PaddleOCR-EAST
2022-10-23 21:00:59
寫在前面:基於PaddleOCR程式碼庫對其中所涉及到的演演算法進行程式碼簡讀,如果有必要可能會先研讀一下原論文。
Abstract
- 論文連結:arxiv
- 應用場景:文字檢測
- 程式碼組態檔:configs/det/det_r50_vd_east.yml
Train
PreProcess
class EASTProcessTrain(object):
def __init__(self,
image_shape=[512, 512],
background_ratio=0.125,
min_crop_side_ratio=0.1,
min_text_size=10,
**kwargs):
self.input_size = image_shape[1]
self.random_scale = np.array([0.5, 1, 2.0, 3.0])
self.background_ratio = background_ratio
self.min_crop_side_ratio = min_crop_side_ratio
self.min_text_size = min_text_size
...
def __call__(self, data):
im = data['image']
text_polys = data['polys']
text_tags = data['ignore_tags']
if im is None:
return None
if text_polys.shape[0] == 0:
return None
#add rotate cases
if np.random.rand() < 0.5:
# 旋轉圖片和文字方塊(90,180,270)
im, text_polys = self.rotate_im_poly(im, text_polys)
h, w, _ = im.shape
# 限制文字方塊座標到有效範圍內、檢查文字方塊的有效性(基於文字方塊的面積)、以及點的順序是否是順時針
text_polys, text_tags = self.check_and_validate_polys(text_polys,
text_tags, h, w)
if text_polys.shape[0] == 0:
return None
# 隨機縮放圖片以及文字方塊
rd_scale = np.random.choice(self.random_scale)
im = cv2.resize(im, dsize=None, fx=rd_scale, fy=rd_scale)
text_polys *= rd_scale
if np.random.rand() < self.background_ratio:
# 只切純背景圖,如果有文字方塊會返回None
outs = self.crop_background_infor(im, text_polys, text_tags)
else:
"""
隨機切圖並以及crop圖所包含的文字方塊,並基於縮小的文字方塊生成了幾個label map:
- score_map: shape=[h,w],得分圖,有文字的地方是1,其餘地方為0
- geo_map: shape=[h,w,9]。前8個通道為縮小文字方塊內的畫素到真實文字方塊的水平以及垂直距離,
最後一個通道用來做loss歸一化,其值為每個框最短邊長的倒數
- training_mask: shape=[h,w],使無效文字方塊不參與訓練,有效的地方為1,無效的地方為0
"""
outs = self.crop_foreground_infor(im, text_polys, text_tags)
if outs is None:
return None
im, score_map, geo_map, training_mask = outs
# 產生最終降取樣的score map,shape=[1,h//4,w//4]
score_map = score_map[np.newaxis, ::4, ::4].astype(np.float32)
# 產生最終降取樣的gep map, shape=[9,h//4,w//4]
geo_map = np.swapaxes(geo_map, 1, 2)
geo_map = np.swapaxes(geo_map, 1, 0)
geo_map = geo_map[:, ::4, ::4].astype(np.float32)
# 產生最終降取樣的training mask,shape=[1,h//4,w//4]
training_mask = training_mask[np.newaxis, ::4, ::4]
training_mask = training_mask.astype(np.float32)
data['image'] = im[0]
data['score_map'] = score_map
data['geo_map'] = geo_map
data['training_mask'] = training_mask
return data
Architecture
Backbone
採用resnet50_vd,得到1/4、1/8、1/16以及1/32倍共計4張降取樣特徵圖。
Neck
基於Unect decoder架構,完成自底向上的特徵融合過程,從1/32特徵圖逐步融合到1/4的特徵圖,最終得到一張帶有多尺度資訊的1/4特徵圖。
def forward(self, x):
# x是儲存4張從backbone獲取的特徵圖
f = x[::-1] # 此時特徵圖從小到大排列
h = f[0] # [b,512,h/32,w/32]
g = self.g0_deconv(h) # [b,128,h/16,w/16]
h = paddle.concat([g, f[1]], axis=1) # [b,128+256,h/16,w/16]
h = self.h1_conv(h) # [b,128,h/16,w/16]
g = self.g1_deconv(h) # [b,128,h/8,w/8]
h = paddle.concat([g, f[2]], axis=1) # [b,128+128,h/8,w/8]
h = self.h2_conv(h) # [b,128,h/8,w/8]
g = self.g2_deconv(h) # [b,128,h/4,w/4]
h = paddle.concat([g, f[3]], axis=1) # [b,128+64,h/4,w/4]
h = self.h3_conv(h) # [b,128,h/4,w/4]
g = self.g3_conv(h) # [b,128,h/4,w/4]
return g
Head
輸出分類頭和迴歸頭(quad),部分引數共用。
def forward(self, x, targets=None):
