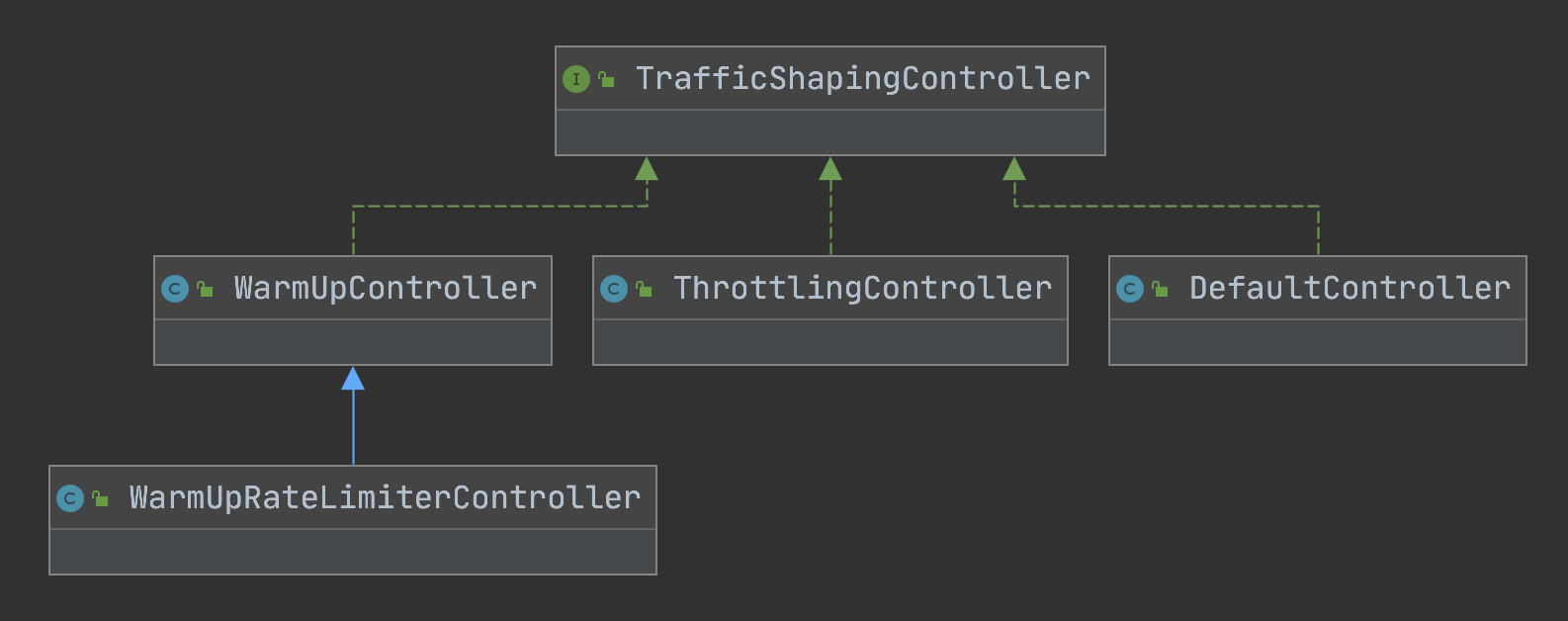
上面我們看到根據限流規則controlBehavior屬性(流控效果),會初始化以下實現:
•DefaultController:是一個非常典型的滑動視窗計數器演演算法實現,將當前統計的qps和請求進來的qps進行求和,小於限流值則通過,大於則計算一個等待時間,稍後再試
•ThrottlingController:是漏斗演演算法的實現,實現思路已經在原始碼片段中加了備註
•WarmUpController:實現參考了Guava的帶預熱的RateLimiter,區別是Guava側重於請求間隔,類似前面提到的令牌桶,而Sentinel更關注於請求數,和令牌桶演演算法有點類似
•WarmUpRateLimiterController:低水位使用預熱演演算法,高水位使用滑動視窗計數器演演算法排隊。
DefaultController
@Override
public boolean canPass(Node node, int acquireCount, boolean prioritized) {
int curCount = avgUsedTokens(node);
if (curCount + acquireCount > count) {
if (prioritized && grade == RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS) {
long currentTime;
long waitInMs;
currentTime = TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis();
waitInMs = node.tryOccupyNext(currentTime, acquireCount, count);
if (waitInMs < OccupyTimeoutProperty.getOccupyTimeout()) {
node.addWaitingRequest(currentTime + waitInMs, acquireCount);
node.addOccupiedPass(acquireCount);
sleep(waitInMs);
// PriorityWaitException indicates that the request will pass after waiting for {@link @waitInMs}.
throw new PriorityWaitException(waitInMs);
}
}
return false;
}
return true;
}
ThrottlingController
public ThrottlingController(int queueingTimeoutMs, double maxCountPerStat) {
this(queueingTimeoutMs, maxCountPerStat, 1000);
}
public ThrottlingController(int queueingTimeoutMs, double maxCountPerStat, int statDurationMs) {
AssertUtil.assertTrue(statDurationMs > 0, "statDurationMs should be positive");
AssertUtil.assertTrue(maxCountPerStat >= 0, "maxCountPerStat should be >= 0");
AssertUtil.assertTrue(queueingTimeoutMs >= 0, "queueingTimeoutMs should be >= 0");
this.maxQueueingTimeMs = queueingTimeoutMs;
this.count = maxCountPerStat;
this.statDurationMs = statDurationMs;
// Use nanoSeconds when durationMs%count != 0 or count/durationMs> 1 (to be accurate)
// 可見設定限流值count大於1000時useNanoSeconds會是true否則是false
if (maxCountPerStat > 0) {
this.useNanoSeconds = statDurationMs % Math.round(maxCountPerStat) != 0 || maxCountPerStat / statDurationMs > 1;
} else {
this.useNanoSeconds = false;
}
}
@Override
public boolean canPass(Node node, int acquireCount) {
return canPass(node, acquireCount, false);
}
private boolean checkPassUsingNanoSeconds(int acquireCount, double maxCountPerStat) {
final long maxQueueingTimeNs = maxQueueingTimeMs * MS_TO_NS_OFFSET;
long currentTime = System.nanoTime();
// Calculate the interval between every two requests.
