Python資料分析教學(三):實用程式碼
2022-10-29 18:00:49
Python資料分析教學專欄:資料分析 - 標籤 - 孤飛 - 部落格園 (cnblogs.com)
Python資料分析教學(一):Numpy - 孤飛 - 部落格園 (cnblogs.com)
Python資料分析教學(二):Pandas - 孤飛 - 部落格園 (cnblogs.com)
檔案處理
導包
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
%matplotlib inline
新增映象
https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/
https://developer.aliyun.com/mirror/
http://mirrors.163.com/ubuntu/
https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/
http://mirrors.zju.edu.cn/
http://mirrors.sohu.com/
http://ftp.sjtu.edu.cn/
http://mirror.bjtu.edu.cn/
http://mirror.bjtu.edu.cn/
語法
其中http和https是可選的
! pip install xxx -i https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/
匯入檔案
excel
data=pd.read_excel(r"C:\Users\ranxi\Desktop\附錄1 目標客戶體驗資料.xlsx", sheet_name='data')
data.head()
csv
data=pd.read_csv()
EDA報告
#生成報告
import pandas_profiling
data.profile_report()
#輸出報告檔案
pfr = pandas_profiling.ProfileReport(data)
pfr.to_file('report.html')
dataframe匯出excel檔案
data.to_excel('data.xlsx')
資料處理
資料篩選
分類均值展示
cvr_summary = data.groupby("cvr_group_high")
cvr_summary.mean().reset_index()
標籤編碼
print("client","--" ,data.client.unique())
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
data.client = LabelEncoder().fit_transform(data.client)
print("client","--" ,data.client.unique())
交叉比例表
pd.crosstab(data['invited_is'],data["cvr_group_high"],normalize=0)
計算分佈比例
def percent_value_counts(df, feature):
"""This function takes in a dataframe and a column and finds the percentage of the value_counts"""
percent = pd.DataFrame(round(df.loc[:,feature].value_counts(dropna=False, normalize=True)*100,2))
## creating a df with th
total = pd.DataFrame(df.loc[:,feature].value_counts(dropna=False))
## concating percent and total dataframe
total.columns = ["Total"]
percent.columns = ['Percent']
return pd.concat([total, percent], axis = 1)
percent_value_counts(data, "B7")
多列apply函數
with_N['B7'] = with_N.apply(lambda x: child_estimator(x['B6'], x['B5']), axis=1)
卡方檢驗
#分組間確實是有顯著性差異,頻數比較的結論才有可信度,故需進行」卡方檢驗「
from scipy.stats import chi2_contingency #統計分析 卡方檢驗
#自定義卡方檢驗函數
def KF(x):
df1=pd.crosstab(data2['購買意願'],data2[x])
li1=list(df1.iloc[0,:])
li2=list(df1.iloc[1,:])
kf_data=np.array([li1,li2])
kf=chi2_contingency(kf_data)
if kf[1]<0.05:
print('購買意願 by {} 的卡方臨界值是{:.2f},小於0.05,表明{}組間有顯著性差異,可進行【交叉分析】'.format(x,kf[1],x),'\n')
else:
print('購買意願 by {} 的卡方臨界值是{:.2f},大於0.05,表明{}組間無顯著性差異,不可進行交叉分析'.format(x,kf[1],x),'\n')
#對 kf_var進行卡方檢驗
print('kf_var的卡方檢驗結果如下:','\n')
print(list(map(KF, kf_var)))
條件篩選
specific=data[(data['a1']>100)|(data['a2']>100)|(data['a3']>100)|(data['a4']>100)|(data['a5']>100)|(data['a6']>100)|(data['a7']>100)|(data['a8']>100)]
specific
specific=data[(data['']>x)|&()]
data[data.Cabin=='N']
map函數分組
def hour_group_fun(hour):
x = ''
if 0<=hour<8:
x=1
elif 8<=hour<16:
x=2
else:
x=3
return x
## Applying function to the column.
police['hour_group'] =police['hour'].map(hour_group_fun)
apply多列賦值
with_N['B7'] = with_N.apply(lambda x: child_estimator(x['B6'], x['B5']), axis=1)
這是一個分佈比例函數
def percent_value_counts(df, feature):
"""This function takes in a dataframe and a column and finds the percentage of the value_counts"""
percent = pd.DataFrame(round(df.loc[:,feature].value_counts(dropna=False, normalize=True)*100,2))
## creating a df with th
total = pd.DataFrame(df.loc[:,feature].value_counts(dropna=False))
## concating percent and total dataframe
total.columns = ["Total"]
percent.columns = ['Percent']
return pd.concat([total, percent], axis = 1)
特徵工程
時間資料處理
police['date'] = pd.to_datetime(police['接警日期'],errors='coerce')
police['year'] =police['date'].dt.year.fillna(0).astype("int") #轉化提取年
police['month'] = police['date'].dt.month.fillna(0).astype("int") #轉化提取月
police['day'] = police['date'].dt.day.fillna(0).astype("int") #轉化提取天
police['dates'] = police['month'].map(str) + '-' + police['day'].map(str) #轉化獲取月-日
police['time'] = pd.to_datetime(police['接警時間點'],errors='coerce').dt.time
police['hour'] = pd.to_datetime(police['接警時間點'],errors='coerce').dt.hour.fillna(0).astype("int") #轉化提取小時
SMOTE過抽樣
from imblearn.over_sampling import SMOTE
model_smote=SMOTE()
X,y=model_smote.fit_resample(X,y)
X=pd.DataFrame(X,columns=t.columns)
#分拆資料集:訓練集 和 測試集
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.3,random_state=0)
print('過抽樣資料特徵:', X.shape,
'訓練資料特徵:',X_train.shape,
'測試資料特徵:',X_test.shape)
print('過抽樣後資料標籤:', y.shape,
' 訓練資料標籤:',y_train.shape,
' 測試資料標籤:',y_test.shape)
輸出缺失值
print ("Train age missing value: " + str((train.Age.isnull().sum()/len(train))*100)+str("%"))
影響分析
xgb輸出特徵重要性
model_xgb= XGBClassifier()
model_xgb.fit(X,y)
from xgboost import plot_importance
plot_importance(model_xgb,height=0.5,color='green',title='')
# plt.savefig('imp.png')
plt.show()
計算相關係數並畫圖
plt.style.use('classic')
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 黑體
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解決無法顯示符號的問題
plt.rc("figure", facecolor="white") #去除灰色邊框
plt.figure(figsize=(15,6),dpi=300)
df_onehot.corr()['購買意願'].sort_values(ascending=False).plot(kind='bar',color='dodgerblue')
plt.savefig('buyvary1.png', dpi=300)
plt.show()
data.corr(method='pearson')
data.corr(method='spearman')
data.corr(method='kendall')
Pandas處理
常用操作
為dataframe新增1列
data['age']=list
合併表格再排序
data = pd.concat([with_N, without_N], axis=0)
data.sort_values(by = '目標客戶編號', inplace=True)
dataframe排序
useful=useful.sort_values(by = ['購買難度'], ascending = [True])
選取指定行(以列的值篩選)
first1=data3[(data3['品牌編號']==1)]
獲取列名
kf=list(data2.columns[1:7])
for x in [9,11,12,20,21,24,25,26]:
kf.append(data2.columns[x])
print(kf)
修改列名
#1、修改列名a,b為A、B。
df.columns = ['A','B']
#2、只修改列名a為A
df.rename(columns={'a':'A'})
刪除一列
data3=data3.drop(1,axis=0)
列表轉dataframe(巢狀列表)
from pandas.core.frame import DataFrame
data7=DataFrame(week)
data7
型別轉換
Dataframe到Series
Series = Dataframe['column']
Series到list
list = Series.to_list()
list 轉 array
array = np.array(list)
array 轉 torch.Tensor
tensor = torch.from_numpy(array)
torch.Tensor 轉 array
array = tensor.numpy()
# gpu情況下需要如下的操作
array = tensor.cpu().numpy()
torch.Tensor 轉 list
# 先轉numpy,後轉list
list = tensor.numpy().tolist()
array 轉 list
list = array.tolist()
