elasticsearch 之 histogram 直方圖聚合
1. 簡介
直方圖聚合是一種基於多桶值聚合,可從檔案中提取的數值或數值範圍值來進行聚合。它可以對參與聚合的值來動態的生成固定大小的桶。
2. bucket_key如何計算
假設我們有一個值是32,並且桶的大小是5,那麼32四捨五入後變成30,因此檔案將落入與鍵30關聯的儲存桶中。下面的算式可以精確的確定每個檔案的歸屬桶
bucket_key = Math.floor((value - offset) / interval) * interval + offset
offset:的值預設是從0開始。並且offset的值必須在[0, interval)之間。且需要是一個正數。value:值的參與計算的值,比如某個檔案中的價格欄位等。
3. 有一組資料,如何確定是落入到那個桶中
此處是我自己的一個理解,如果錯誤歡迎指出。
存在的資料: [3, 8, 15]
offset = 0
interval = 5
那麼可能會分成如下幾個桶 [0,5) [5,10) [10, 15) [15,+∞)
- 數位3落入的桶 buket_key=
Math.floor((3 - 0) / 5) * 5 + 0 = 0,即落入[0,5)這個桶中 - 數位8落入的桶 buket_key=
Math.floor((8 - 0) / 5) * 5 + 0 = 5,即落入[5,10)這個桶中 - 數位15落入的桶 buket_key=
Math.floor((15 - 0) / 5) * 5 + 0 = 15,即落入[15,+∞)這個桶中
4、需求
我們有一組api響應時間資料,根據這組資料進行histogram聚合統計
4.1 準備mapping
PUT /index_api_response_time
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 1
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "long"
},
"api": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"response_time": {
"type": "integer"
}
}
}
}
此處的mapping比較簡單,就3個欄位id,api和response_time。
4.2 準備資料
PUT /index_api_response_time/_bulk
{"index":{"_id":1}}
{"api":"/user/infos","response_time": 3}
{"index":{"_id":2}}
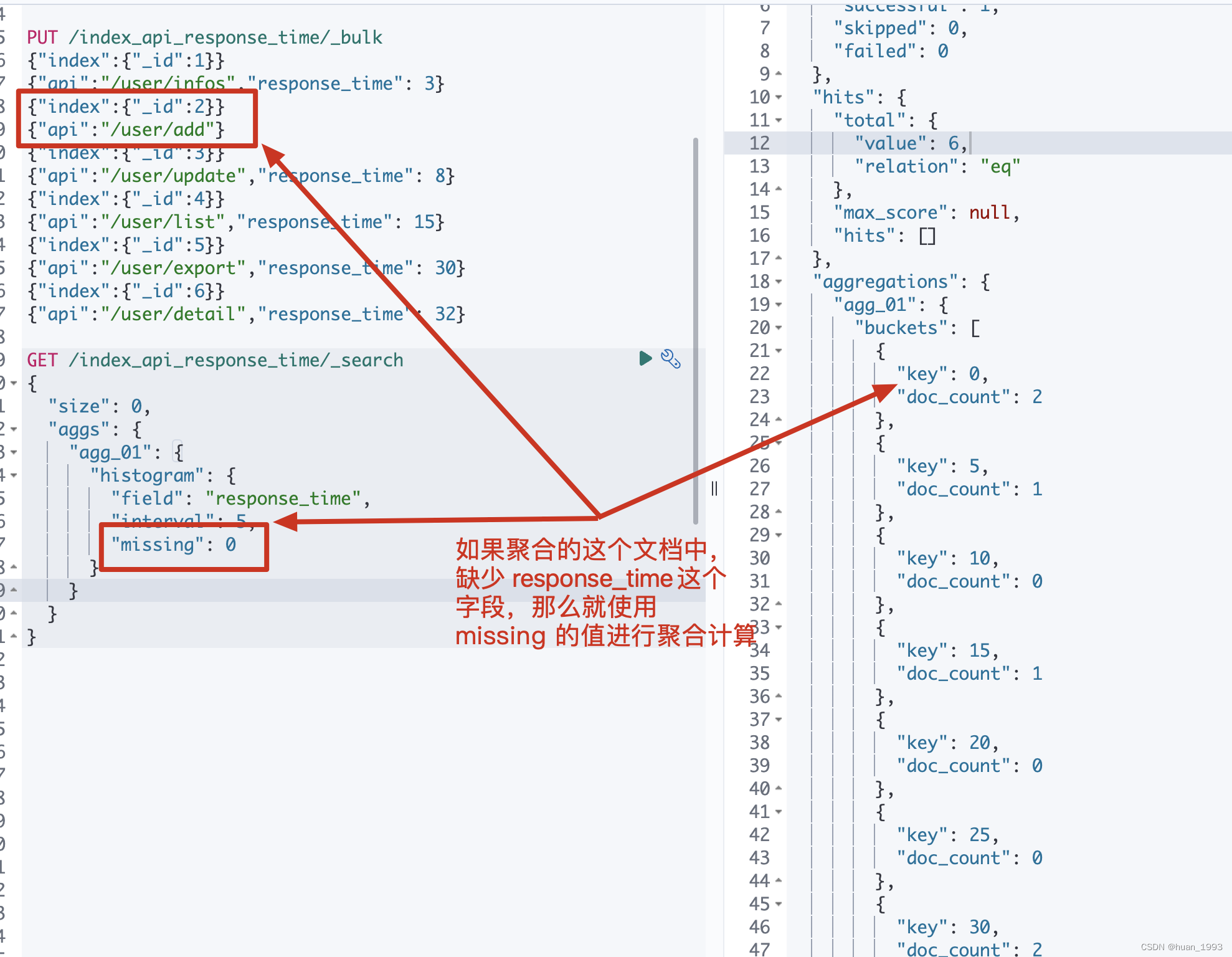
{"api":"/user/add"}
{"index":{"_id":3}}
{"api":"/user/update","response_time": 8}
{"index":{"_id":4}}
{"api":"/user/list","response_time": 15}
{"index":{"_id":5}}
{"api":"/user/export","response_time": 30}
{"index":{"_id":6}}
{"api":"/user/detail","response_time": 32}
此處先記錄 id=2的資料,這個是沒有response_time的,後期聚合時額外處理。
5、histogram聚合操作
5.1、根據response_time聚合,間隔為5
5.1.1 dsl
GET /index_api_response_time/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"agg_01": {
"histogram": {
"field": "response_time",
"interval": 5
}
}
}
}
5.1.2 java程式碼
@Test
@DisplayName("根據response_time聚合,間隔為5")
public void test01() throws IOException {
SearchRequest request = SearchRequest.of(search ->
search
.index("index_api_response_time")
.size(0)
.aggregations("agg_01", agg -> agg.histogram(histogram -> histogram.field("response_time")
.interval(5D))));
System.out.println("request: " + request);
SearchResponse<String> response = client.search(request, String.class);
System.out.println("response: " + response);
}
5.1.3 執行結果

