LeetCode 周賽 336,多少人直接 CV?
本文已收錄到 AndroidFamily,技術和職場問題,請關注公眾號 [彭旭銳] 提問。
大家好,我是小彭。
今天早上是 LeetCode 第 336 場周賽,你參加了嗎?這場周賽整體質量比較高,但是最後一題是老題,CV 能過。但是輸入資料範圍被降低了,這操作也是沒誰了。

2587. 統計範圍內的母音字串數(Easy)
題目地址
https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-the-number-of-vowel-strings-in-range/
題目描述
給你一個下標從 0 開始的字串陣列 words 和兩個整數:left 和 right 。
如果字串以母音字母開頭並以母音字母結尾,那麼該字串就是一個 母音字串 ,其中母音字母是 'a'、'e'、'i'、'o'、'u' 。
返回 words[i] 是母音字串的數目,其中 i 在閉區間 [left, right] 內。

題解(模擬)
簡單模擬題。
class Solution {
fun vowelStrings(words: Array<String>, left: Int, right: Int): Int {
val set = hashSetOf('a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u')
var count = 0
for (index in left..right) {
val word = words[index]
if (set.contains(word[0]) && set.contains(word[word.length - 1])) count++
}
return count
}
}
複雜度分析:
- 時間複雜度:$O(n)$
- 空間複雜度:$O(1)$
2588. 重排陣列以得到最大字首分數(Medium)
題目地址
https://leetcode.cn/problems/rearrange-array-to-maximize-prefix-score/
題目描述
給你一個下標從 0 開始的整數陣列 nums 。你可以將 nums 中的元素按 任意順序 重排(包括給定順序)。
令 prefix 為一個陣列,它包含了 nums 重新排列後的字首和。換句話說,prefix[i] 是 nums 重新排列後下標從 0 到 i 的元素之和。nums 的 分數 是 prefix 陣列中正整數的個數。
返回可以得到的最大分數。

題解(貪心)
貪心思路:負數會降低字首和,為了延緩字首和變小的速度,正權值應該放在儘可能前的位置,負權值放在儘可能後的位置,即對陣列降序排序。
class Solution {
fun maxScore(nums: IntArray): Int {
// 3 2 1 0 -1 -3 -3
// 3 5 6 6 5 2 -1
nums.sortDescending()
var preSum = 0L
for (index in nums.indices) {
preSum += nums[index]
if (preSum <= 0L) return index
}
return nums.size
}
}
複雜度分析:
- 時間複雜度:$O(nlgn + n)$ 排序加線性遍歷;
- 空間複雜度:$O(lgn)$ 排序遞迴棧空間。
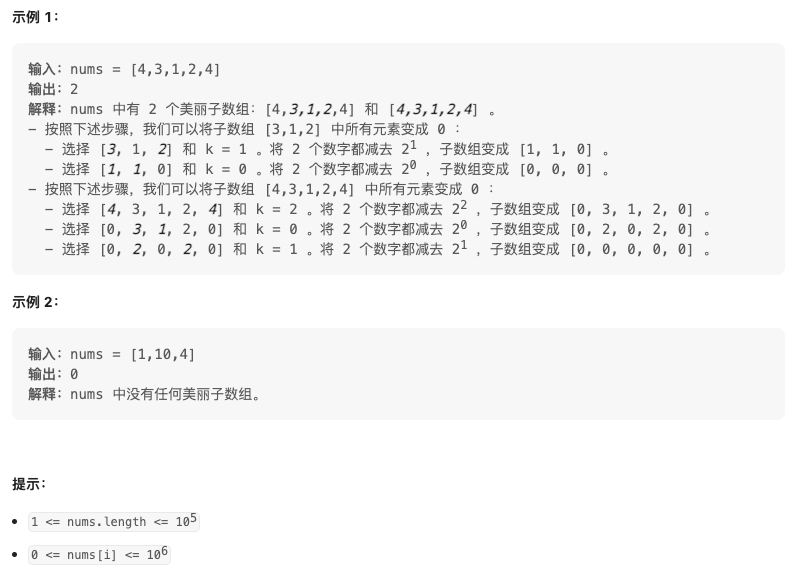
2589. 統計美麗子陣列數目(Medium)
題目地址
https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-the-number-of-beautiful-subarrays/
題目描述
給你一個下標從 0 開始的整數陣列nums 。每次操作中,你可以:
- 選擇兩個滿足
0 <= i, j < nums.length的不同下標i和j。 - 選擇一個非負整數
k,滿足nums[i]和nums[j]在二進位制下的第k位(下標編號從 0 開始)是1。 - 將
nums[i]和nums[j]都減去2k。
如果一個子陣列內執行上述操作若干次後,該子陣列可以變成一個全為 0 的陣列,那麼我們稱它是一個 美麗 的子陣列。
請你返回陣列 nums 中 美麗子陣列 的數目。
子陣列是一個陣列中一段連續 非空 的元素序列。
題解一(滑動視窗)
分析題目操作:當兩個數在某一位都是 1 時,可以執行一次消除操作。因此,在滿足題目要去的子陣列中,所有位上 1 出現的次數要麼是 0,要麼是大於 0 的偶數,符合互斥或的性質。於是,我們可以將題目轉換為求 「互斥或值為 0 的子陣列」 個數,與以下題目類似:
樸素的解法我們考慮列舉所有子陣列:
class Solution {
fun beautifulSubarrays(nums: IntArray): Long {
val n = nums.size
var count = 0L
for (left in 0 until n) {
var xorSum = 0
for (right in left until n) {
xorSum = xorSum xor nums[right]
if (xorSum == 0) count++
}
}
return count
}
}
複雜度分析:
- 時間複雜度:$O(n^2)$ 其中 $n$ 是 $nums$ 陣列的長度,在這道題中將超出時間限制;
- 空間複雜度:$O(1)$。
題解二(字首和 + 雜湊表)
「和為 k 的子陣列」 有 $O(n)$ 的解法:
class Solution {
fun beautifulSubarrays(nums: IntArray): Long {
