Spring Boot自動設定原理懂後輕鬆寫一個自己的starter
目前很多Spring專案的開發都會直接用到Spring Boot。因為Spring原生開發需要加太多的設定,而使用Spring Boot開發很容易上手,只需遵循Spring Boot開發的約定就行了,也就是約定大於設定,無需覺得它神奇,它的底層都是使用的Spring。聊完這個原理帶著大家輕鬆寫一個自己的starter。
要學習它的自動設定原理首先自己要建立一個Spring Boot專案,建立專案過程很簡單就不介紹了。學習它的自動設定原理,首先要看的就是如下這個註解(SpringBootApplication)。這個註解大家都是很熟悉,這個註解是由如下三個註解組成如下:
//第一個註解 @SpringBootConfiguration //第二個註解 @EnableAutoConfiguration //第三個註解 @ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class), @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) }) public @interface SpringBootApplication {
上面三個註解都是太太重要了,本文由於聊自動設定所以就只講EnableAutoConfiguration這個註解,Spring Boot的自動設定原理精髓都在這個註解裡面。好了那就先看這個註解的程式碼如下:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @AutoConfigurationPackage @Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class) public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
看到這個註解一眼就能瞧到它幫助我們匯入了一個AutoConfigurationImportSelector 。由於很多地方遇到了這個Import註解,所以先簡單說一下這個註解的作用。
1:給Spring容器自動注入匯入的類。如下使用,就是幫助Spring容器自動匯入了一個TableEntity物件,在專案中你不需要new 物件,也不需要給這個物件加任何註解了,就可以直接使用TableEntity物件了。
@Configuration @Import(TableEntity.class) public class TestConfig { }
2:給容器匯入一個ImportSelector,比如上文講的那個AutoConfigurationImportSelector 。通過字串陣列的方式返回設定類的全限定名,然後把這些類注入到Spring容器中,我們也就可以直接在Spring容器中使用這些類了。
好了講了上面那2段作用我們主要分析的也就是下面這段程式碼了。
public class AutoConfigurationImportSelector { @Override //作用就是Spring會把這個方法返回的陣列中所有全限定名的類注入到Spring容器中 //供使用者直接去使用這些類。 public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) { if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) { return NO_IMPORTS; } AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader .loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader); //這個方法是Spring Boot 自動設定要說的 AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = getAutoConfigurationEntry(autoConfigurationMetadata, annotationMetadata); return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations()); }
然後我們後面主要分析的也就是getAutoConfigurationEntry(autoConfigurationMetadata,annotationMetadata),這個方法。
//這個方法中的每個方法都很重要,一個一個說 protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata, AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) { AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata); //1:見名知意,獲取候選設定類 List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes); // 2:去除重複的設定類,這個方法太好了。 configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations); //3 :去除使用者排除的設定類。 Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes); checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions); configurations.removeAll(exclusions); configurations = filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata); fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions); return new AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions); }