5.2 在5.1基礎上聚合出每個桶總的響應時間
此處聚合一下是為了結合已有的資料,看看每個資料是否落入到了相應的桶中
5.2.1 dsl
GET /index_api_response_time/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"agg_01": {
"histogram": {
"field": "response_time",
"interval": 5
},
"aggs": {
"agg_sum": {
"sum": {
"field": "response_time"
}
}
}
}
}
}
5.2.2 java程式碼
@Test
@DisplayName("在test01基礎上聚合出每個桶總的響應時間")
public void test02() throws IOException {
SearchRequest request = SearchRequest.of(search ->
search
.index("index_api_response_time")
.size(0)
.aggregations("agg_01", agg ->
agg.histogram(histogram -> histogram.field("response_time").interval(5D))
.aggregations("agg_sum", aggSum -> aggSum.sum(sum -> sum.field("response_time")))
));
System.out.println("request: " + request);
SearchResponse<String> response = client.search(request, String.class);
System.out.println("response: " + response);
}
5.2.3 執行結果

5.3 每個桶中必須存在1個檔案的結果才返回-min_doc_count
從5.1中的結果我們可以知道,不管桶中是否存在資料,我們都返回了,即返回了很多空桶。 簡單理解就是返回的 桶中存在 doc_count=0 的資料,此處我們需要將這個資料不返回
5.3.1 dsl
GET /index_api_response_time/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"agg_01": {
"histogram": {
"field": "response_time",
"interval": 5,
"min_doc_count": 1
}
}
}
}
5.3.2 java程式碼
@Test
@DisplayName("每個桶中必須存在1個檔案的結果才返回-min_doc_count")
public void test03() throws IOException {
SearchRequest request = SearchRequest.of(search ->
search
.index("index_api_response_time")
.size(0)
.aggregations("agg_01", agg -> agg.histogram(
histogram -> histogram.field("response_time").interval(5D).minDocCount(1)
)
)
);
System.out.println("request: " + request);
SearchResponse<String> response = client.search(request, String.class);
System.out.println("response: " + response);
}
5.3.3 執行結果