val n = nums.size
var count = 0L
// xorSun - index
val xorSumMap = HashMap<Int, Int>().apply {
this[0] = 1
}
var preXorSum = 0
for (num in nums) {
preXorSum = preXorSum xor num
if (xorSumMap.containsKey(preXorSum)) {
count += xorSumMap[preXorSum]!!
}
xorSumMap[preXorSum] = xorSumMap.getOrDefault(preXorSum, 0) + 1
}
return count
}
}
複雜度分析:
- 時間複雜度:$O(n)$ 線性遍歷;
- 空間複雜度:$O(n)$ 雜湊表空間。
2590. 完成所有任務的最少時間(Hard)
題目地址
https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-time-to-complete-all-tasks/
題目描述
你有一臺電腦,它可以 同時 執行無數個任務。給你一個二維整數陣列 tasks ,其中 tasks[i] = [starti, endi, durationi] 表示第 i 個任務需要在 閉區間 時間段 [starti, endi] 內執行 durationi 個整數時間點(但不需要連續)。
當電腦需要執行任務時,你可以開啟電腦,如果空閒時,你可以將電腦關閉。
請你返回完成所有任務的情況下,電腦最少需要執行多少秒。

題解一(貪心)
這道題其實是 LCP 原題:LCP 32. 批次處理任務
區間任務問題一般有按照 「開始時間」 排序或 「結束時間」 排序兩種排序方法:
- 按照開始時間排序: 對於任務 task,我們無法判斷應該優選選擇較早點時間還是較晚的時間。
- 按照結束時間排序: 對於任務 task,如果優先選擇越晚的開始時間(推遲開機),那麼越有可能被後續任務覆蓋。可以用反證法證明:假設推遲到最晚時間 $task_{end}$ 不是最優解,即存在非最晚時間 $task_{end - 1}$ 是最優解,那麼對於下一個任務來說,如果它的開始時間晚於 $task_{end - 1}$,那麼它就錯過了一次開機時間,說明 $task_{end - 1}$ 不可能是最優解。
另外,由於任務的開機時間允許不連續,所以我們需要用一個額外的陣列儲存開機時間。在處理每個任務時,我們先講已開始時間去掉,再將剩下的時間安排在儘可能晚的時間。
class Solution {
fun findMinimumTime(tasks: Array<IntArray>): Int {
// 按照結束時間排序
Arrays.sort(tasks) { e1, e2 ->
e1[1] - e2[1]
}
val used = BooleanArray(2001)
var time = 0
for (task in tasks) {
var count = task[2]
// 消除已開機時間
for (index in task[0]..task[1]) {
if (used[index]) count--
}
if (count <= 0) continue
time += count
// 推遲最晚開機時間
for (index in task[1] downTo task[0]) {
if (used[index]) continue
used[index] = true
if (--count == 0) break
}
}
return time
}
}
複雜度分析:
- 時間複雜度:$O(nlgn + nm)$ 其中 n 是任務個數,m 是任務的平均時間;
- 空間複雜度:$O(lgn + U)$ 其中 $U$ 是資料範圍 2000,排序遞迴棧空間 + $used$ 陣列空間。
題解二(樸素線段樹)
回顧題解一中的 2個關鍵操作:
- 1、消除已開機時間: 計算 [start, end] 之間為 true 的時間點個數(等價於區間和);
- 2、推遲最晚開機時間: 逆序將 [start, end] 中最後 count 個時間點標記為 true(等價於區間更新)。
因此,我們發現題目可能存線上段樹、樹狀陣列之類優化手段:類似的區間求和問題,我們先回顧一下解決方案:
- 1、靜態陣列求區間和:「字首和陣列」、「樹狀陣列」、「線段樹」
- 2、頻繁單點更新,求區間和:「樹狀陣列」、「線段樹」
- 3、頻繁區間更新,求具體位置:「差分陣列」
- 4、頻繁區間更新,求區間和:「線段樹 + 懶更新」
這道題涉及 「區間更新」 和 「區間求和」,所以屬於線段樹的覆蓋範圍。相對於在函數中重複傳遞節點所代表的區間範圍(例如 update(i: int, l: int, r: int, L: int, R: int)),使用 Node 節點記錄更為方便。
class Solution {
fun findMinimumTime(tasks: Array<IntArray>): Int {
// 按照結束時間排序
Arrays.sort(tasks) { e1, e2 ->
e1[1] - e2[1]
}
// 線段樹
val tree = SegmentTree(2001)
for (task in tasks) {
// 消除已開機時間
val count = task[2] - tree.query(task[0], task[1])
if (count <= 0) continue
// 推遲最晚開機時間
tree.update(task[0], task[1], count)
}
// 根節點即為所有開機時間
return tree.query(1, 2000)
}
private class SegmentTree(private val n: Int) {
// 線段樹節點(區間範圍與區間值)
private class Node(val left: Int, val right: Int, var value: Int)
// 線段樹陣列
private val tree = Array<Node?>(n * 4) { null } as Array<Node>
// 左子節點索引
private val Int.left get() = 2 * this + 1
// 右子節點索引
private val Int.right get() = 2 * this + 2
init {
// 建樹
buildNode(0, 0, n - 1)
}
private fun buildNode(index: Int, left: Int, right: Int) {
// 葉子節點
if (left == right) {
tree[index] = Node(left, right, 0)
return
}
val mid = (left + right) ushr 1
// 構建左子節點
buildNode(index.left, left, mid)
// 構建右子節點
buildNode(index.right, mid + 1, right)
// 合併左右子節點
tree[index] = Node(left, right, tree[index.left].value + tree[index.right].value)
}
// 開機(推遲到最晚時間)
fun update(left: Int, right: Int, count: Int) {
update(0, left, right, count)
}
// return:有效修改個數
private fun update(index: Int, left: Int, right: Int, count: Int): Int {
// 1、當前節點不處於區間內
if (tree[index].left > right || tree[index].right < left) return 0
// 2、葉子結點
if (tree[index].left == tree[index].right) {
// 開機
if (0 == tree[index].value) {
tree[index].value = 1
return 1
} else {
return 0
}
}
// 3、更新右子樹(貪心思路:推遲開機)
var realUpdate = update(index.right, left, right, count)
if (count - realUpdate > 0) {
// 4、更新左子樹
realUpdate += update(index.left, left, right, count - realUpdate)
}
// 5、合併左右子節點
tree[index].value = tree[index.left].value + tree[index.right].value
return realUpdate
}
// 查詢
fun query(left: Int, right: Int): Int {
return query(0, left, right)
}
private fun query(index: Int, left: Int, right: Int): Int {
// 1、當前節點不處於區間範圍內
if (tree[index].left > right || tree[index].right < left) return 0
// 2、當前節點完全處於區間範圍內
if (tree[index].left >= left && tree[index].right <= right) return tree[index].value
// 3、合併左右子節點
return query(index.left, left, right) + query(index.right, left, right)
}
}
}
複雜度分析:
- 時間複雜度:$O(nlgn + U + nU + nlgU)$ 線段樹單次區間和操作是 $O(lgU)$,單次區間更新是 $O(U)$。其中 $O(nlgn)$ 是排序時間,$O(U)$ 是建樹時間,$O(nU)$ 是 $n$ 次區間更新,$O(nlgU)$ 是 $n$ 次區間查詢;
- 空間複雜度:$O(lgn + U)$ 排序遞迴棧空間 + 線段樹空間。
題解三(線段樹 + Lazy)
樸素線段樹的效能瓶頸在於:區間更新需要改動從根節點到葉子節點中所有與目標區間有交集的節點,因此單次區間更新操作的時間複雜度是 $O(n)$。
懶更新線段樹的核心思想是:當一個節點代表的區間完全包含於目標區間內時,我們沒有必要繼續向下遞迴更新,而是在當前節點上標記 Lazy Tag 。只有將來更新該節點的某個子區間時,才會將懶更新 pushdown 到子區間。
class Solution {
fun findMinimumTime(tasks: Array<IntArray>): Int {
// 按照結束時間排序
Arrays.sort(tasks) { e1, e2 ->
e1[1] - e2[1]
}
// 線段樹
val tree = SegmentTree(2001)
for (task in tasks) {
// 消除已開機時間
val count = task[2] - tree.query(task[0], task[1])
if (count <= 0) continue
// 推遲最晚開機時間
tree.update(task[0], task[1], count)
