在nodejs中體驗http/2
2022-12-21 06:00:59
前言
2015年,HTTP/2 釋出,直到2021年公司的專案才開始在實踐中應用;自己對http2諸多特點的理解只存在於字面上,於是嘗試在nodejs中實踐一下,加深自己的理解。
多路複用
同域名下所有通訊都在單個連線上完成,消除了因多個 TCP 連線而帶來的延時和記憶體消耗,這在大量請求同時發出的情況下能夠減少載入時間。
使用如下程式碼檢視http2環境下,資源下載的情況(瀏覽器開啟限流和disable cache):
const http2 = require('http2');
const fs = require('fs');
const { HTTP2_HEADER_PATH } = http2.constants;
const server = http2.createSecureServer({
key: fs.readFileSync('localhost-privkey.pem'),
cert: fs.readFileSync('localhost-cert.pem')
});
server.on('error', (err) => console.error(err));
server.on('stream', (stream, headers) => {
// stream is a Duplex
const path = headers[':path'];
if(path === '/img.png' || path === '/favicon.ico'){
const fd = fs.openSync('img.png', 'r');
const stat = fs.fstatSync(fd);
const headers = {
'content-length': stat.size,
'last-modified': stat.mtime.toUTCString(),
'content-type': 'image/png'
};
stream.respondWithFD(fd, headers);
} else if(path === '/') {
stream.respond({
'content-type': 'text/html; charset=utf-8',
':status': 200
});
stream.end(`
<h1>Hello World</h1>
<script>
for(var i=0;i<50;i++){
fetch('/img.png')
}
</script>
`);
}
});
server.listen(8443);
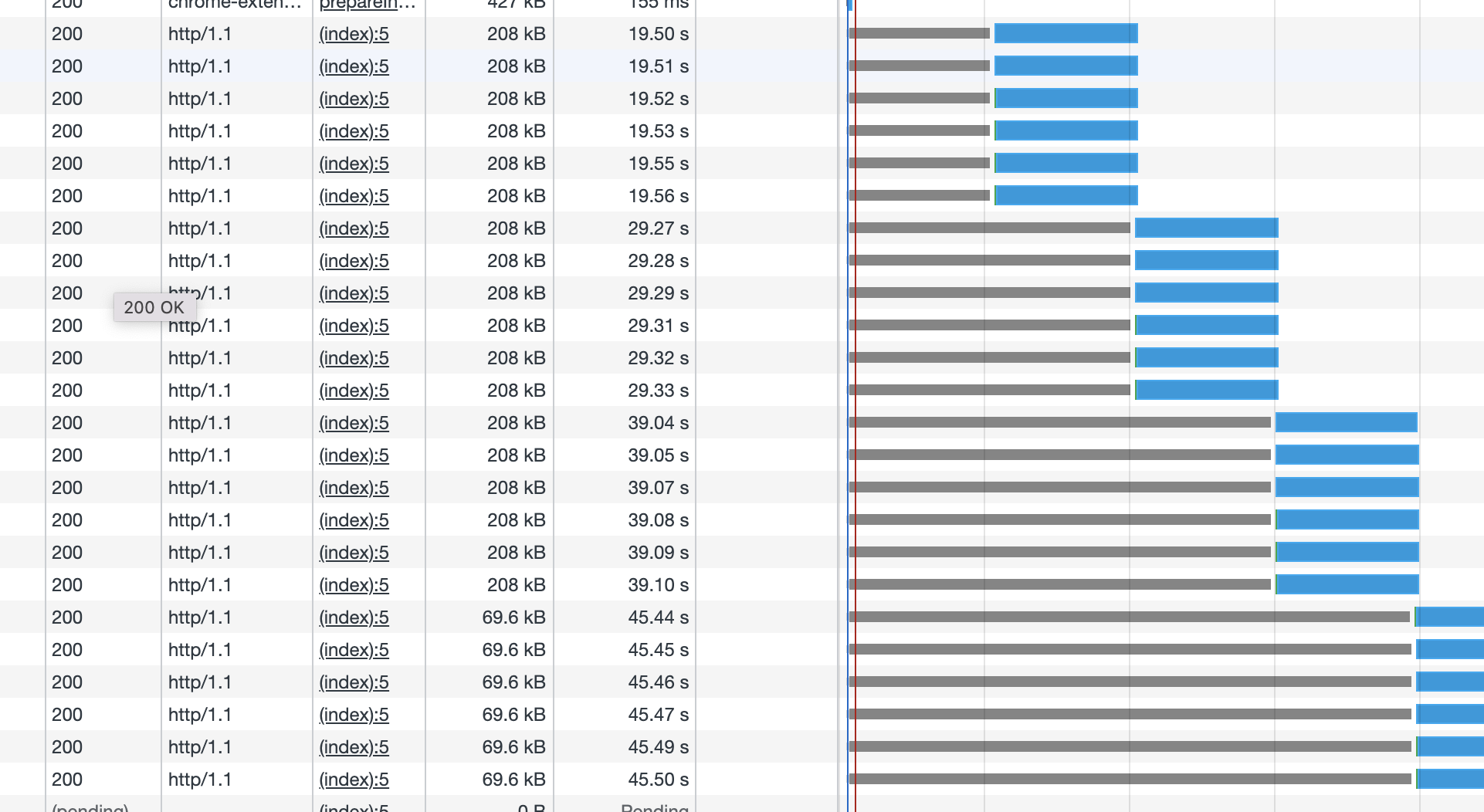
可以看到當資源開始同時請求,所有的請求形成一個佇列,請求之間開始時間相差大概1ms, 因為下載的是同一個圖片,50張圖片同時下載,最後幾乎在同時完成下載。
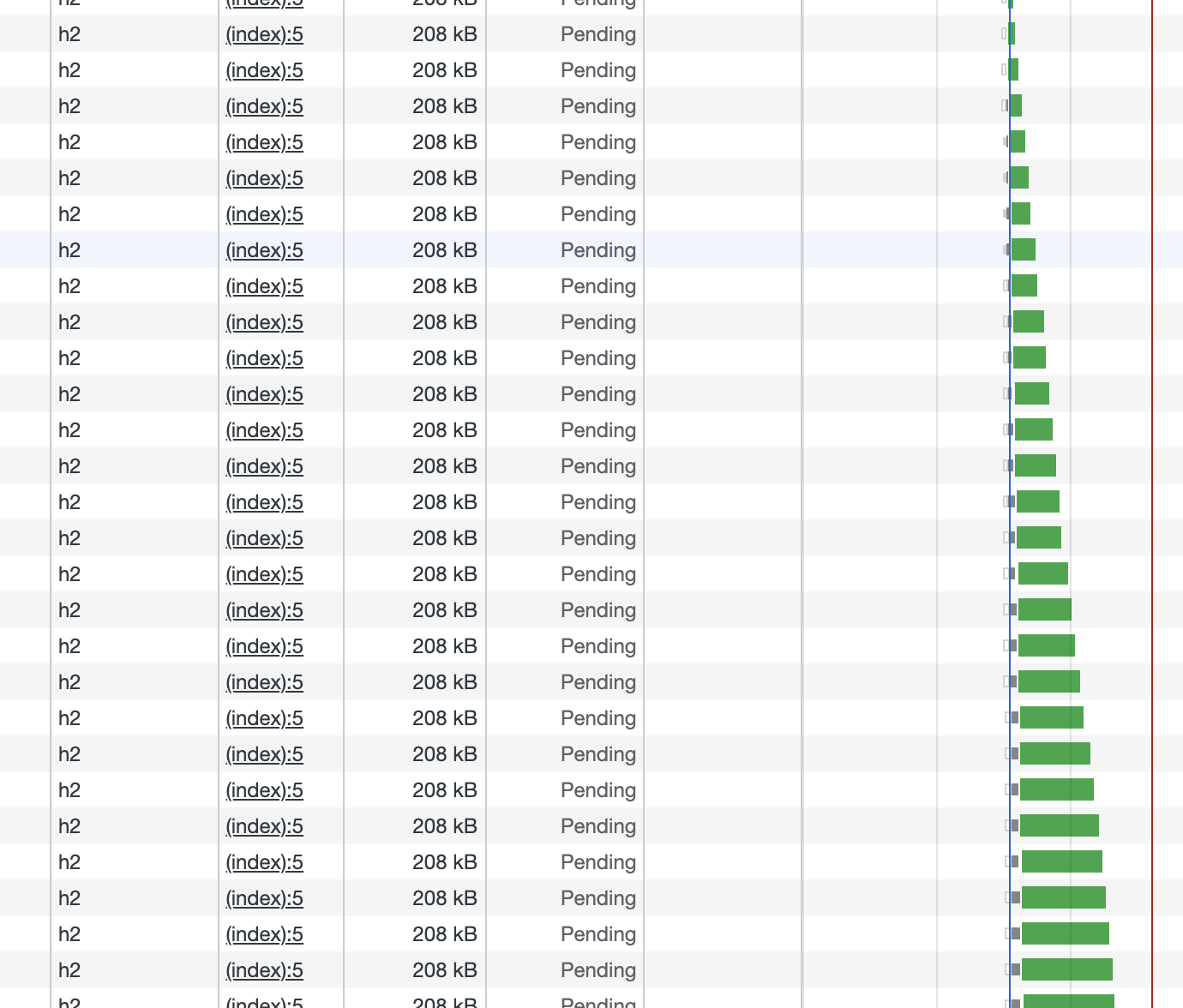
下面是http1.1的例子,通過對比發現瀏覽器按照自己的最大並行量同時發出請求,只有當請求返回後才發出新的請求(瀏覽器開啟限流和disable cache):
const http = require('http');
const fs = require('fs');
const server = http.createServer(function(req,res){
const path = req.url;
if(path === '/img.png' || path === '/favicon.ico'){
res.writeHead(200,{'Content-type':'image/png'})
var stream = fs.createReadStream('img.png')
stream.pipe(res)
} else {
res.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'text/html; charset=utf-8' });
res.end(`
<h1>Hello World</h1>
<script>
for(var i=0;i<50;i++){
fetch('/img.png')
}
</script>
`);
}
});
server.listen(8444);
伺服器端推播
按照如下程式碼測試
const http2 = require('http2');
const fs = require('fs');
const { HTTP2_HEADER_PATH } = http2.constants;
const server = http2.createSecureServer({
key: fs.readFileSync('localhost-privkey.pem'),
cert: fs.readFileSync('localhost-cert.pem')
});
server.on('error', (err) => console.error(err));
server.on('stream', (stream, headers) => {
const path = headers[':path'];
if(path === '/') {
stream.respond({
'content-type': 'text/html; charset=utf-8',
':status': 200
});
stream.pushStream({ [HTTP2_HEADER_PATH]: '/style.css' }, (err, pushStream, headers) => {
if (err) throw err;
const fd = fs.openSync('style.css', 'r');
const stat = fs.fstatSync(fd);
const header = {
'content-length': stat.size,
'last-modified': stat.mtime.toUTCString(),
'content-type': 'text/css'
};
pushStream.respondWithFD(fd, header)
});
stream.end(`
<h1>Hello World</h1>
<script>
setTimeout(()=>{
fetch('/style.css')
},2000)
</script>
`);
} else if(path === '/style.css'){
const fd = fs.openSync('style.css', 'r');
const stat = fs.fstatSync(fd);
const headers = {
'content-length': stat.size,
'last-modified': stat.mtime.toUTCString(),
'content-type': 'text/css'
};
stream.respondWithFD(fd, headers);
}
});
server.listen(8442);
資源載入情況如下,style.css的Initiator是Push,大小是66 B, 同時首頁載入的大小是207 B,

註釋掉stream.pushStream部分後,不使用推播,資源載入如下,style.css大小是89B, 同時首頁載入的大小是182B,

綜上所看,伺服器端推播可以提前載入資源,優化非首頁載入有益。
令人高興的是,因為使用率低,chrome在105版本後不再支援http2的伺服器端推播,導致這個特點在前端開發中可以忽略了。並且如果要測試改特點需要使用低版本的chrome,比如本例子使用的是chrome 96 mac版本。
本文所用程式碼:https://github.com/blank-x/pg/tree/master/http2,nodejs版本是v16.19.0.