5.4 補充空桶資料-extended_bounds
這個是什麼意思?假設我們通過 response_time >= 10 進行過濾,並且 interval=5 那麼es預設情況下就不會返回 bucket_key =0,5,10的桶,那麼如果我想返回那麼該如何處理呢?可以通過 extended_bounds 來實現。
使用extended_bounds時,min_doc_count=0時才有意義。 extended_bounds不會過濾桶。

5.4.1 dsl
GET /index_api_response_time/_search
{
"size": 0,
"query": {
"range": {
"response_time": {
"gte": 10
}
}
},
"aggs": {
"agg_01": {
"histogram": {
"field": "response_time",
"interval": 5,
"min_doc_count": 0,
"extended_bounds": {
"min": 0,
"max": 50
}
}
}
}
}
5.4.2 java程式碼
@Test
@DisplayName("補充空桶資料-extended_bounds")
public void test04() throws IOException {
SearchRequest request = SearchRequest.of(search ->
search
.index("index_api_response_time")
.size(0)
.query(query-> query.range(range -> range.field("response_time").gte(JsonData.of(10))))
.aggregations("agg_01", agg -> agg.histogram(
histogram -> histogram.field("response_time").interval(5D).minDocCount(0)
.extendedBounds(bounds -> bounds.min(1D).max(50D))
)
)
);
System.out.println("request: " + request);
SearchResponse<String> response = client.search(request, String.class);
System.out.println("response: " + response);
}
5.4.3 執行結果

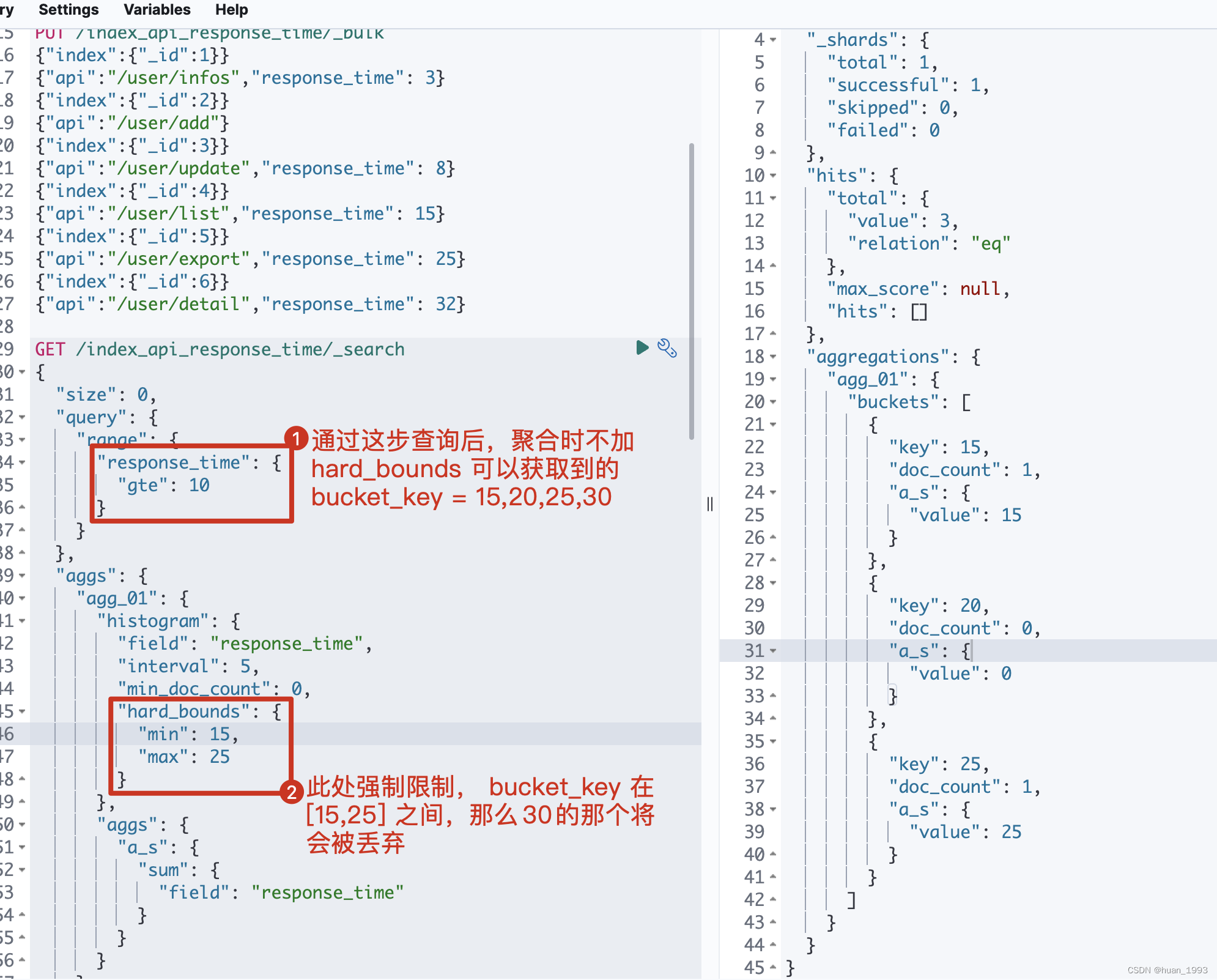
5.5 只展示min-max之間的桶-hard_bounds

此處的資料:
PUT /index_api_response_time/_bulk
{"index":{"_id":1}}
{"api":"/user/infos","response_time": 3}
{"index":{"_id":2}}
{"api":"/user/add"}
{"index":{"_id":3}}
{"api":"/user/update","response_time": 8}
{"index":{"_id":4}}
{"api":"/user/list","response_time": 15}
{"index":{"_id":5}}
{"api":"/user/export","response_time": 25}
{"index":{"_id":6}}
{"api":"/user/detail","response_time": 32}
5.5.1 dsl
GET /index_api_response_time/_search
{
"size": 0,
"query": {
"range": {
"response_time": {
"gte": 10
}
}
},
"aggs": {
"agg_01": {
"histogram": {
"field": "response_time",
"interval": 5,
"min_doc_count": 0,
"hard_bounds": {
"min": 15,
"max": 25
}
},
"aggs": {
"a_s": {
"sum": {
"field": "response_time"
}
}
}
}
}
}
5.5.2 java程式碼
@Test
@DisplayName("只展示min-max之間的桶-hard_bounds")
public void test05() throws IOException {
SearchRequest request = SearchRequest.of(search ->
search
.index("index_api_response_time")
.size(0)
.query(query-> query.range(range -> range.field("response_time").gte(JsonData.of(10))))
.aggregations("agg_01", agg ->
agg.histogram(
histogram -> histogram.field("response_time").interval(5D).minDocCount(0)
.hardBounds(bounds -> bounds.min(1D).max(50D))
)
.aggregations("a_s", sumAgg -> sumAgg.sum(sum -> sum.field("response_time")))
)
);
System.out.println("request: " + request);
SearchResponse<String> response = client.search(request, String.class);
System.out.println("response: " + response);
}
5.5.3 執行結果
5.6 排序-order
By default the returned buckets are sorted by their key ascending, though the order behaviour can be controlled using the order setting. Supports the same order functionality as the Terms Aggregation.
5.6.1 dsl
GET /index_api_response_time/_search
{
"size": 0,
"query": {
"range": {
"response_time": {
"gte": 10
}
}
},
"aggs": {
"agg_01": {
"histogram": {
"field": "response_time",
"interval": 5,
"order": {
"_count": "desc"
}
}
}
}
}
5.6.2 java程式碼
@Test
@DisplayName("排序order")
public void test06() throws IOException {
SearchRequest request = SearchRequest.of(search ->
search
.index("index_api_response_time")
.size(0)
.query(query-> query.range(range -> range.field("response_time").gte(JsonData.of(10))))
.aggregations("agg_01", agg ->
agg.histogram(
histogram -> histogram.field("response_time").interval(5D)
.order(NamedValue.of("_count", SortOrder.Desc))
)
)
);
System.out.println("request: " + request);
SearchResponse<String> response = client.search(request, String.class);
System.out.println("response: " + response);
}
5.6.3 執行結果

5.7 檔案中缺失聚合欄位時如何處理-missing

5.7.1 dsl
GET /index_api_response_time/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"agg_01": {
"histogram": {
"field": "response_time",
"interval": 5,
"missing": 0
}
}
}
}
5.7.2 java程式碼
@Test
@DisplayName("檔案中缺失聚合欄位時如何處理-missing")
public void test07() throws IOException {
SearchRequest request = SearchRequest.of(search ->
search
.index("index_api_response_time")
.size(0)
.query(query-> query.range(range -> range.field("response_time").gte(JsonData.of(10))))
.aggregations("agg_01", agg ->
agg.histogram(
histogram -> histogram.field("response_time").interval(5D) .missing(0D)
)
)
);
System.out.println("request: " + request);
SearchResponse<String> response = client.search(request, String.class);
System.out.println("response: " + response);
}
5.7.3 執行結果
6、完整程式碼
7、參考檔案
本文來自部落格園,作者:huan1993,轉載請註明原文連結:https://www.cnblogs.com/huan1993/p/16924849.html