final long costTimeNs = Math.round(1.0d * MS_TO_NS_OFFSET * statDurationMs * acquireCount / maxCountPerStat);
// Expected pass time of this request.
long expectedTime = costTimeNs + latestPassedTime.get();
if (expectedTime <= currentTime) {
// Contention may exist here, but it's okay.
latestPassedTime.set(currentTime);
return true;
} else {
final long curNanos = System.nanoTime();
// Calculate the time to wait.
long waitTime = costTimeNs + latestPassedTime.get() - curNanos;
if (waitTime > maxQueueingTimeNs) {
return false;
}
long oldTime = latestPassedTime.addAndGet(costTimeNs);
waitTime = oldTime - curNanos;
if (waitTime > maxQueueingTimeNs) {
latestPassedTime.addAndGet(-costTimeNs);
return false;
}
// in race condition waitTime may <= 0
if (waitTime > 0) {
sleepNanos(waitTime);
}
return true;
}
}
// 漏斗演演算法具體實現
private boolean checkPassUsingCachedMs(int acquireCount, double maxCountPerStat) {
long currentTime = TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis();
// 計算兩次請求的間隔(分為秒級和納秒級)
long costTime = Math.round(1.0d * statDurationMs * acquireCount / maxCountPerStat);
// 請求的期望的時間
long expectedTime = costTime + latestPassedTime.get();
if (expectedTime <= currentTime) {
// latestPassedTime是AtomicLong型別,支援volatile語意
latestPassedTime.set(currentTime);
return true;
} else {
// 計算等待時間
long waitTime = costTime + latestPassedTime.get() - TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis();
// 如果大於最大排隊時間,則觸發限流
if (waitTime > maxQueueingTimeMs) {
return false;
}
long oldTime = latestPassedTime.addAndGet(costTime);
waitTime = oldTime - TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis();
if (waitTime > maxQueueingTimeMs) {
latestPassedTime.addAndGet(-costTime);
return false;
}
// in race condition waitTime may <= 0
if (waitTime > 0) {
sleepMs(waitTime);
}
return true;
}
}
@Override
public boolean canPass(Node node, int acquireCount, boolean prioritized) {
// Pass when acquire count is less or equal than 0.
if (acquireCount <= 0) {
return true;
}
// Reject when count is less or equal than 0.
// Otherwise, the costTime will be max of long and waitTime will overflow in some cases.
if (count <= 0) {
return false;
}
if (useNanoSeconds) {
return checkPassUsingNanoSeconds(acquireCount, this.count);
} else {
return checkPassUsingCachedMs(acquireCount, this.count);
}
}
private void sleepMs(long ms) {
try {
Thread.sleep(ms);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
private void sleepNanos(long ns) {
LockSupport.parkNanos(ns);
}
long costTime = Math.round(1.0d * statDurationMs * acquireCount / maxCountPerStat);
由上述計算兩次請求間隔的公式我們可以發現,當maxCountPerStat(規則設定的限流值QPS)超過1000後,就無法準確計算出勻速排隊模式下的請求間隔時長,因此對應前面介紹的,當規則設定限流值超過1000QPS後,會採用checkPassUsingNanoSeconds,小於1000QPS會採用checkPassUsingCachedMs,對比一下checkPassUsingNanoSeconds和checkPassUsingCachedMs,可以發現主體思路沒變,只是統計維度從毫秒換算成了納秒,因此只看checkPassUsingCachedMs實現就可以
WarmUpController
@Override
public boolean canPass(Node node, int acquireCount, boolean prioritized) {
long passQps = (long) node.passQps();
long previousQps = (long) node.previousPassQps();
syncToken(previousQps);
// 開始計算它的斜率
// 如果進入了警戒線,開始調整他的qps
long restToken = storedTokens.get();
if (restToken >= warningToken) {
long aboveToken = restToken - warningToken;
// 消耗的速度要比warning快,但是要比慢
// current interval = restToken*slope+1/count
double warningQps = Math.nextUp(1.0 / (aboveToken * slope + 1.0 / count));
if (passQps + acquireCount <= warningQps) {
return true;
}
} else {
if (passQps + acquireCount <= count) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
protected void syncToken(long passQps) {
long currentTime = TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis();
currentTime = currentTime - currentTime % 1000;
long oldLastFillTime = lastFilledTime.get();
if (currentTime <= oldLastFillTime) {
return;
}
long oldValue = storedTokens.get();
long newValue = coolDownTokens(currentTime, passQps);
if (storedTokens.compareAndSet(oldValue, newValue)) {
long currentValue = storedTokens.addAndGet(0 - passQps);
if (currentValue < 0) {
storedTokens.set(0L);
}
lastFilledTime.set(currentTime);
}
}
private long coolDownTokens(long currentTime, long passQps) {
long oldValue = storedTokens.get();
long newValue = oldValue;
// 新增令牌的判斷前提條件:
// 當令牌的消耗程度遠遠低於警戒線的時候
if (oldValue < warningToken) {
newValue = (long)(oldValue + (currentTime - lastFilledTime.get()) * count / 1000);
} else if (oldValue > warningToken) {
if (passQps < (int)count / coldFactor) {
newValue = (long)(oldValue + (currentTime - lastFilledTime.get()) * count / 1000);
}
}
return Math.min(newValue, maxToken);
}
2.4.3 叢集限流
passClusterCheck方法(因為clusterService找不到會降級到非叢集限流)
private static boolean passClusterCheck(FlowRule rule, Context context, DefaultNode node, int acquireCount,
boolean prioritized) {
try {
// 獲取當前節點是Token Client還是Token Server
TokenService clusterService = pickClusterService();
if (clusterService == null) {
return fallbackToLocalOrPass(rule, context, node, acquireCount, prioritized);
}
long flowId = rule.getClusterConfig().getFlowId();
// 根據獲取的flowId通過TokenService進行申請token。從上面可知,它可能是TokenClient呼叫的,也可能是ToeknServer呼叫的。分別對應的類是DefaultClusterTokenClient和DefaultTokenService
TokenResult result = clusterService.requestToken(flowId, acquireCount, prioritized);
return applyTokenResult(result, rule, context, node, acquireCount, prioritized);
// If client is absent, then fallback to local mode.
