LFU 的設計與實現
LFU 的設計與實現
作者:Grey
原文地址:
題目描述
LFU(least frequently used)。即最不經常使用頁置換演演算法。
主要思路
首先,定義一個輔助資料結構 Node
public static class Node {
public Integer key;
public Integer value;
public Integer times; // 這個節點發生get或者set的次數總和
public Node up; // 節點之間是雙向連結串列所以有上一個節點
public Node down; // 節點之間是雙向連結串列所以有下一個節點
public Node(int k, int v, int t) {
key = k;
value = v;
times = t;
}
}
這個 Node 用於封裝 LFU Cache 每次加入的元素,其中 key 和 value 兩個變數記錄每次加入的 KV 值,times 用於記錄該 KV 值被操作(get/set)的次數之和, up 和 down 兩個變數用於連結和 KV 出現詞頻一樣的資料項,用連結串列串聯。
接下來需要另外一個輔助資料結構 NodeList,前面的 Node 結構已經把詞頻一致的資料項組織在同一個桶裡,這個 NodeList 用於連線出現不同詞頻的桶,用雙向連結串列組織
public static class NodeList {
public Node head; // 桶的頭節點
public Node tail; // 桶的尾節點
public NodeList last; // 桶之間是雙向連結串列所以有前一個桶
public NodeList next; // 桶之間是雙向連結串列所以有後一個桶
public NodeList(Node node) {
head = node;
tail = node;
}
……
}
使用一個具體的範例來表示上述兩個結構如何組織的
例如,LFU Cache 在初始為空的狀態下,進來如下資料
key = A, value = 3
key = B, value = 30
key = C, value = 4
key = D, value = 12
那麼 LFU 會做如下組織
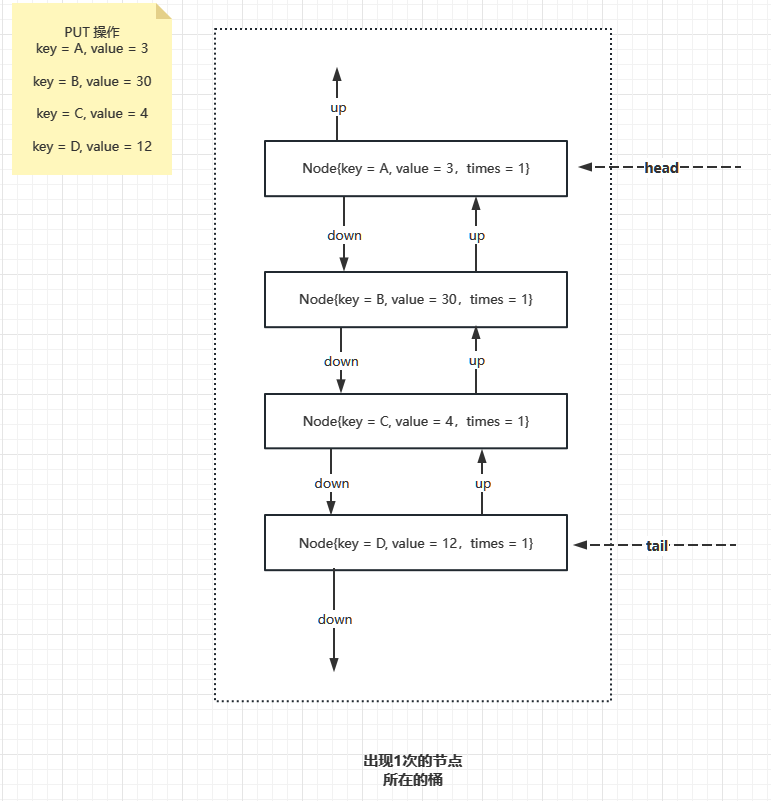
此時只有出現一次的桶,接下來,如果 key = C 這條記錄 被存取過了,所以詞頻變為2,接下來要把 key = C 這條記錄先從詞頻為1的桶裡面取出來,然後再新建一個詞頻為 2 的桶,把這個 key = C 的資料項掛上去,結果如下
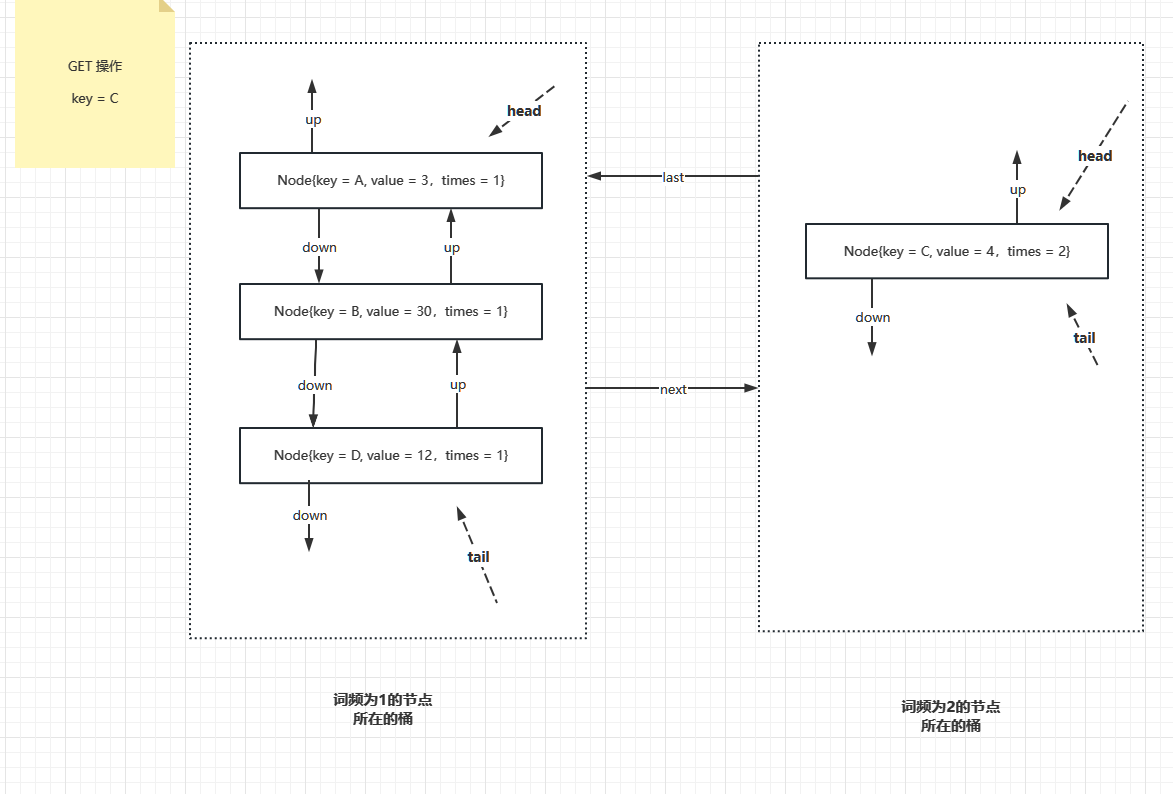
接下來,如果又操作了 key = C 這條記錄,那麼這條記錄的詞頻就是 3, 又需要新增一個詞頻為 3 的桶,原來詞頻為 2 的桶已經沒有資料項了,要銷燬,並且把詞頻為 1 的桶和詞頻為 3 的桶連線在一起。
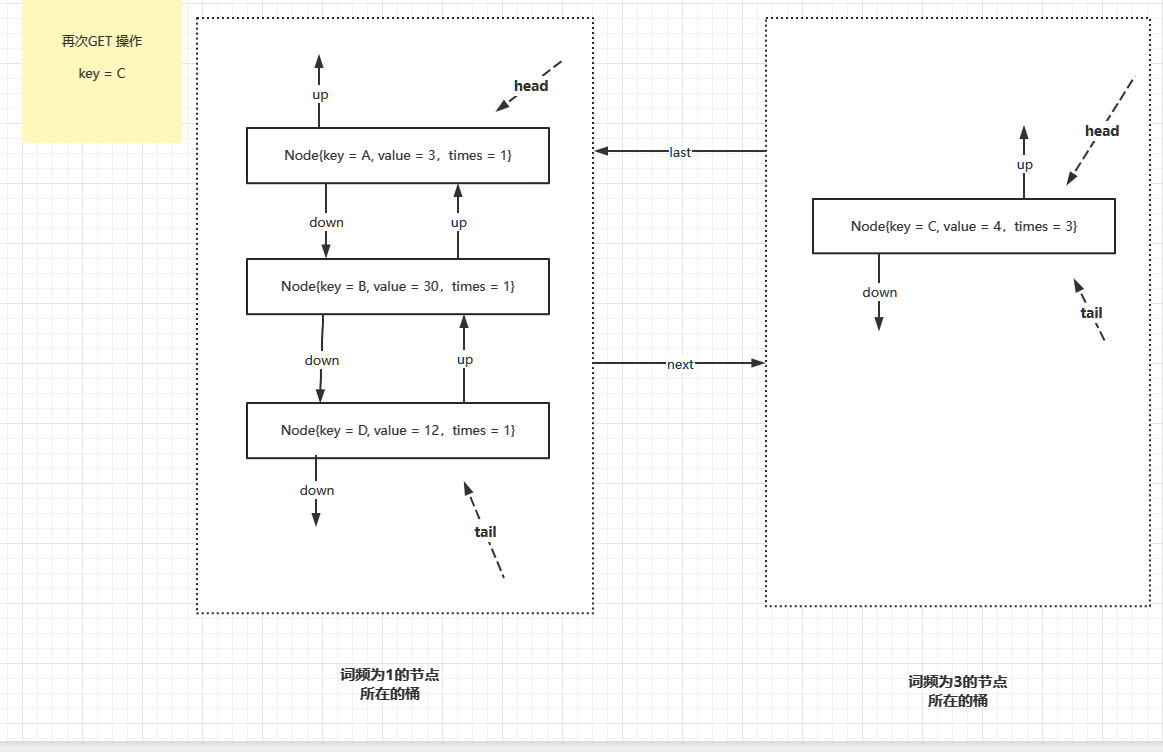
接下來,如果操作了 key = A,則 key = A 成為詞頻為 2 的資料項,再次新增詞頻為 2 的桶,並把這個桶插入到詞頻為 1 和詞頻為 3 的桶之間,如下圖
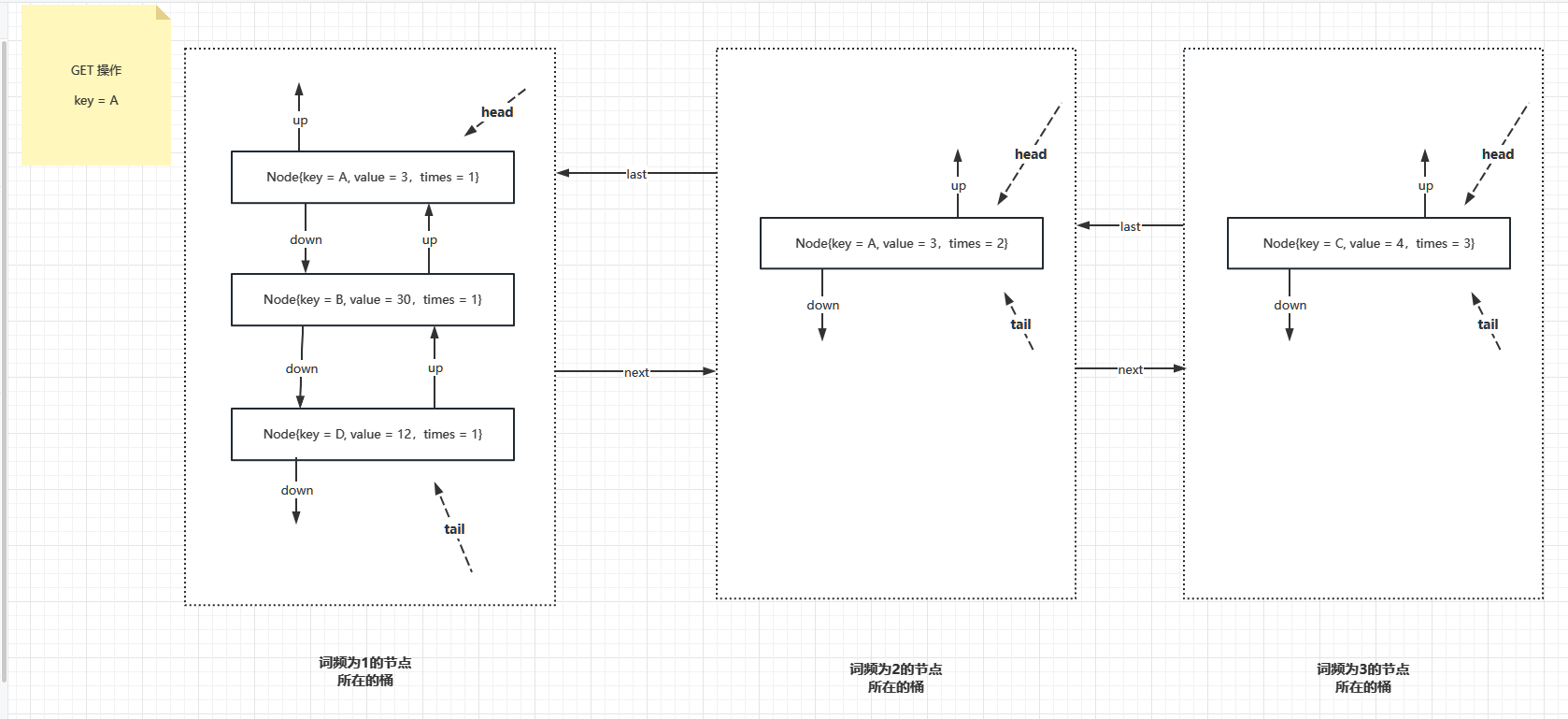