}
// 根節點即為所有開機時間
return tree.query(1, 2000)
}
private class SegmentTree(private val n: Int) {
// 線段樹節點(區間範圍與區間值)
private class Node(val left: Int, val right: Int, var value: Int, var lazy: Boolean = false)
// 線段樹陣列
private val tree = Array<Node?>(n * 4) { null } as Array<Node>
// 左子節點索引
private val Int.left get() = 2 * this + 1
// 右子節點索引
private val Int.right get() = 2 * this + 2
init {
// 建樹
buildNode(0, 0, n - 1)
}
private fun buildNode(index: Int, left: Int, right: Int) {
// 葉子節點
if (left == right) {
tree[index] = Node(left, right, 0)
return
}
val mid = (left + right) ushr 1
// 構建左子節點
buildNode(index.left, left, mid)
// 構建右子節點
buildNode(index.right, mid + 1, right)
// 合併左右子節點
tree[index] = Node(left, right, tree[index.left].value + tree[index.right].value)
}
// 開機(推遲到最晚時間)
fun update(left: Int, right: Int, count: Int) {
update(0, left, right, count)
}
// return:有效修改個數
private fun update(index: Int, left: Int, right: Int, count: Int): Int {
// 1、當前節點不處於區間內
if (tree[index].left > right || tree[index].right < left) return 0
val size = tree[index].right - tree[index].left + 1
val unUsedSize = size - tree[index].value
if (unUsedSize == 0) return 0 // 整個區間已開機
// 2、當前節點完全處於區間範圍之內
if (tree[index].left >= left && tree[index].right <= right && unUsedSize <= count) {
// 整個區間可以改為開機
lazyUpdate(index)
return unUsedSize
}
// pushdown
if (tree[index].lazy) {
lazyUpdate(index.left)
lazyUpdate(index.right)
tree[index].lazy = false
}
// 3、更新右子樹(貪心思路:推遲開機)
var realUpdate = update(index.right, left, right, count)
if (count - realUpdate > 0) {
// 4、更新左子樹
realUpdate += update(index.left, left, right, count - realUpdate)
}
// 5、合併左右子節點
tree[index].value = tree[index.left].value + tree[index.right].value
return realUpdate
}
private fun lazyUpdate(index: Int) {
tree[index].value = tree[index].right - tree[index].left + 1
tree[index].lazy = true
}
// 查詢
fun query(left: Int, right: Int): Int {
return query(0, left, right)
}
private fun query(index: Int, left: Int, right: Int): Int {
// 1、當前節點不處於區間範圍內
if (tree[index].left > right || tree[index].right < left) return 0
// 2、當前節點完全處於區間範圍內
if (tree[index].left >= left && tree[index].right <= right) return tree[index].value
// pushdown
if (tree[index].lazy) {
lazyUpdate(index.left)
lazyUpdate(index.right)
tree[index].lazy = false
}
// 3、合併左右子節點
return query(index.left, left, right) + query(index.right, left, right)
}
}
}
複雜度分析:
- 時間複雜度:$O(nlgn + U + nlgU)$ 線段樹單次區間和操作是 $O(lgU)$,單次區間更新是 $O(lgU)$;
- 空間複雜度:$O(lgn + U)$ 排序遞迴棧空間 + 線段樹空間。