淺談如何使用 github.com/kardianos/service
在實際開發過程中,有時候會遇到如何編寫Go開機自啟服務的需求,在linux中我們可以使用systemd來進行託管,windows下可以通過登入檔來實現,mac下可以通過launchd來實現,上面的方式對於開發者來說,並不是什麼困難的事情,但是對於使用者而言,是並不希望通過這麼複雜的方式來達到開機自啟的功能的。這個時候,作為開發者,就需要使用其他的方式來實現開機自啟的功能,下面講一個Go中,藉助這個庫 github.com/kardianos/service 來簡化如何實現開機自啟功能。
1、github.com/kardianos/service 基礎介紹
1.1 kardianos/service 簡介
我們先來看一看 github.com/kardianos/service 上面的自我介紹:Run go programs as a service on major platforms.
如何理解上面這句話呢,上面這句話翻譯出來的意思是:"在主要平臺上將Go程式作為服務執行"。
這意味著我們可以將Go編寫的程式以服務的形式在主要作業系統上執行,例如Windows、Linux、macOS等。這意味著程式可以在後臺持續執行,而不需要使用者手動啟動或停止它們。這種方式可以提高程式的可靠性和穩定性,同時也方便了程式的管理和監控。
那該如何理解服務呢?
服務(Service)是指在計算機系統中,為使用者或其他程式提供某種功能的程式或程序。服務通常在後臺執行,可以長時間執行,不需要使用者互動,可以自動啟動和停止。服務可以提供各種功能,如網路服務、資料庫服務、檔案共用服務等。在作業系統中,服務通常以服務程序的形式執行,可以通過系統管理工具進行管理和設定。
有了上面的瞭解過後,再來看看官方自己的描述。service will install / un-install, start / stop, and run a program as a service (daemon). Currently supports Windows XP+, Linux/(systemd | Upstart | SysV), and OSX/Launchd. 如何理解上面這句話呢,我說說自己的理解。
我們可以將編寫好的程式碼打包成二進位制檔案後,通過
二進位制檔名 + install / un-install, start / stop來執行我們的服務,程式將作為服務(守護行程)執行。目前支援Windows XP+、Linux/(systemd|Upstart|SysV)和OSX/Launchd。
Windows controls services by setting up callbacks that is non-trivial. This is very different then other systems. This package provides the same API despite the substantial differences. It also can be used to detect how a program is called, from an interactive terminal or from a service manager. 下面是我的理解:
Windows 通過設定回撥來控制服務,這與其他系統非常不同。這個包提供了相同的API,儘管存在很大差異。它還可以用於檢測程式是從互動式終端還是從服務管理器呼叫的。
看到這裡的時候,我其他不太理解最後一句話,什麼叫從
服務管理器呼叫。將在 2.2 章節中介紹。
1.2 kardianos/service 安裝
安裝 github.com/kardianos/service 的方式和其他方式一樣。
go get github.com/kardianos/service
指定版本方式
go get github.com/kardianos/[email protected]
2、kardianos/service 使用方式
以下介紹都是基於 github.com/kardianos/[email protected] 進行講解的。
2.1 kardianos/service 簡單的使用
我們先來看一個簡單的例子,程式碼如下:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/kardianos/service"
"os"
)
type SystemService struct {}
func (ss *SystemService) Start(s service.Service) error {
fmt.Println("coming Start.......")
go ss.run()
return nil
}
func (ss *SystemService) run() {
fmt.Println("coming run.......")
}
func (ss *SystemService) Stop(s service.Service) error {
fmt.Println("coming Stop.......")
return nil
}
func main() {
fmt.Println("service.Interactive()---->", service.Interactive())
svcConfig := &service.Config{
Name: "custom-service",
DisplayName: "custom service",
Description: "this is github.com/kardianos/service test case",
}
ss := &SystemService{}
s, err := service.New(ss, svcConfig)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("service New failed, err: %v\n", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
if len(os.Args) > 1 {
err = service.Control(s, os.Args[1])
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("service Control 111 failed, err: %v\n", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
return
}
// 預設 執行 Run
err = s.Run()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("service Control 222 failed, err: %v\n", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
}
通過go run main.go得到如下結果,注意:程式並不會終止,而是阻塞住了。
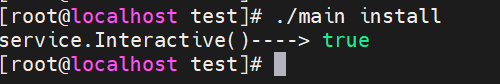
service.Interactive()----> true
coming Start.......
coming run.......
實際上,kardianos/service為我們提供了下面的引數使用,我們可以通過go build -o main main.go編譯得到二進位制檔案,然後使用下面的命令來執行服務。
# 生成開機自啟服務所需要的檔案,檔案位置根據作業系統的不同而不用,linux在 /etc/systemd/system 或者 /lib/systemd/system 下
./main install
# 刪除上面生成的檔案
./main uninstall
# 開啟服務
./main start
# 重啟服務
./main restart
# 停止服務
./main stop
2.2 kardianos/service 如何做開機自啟服務
接下來以 Linux 為例,進行講解。其他系統大家可自行嘗試。
具體的步驟如下:
1、第一步是編寫程式碼,編寫完成後,編譯成二進位制檔案。
程式碼就以 2.1 中的為例。首先編譯成二進位制檔案。
go build -o main main.go
2、執行 可執行檔案。
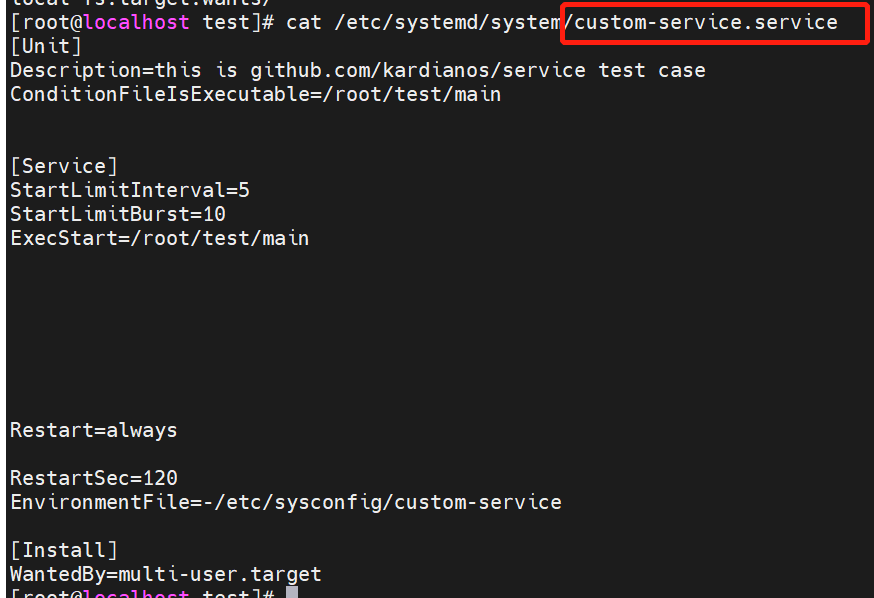
# 這將在 /etc/systemd/system 或者 /lib/systemd/system 中生成 custom-service.service 檔案
# 我這裡測試的時候是在 /etc/systemd/system 中生成的
./main install
看到這裡,用過systemd的朋友應該可以猜到 kardianos/service 背後是通過什麼來實現開機自啟的。就是通過
systemd來管理的。
3、將 custom-service.service 服務設定為開機自啟.
執行下面命令將我們編寫的程式設定為開機自啟服務。
# 設定服務開機自啟動
systemctl enable test-service.service
# 啟動
systemctl start test-service.service
下面是systemctl常用的命令。
# 啟動
systemctl start test-service.service
# 停止
systemctl stop test-service.service
# 設定服務開機自啟動
systemctl enable test-service.service
# 查詢是否自啟動服務
systemctl is-enabled test-service.service
# 取消伺服器開機自啟動
systemctl disable test-service.service
# 列出正在執行的服務
systemctl list-units --type=service
接下來我們看看服務管理器是什麼意思?
1、./main install
2、檢視custom-service.service檔案
3、執行systemctl start custom-service.service後,檢視服務執行過程
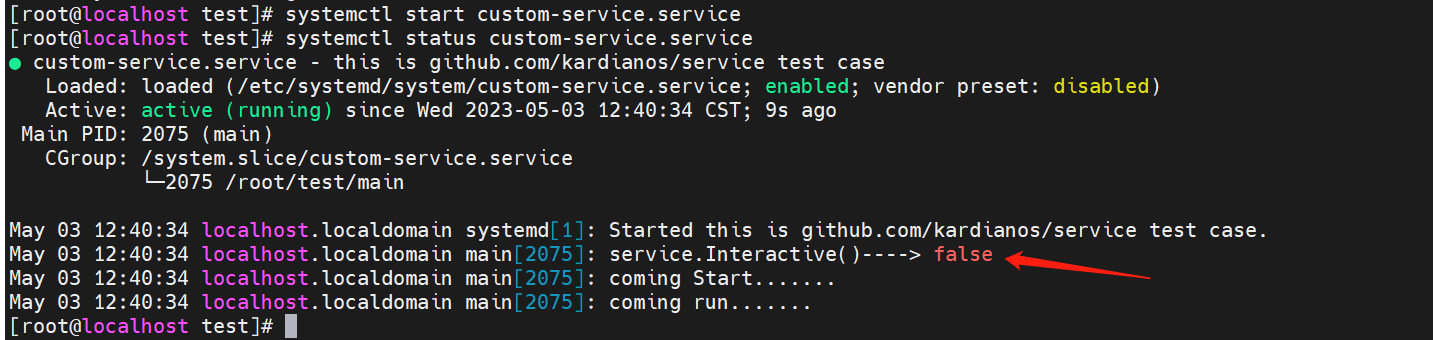
這裡就是上面
服務管理器的作用,也就是說,如何服務是手動執行的,那麼service.Interactive()返回 true,比如:./main start。如何是系統管理器執行的,則返回 false,比如:systemctl start custom-service.service。
2.3 結合 cli 使用
通過上面的例子,我們大概知道了如何使用 github.com/kardianos/service 。實際使用中,一般的服務都可以通過-h來檢視幫助檔案,但是我們我們通過./main -h會報錯,所以需要完善下程式碼,使我們的程式更容易使用。下面,我們一起看看,藉助 github.com/urfave/cli/v2 來完成上面的需求。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/kardianos/service"
"github.com/urfave/cli/v2"
"os"
)
type SystemService struct {}
func (ss *SystemService) Start(s service.Service) error {
fmt.Println("coming Start.......")
go ss.run()
return nil
}
func (ss *SystemService) run() {
fmt.Println("coming run.......")
}
func (ss *SystemService) Stop(s service.Service) error {
fmt.Println("coming Stop.......")
return nil
}
func main() {
app := cli.NewApp()
app.Name = "custom-service"
app.Usage = "how to use custom service"
app.Commands = []*cli.Command{
{
Name: "install",
Action: ctrlAction,
},
{
Name: "uninstall",
Action: ctrlAction,
},
{
Name: "start",
Action: ctrlAction,
},
{
Name: "restart",
Action: ctrlAction,
},
{
Name: "stop",
Action: ctrlAction,
},
}
app.Flags = []cli.Flag{
&cli.StringFlag{
Name: "install",
Value: "install",
Usage: "Write the files required for startup",
},
&cli.StringFlag{
Name: "uninstall",
Value: "uninstall",
Usage: "Delete startup files",
},
&cli.StringFlag{
Name: "start",
Value: "start",
Usage: "start the service",
},
&cli.StringFlag{
Name: "stop",
Value: "stop",
Usage: "stop the service",
},
&cli.StringFlag{
Name: "restart",
Value: "restart",
Usage: "restart the service",
},
}
app.Action = startAction
app.Run(os.Args)
}
func createSystemService() (service.Service, error) {
fmt.Println("service.Interactive()---->", service.Interactive())
svcConfig := &service.Config{
Name: "custom-service",
DisplayName: "custom service",
Description: "this is github.com/kardianos/service test case",
}
ss := &SystemService{}
s, err := service.New(ss, svcConfig)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("service New failed, err: %v\n", err)
}
return s, nil
}
func ctrlAction(c *cli.Context) error {
s, err := createSystemService()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("createSystemService failed, err: %v\n", err)
return err
}
err = service.Control(s, c.Command.Name)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("service Run 222 failed, err: %v\n", err)
return err
}
return nil
}
func startAction(c *cli.Context) error {
s, err := createSystemService()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("createSystemService failed, err: %v\n", err)
return err
}
// 預設 執行 Run
err = s.Run()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("service Run failed, err: %v\n", err)
return err
}
return nil
}
大家可以根據自己的需求進行開發,這裡只是講一個簡單的案例而已。
編譯:
go build -o main main.go
執行:
./main -h
NAME:
custom-service - how to use custom service
USAGE:
custom-service [global options] command [command options] [arguments...]
COMMANDS:
install
uninstall
start
restart
stop
help, h Shows a list of commands or help for one command
GLOBAL OPTIONS:
--install value Write the files required for startup (default: "install")
--uninstall value Delete startup files (default: "uninstall")
--start value start the service (default: "start")
--stop value stop the service (default: "stop")
--restart value restart the service (default: "restart")
--help, -h show help
3、淺談 service 的執行過程
這裡以 mac 為例,通過 goland 來檢視呼叫的鏈路方便些。
使用 github.com/kardianos/service 的步驟大概是這樣的:
1、定義 service.Config
2、通過 service.New 建立 service
3、通過 service.Control 來執行上面 生成好的 service。
第一步沒啥好說的,注意 service.Config 中的 Name 是必須的,且生成的開機自啟檔名就是以他命名的。
重點看看第二步,service.New原始碼入下:
// New creates a new service based on a service interface and configuration.
func New(i Interface, c *Config) (Service, error) {
//這就是為啥 Name 是必填的原因
if len(c.Name) == 0 {
return nil, ErrNameFieldRequired
}
// 注意看這裡,system 在使用到時候就已經初始化了,但是我們使用的時候,並沒有做初始化 system 的動作。
// 那麼什麼時候初始化的 system 呢?