} catch (Throwable ex) {
RecordLog.warn("[FlowRuleChecker] Request cluster token unexpected failed", ex);
}
// Fallback to local flow control when token client or server for this rule is not available.
// If fallback is not enabled, then directly pass.
return fallbackToLocalOrPass(rule, context, node, acquireCount, prioritized);
}
//獲取當前節點是Token Client還是Token Server。
//1) 如果當前節點的角色是Client,返回的TokenService為DefaultClusterTokenClient;
//2)如果當前節點的角色是Server,則預設返回的TokenService為DefaultTokenService。
private static TokenService pickClusterService() {
if (ClusterStateManager.isClient()) {
return TokenClientProvider.getClient();
}
if (ClusterStateManager.isServer()) {
return EmbeddedClusterTokenServerProvider.getServer();
}
return null;
}
叢集限流模式
Sentinel 叢集限流伺服器端有兩種啟動方式:
•嵌入模式(Embedded)適合應用級別的限流,部署簡單,但對應用效能有影響
•獨立模式(Alone)適合全域性限流,需要獨立部署
考慮到文章篇幅,叢集限流有機會再展開詳細介紹。
叢集限流模式降級
private static boolean passClusterCheck(FlowRule rule, Context context, DefaultNode node, int acquireCount,
boolean prioritized) {
try {
TokenService clusterService = pickClusterService();
if (clusterService == null) {
return fallbackToLocalOrPass(rule, context, node, acquireCount, prioritized);
}
long flowId = rule.getClusterConfig().getFlowId();
TokenResult result = clusterService.requestToken(flowId, acquireCount, prioritized);
return applyTokenResult(result, rule, context, node, acquireCount, prioritized);
// If client is absent, then fallback to local mode.
} catch (Throwable ex) {
RecordLog.warn("[FlowRuleChecker] Request cluster token unexpected failed", ex);
}
// Fallback to local flow control when token client or server for this rule is not available.
// If fallback is not enabled, then directly pass.
// 可以看到如果叢集限流有異常,會降級到單機限流模式,如果設定不允許降級,那麼直接會跳過此次校驗
return fallbackToLocalOrPass(rule, context, node, acquireCount, prioritized);
}
2.5 DegradeSlot
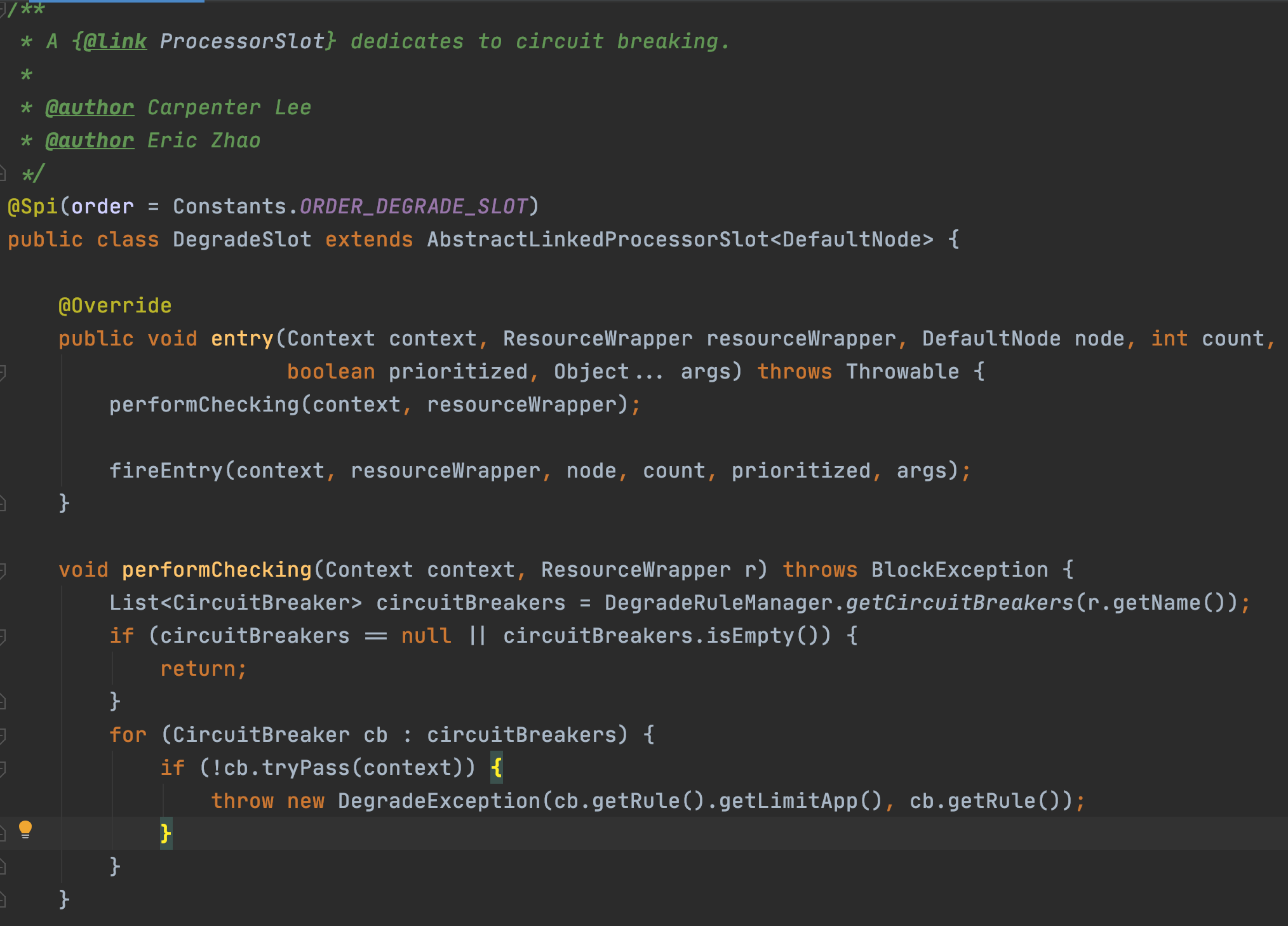
CircuitBreaker
大神對斷路器的解釋:https://martinfowler.com/bliki/CircuitBreaker.html
首先就看到了根據資源名稱獲取斷路器列表,Sentinel的斷路器有兩個實現:RT模式使用ResponseTimeCircuitBreaker、異常模式使用ExceptionCircuitBreaker
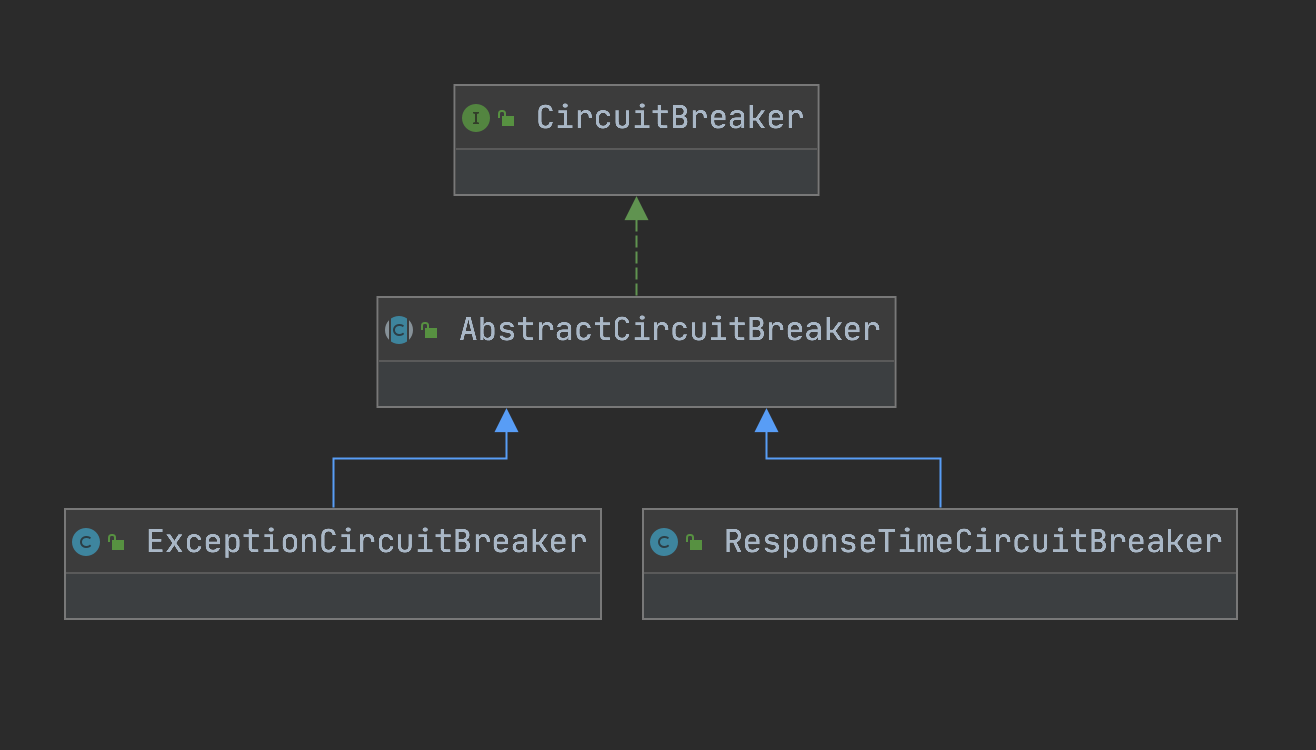
public interface CircuitBreaker {
/**
* Get the associated circuit breaking rule.
*
* @return associated circuit breaking rule
*/
DegradeRule getRule();
/**
* Acquires permission of an invocation only if it is available at the time of invoking.
*
* @param context context of current invocation
* @return {@code true} if permission was acquired and {@code false} otherwise
*/
boolean tryPass(Context context);
/**
* Get current state of the circuit breaker.
*
* @return current state of the circuit breaker
*/
State currentState();
/**
* <p>Record a completed request with the context and handle state transformation of the circuit breaker.</p>
* <p>Called when a <strong>passed</strong> invocation finished.</p>
*
* @param context context of current invocation
*/
void onRequestComplete(Context context);
/**
* Circuit breaker state.
*/
enum State {
/**
* In {@code OPEN} state, all requests will be rejected until the next recovery time point.
*/
OPEN,
/**
* In {@code HALF_OPEN} state, the circuit breaker will allow a "probe" invocation.
* If the invocation is abnormal according to the strategy (e.g. it's slow), the circuit breaker
* will re-transform to the {@code OPEN} state and wait for the next recovery time point;
* otherwise the resource will be regarded as "recovered" and the circuit breaker
* will cease cutting off requests and transform to {@code CLOSED} state.
*/
HALF_OPEN,
/**
* In {@code CLOSED} state, all requests are permitted. When current metric value exceeds the threshold,
* the circuit breaker will transform to {@code OPEN} state.
