深入瞭解vuex的實現原理
當面試被問vuex的實現原理,你要怎麼回答?下面本篇文章就來帶大家深入瞭解一下vuex的實現原理,希望對大家有所幫助!

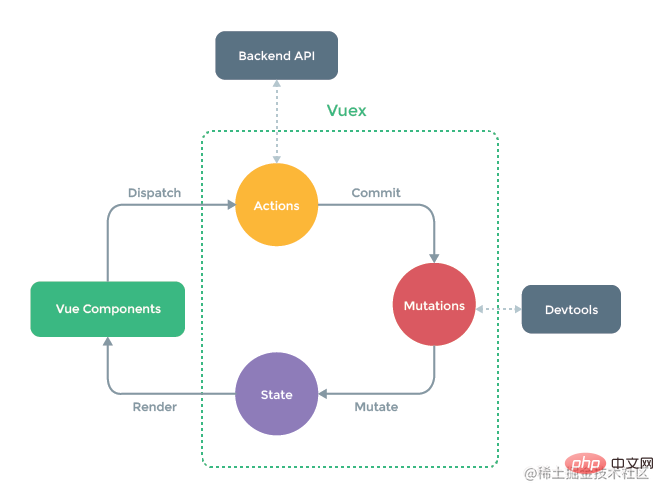
關於vuex就不再贅述,簡單回顧一下:當應用碰到多個元件共用狀態時,簡單的單向資料流很容易被破壞:第一,多個檢視依賴於同一狀態;第二,來自不同檢視的行為需要變更同一狀態。若解決前者使用傳參的方式,則不適用於多層巢狀的元件以及兄弟元件;若解決後者使用父子元件直接參照或事件變更和同步狀態的多份拷貝,則不利於程式碼維護。
所以,最好的辦法是:把元件的共用狀態抽取出,以一個全域性單例模式管理!這也正是vuex背後的基本思想。
【相關推薦:、】
所以,vuex的大致框架如下:
class Store {
constructor() {
// state
// getters
// mutations
// actions
}
// commit
// dipatch
}登入後複製接下來,就寫寫看。
一、建立vue專案
vue create vue2-vuex//建立vue2專案
yarn add vuex@next --save//安裝vuex
yarn serve//啟動專案
登入後複製二、實現原理
1、State
(1)使用
//store.js
// 倉庫
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import extra from './extra.js'
Vue.use(Vuex) //引入vuex的方式,說明Store需要install方法
export default new Vuex.Store({
// 倉庫資料來源
state: {
count: 1,
dowhat: 'addCount'
},
}登入後複製//app.vue
<template>
<div class="testState">
<p>{{mycount}}</p>
<p>{{dowhat}}:{{count}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
import {
mapState
} from 'vuex'
// 推薦方式
computed: mapState()({
mycount: state => state.count
}),
// 推薦方式的簡寫方式
computed: {
// 解構的是getters
...mapState(['count', 'dowhat'])
},
}
</script>登入後複製(2)注意
由於 Vuex 的狀態儲存是響應式的,從 store 範例中讀取狀態最簡單的方法就是在計算屬性 中返回某個狀態,這種模式導致元件依賴全域性狀態單例。在模組化的構建系統中,在每個需要使用 state 的元件中需要頻繁地匯入,並且在測試元件時需要模擬狀態
Vuex 通過 store 選項,提供了一種機制將狀態從根元件「注入」到每一個子元件中(需呼叫 Vue.use(Vuex))
(3)實現
所以除了Store內部的五大屬性以外,還需要考慮外掛的一個install方法,所以大致框架如下:
class Store {
constructor() {
// state
// getters
// mutations
// actions
//modules
}
// commit
// dipatch
}
let Vuex = {
Store,
Install
}
export default Vuex登入後複製所以,接下來就可以具體實現了,
class Store {
constructor(options) {
// state
this.state = options.state
}
}
let install = function(_Vue) {
_Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate() { //在元件建立之前自動呼叫,每個元件都有這個勾點
if (this.$options && this.$options.store) { //this.$options讀取根元件
this.$store = this.$options.store
} else {
this.$store = this.$parent && this.$parent.$store
}
}
})
}登入後複製然而,上述的state的實現有一個缺點:當改變資料的時候,state的資料不能動態的渲染。所以如何把state裡的資料成為響應式成為關鍵問題?實際上,類似vue裡的data,也可以通過這種方式讓其成為響應式。那麼就得從install方法中傳入Vue,所以改變後:
let Vue=null
class Store {
constructor(options) {
// state
this.vm = new _Vue({
data: {
state: options.state//data中的資料才是響應式
}
})
}
get state() {
return this.vm.state
}
}
let install = function(_Vue) {//用於Vue.use(plugin)
Vue=_Vue
_Vue.mixin({
onBeforeCreate() { //在元件建立之前自動呼叫,每個元件都有這個勾點
if (this.$options && this.$options.store) { //this.$options讀取根元件