getCandidateConfigurations這個方法的意思就是獲取候選的設定類(也就是Spring Boot已經自動設定的那些類),如下:(PS我們一看那個報錯資訊就能猜出來Spring從這個【META-INF/spring.factories】下找設定類)
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) { List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), getBeanClassLoader()); Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you " + "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct."); return configurations; }
主要找設定類資訊的就是如下程式碼了。
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName(); return loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryClassName, Collections.emptyList()); } private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { // 1:第一步先從快取中找,找不到在迴圈遍歷找, // 由於Spring程式碼邏輯太複雜,Spring很多地方都採用這種快取的設計 MultiValueMap<String, String> result = cache.get(classLoader); if (result != null) { return result; } // public static final String 下面程式碼用到的常數值如下 // FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories"; try { // 掃描 程式碼中的所有META-INF/spring.factories"檔案 Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) : ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION)); result = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>(); //迴圈遍歷載入上面所說的檔案下的檔案,並把它們放入到 // LinkedMultiValueMap中 while (urls.hasMoreElements()) { URL url = urls.nextElement(); UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url); Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) { String factoryClassName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim(); for (String factoryName : StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue())) { result.add(factoryClassName, factoryName.trim()); } } } //放快取中一份,後面要載入從這個快取中直接取, // 如果看全程式碼可知Spring Boot 快取的不止有設定類,還有其他類。 cache.put(classLoader, result); return result; } catch (IOException ex) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" + FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex); } }
從上面程式碼可知Spring主要是從META-INF/spring.factories檔案中載入設定類,那麼就帶大家看一看Spring Boot自己已經設定的類有哪些。

後面就回到這個(removeDuplicates)去重方法,如下:
protected final <T> List<T> removeDuplicates(List<T> list) { return new ArrayList<>(new LinkedHashSet<>(list)); }
為什麼要把這單獨一行程式碼列出來呢?是因為我感覺這段去重複程式碼用的太好了,自從看了這段程式碼,後面博主自己寫去重邏輯的時候也就參照Spring大佬這一行程式碼寫去重邏輯(PS:如果自己業務去重邏輯沒有其他邏輯的時候參考使用),簡單,效率應該也不低畢竟大佬們這樣用了。