// 這個時候就會想到 init() 這個函數,這個函數在 import 時就會自動執行。
if system == nil {
return nil, ErrNoServiceSystemDetected
}
return system.New(i, c)
}
System 介面如下:
var (
system System
systemRegistry []System
)
// System represents the service manager that is available.
type System interface {
// String returns a description of the system.
String() string
// Detect returns true if the system is available to use.
Detect() bool
// Interactive returns false if running under the system service manager
// and true otherwise.
Interactive() bool
// New creates a new service for this system.
New(i Interface, c *Config) (Service, error)
}
以 mac 的系統為例, 講講system.New(i, c)
type darwinSystem struct{}
func (darwinSystem) String() string {
return version
}
func (darwinSystem) Detect() bool {
return true
}
func (darwinSystem) Interactive() bool {
return interactive
}
func (darwinSystem) New(i Interface, c *Config) (Service, error) {
s := &darwinLaunchdService{
i: i,
Config: c,
userService: c.Option.bool(optionUserService, optionUserServiceDefault),
}
return s, nil
}
func init() {
//這裡就是給 system 變數賦值
//這裡賦值有點不同,是在編譯階段由編譯器根據系統的不同,初始化不同的 結構體。
//這個我也不敢確定,希望知道的朋友不吝賜教,感謝感謝!
ChooseSystem(darwinSystem{})
}
// ChooseSystem chooses a system from the given system services.
// SystemServices are considered in the order they are suggested.
// Calling this may change what Interactive and Platform return.
func ChooseSystem(a ...System) {
systemRegistry = a
system = newSystem()
}
darwinLaunchdService實現了 Service interface 定義的方法。這裡就不復制原始碼了,有興趣可以看看原始碼。
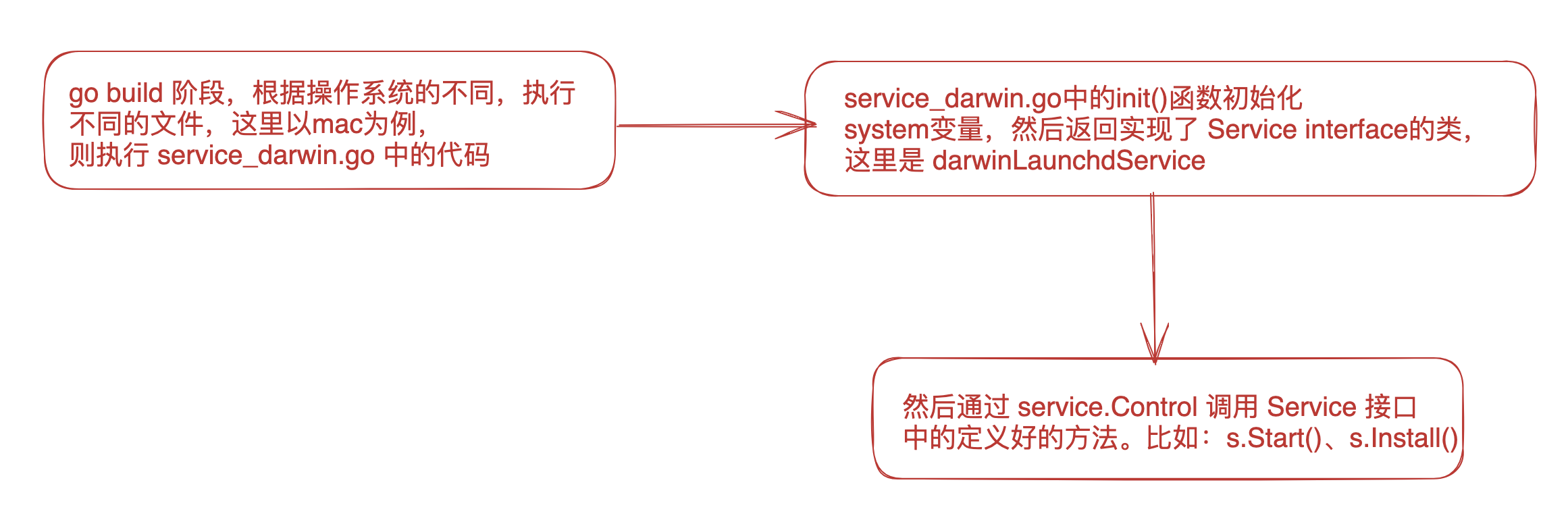
以上就是我對 github.com/kardianos/service 的理解,有不對的地方,請不吝賜教。謝謝!