this.$store = this.$options.store
} else {
this.$store = this.$parent && this.$parent.$store
}
}
})
}登入後複製2、getters
(1)使用
//store.js
export default new Vuex.Store({
// 計算屬性
getters: {
// 這裡的函數不需要呼叫,可以直接使用,官方預設前面有get
getCount(state) {//接受 state 作為其第一個引數
return state.count * 100;
}
},
}登入後複製(2)注意
有時候我們需要從 store 中的 state 中派生出一些狀態(比如增加,刪除,過濾等等),Vuex 允許我們在 store 中定義「getter」(可以認為是 store 的計算屬性)。就像計算屬性一樣,getter 的返回值會根據它的依賴被快取起來,且只有當它的依賴值發生了改變才會被重新計算,Getter 接受 state 作為其第一個引數,getter 在通過方法存取時,每次都會去進行呼叫,而不會快取結果
(3)實現
// getters
let getters = options.getters || {}
this.getters = {}
Object.keys(getters).forEach(getterName => {
Object.defineProperty(this.getters, getterName, {
get: () => {
return getters[getterName](this.state)
}
})
})登入後複製3、mutations
(1)使用
//store.js
export default new Vuex.Store({
// 相當於methods
mutations: {
// mutations內部的函數,天生具備一個形參
add(state, n) {
state.count += n;
},
decrease(state, n) {
state.count -= n;
}
},
}登入後複製methods: {
submit() {
console.log('success');
},
// 解構倉庫mutations裡面的方法,要啥解構啥
...mapMutations(['add', 'decrease']),
// this.$store.commit('add'),
...mapActions(['addAction', 'decreaseAction']),
// this.addAction()呼叫actions裡面的方法
// this.$store.dispatch('add'),
}登入後複製(2)注意
更改 Vuex 的 store 中的狀態的唯一方法是提交 mutation。Vuex 中的 mutation 類似於事件:每個 mutation 都有一個字串的 事件型別 (type) 和 一個 回撥函數 (handler) 。這個回撥函數就是進行狀態更改的地方,並且它會接受 state 作為第一個引數,不能直接呼叫一個 mutation handler。這個選項更像是事件註冊:「當觸發一個型別為 increment 的 mutation 時,呼叫此函數。」要喚醒一個 mutation handler,你需要以相應的 type 呼叫 store.commit 方法
可以向 store.commit 傳入額外的引數,即 mutation 的 載荷(payload) ,在大多數情況下,載荷應該是一個物件,這樣可以包含多個欄位並且記錄的 mutation 會更易讀
(3)實現
// mutations
let mutations = options.mutations || {}
this.mutations = {}
Object.keys(mutations).forEach(mutationName => {
this.mutations[mutationName] = (arg) => {//保證多個(第二個)引數的傳入
mutations[mutationName](this.state, arg)
}
})
commit = (method, arg) => {//使用箭頭函數改變被呼叫的this的指向
// console.log(this);
this.mutations[method](arg)
}登入後複製4、actions
(1)使用
//store.js
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions: {
addAction(context) {
// 在這裡呼叫add方法
context.commit('add', 10);
},
decreaseAction({
commit
}) {
commit('decreaseAction', 5)
}
},
}登入後複製(2)注意
- Action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接變更狀態。
- Action 可以包含任意非同步操作
- Action 函數接受一個與 store 範例具有相同方法和屬性的 context 物件
- Action 通過
store.dispatch方法觸發 - Action 通常是非同步的,
store.dispatch可以處理被觸發的 action 的處理常式返回的 Promise,並且store.dispatch仍舊返回 Promise - 一個