list 轉 torch.Tensor
tensor=torch.Tensor(list)
array或者list轉Series
series = pd.Series({'a': array})
series2 = pd.Series({'a': list})
list轉dataframe
data4=DataFrame(li)
array轉dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame(data=data[0:,0:],columns='pregnants','Plasma_glucose_concentration','blood_pressure','Triceps_skin_fold_thickness','serum_insulin','BMI','Diabetes_pedigree_function','Age','Target'] )
python需要注意的地方
變數
列表的複製:直接採用a=b的方式會指向同一個記憶體地址
全域性變數:函數內部的變數,外部是無法存取的,在函數內部定義global 後函數執行過才可存取
迴圈
- continue: 跳出本次迴圈
- break: 跳出本層迴圈
運算
矩陣numpy乘法:
- 點乘: np.dot(xy)
- 數乘: np.mat(x,int)
亂數
import random
print( random.randint(1,10) ) # 產生 1 到 10 的一個整數型亂數
print( random.random() ) # 產生 0 到 1 之間的隨機浮點數
print( random.uniform(1.1,5.4) ) # 產生 1.1 到 5.4 之間的隨機浮點數,區間可以不是整數
print( random.choice('tomorrow') ) # 從序列中隨機選取一個元素
print( random.randrange(1,100,2) ) # 生成從1到100的間隔為2的隨機整數
a=[1,3,5,6,7] # 將序列a中的元素順序打亂
random.shuffle(a)
print(a)
import random
import string
# 隨機整數:
print random.randint(1,50)
# 隨機選取0到100間的偶數:
print random.randrange(0, 101, 2)
# 隨機浮點數:
print random.random()
print random.uniform(1, 10)
# 隨機字元:
print random.choice('abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz!@#$%^&*()')
# 多個字元中生成指定數量的隨機字元:
print random.sample('zyxwvutsrqponmlkjihgfedcba',5)
# 從a-zA-Z0-9生成指定數量的隨機字元:
ran_str = ''.join(random.sample(string.ascii_letters + string.digits, 8))
print ran_str
# 多個字元中選取指定數量的字元組成新字串:
print ''.join(random.sample(['z','y','x','w','v','u','t','s','r','q','p','o','n','m','l','k','j','i','h','g','f','e','d','c','b','a'], 5))
# 隨機選取字串:
print random.choice(['剪刀', '石頭', '布'])
# 打亂排序
items = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0]
print random.shuffle(items)
畫圖
畫圖準備
解決中文符號顯示問題
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 黑體
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解決無法顯示符號的問題
sns.set(font='SimHei', font_scale=0.8) # 解決Seaborn中文顯示問題
設定背景樣式
plt.style.use('classic')
plt.rc("figure", facecolor="white") #去除灰色邊框
繪圖
這是一個畫箱線圖程式碼
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
sns.set_style('darkgrid')
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(16,12),ncols=2)
ax1 = sns.boxplot(x="Embarked", y="Fare", hue="Pclass", data=train, ax = ax[0]);
ax2 = sns.boxplot(x="Embarked", y="Fare", hue="Pclass", data=test, ax = ax[1]);
ax1.set_title("Training Set", fontsize = 18)
ax2.set_title('Test Set', fontsize = 18)
fig.show()
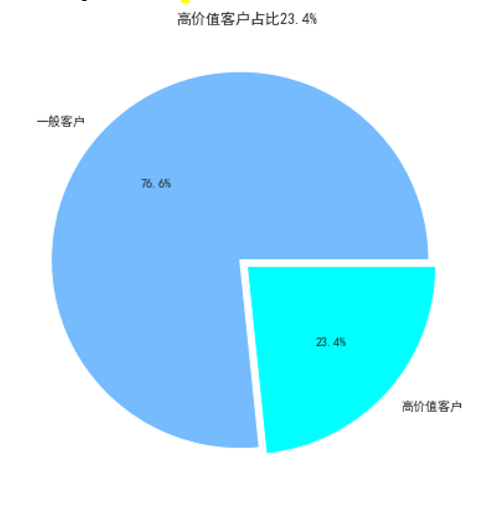
畫缺口餅圖
churn_value=data['cvr_group_high'].value_counts()
labels=data['cvr_group_high'].value_counts().index
plt.figure(figsize=(7,7))
plt.pie(churn_value,labels=['一般客戶', '高價值客戶'],colors=["#75bbfd","#00ffff"], explode=(0.05,0),autopct='%1.1f%%', shadow=False)
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
plt.title("高價值客戶佔比23.4%")
#plt.savefig('pie.png', dpi=300)
畫相關性係數圖
mask = np.zeros_like(data.corr(), dtype=np.bool)
#mask[np.triu_indices_from(mask)] = True
plt.subplots(figsize = (15,12))
sns.heatmap(data.corr(),
annot=True,
# mask = mask,
cmap = 'RdBu', ## in order to reverse the bar replace "RdBu" with "RdBu_r"
linewidths=.9,
linecolor='gray',
fmt='.2g',
center = 0,
square=True)
plt.title("Correlations Among Features", y = 1.03,fontsize = 20, pad = 40) #相關性矩陣
plt.savefig('cor.png', dpi=300)
plt.show()
畫核密度估計
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15,8),)
## I have included to different ways to code a plot behigh, choose the one that suites you.
ax=sns.kdeplot(data.client[data.cvr_group_high == 0] ,
color='gray',
shade=True,
label='high')
ax=sns.kdeplot(data.loc[(data['cvr_group_high'] == 1),'client'] ,
color='g',
shade=True,
label='high',
)
plt.title('client - high vs high', fontsize = 25, pad = 40)
plt.ylabel("Frequency of cvr", fontsize = 15, labelpad = 20)
plt.xlabel("Client", fontsize = 15,labelpad =20)
## Converting xticks into words for better understanding
labels = ['H5', 'android', 'ios','pc','wap']
plt.xticks(sorted(data.client.unique()), labels)
plt.legend()

模型訓練
匯入模組
#載入模組
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") #過濾掉警告的意思
from pyforest import *
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier #隨機森林
from sklearn.svm import SVC,LinearSVC #支援向量機
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression #邏輯迴歸
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier #KNN演演算法
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans #K-Means 聚類演演算法
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB #樸素貝葉斯
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier #決策樹
import xgboost as xgb
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
from catboost import CatBoostClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report,precision_score,recall_score,f1_score,accuracy_score #分類報告
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix #混淆矩陣
from sklearn.metrics import silhouette_score #輪廓係數(評價k-mean聚類效果)
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV #交叉驗證
from sklearn.metrics import make_scorer
from sklearn.ensemble import VotingClassifier #投票
def plot_predictions(test,predicted):
#整體平移
x=np.arange(0,len(test))+1
# x[0]=1
# my_x_ticks = np.arange(1, 14, 1)
# plt.xticks(my_x_ticks)
plt.plot(x,test,label='Real')
plt.plot(x,predicted,color='darkOrange',linestyle='--',label='Predicted')
# plt.xlabel('month')
plt.ylabel('count')
plt.legend()
import math
def mse_loss(y_true, y_pred):
return np.sum(np.power(y_true - y_pred, 2)) / y_true.shape[0] / 2
def return_rmse(test,predicted):
rmse = math.sqrt(mse_loss(test, predicted))
return rmse
# print("The mean squared error is {}.".format(rmse))
Classifiers=[
["Random Forest",RandomForestClassifier()],
["Support Vector Machine",SVC()],
["LogisticRegression",LogisticRegression()],
["KNN",KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5)],
["Naive Bayes",GaussianNB()],
["Decision Tree",DecisionTreeClassifier()],
["AdaBoostClassifier",AdaBoostClassifier()],
["GradientBoostingClassifier", GradientBoostingClassifier()],
["XGB", XGBClassifier()],
]
設定訓練集
X=train.drop(['目標客戶編號','品牌型別','購買意願'], axis = 1)
# X=train.drop(['目標客戶編號','品牌型別'], axis = 1)
t=X
headers = X.columns
X= X.astype(float)
y = train["購買意願"]
訓練模型
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
Classify_result=[]
names=[]
prediction=[]
for name,classifier in Classifiers:
classifier=classifier
classifier.fit(X_train,y_train)
y_pred=classifier.predict(X_test)
recall=recall_score(y_test,y_pred,average='macro')
precision=precision_score(y_test,y_pred,average='macro')
f1score = f1_score(y_test, y_pred,average='macro')
mse = return_rmse(y_test,y_pred)
class_eva=pd.DataFrame([recall,precision,f1score,mse])
Classify_result.append(class_eva)
name=pd.Series(name)
names.append(name)
y_pred=pd.Series(y_pred)
prediction.append(y_pred)
plot_predictions(y_test,y_pred)
# # plt.savefig('seven1.png', dpi=300)
plt.show()
模型評估
names=pd.DataFrame(names)
names=names[0].tolist()
result=pd.concat(Classify_result,axis=1)
result.columns=names
result.index=["recall","precision","f1score","mse"]
result
小工具
tqdm顯示進度條
from tqdm import tqdm
for I in tqdm():
記錄時間
Import time
time_begin = time.time()
#code,你的程式
time_end = time.time()
time = time_end - time_begin
print('time:', time)
jupyter操作
- Shift+上下鍵 # 按住Shift進行上下鍵操作可複選多個cell
- Shift-M # 合併所選cell或合併當前cell和下方的cell
- Ctrl + Shift + - # 從遊標所在的位置拆分cell
原創作者:孤飛-部落格園
原文連結:https://www.cnblogs.com/ranxi169/p/16838967.html