# x是融合後的1/4特徵圖,det_conv1和det_conv2用於進一步加強特徵抽取
f_det = self.det_conv1(x) # [b,128,h/4,w/4]
f_det = self.det_conv2(f_det) # [b,64,h/4,w/4]
# # [b,1,h/4,w/4] 用於前、背景分類,注意kernel_size=1
f_score = self.score_conv(f_det)
f_score = F.sigmoid(f_score) # 獲取相應得分
# # [b,8,h/4,w/4],8的意義:dx1,dy1,dx2,dy2,dx3,dy3,dx4,dy4
f_geo = self.geo_conv(f_det)
# 迴歸的range變為:[-800,800],那麼最終獲取的文字方塊的最大邊長不會超過1600
f_geo = (F.sigmoid(f_geo) - 0.5) * 2 * 800
pred = {'f_score': f_score, 'f_geo': f_geo}
return pred
Loss
分類採用dice_loss,迴歸採用smooth_l1_loss。
class EASTLoss(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self,
eps=1e-6,
**kwargs):
super(EASTLoss, self).__init__()
self.dice_loss = DiceLoss(eps=eps)
def forward(self, predicts, labels):
"""
Params:
predicts: {'f_score': 前景得分圖,'f_geo': 迴歸圖}
labels: [imgs, l_score, l_geo, l_mask]
"""
l_score, l_geo, l_mask = labels[1:]
f_score = predicts['f_score']
f_geo = predicts['f_geo']
# 分類loss
dice_loss = self.dice_loss(f_score, l_score, l_mask)
channels = 8
# channels+1的原因是最後一個圖對應了短邊的歸一化係數(後面會講),前8個代表相對偏移的label
# [[b,1,h/4,w/4], ...]共9個
l_geo_split = paddle.split(
l_geo, num_or_sections=channels + 1, axis=1)
# [[b,1,h/4,w/4], ...]共8個
f_geo_split = paddle.split(f_geo, num_or_sections=channels, axis=1)
smooth_l1 = 0
for i in range(0, channels):
geo_diff = l_geo_split[i] - f_geo_split[i] # diff=label-pred
abs_geo_diff = paddle.abs(geo_diff) # abs_diff
# 計算abs_diff中小於1的且有文字的部分
smooth_l1_sign = paddle.less_than(abs_geo_diff, l_score)
smooth_l1_sign = paddle.cast(smooth_l1_sign, dtype='float32')
# smoothl1 loss,大於1和小於1的兩個部分對應loss相加,只不過這裡<1的部分沒乘0.5,問題不大
in_loss = abs_geo_diff * abs_geo_diff * smooth_l1_sign + \
(abs_geo_diff - 0.5) * (1.0 - smooth_l1_sign)
# 用短邊*8做歸一化
out_loss = l_geo_split[-1] / channels * in_loss * l_score
smooth_l1 += out_loss
# paddle.mean(smooth_l1)就可以了,前面都乘過了l_score,這裡再乘沒卵用
smooth_l1_loss = paddle.mean(smooth_l1 * l_score)
# dice_loss權重為0.01,smooth_l1_loss權重為1
dice_loss = dice_loss * 0.01
total_loss = dice_loss + smooth_l1_loss
losses = {"loss":total_loss, \
"dice_loss":dice_loss,\
"smooth_l1_loss":smooth_l1_loss}
return losses
Dice Loss
公式:
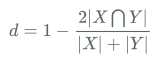
程式碼:
class DiceLoss(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, eps=1e-6):
super(DiceLoss, self).__init__()
self.eps = eps
def forward(self, pred, gt, mask, weights=None):
# mask代表了有效文字的mask,有文字的地方是1,否則為0
assert pred.shape == gt.shape
assert pred.shape == mask.shape
if weights is not None:
assert weights.shape == mask.shape
mask = weights * mask
intersection = paddle.sum(pred * gt * mask) # 交集
union = paddle.sum(pred * mask) + paddle.sum(gt * mask) + self.eps # 並集
loss = 1 - 2.0 * intersection / union
assert loss <= 1
return loss
SmoothL1 Loss
公式:
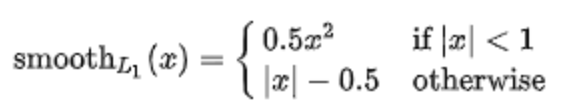
Infer
PostProcess
class EASTPostProcess(object):
def __init__(self,
score_thresh=0.8,
cover_thresh=0.1,
nms_thresh=0.2,
**kwargs):
self.score_thresh = score_thresh
self.cover_thresh = cover_thresh
self.nms_thresh = nms_thresh
...