*/
CLOSED
}
}
以ExceptionCircuitBreaker為例看一下具體實現
public class ExceptionCircuitBreaker extends AbstractCircuitBreaker {
// 異常模式有兩種,異常率和異常數
private final int strategy;
// 最小請求數
private final int minRequestAmount;
// 閾值
private final double threshold;
// LeapArray是sentinel統計資料非常重要的一個結構,主要封裝了時間視窗相關的操作
private final LeapArray<SimpleErrorCounter> stat;
public ExceptionCircuitBreaker(DegradeRule rule) {
this(rule, new SimpleErrorCounterLeapArray(1, rule.getStatIntervalMs()));
}
ExceptionCircuitBreaker(DegradeRule rule, LeapArray<SimpleErrorCounter> stat) {
super(rule);
this.strategy = rule.getGrade();
boolean modeOk = strategy == DEGRADE_GRADE_EXCEPTION_RATIO || strategy == DEGRADE_GRADE_EXCEPTION_COUNT;
AssertUtil.isTrue(modeOk, "rule strategy should be error-ratio or error-count");
AssertUtil.notNull(stat, "stat cannot be null");
this.minRequestAmount = rule.getMinRequestAmount();
this.threshold = rule.getCount();
this.stat = stat;
}
@Override
protected void resetStat() {
// Reset current bucket (bucket count = 1).
stat.currentWindow().value().reset();
}
@Override
public void onRequestComplete(Context context) {
Entry entry = context.getCurEntry();
if (entry == null) {
return;
}
Throwable error = entry.getError();
SimpleErrorCounter counter = stat.currentWindow().value();
if (error != null) {
counter.getErrorCount().add(1);
}
counter.getTotalCount().add(1);
handleStateChangeWhenThresholdExceeded(error);
}
private void handleStateChangeWhenThresholdExceeded(Throwable error) {
if (currentState.get() == State.OPEN) {
return;
}
if (currentState.get() == State.HALF_OPEN) {
// In detecting request
if (error == null) {
fromHalfOpenToClose();
} else {
fromHalfOpenToOpen(1.0d);
}
return;
}
List<SimpleErrorCounter> counters = stat.values();
long errCount = 0;
long totalCount = 0;
for (SimpleErrorCounter counter : counters) {
+= counter.errorCount.sum();
totalCount += counter.totalCount.sum();
}
if (totalCount < minRequestAmount) {
return;
}
double curCount = errCount;
if (strategy == DEGRADE_GRADE_EXCEPTION_RATIO) {
// Use errorRatio
curCount = errCount * 1.0d / totalCount;
}
if (curCount > threshold) {
transformToOpen(curCount);
}
}
static class SimpleErrorCounter {
private LongAdder errorCount;
private LongAdder totalCount;
public SimpleErrorCounter() {
this.errorCount = new LongAdder();
this.totalCount = new LongAdder();
}
public LongAdder getErrorCount() {
return errorCount;
}
public LongAdder getTotalCount() {
return totalCount;
}
public SimpleErrorCounter reset() {
errorCount.reset();
totalCount.reset();
return this;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "SimpleErrorCounter{" +
"errorCount=" + errorCount +
", totalCount=" + totalCount +
'}';
}
}
static class SimpleErrorCounterLeapArray extends LeapArray<SimpleErrorCounter> {
public SimpleErrorCounterLeapArray(int sampleCount, int intervalInMs) {
super(sampleCount, intervalInMs);
}
@Override
public SimpleErrorCounter newEmptyBucket(long timeMillis) {
return new SimpleErrorCounter();
}
@Override
protected WindowWrap<SimpleErrorCounter> resetWindowTo(WindowWrap<SimpleErrorCounter> w, long startTime) {
// Update the start time and reset value.
w.resetTo(startTime);
w.value().reset();
return w;
}
}
}
2.6 SystemSlot
校驗邏輯主要集中在com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.system.SystemRuleManager#checkSystem,以下是片段,可以看到,作為負載保護規則校驗,實現了叢集的QPS、執行緒、RT(響應時間)、系統負載的控制,除系統負載以外,其餘統計都是依賴StatisticSlot實現,系統負載是通過SystemRuleManager定時排程SystemStatusListener,通過OperatingSystemMXBean去獲取
/**
* Apply {@link SystemRule} to the resource. Only inbound traffic will be checked.
*
* @param resourceWrapper the resource.
* @throws BlockException when any system rule's threshold is exceeded.
*/
public static void checkSystem(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count) throws BlockException {
if (resourceWrapper == null) {
return;
}
// Ensure the checking switch is on.
if (!checkSystemStatus.get()) {
return;
}
// for inbound traffic only
if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() != EntryType.IN) {
return;
}
// total qps 此處是拿到某個資源在叢集中的QPS總和,相關概念可以會看初始化關於Node的介紹
double currentQps = Constants.ENTRY_NODE.passQps();
if (currentQps + count > qps) {
throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "qps");
}
// total thread
int currentThread = Constants.ENTRY_NODE.curThreadNum();
if (currentThread > maxThread) {
throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "thread");
}
double rt = Constants.ENTRY_NODE.avgRt();
if (rt > maxRt) {
throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "rt");
}
// load. BBR algorithm.
if (highestSystemLoadIsSet && getCurrentSystemAvgLoad() > highestSystemLoad) {
if (!checkBbr(currentThread)) {
throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "load");
}
}
// cpu usage
if (highestCpuUsageIsSet && getCurrentCpuUsage() > highestCpuUsage) {
throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "cpu");
}
}
private static boolean checkBbr(int currentThread) {
if (currentThread > 1 &&
currentThread > Constants.ENTRY_NODE.maxSuccessQps() * Constants.ENTRY_NODE.minRt() / 1000) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
public static double getCurrentSystemAvgLoad() {
return statusListener.getSystemAverageLoad();
}
public static double getCurrentCpuUsage() {
return statusListener.getCpuUsage();
}
public class SystemStatusListener implements Runnable {
volatile double currentLoad = -1;
volatile double currentCpuUsage = -1;
volatile String reason = StringUtil.EMPTY;
volatile long processCpuTime = 0;
volatile long processUpTime = 0;
public double getSystemAverageLoad() {
return currentLoad;
}
public double getCpuUsage() {
return currentCpuUsage;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
OperatingSystemMXBean osBean = ManagementFactory.getPlatformMXBean(OperatingSystemMXBean.class);
currentLoad = osBean.getSystemLoadAverage();
/*
* Java Doc copied from {@link OperatingSystemMXBean#getSystemCpuLoad()}:</br>
* Returns the "recent cpu usage" for the whole system. This value is a double in the [0.0,1.0] interval.