store.dispatch在不同模組中可以觸發多個 action 函數。在這種情況下,只有當所有觸發函數完成後,返回的 Promise 才會執行
(3)實現
// actions
let actions = options.actions || {}
this.actions = {}
Object.keys(actions).forEach(actionName => {
this.actions[actionName] = (arg) => {
actions[actionName](this, arg)
}
})
dispatch=(method, arg) =>{
this.actions[method](arg)
}登入後複製5、modules
(1)使用
// actions
let actions = options.actions || {}
this.actions = {}
Object.keys(actions).forEach(actionName => {
this.actions[actionName] = (arg) => {
actions[actionName](this, arg)
}
})
dispatch=(method, arg) =>{
this.actions[method](arg)
}登入後複製 //store.js
modules: {
extra: extra
}登入後複製(2)注意
- 由於使用單一狀態樹,應用的所有狀態會集中到一個比較大的物件。當應用變得非常複雜時,store 物件就有可能變得相當臃腫,Vuex 允許我們將 store 分割成模組(module) 。每個模組擁有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是巢狀子模組——從上至下進行同樣方式的分割
- 對於模組內部的 mutation 和 getter,接收的第一個引數是模組的區域性狀態物件
- 對於模組內部的 action,區域性狀態通過
context.state暴露出來,根節點狀態則為context.rootState 對於模組內部的 getter,根節點狀態(rootState)會作為第三個引數暴露出來
三、整體程式碼
let Vue = null//全域性的_Vue
class Store {
constructor (options) {
// state
//this.state = options.state 寫法不完美,當改變資料的時候,不能動態的渲染,所以需要把data中的資料做成響應式的
this.vm = new _Vue({
data: {
state: options.state//data中的資料才是響應式
}
})
// getters
let getters = options.getters || {}
this.getters = {}
Object.keys(getters).forEach(getterName => {
Object.defineProperty(this.getters, getterName, {
get: () => {
return getters[getterName](this.state)
}
})
})
// mutations
let mutations = options.mutations || {}
this.mutations = {}
Object.keys(mutations).forEach(mutationName => {
this.mutations[mutationName] = (arg) => {//保證多個(第二個)引數的傳入
mutations[mutationName](this.state, arg)
}
})
// actions
let actions = options.actions || {}
this.actions = {}
Object.keys(actions).forEach(actionName => {
this.actions[actionName] = (arg) => {
actions[actionName](this, arg)
}
})
}
dispatch=(method, arg) =>{
this.actions[method](arg)
}
commit = (method, arg) => {
// console.log(this);
this.mutations[method](arg)
}
get state() {
return this.vm.state
}
}
let install = function(_Vue) {
Vue = _Vue
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate() {//在元件建立之前自動呼叫,每個元件都有這個勾點
if (this.$options && this.$options.store) { // this.$options讀取到根元件
this.$store = this.$options.store
} else { // //如果不是根元件的話,也把$store掛到上面,因為是樹狀元件
this.$store = this.$parent && this.$parent.$store
}
}
})
}
let Vuex = {
Store,
install
}
export default Vuex登入後複製(學習視訊分享:、)
以上就是深入瞭解vuex的實現原理的詳細內容,更多請關注TW511.COM其它相關文章!