def __call__(self, outs_dict, shape_list):
score_list = outs_dict['f_score'] # shape=[b,1,h//4,w//4]
geo_list = outs_dict['f_geo'] # shape=[b,8,h//4,w//4]
if isinstance(score_list, paddle.Tensor):
score_list = score_list.numpy()
geo_list = geo_list.numpy()
img_num = len(shape_list)
dt_boxes_list = []
for ino in range(img_num):
score = score_list[ino]
geo = geo_list[ino]
# 根據score、geo以及一些預設閾值和locality_nms操作拿到檢測框
boxes = self.detect(
score_map=score,
geo_map=geo,
score_thresh=self.score_thresh,
cover_thresh=self.cover_thresh,
nms_thresh=self.nms_thresh)
boxes_norm = []
if len(boxes) > 0:
h, w = score.shape[1:]
src_h, src_w, ratio_h, ratio_w = shape_list[ino]
boxes = boxes[:, :8].reshape((-1, 4, 2))
# 文字方塊座標根於縮放係數對映回輸入影象上
boxes[:, :, 0] /= ratio_w
boxes[:, :, 1] /= ratio_h
for i_box, box in enumerate(boxes):
# 根據寬度比高度大這一先驗,將座標調整為以「左上角」點為起始點的順時針4點框
box = self.sort_poly(box.astype(np.int32))
# 邊長小於5的再進行一次過濾,拿到最終的檢測結果
if np.linalg.norm(box[0] - box[1]) < 5 \
or np.linalg.norm(box[3] - box[0]) < 5:
continue
boxes_norm.append(box)
dt_boxes_list.append({'points': np.array(boxes_norm)})
return dt_boxes_list
def detect(self,
score_map,
geo_map,
score_thresh=0.8,
cover_thresh=0.1,
nms_thresh=0.2):
score_map = score_map[0] # shape=[h//4,w//4]
geo_map = np.swapaxes(geo_map, 1, 0)
geo_map = np.swapaxes(geo_map, 1, 2) # shape=[h//4,w//4,8]
# 獲取score_map上得分大於閾值的點的座標,shape=[n,2]
xy_text = np.argwhere(score_map > score_thresh)
if len(xy_text) == 0:
return []
# 按y軸從小到大的順序對這些點進行排序
xy_text = xy_text[np.argsort(xy_text[:, 0])]
# 恢復成基於原圖的文字方塊座標
text_box_restored = self.restore_rectangle_quad(
xy_text[:, ::-1] * 4, geo_map[xy_text[:, 0], xy_text[:, 1], :])
# shape=[n,9] 前8個通道代表x1,y1,x2,y2的座標,最後一個通道代表每個框的得分
boxes = np.zeros((text_box_restored.shape[0], 9), dtype=np.float32)
boxes[:, :8] = text_box_restored.reshape((-1, 8))
boxes[:, 8] = score_map[xy_text[:, 0], xy_text[:, 1]]
try:
import lanms
boxes = lanms.merge_quadrangle_n9(boxes, nms_thresh)
except:
print(
'you should install lanms by pip3 install lanms-nova to speed up nms_locality'
)
# locality nms,比傳統nms要快,因為進入nms中的文字方塊的數量要比之前少很多。前面按y軸排序其實是在為該步驟做鋪墊
boxes = nms_locality(boxes.astype(np.float64), nms_thresh)
if boxes.shape[0] == 0:
return []
# 最終還會根據框預測出的文字方塊內的畫素在score_map上的得分再做一次過濾,感覺有一些不合理,因為score_map
# 上預測的是shrink_mask,會導致框內有很多背景畫素,拉低平均得分,可能會讓一些原本有效的文字方塊變得無效
# 當然這裡的cover_thresh取的比較低,可能影響就比較小
for i, box in enumerate(boxes):
mask = np.zeros_like(score_map, dtype=np.uint8)
cv2.fillPoly(mask, box[:8].reshape(
(-1, 4, 2)).astype(np.int32) // 4, 1)
boxes[i, 8] = cv2.mean(score_map, mask)[0]
boxes = boxes[boxes[:, 8] > cover_thresh]
return boxes
def nms_locality(polys, thres=0.3):
def weighted_merge(g, p):
"""
框間merge的邏輯:座標變為coor1*score1+coor2*score2,得分變為score1+score2
"""
g[:8] = (g[8] * g[:8] + p[8] * p[:8]) / (g[8] + p[8])
g[8] = (g[8] + p[8])
return g
S = []
p = None
for g in polys:
# 由於是按y軸排了序,所以迴圈遍歷就可以了
if p is not None and intersection(g, p) > thres:
# 交集大於閾值那麼就merge
p = weighted_merge(g, p)
else:
# 不能再merge的時候該框臨近區域已無其他框,那麼其加入進S
if p is not None:
S.append(p)
p = g
if p is not None:
S.append(p)
if len(S) == 0:
return np.array([])
# 將S保留下的文字方塊進行標準nms,略
return standard_nms(np.array(S), thres)