* A value of 0.0 means that all CPUs were idle during the recent period of time observed, while a value
* of 1.0 means that all CPUs were actively running 100% of the time during the recent period being
* observed. All values between 0.0 and 1.0 are possible depending of the activities going on in the
* system. If the system recent cpu usage is not available, the method returns a negative value.
*/
double systemCpuUsage = osBean.getSystemCpuLoad();
// calculate process cpu usage to support application running in container environment
RuntimeMXBean runtimeBean = ManagementFactory.getPlatformMXBean(RuntimeMXBean.class);
long newProcessCpuTime = osBean.getProcessCpuTime();
long newProcessUpTime = runtimeBean.getUptime();
int cpuCores = osBean.getAvailableProcessors();
long processCpuTimeDiffInMs = TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS
.toMillis(newProcessCpuTime - processCpuTime);
long processUpTimeDiffInMs = newProcessUpTime - processUpTime;
double processCpuUsage = (double) processCpuTimeDiffInMs / processUpTimeDiffInMs / cpuCores;
processCpuTime = newProcessCpuTime;
processUpTime = newProcessUpTime;
currentCpuUsage = Math.max(processCpuUsage, systemCpuUsage);
if (currentLoad > SystemRuleManager.getSystemLoadThreshold()) {
writeSystemStatusLog();
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
RecordLog.warn("[SystemStatusListener] Failed to get system metrics from JMX", e);
}
}
private void writeSystemStatusLog() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("Load exceeds the threshold: ");
sb.append("load:").append(String.format("%.4f", currentLoad)).append("; ");
sb.append("cpuUsage:").append(String.format("%.4f", currentCpuUsage)).append("; ");
sb.append("qps:").append(String.format("%.4f", Constants.ENTRY_NODE.passQps())).append("; ");
sb.append("rt:").append(String.format("%.4f", Constants.ENTRY_NODE.avgRt())).append("; ");
sb.append("thread:").append(Constants.ENTRY_NODE.curThreadNum()).append("; ");
sb.append("success:").append(String.format("%.4f", Constants.ENTRY_NODE.successQps())).append("; ");
sb.append("minRt:").append(String.format("%.2f", Constants.ENTRY_NODE.minRt())).append("; ");
sb.append("maxSuccess:").append(String.format("%.2f", Constants.ENTRY_NODE.maxSuccessQps())).append("; ");
RecordLog.info(sb.toString());
}
}
三、京東版最佳實踐
3.1 使用方式
Sentinel使用方式本身非常簡單,就是一個註解,但是要考慮規則載入和規則持久化的方式,現有的方式有:
•使用Sentinel-dashboard功能:使用面板接入需要維護一個設定規則的管理端,考慮到偏後端的系統需要額外維護一個面板成本較大,如果是像RPC框架這種本身有管理端的接入可以考慮次方案。
•中介軟體(如:zookepper、nacos、eureka、redis等):Sentinel原始碼extension包裡提供了類似的實現,如下圖
結合京東實際,我實現了一個規則熱部署的Sentinel元件,實現方式類似zookeeper的方式,將規則記錄到ducc的一個key上,在spring容器啟動時做第一次規則載入和監聽器註冊,元件也做一了一些規則讀取,校驗、範例化不同規則物件的工作
外掛使用方式:註解+設定
第一步 引入元件
<dependency>
<groupId>com.jd.ldop.tools</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-tools</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
第二步 初始化sentinelProcess
支援ducc、本地檔案讀取、直接寫入三種方式規則寫入方式
目前支援限流規則、熔斷降級規則兩種模式,系統負載保護模式待開發和驗證
<!-- 基於sentinel的降級、限流、熔斷元件 -->
<bean id="sentinelProcess" class="com.jd.ldop.sentinel.SentinelProcess">
<property name="ruleResourceWrappers">
<list>
<ref bean="degradeRule"/>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 降級或限流規則設定 -->
<bean id="degradeRule" class="com.jd.ldop.sentinel.dto.RuleResourceWrapper">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="ducc.degradeRule"/>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="0"/>
<constructor-arg index="2" value="0"/>
</bean>
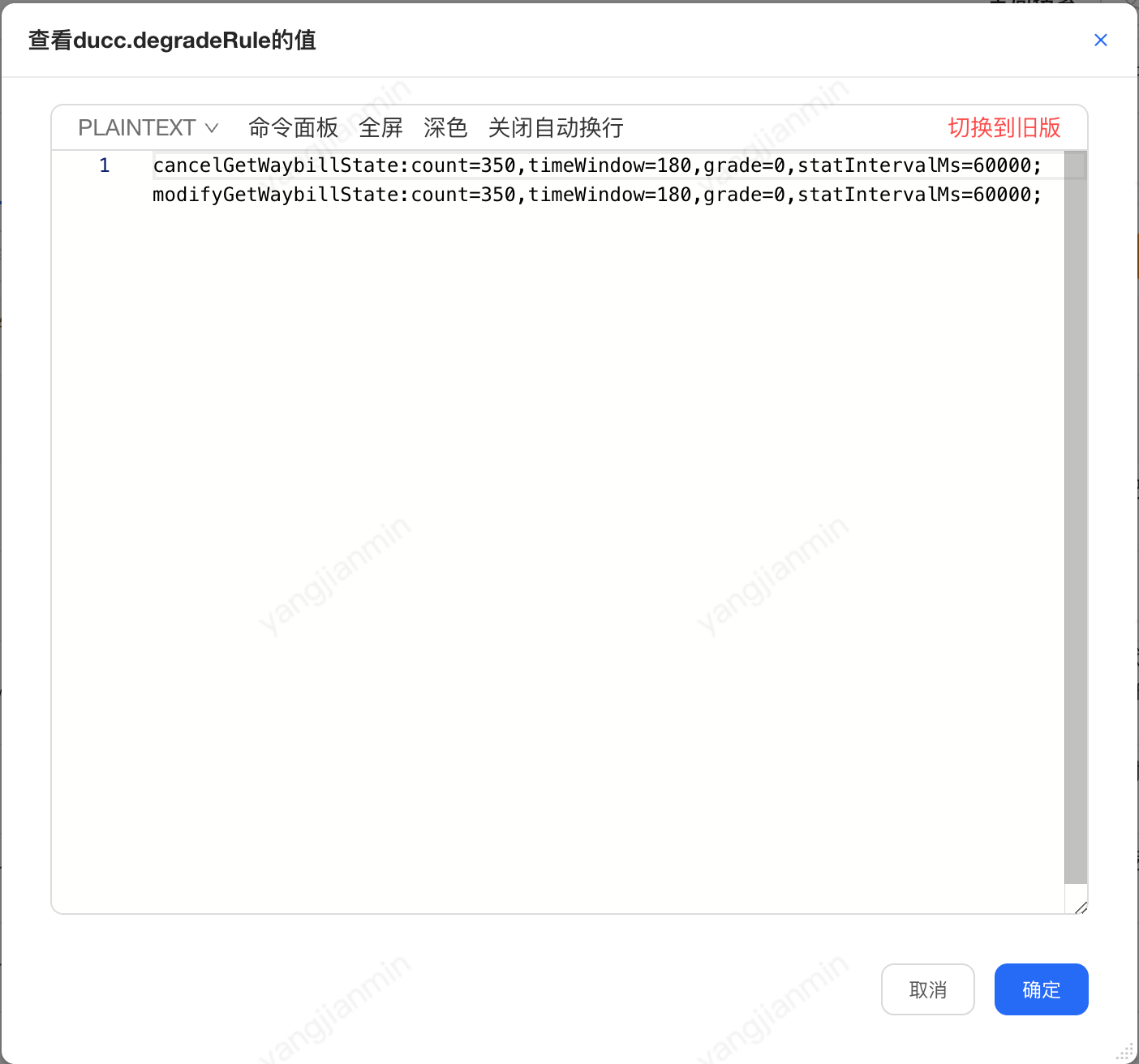
ducc上設定如下:
第三步 定義資源和關聯型別
通過@SentinelResource可以直接在任意位置定義資源名以及對應的熔斷降級或者限流方式、回撥方法等,同時也可以指定關聯型別,支援直接、關聯、指定鏈路三種
@Override
@SentinelResource(value = "modifyGetWaybillState", fallback = "executeDegrade")
public ExecutionResult<List<Integer>> execute(@NotNull Model imodel) {
// 業務邏輯處理
}
public ExecutionResult<List<Integer>> executeDegrade(@NotNull Model imodel) {
// 降級業務邏輯處理
}
3.2 應用場景
元件支援任意的業務降級、限流、負載保護
四、Sentinel壓測資料
4.1 壓測目標
呼叫量:1.2W/m
應用機器記憶體穩定在50%以內
機器規格: 8C16G50G磁碟*2
Sentinel降級規則:
count=350-------慢呼叫臨界閾值350ms
timeWindow=180------熔斷時間視窗180s
grade=0-----降級模式 慢呼叫
statIntervalMs=60000------統計時長1min
4.2 壓測結果
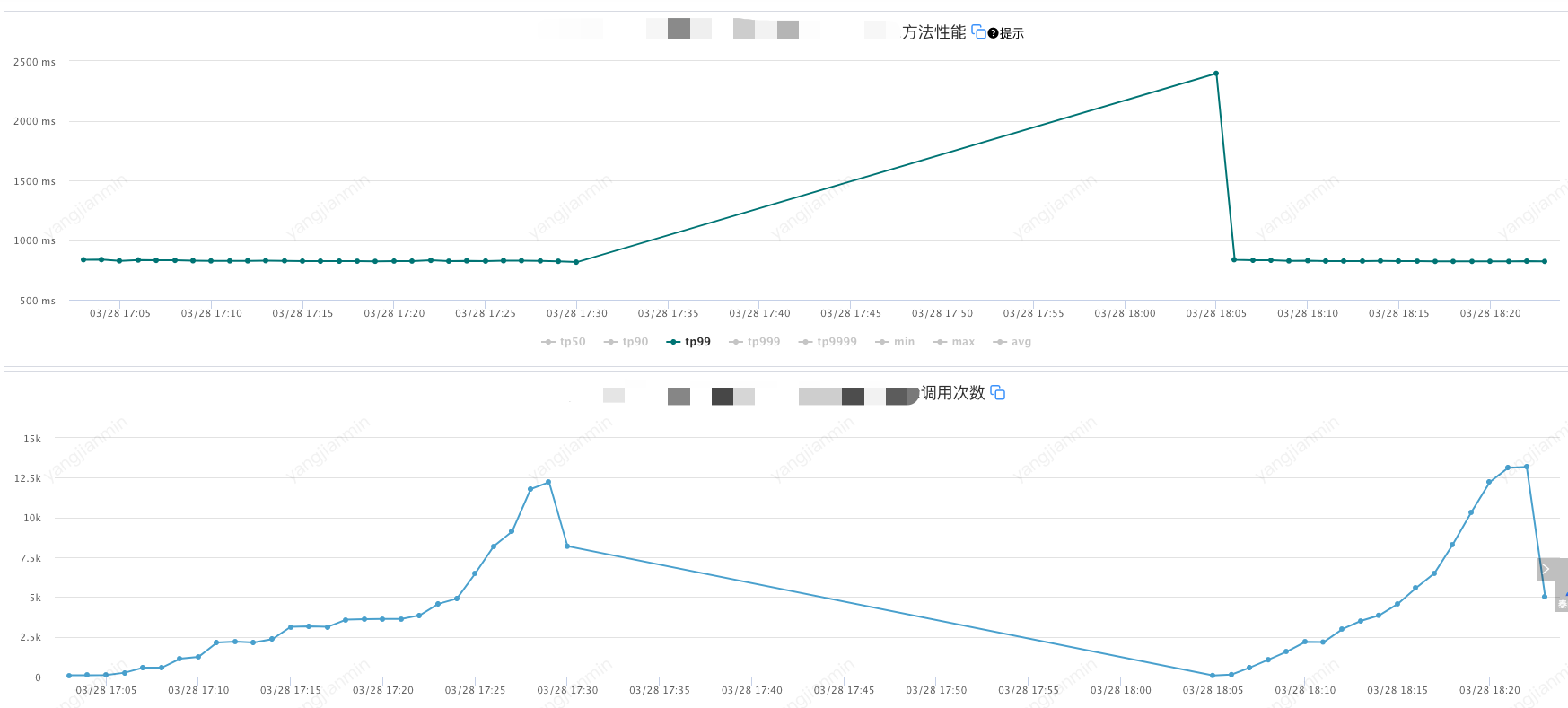
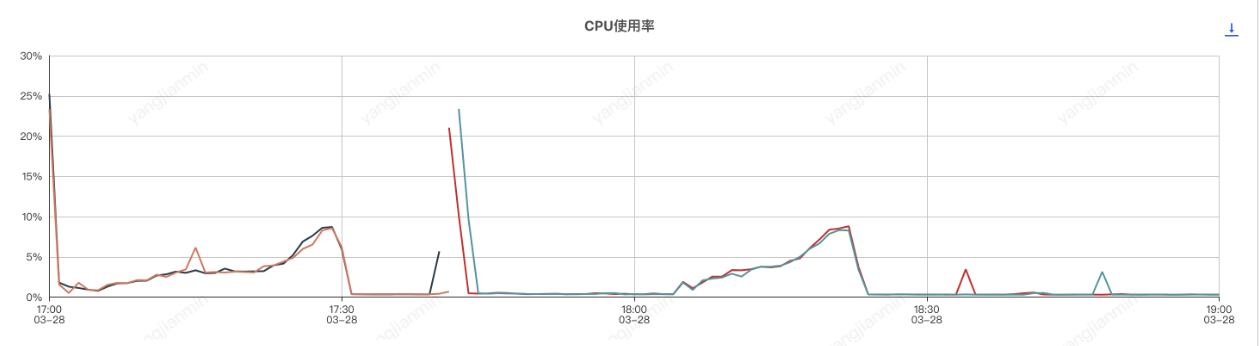
應用機器監控:
壓測分為了兩個階段,分別是元件開啟和元件關閉兩次,前半部分是元件開啟的情況,後半部分是元件關閉的情況
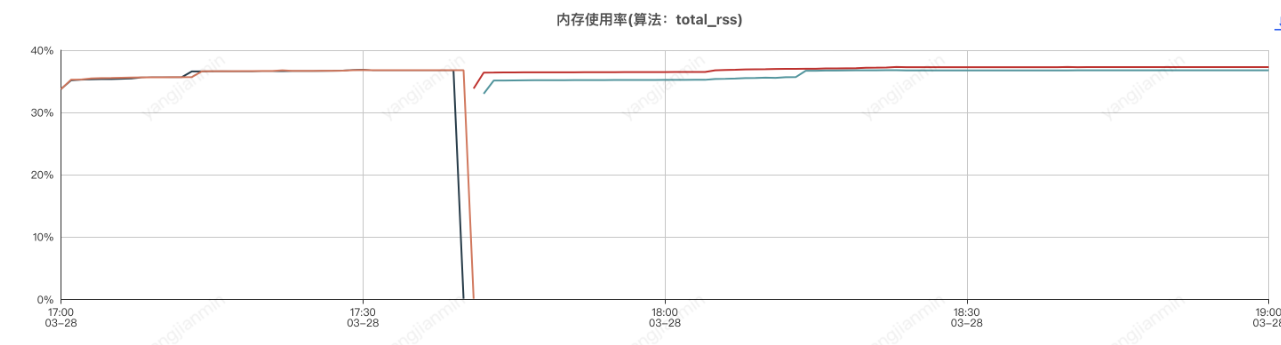
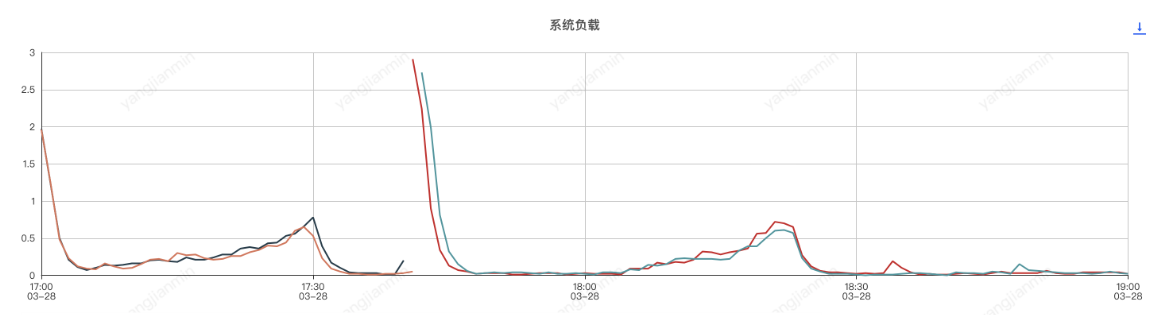
應用程序記憶體分析,和sentinel有關的前三物件是
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.node.metric.MetricNode





com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.CtEntry


com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.context.Context



4.3 壓測結論
使Sentinel元件實現系統服務自動降級或限流,由於sentinel會按照滑動視窗週期性統計資料,因此會佔用一定的機器記憶體,使用時應設定合理的規則,如:合理的統計時長、避免過多的Sentinel資源建立等。
總體來說,使用sentinel元件對應用cpu和記憶體影響不大。