以上範例就可以很清楚說明了 Node 和 NodeList 兩個資料結構在 LFU 中的作用,接下來,為了實現快速的 put 和 get 操作,需要定義如下成員變數
int capacity; // 快取的大小限制
int size; // 快取目前有多少個節點
HashMap<Integer, Node> records; // 表示key(Integer)由哪個節點(Node)代表
HashMap<Node, NodeList> heads; // 表示節點(Node)在哪個桶(NodeList)裡
NodeList headList; // 整個結構中位於最左的桶,是一個雙向連結串列
說明:records 這個變數就是用於快速得到某個 key 的節點(Node)是什麼,由於這裡的 kv 都是整型,所以用 Integer 作為 key 可以定位到對應的 Node 資料項資訊。
heads 則用於快速定位某個 Node 在哪個桶裡面。
headList 表示整個結構中位於最左側的桶,這個桶一定是出現次數最少的桶,所以淘汰的時候,優先淘汰這個桶裡面的末尾位置,即 tail 位置的 node!
兩個核心方法 put 和 get 的核心程式碼說明如下
public void put(int key, int value) {
if (records.containsKey(key)) {
// put 的元素是已經存在的
// 更新元素值,更新出現次數
Node node = records.get(key);
node.value = value;
node.times++;
// 通過heads以O(1)複雜度定位到所在的桶
NodeList curNodeList = heads.get(node);
// 把這個更新後的 Node 從 舊的桶遷移到新的桶
move(node, curNodeList);
} else {
if (size == capacity) {
// 容量已經滿了
// 淘汰 headList 尾部的節點!因為這個節點是最久且最少用過的節點
Node node = headList.tail;
headList.deleteNode(node);
// 刪掉的節點有可能會讓 headList 換頭,因為最右側的桶可能只有一個節點,被刪除後,就沒有了。
modifyHeadList(headList);
// records和 heads 中都要刪掉其記錄
records.remove(node.key);
heads.remove(node);
size--;
}
// 以上操作就是淘汰了一個節點
// 接下來就放心加入節點
// 先建立Node,詞頻設定為 1
Node node = new Node(key, value, 1);
if (headList == null) {
// 如果headList為空,說明最左側的桶沒有了,新來節點正好充當最左側節點的桶中元素
headList = new NodeList(node);
} else {
if (headList.head.times.equals(node.times)) {
// 最右側桶不為空的情況下,這個節點出現的次數又正好等於最左側桶所代表的節點數
// 則直接加入最左側桶中
headList.addNodeFromHead(node);
} else {
// 將加入的節點作為做左側桶,接上原先的headList
// eg:新加入的節點出現的次數是1,原先的 headList代表的桶是詞頻為2的資料
// 就會走這個分支
NodeList newList = new NodeList(node);
newList.next = headList;
headList.last = newList;
headList = newList;
}
}
records.put(key, node);
heads.put(node, headList);
size++;
}
}
public int get(int key) {
if (!records.containsKey(key)) {
// 不包含這個key
// 按題目要求直接返回 -1
return -1;
}
// 否則,先取出這個節點
Node node = records.get(key);
// 詞頻+1
node.times++;
// 將這個節點所在的桶找到
NodeList curNodeList = heads.get(node);
// 將這個節點從原桶調整到新桶
move(node, curNodeList);
return node.value;
}
PS:這裡涉及的對雙向連結串列和桶連結串列的兩個操作move和modifyHeadList邏輯不難,但是很多繁瑣的邊界條件要處理,具體方法的說明見上述程式碼註釋,不贅述。
完整程式碼如下
static class LFUCache {
private int capacity; // 快取的大小限制
private int size; // 快取目前有多少個節點
private HashMap<Integer, Node> records; // 表示key(Integer)由哪個節點(Node)代表
private HashMap<Node, NodeList> heads; // 表示節點(Node)在哪個桶(NodeList)裡
private NodeList headList; // 整個結構中位於最左的桶
public LFUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
size = 0;
records = new HashMap<>();
heads = new HashMap<>();
headList = null;
}
// 節點的資料結構
public static class Node {
public Integer key;
public Integer value;
public Integer times; // 這個節點發生get或者set的次數總和
public Node up; // 節點之間是雙向連結串列所以有上一個節點
public Node down; // 節點之間是雙向連結串列所以有下一個節點
public Node(int k, int v, int t) {
key = k;
value = v;
times = t;
}
}
// 桶結構
public static class NodeList {
public Node head; // 桶的頭節點
public Node tail; // 桶的尾節點
public NodeList last; // 桶之間是雙向連結串列所以有前一個桶
public NodeList next; // 桶之間是雙向連結串列所以有後一個桶
public NodeList(Node node) {
head = node;
tail = node;
}
// 把一個新的節點加入這個桶,新的節點都放在頂端變成新的頭部
public void addNodeFromHead(Node newHead) {
newHead.down = head;
head.up = newHead;
head = newHead;
}
// 判斷這個桶是不是空的
public boolean isEmpty() {
return head == null;
}
// 刪除node節點並保證node的上下環境重新連線
public void deleteNode(Node node) {
if (head == tail) {
head = null;
tail = null;
} else {
if (node == head) {
head = node.down;
head.up = null;
} else if (node == tail) {
tail = node.up;
tail.down = null;
} else {
node.up.down = node.down;
node.down.up = node.up;
}
}
node.up = null;
node.down = null;
}
}
private boolean modifyHeadList(NodeList removeNodeList) {
if (removeNodeList.isEmpty()) {
if (headList == removeNodeList) {
headList = removeNodeList.next;
if (headList != null) {
headList.last = null;
}
} else {
removeNodeList.last.next = removeNodeList.next;
if (removeNodeList.next != null) {
removeNodeList.next.last = removeNodeList.last;
}
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
private void move(Node node, NodeList oldNodeList) {
oldNodeList.deleteNode(node);
NodeList preList = modifyHeadList(oldNodeList) ? oldNodeList.last : oldNodeList;
NodeList nextList = oldNodeList.next;
if (nextList == null) {
NodeList newList = new NodeList(node);
if (preList != null) {
preList.next = newList;
}
newList.last = preList;
if (headList == null) {
headList = newList;
}
heads.put(node, newList);
} else {
if (nextList.head.times.equals(node.times)) {
nextList.addNodeFromHead(node);
heads.put(node, nextList);
} else {
NodeList newList = new NodeList(node);
if (preList != null) {
preList.next = newList;
}
newList.last = preList;
newList.next = nextList;
nextList.last = newList;
if (headList == nextList) {
headList = newList;
}
heads.put(node, newList);
}
}
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
if (capacity == 0) {
return;
}
if (records.containsKey(key)) {
Node node = records.get(key);
node.value = value;
node.times++;
NodeList curNodeList = heads.get(node);
move(node, curNodeList);
} else {
if (size == capacity) {
Node node = headList.tail;
headList.deleteNode(node);
modifyHeadList(headList);
records.remove(node.key);
heads.remove(node);
size--;
}
Node node = new Node(key, value, 1);
if (headList == null) {
headList = new NodeList(node);
} else {
if (headList.head.times.equals(node.times)) {
headList.addNodeFromHead(node);
} else {
NodeList newList = new NodeList(node);
newList.next = headList;
headList.last = newList;
headList = newList;
}
}
records.put(key, node);
heads.put(node, headList);
size++;
}
}
public int get(int key) {
if (!records.containsKey(key)) {
return -1;
}
Node node = records.get(key);
node.times++;
NodeList curNodeList = heads.get(node);
move(node, curNodeList);
return node.value;
}
}
更多
參考資料
本文來自部落格園,作者:Grey Zeng,轉載請註明原文連結:https://www.cnblogs.com/greyzeng/p/17009092.html