聊一聊 Valgrind 監視非託管記憶體洩露和崩潰
一:背景
1. 講故事
只要是程式總會出現各種莫名其妙的問題,比如:非託管記憶體洩露,程式崩潰,在 Windows 平臺上一般用微軟自家的官方工具 App Verifier 就可以洞察,那問題出在 Linux 上怎麼辦呢?由於 Linux 崇尚自由,需要在各種牛鬼蛇神寫的非官方開源軟體中尋找一個比較靠譜的,比如本篇所說的 Valgrind。
個人感覺 Valgrind 和 App Verifer 定位是差不多的,技術上前者使用 hook 勾點,後者使用模擬cpu,有點像 windbg 的 TTD 偵錯,具體資訊參考:https://valgrind.org/
二:Valgrind 記憶體洞察
1. 安裝
如果你用的是 ubuntu,可以用 apt-get 直接安裝,方便快捷,目前最新的版本是 3.15.0 。
root@skyfly-virtual-machine:/home/skyfly/Desktop# apt-get install valgrind
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
valgrind is already the newest version (1:3.15.0-1ubuntu9.1).
0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 0 to remove and 23 not upgraded.
root@skyfly-virtual-machine:/home/skyfly/Desktop# valgrind --version
valgrind-3.15.0
2. 記憶體洩露洞察
記憶體洩露大多是 new/delete , malloc/free 不匹配造成的,接下來寫一個不匹配的 malloc/free 觀察下。
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
int *p = (int *)malloc(4);
*p = 10;
printf("p=%d", *p);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
這裡使用 vscode 進行編譯,怎麼編譯就不說了,參見上一篇,接下來用 algrind --leak-check=full ./main.out 以模擬的方式把程式跑起來,截圖如下:
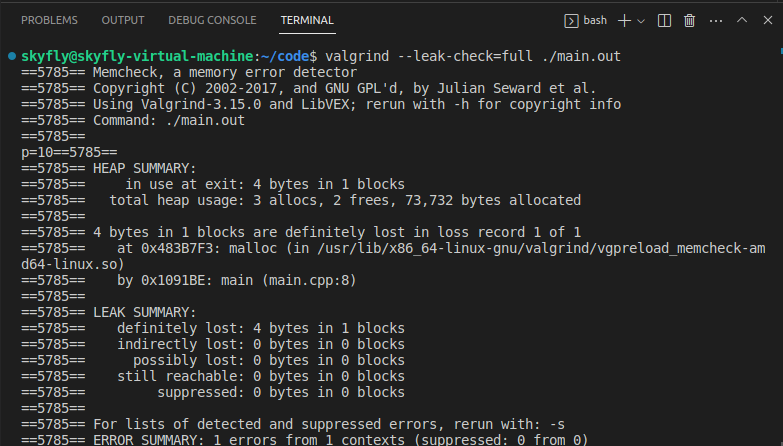
從圖中的 HEAP SUMMARY 區域可以看到,當前有 3 個 malloc,但只有 2 個 free,而且還找到了那個沒有 free 的 malloc,在程式碼的 main.cpp:8 行,即 int *p = (int *)malloc(4); 處。

3. 棧溢位洞察
相信經常寫遞迴的朋友總會遇到這類問題,為了方便演示,我故意實現一個 棧上溢 的例子吧。
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
int num = 10;
int *ptr = #
ptr -= 0x40;
*ptr = 15;
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
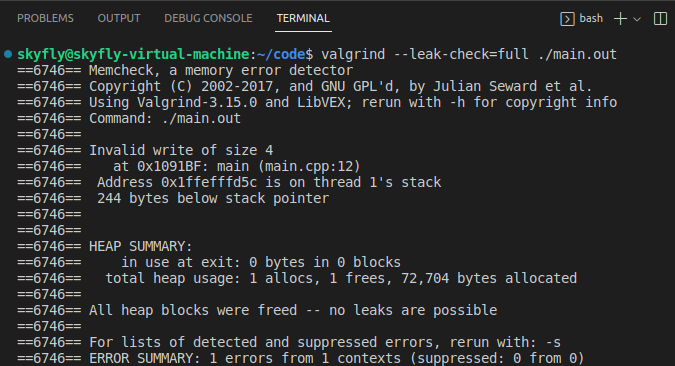
從圖中可以清晰的看到,主執行緒棧上的地址 0x1ffefffd5c 無法寫入,還指出了在 main.cpp:12 行,即 *ptr = 15; 處。
為了方便驗證,這裡用 g++ 偵錯的方式洞察一下。
-exec p num
$5 = 10
-exec x ptr
0x7fffffffde2c: 0xf7fb0e9800007fff
-exec info reg
...
rbp 0x7fffffffdf40 0x7fffffffdf40
rsp 0x7fffffffdf20 0x7fffffffdf20
...
從輸出看,ptr 已經逃出了 rsp ~ rbp 範圍之內,很明顯上溢了,如果用 x 命令觀察的話,可以看到裡面的內容就很隨機,在 windbg 中用以 ??? 來表示的。
-exec x ptr
0x7fffffffde2c: 0xf7fb0e9800007fff
-exec x 0xf7fb0e9800007fff
0xf7fb0e9800007fff: Cannot access memory at address 0xf7fb0e9800007fff
除了觀察 rsp,rbp,還可以看虛擬地址中的 stack 空間。
-exec i proc mapping
process 8327
Mapped address spaces:
Start Addr End Addr Size Offset objfile
...
0x7ffff7ffd000 0x7ffff7ffe000 0x1000 0x2d000 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ld-2.31.so
0x7ffff7ffe000 0x7ffff7fff000 0x1000 0x0
0x7ffffffde000 0x7ffffffff000 0x21000 0x0 [stack]
4. 陣列越界洞察
valgrind 這玩意也有弱雞的時候,比如陣列越界之類的問題它就搞不定,比如下面的程式碼:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
int num[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int num2[10];
num[6] = 15;
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
通過下面的組合程式碼觀察,可以看到目前分配了 0x30 = 0n48 byte 的棧空間,截圖如下:
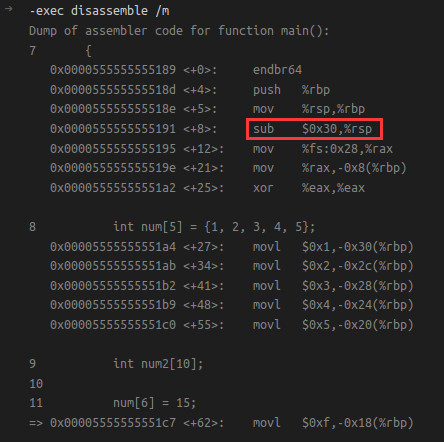
雖然 num[6] 是越界操作,但是在合理的 棧空間 內,這種仿生cpu的方式洞察不出來,App Verifier 這種 hook 的方式是沒有問題的。
接下來用 valgrind 嘗試一下,可以看到果然沒發現任何問題,輸出如下:
skyfly@skyfly-virtual-machine:~/code$ valgrind ./main.out
==10244== Memcheck, a memory error detector
==10244== Copyright (C) 2002-2017, and GNU GPL'd, by Julian Seward et al.
==10244== Using Valgrind-3.15.0 and LibVEX; rerun with -h for copyright info
==10244== Command: ./main.out
==10244==
==10244==
==10244== HEAP SUMMARY:
==10244== in use at exit: 0 bytes in 0 blocks
==10244== total heap usage: 1 allocs, 1 frees, 72,704 bytes allocated
==10244==
==10244== All heap blocks were freed -- no leaks are possible
==10244==
==10244== For lists of detected and suppressed errors, rerun with: -s
==10244== ERROR SUMMARY: 0 errors from 0 contexts (suppressed: 0 from 0)
三:總結
總的來說,Valgrind 在洞察記憶體方面還是非常強大的,但也有它不能觸及到的地方,熟悉它的優點和缺點,全面瞭解對我們偵錯師來說至關重要,希望本篇對你有幫助。