後面程式碼邏輯就是一些去除使用者自己要排除,要過濾掉的設定類。然後就會使用Spring的ImportSelector這個特性(PS具體Spring是怎麼把這些返回許可權定名的類載入的容器中的,是Spring載入類方面的知識,本文不做具體介紹)
好了,然後帶著大家建立一個自己的starter(PS:命名規範我是參考了mybatis-spring,畢竟是大神們的命名規範,記好約定大於設定,哈哈哈)的starter 。
1: 建立一個工程,資訊如下: <groupId>scott-spring-boot-starter</groupId> <artifactId>scottspringbootstarter</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> 2:再建立一個工程 也就是autoconfigure專案。 如下: <groupId>com.spring.starter</groupId> <artifactId>scott-spring-boot-starter-autoconfigure</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> 在pom檔案中引入如下(一般下面的是必須引入的): <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.1.8.RELEASE</version> <relativePath></relativePath> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> 3:建立HelloService。 public class HelloService { HelloProperties helloProperties ; public String sayHello(String name){ return helloProperties.getPrefix()+"-"+name+helloProperties.getSuffix() ; } public HelloProperties getHelloProperties() { return helloProperties; } public void setHelloProperties(HelloProperties helloProperties) { this.helloProperties = helloProperties; } } 4: 建立相應的properies檔案。 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix="scott.hello") //以 scott.hello開頭的。 public class HelloProperties { private String prefix ; private String suffix ; public String getPrefix() { return prefix; } public void setPrefix(String prefix) { this.prefix = prefix; } public String getSuffix() { return suffix; } public void setSuffix(String suffix) { this.suffix = suffix; } 5:建立自定義的組態檔如下: @Configuration @ConditionalOnWebApplication // 在web環境下才生效 @EnableConfigurationProperties(HelloProperties.class) // 屬性檔案生效 public class HelloServiceAutoConfiguration { @Autowired HelloProperties helloProperties; @Bean public HelloService helloService() { HelloService service = new HelloService(); service.setHelloProperties(helloProperties); return service; }; }
6:在META-INF 資料夾下建立 spring.factories 檔案,寫入如下自己的設定類 。Spring Boot自動設定規約,約定大於規範,如下圖的設定所示:
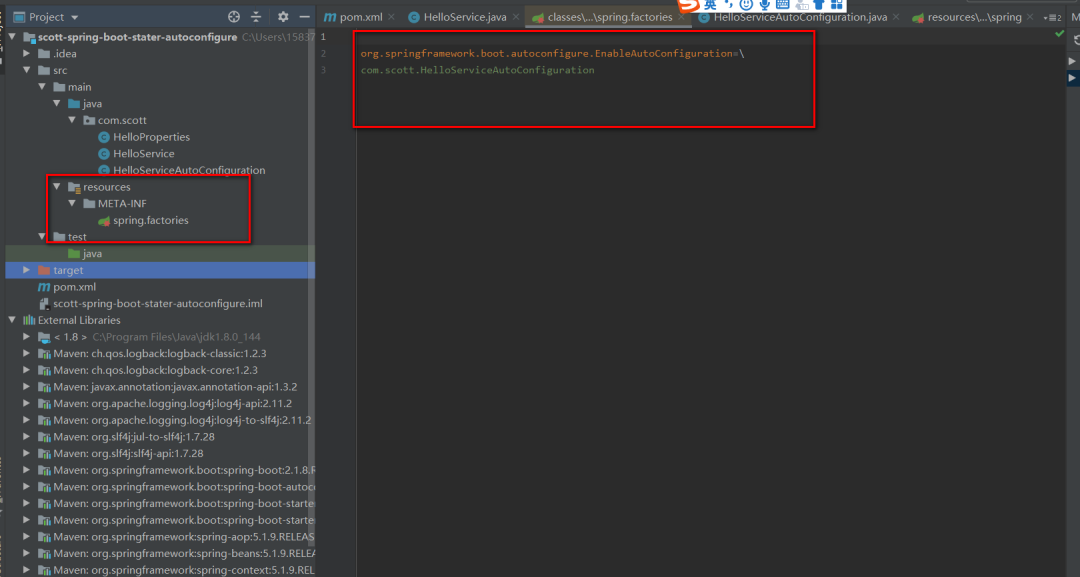
7:在scottspringbootstarter專案的pom檔案中引入自定義的 autoconfigure如下:
<groupId>scott-spring-boot-starter</groupId>
<artifactId>scottspringbootstarter</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.spring.starter</groupId>
<artifactId>scott-spring-boot-starter-autoconfigure</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
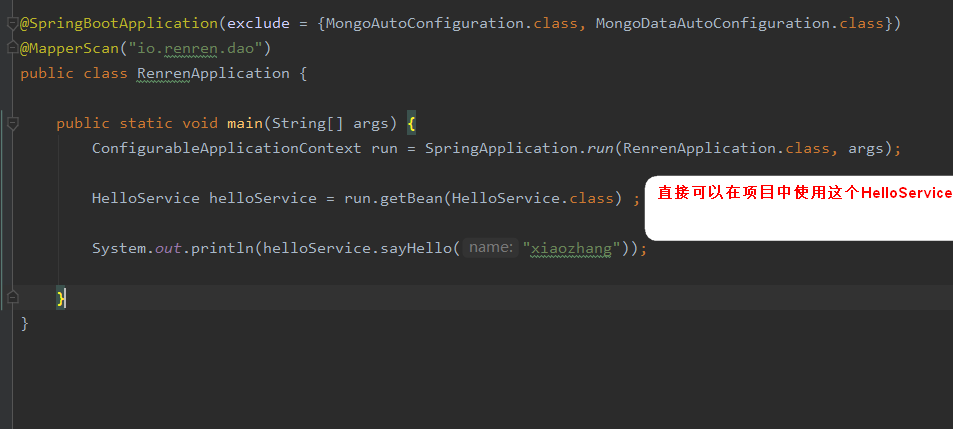
8:自定義starter就好了,然後就可以在我們自定義的工程中引入scottspringbootstarter就可以使用了。
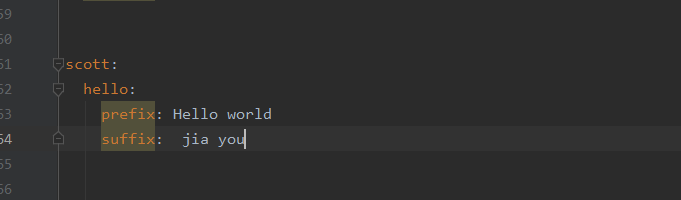
如下使用方法,設定yml檔案,然後使用對應的服務,So Easy: