linux有核心級執行緒麼
linux有核心級執行緒,linux支援核心級的多執行緒。Linux核心可以看作服務程序(管理軟硬體資源,響應使用者程序的各種程序);核心需要多個執行流並行,為了防止可能的阻塞,支援多執行緒。核心執行緒就是核心的一個分身,可以用以處理一件特定事情,核心執行緒的排程由核心負責,一個核心執行緒的處於阻塞狀態時不影響其他的核心執行緒。

程式設計師必備介面測試偵錯工具:
本教學操作環境:linux7.3系統、Dell G3電腦。
執行緒通常被定義為一個程序中程式碼的不同執行路線。從實現方式上劃分,執行緒有兩種型別:「使用者級執行緒」和「核心級執行緒」。
使用者執行緒指不需要核心支援而在使用者程式中實現的執行緒,其不依賴於作業系統核心,應用程序利用執行緒庫提供建立、同步、排程和管理執行緒的函數來控制使用者執行緒。這種執行緒甚至在象 DOS 這樣的作業系統中也可實現,但執行緒的排程需要使用者程式完成,這有些類似 Windows 3.x 的共同作業式多工。
另外一種則需要核心的參與,由核心完成執行緒的排程。其依賴於作業系統核心,由核心的內部需求進行建立和復原,這兩種模型各有其好處和缺點。
使用者執行緒不需要額外的核心開支,並且使用者態執行緒的實現方式可以被客製化或修改以適應特殊應用的要求,但是當一個執行緒因 I/O 而處於等待狀態時,整個程序就會被排程程式切換為等待狀態,其他執行緒得不到執行的機會;而核心執行緒則沒有各個限制,有利於發揮多處理器的並行優勢,但卻佔用了更多的系統開支。
Windows NT和OS/2支援核心執行緒。Linux 支援核心級的多執行緒。
linux中的核心級線
1.核心執行緒概述
Linux核心可以看作服務程序(管理軟硬體資源,響應使用者程序的各種程序)
核心需要多個執行流並行,為了防止可能的阻塞,支援多執行緒。
核心執行緒就是核心的一個分身,可以用以處理一件特定事情,核心執行緒的排程由核心負責,一個核心執行緒的處於阻塞狀態時不影響其他的核心執行緒。
核心執行緒是直接由核心本身啟動的程序。核心執行緒實際上是將核心函數委託給獨立的程序執行,它與核心中的其他「程序」並行執行。核心執行緒經常被稱之為核心守護行程。當前的核心中,核心執行緒就負責下面的工作:
- 週期性地將修改的記憶體頁與頁來源塊裝置同步
- 實現檔案系統的事務紀錄檔
核心執行緒由核心建立,所以核心執行緒在核心態執行,只能存取核心虛擬地址空間,不能存取使用者空間。
在linux所有的執行緒都當作程序來實現,也沒有單獨為執行緒定義排程演演算法以及資料結構,一個程序相當於包含一個執行緒,就是自身,多執行緒,原本的執行緒稱為主執行緒,他們一起構成執行緒組。
程序擁有自己的地址空間,所以每個程序都有自己的頁表,而執行緒卻沒有,只能和其它執行緒共用主執行緒的地址空間和頁表
2.三個資料結構
每個程序或執行緒由三個重要的資料結構,分別是struct thread_info, struct task_struct 和核心棧。
thread_info物件存放的程序/執行緒的基本資訊,它和程序/執行緒的核心棧存放在核心空間裡的一段2倍頁長空間中。其中thread_info結構存放在地址段的末尾,其餘空間作為核心棧。核心使用夥伴系統分配這段空間。
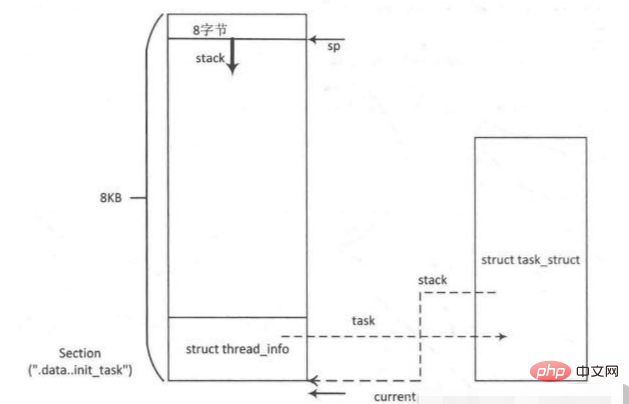
struct thread_info {
int preempt_count; /* 0 => preemptable, <0 => bug */
struct task_struct *task; /* main task structure */
__u32 cpu; /* cpu */};登入後複製thread_info結構體中有一個struct task_struct *task,task指向該執行緒或者程序的task_struct物件,task_struct也叫做任務描述符:
struct task_struct {
pid_t pid;
pid_t tgid;
void *stack;
struct mm_struct *mm, *active_mm;
/* filesystem information */
struct fs_struct *fs;
/* open file information */
struct files_struct *files;};#define task_thread_info(task) ((struct thread_info *)(task)->stack)登入後複製- stack:是指向程序或者執行緒的thread_info
- mm:物件用來管理該程序/執行緒的頁表以及虛擬記憶體區
- active_mm:主要用於核心執行緒存取主核心頁全域性目錄
- pid:每個task_struct都會有一個不同的id,就是pid
- tgid:執行緒組領頭執行緒的PID,就是主執行緒的pid
linux系統上虛擬地址空間分為兩個部分:供使用者態程式存取的虛擬地址空間和供核心存取的核心空間。每當核心執行上下文切換時,虛擬地址空間的使用者層部分都會切換,以便匹配執行的程序,核心空間的部分是不會切換的。
3.核心執行緒建立
在核心版本linux-3.x以後,核心執行緒的建立被延後執行,並且交給名為kthreadd 2號執行緒執行建立過程,但是kthreadd本身是怎麼建立的呢?過程如下:
pid_t kernel_thread(int (*fn)(void *), void *arg, unsigned long flags)
{
return do_fork(flags|CLONE_VM|CLONE_UNTRACED, (unsigned long)fn,
(unsigned long)arg, NULL, NULL);
}
pid = kernel_thread(kthreadd, NULL, CLONE_FS | CLONE_FILES);登入後複製kthreadadd本身最終是通過do_fork實現的,do_fork通過傳入不同的引數,可以分別用於建立使用者態程序/執行緒,核心執行緒等。當kthreadadd被建立以後,核心執行緒的建立交給它實現。
核心執行緒的建立分為建立和啟動兩個部分,kthread_run作為統一的介面,可以同時實現,這兩個功能:
#define kthread_run(threadfn, data, namefmt, ...) \
({ \
struct task_struct *__k \
= kthread_create(threadfn, data, namefmt, ## __VA_ARGS__); \
if (!IS_ERR(__k)) \
wake_up_process(__k); \
__k; \
})
#define kthread_create(threadfn, data, namefmt, arg...) \
kthread_create_on_node(threadfn, data, -1, namefmt, ##arg)
struct task_struct *kthread_create_on_node(int (*threadfn)(void *data),
void *data, int node,
const char namefmt[],
...)
{
DECLARE_COMPLETION_ONSTACK(done);
struct task_struct *task;
/*分配kthread_create_info空間*/
struct kthread_create_info *create = kmalloc(sizeof(*create),
GFP_KERNEL);
if (!create)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
create->threadfn = threadfn;
create->data = data;
create->node = node;
create->done = &done;
/*加入到kthread_creta_list列表中,等待ktherad_add中斷執行緒去建立改執行緒*/
spin_lock(&kthread_create_lock);
list_add_tail(&create->list, &kthread_create_list);
spin_unlock(&kthread_create_lock);
wake_up_process(kthreadd_task);
/*
* Wait for completion in killable state, for I might be chosen by
* the OOM killer while kthreadd is trying to allocate memory for
* new kernel thread.
*/
if (unlikely(wait_for_completion_killable(&done))) {
/*
* If I was SIGKILLed before kthreadd (or new kernel thread)
* calls complete(), leave the cleanup of this structure to
* that thread.
*/
if (xchg(&create->done, NULL))
return ERR_PTR(-EINTR);
/*
* kthreadd (or new kernel thread) will call complete()
* shortly.
*/
wait_for_completion(&done);
}
task = create->result;
.
.
.
kfree(create);
return task;
}登入後複製kthread_create_on_node函數中:
- 首先利用kmalloc分配kthread_create_info變數create,利用函數引數初始化create
- 將create加入kthread_create_list連結串列中,然後喚醒kthreadd核心執行緒建立當前執行緒
- 喚醒kthreadd後,利用completion等待核心執行緒建立完成,completion完成後,釋放create空間
下面來看下kthreadd的處理過程:
int kthreadd(void *unused)
{
struct task_struct *tsk = current;
/* Setup a clean context for our children to inherit. */
set_task_comm(tsk, "kthreadd");
ignore_signals(tsk);
set_cpus_allowed_ptr(tsk, cpu_all_mask);
set_mems_allowed(node_states[N_MEMORY]);
current->flags |= PF_NOFREEZE;
for (;;) {
set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
if (list_empty(&kthread_create_list))
schedule();
__set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
spin_lock(&kthread_create_lock);
while (!list_empty(&kthread_create_list)) {
struct kthread_create_info *create;
create = list_entry(kthread_create_list.next,
struct kthread_create_info, list);
list_del_init(&create->list);
spin_unlock(&kthread_create_lock);
create_kthread(create);
spin_lock(&kthread_create_lock);
}
spin_unlock(&kthread_create_lock);
}
return 0;
}登入後複製kthreadd利用for(;;)一直駐留在記憶體中執行:主要過程如下:
- 檢查kthread_create_list為空時,kthreadd讓出cpu的執行權
- kthread_create_list不為空時,利用while迴圈遍歷kthread_create_list連結串列
- 每取下一個連結串列節點後呼叫create_kthread,建立核心執行緒
static void create_kthread(struct kthread_create_info *create)
{
int pid;
/* We want our own signal handler (we take no signals by default). */
pid = kernel_thread(kthread, create, CLONE_FS | CLONE_FILES | SIGCHLD);
if (pid < 0) {
/* If user was SIGKILLed, I release the structure. */
struct completion *done = xchg(&create->done, NULL);
if (!done) {
kfree(create);
return;
}
create->result = ERR_PTR(pid);
complete(done);
}
}登入後複製可以看到核心執行緒的建立最終還是和kthreadd一樣,呼叫kernel_thread實現。
static int kthread(void *_create)
{
.
.
.
.
/* If user was SIGKILLed, I release the structure. */
done = xchg(&create->done, NULL);
if (!done) {
kfree(create);
do_exit(-EINTR);
}
/* OK, tell user we're spawned, wait for stop or wakeup */
__set_current_state(TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE);
create->result = current;
complete(done);
schedule();
ret = -EINTR;
if (!test_bit(KTHREAD_SHOULD_STOP, &self.flags)) {
__kthread_parkme(&self);
ret = threadfn(data);
}
/* we can't just return, we must preserve "self" on stack */
do_exit(ret);
}登入後複製kthread以struct kthread_create_info 型別的create為引數,create中帶有建立核心執行緒的回撥函數,以及函數的引數。kthread中,完成completion號誌的處理,然後schedule讓出cpu的執行權,等待下次返回 時,執行回撥函數threadfn(data)。
4.核心執行緒的退出
執行緒一旦啟動起來後,會一直執行,除非該執行緒主動呼叫do_exit函數,或者其他的程序呼叫kthread_stop函數,結束執行緒的執行。
int kthread_stop(struct task_struct *k)
{
struct kthread *kthread;
int ret;
trace_sched_kthread_stop(k);
get_task_struct(k);
kthread = to_live_kthread(k);
if (kthread) {
set_bit(KTHREAD_SHOULD_STOP, &kthread->flags);
__kthread_unpark(k, kthread);
wake_up_process(k);
wait_for_completion(&kthread->exited);
}
ret = k->exit_code;
put_task_struct(k);
trace_sched_kthread_stop_ret(ret);
return ret;
}登入後複製如果執行緒函數正在處理一個非常重要的任務,它不會被中斷的。當然如果執行緒函數永遠不返回並且不檢查訊號,它將永遠都不會停止。在執行kthread_stop的時候,目標執行緒必須沒有退出,否則會Oops。所以在建立thread_func時,可以採用以下形式:
thread_func()
{
// do your work here
// wait to exit
while(!thread_could_stop())
{
wait();
}
}
exit_code()
{
kthread_stop(_task); //發訊號給task,通知其可以退出了
}登入後複製如果執行緒中在等待某個條件滿足才能繼續執行,所以只有滿足了條件以後,才能呼叫kthread_stop殺掉核心執行緒。
5.核心執行緒使用
#include "test_kthread.h"
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/timer.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
static struct task_struct *test_thread = NULL;
unsigned int time_conut = 5;
int test_thread_fun(void *data)
{
int times = 0;
while(!kthread_should_stop())
{
printk("\n printk %u\r\n", times);
times++;
msleep_interruptible(time_conut*1000);
}
printk("\n test_thread_fun exit success\r\n\n");
return 0;
}
void register_test_thread(void)
{
test_thread = kthread_run(test_thread_fun , NULL, "test_kthread" );
if (IS_ERR(test_thread)){
printk(KERN_INFO "create test_thread failed!\n");
}
else {
printk(KERN_INFO "create test_thread ok!\n");
}
}
static ssize_t kthread_debug_start(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr, char *buf)
{
register_test_thread();
return 0;
}
static ssize_t kthread_debug_stop(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr, char *buf)
{
kthread_stop(test_thread);
return 0;
}
static DEVICE_ATTR(kthread_start, S_IRUSR, kthread_debug_start,NULL);
static DEVICE_ATTR(kthread_stop, S_IRUSR, kthread_debug_stop,NULL);
struct attribute * kthread_group_info_attrs[] =
{
&dev_attr_kthread_start.attr,
&dev_attr_kthread_stop.attr,
NULL,
};
struct attribute_group kthread_group =
{
.name = "kthread",
.attrs = kthread_group_info_attrs,
};登入後複製相關推薦:《Linux視訊教學》
以上就是linux有核心級執行緒麼的詳細內容,更多請關注TW511.COM其它相關文章!
